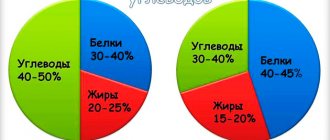
With the help of LJ blogger Znatok-ne, Lyle McDonald and several scientific studies, we tell you whether carbohydrates, so disliked by many after the era of protein diets, turn into fat.
When we eat in a surplus, the body's fat reserves can actually be replenished, both directly from fats and from “non-fat precursors”: mainly from carbohydrates. However, this is only possible as a result of a process called De novo lipogenesis (DNL), which is, to put it mildly, difficult to implement: the daily diet should contain no more than 10% fat + you need to eat a huge amount of carbohydrates (about 700 g). Among other things, the energy efficiency of DNL is very low because the body needs to spend too much energy on this process.
In a number of studies conducted to study DNL, an excess of carbohydrates in the diet provoked weight gain mainly due to an increase in glycogen stores and the water it attracts (you know that every 0.5 kg of carbohydrates in the body retains an additional 1.5 kg of water), and not because fat was synthesized.
Considering all of the above, the contribution of DNL to our adipose tissue is considered extremely insignificant. Even with a calorie surplus, the majority of carbohydrates are oxidized, and almost all the rest is stored as glycogen. In this case, about 5% can go to DNL (and only if the conditions listed at the beginning of the article are met: very little fat + a lot of carbohydrates).
Why women store carbohydrates “in reserve”
- Why do carbohydrates turn into fat?
- How are carbohydrates stored?
- Fast and slow carbohydrates
- How to burn carbs
In the female body, many useful substances are stored “in reserve”.
The body stores proteins in the abdomen, fat under the skin, and sugar in the liver tissue. Why does nature make a woman’s body a real warehouse? After all, this causes so many problems for the poor figure! In fact, a woman’s body always works to accumulate. This is necessary so that a woman can become pregnant, maintain the required amount of estrogen for ovulation and carry a child to term. The male body is not created for accumulation. On the contrary, it is designed in such a way as to constantly consume building material and build up muscles that will help it drive a mammoth or other prey while hunting. As you might guess, nature thought of everything and did its best for us.
Oats

Oats are a dietary product that many people associate with animal feed. In fact, in earlier times, oats occupied a significant place on the tables of many rich people. It contains many vitamins, minerals and... calories. But oats perfectly cleanse the body of toxins and waste. Oatmeal broth will be a real treasure for those who want to lose weight and improve their health. Oatmeal is also a storehouse of vitamins, but it needs to be boiled in water. But the cereal must be without additives, sweeteners and flavors.
Why do carbohydrates turn into fat?

Carbohydrates are very important for our body. Already during a meal, the body, with the help of special receptors in the oral cavity, recognizes that future fats are entering it. Since a woman’s metabolism is much lower than a man’s, and in order to maintain her fragile figure, she does not need a lot of energy, carbohydrates are stored in reserve, turning into fats, which are fuel for our body and a very important building material. Finally, few people know that it is carbohydrates stored in fat that are involved in the construction of hormones.
Where are carbohydrates stored? To ensure that the body always has a reserve, carbohydrates are deposited not only in the liver and muscles, but also under the skin in the form of fatty tissue. They are found in the pancreas.
How are carbohydrates stored?
Carbohydrates tend to be deposited even in the body of an athlete. And if a woman stops leading an active lifestyle, and even eats a lot, then reserves appear faster. Due to the fact that the weaker sex does not require much energy for metabolism, and it itself is slow, carbohydrates accumulate and are stored “in reserve” much faster than it happens in men. Since women do not need energy, fat synthesis occurs. The carbohydrate simply transforms into another form, settling on our wasp waist and beautiful hips.
If you do not exercise, then you should significantly reduce the amount of carbohydrates contained in your food. This will help you avoid gaining the desired weight. It is also worth paying a little attention to your figure and physical activity. The body will begin to spend reserves to supply itself with energy, because it is thanks to it that we walk, breathe, and digest food.
If you are a professional athlete, then in this case the situation will be different. You need to strictly follow your diet and the amount of carbohydrates you consume. This will help control excess weight. It's also worth remembering that carbohydrates don't always turn into fat. Sometimes they are just needed for recovery. Most often this can be observed in sports.

Factors that contribute to the deposition of carbohydrates:
- Age—the older a woman is, the slower her metabolism.
Heredity - often the cause of deposits is a genetic predisposition.
Overeating - some women eat a lot of carbohydrates, but the body does not need them.
- Passive lifestyle - when a woman leads a passive lifestyle, moves little, drives a car all the time, the body does not require much energy, which means carbohydrates are stored in bins.
Fast and slow carbohydrates
Carbohydrates can be divided into fast and slow. Fast carbohydrates are quickly absorbed and increase the amount of sugar. In addition, they contribute to the release of insulin and convert it into fat. Fast carbohydrates only help during training if you intend to “trigger” fat burning.
What foods should you avoid to avoid storing carbohydrates? First of all, it is sugar and various confectionery products - sweets, cakes, buns, pies, jam, and chocolate, beloved from childhood. Finally, various sweet drinks, and even fruit. It's best to eat small amounts of these foods before your workout so that your body knows which substances to target.
Bacon and coffee or oatmeal and bananas?

Research conducted in 2021 has primarily focused on the relationship between carbohydrates and weight. The results provide some clues to experts, but they still can't say for sure which diet will work for everyone. Why, even despite many experiments conducted, scientists still cannot give an exact answer? The main reason is that people are so different that it is almost impossible to derive any single pattern that will work for everyone. But you can find out what has been found out over the past year and draw your own conclusions.
How to burn carbs

Carbohydrates are a source of energy. In order for the body to spend treasured reserves, you need to move a lot and lead an active lifestyle. Just imagine how much energy it takes to run a cross-country race, lift a barbell, or climb to the 9th floor of a house. To force the body to remember about the stored reserves, you need to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Eat right before training. Your favorite chocolate bar or ice cream before a run will do this. Then the body will seem to remember that it has sugar reserves - the coveted glycogen.
Train as long as possible. The intensity of the workout greatly affects how much reserves are used. The longer the session lasts, the more energy is required, and the more the body will take on treasured reserves.
Choose aerobic exercise. Aerobics saturates the body with oxygen, which is necessary for burning glycogen.
Video about carbohydrates:
Expert advice
The studies carried out only prove the fact that all people are very different. What is good for one may be harmful for another. Therefore, you should not generalize and judge everyone by the same standard. However, there are some general rules that experts recommend following regardless of whether you prefer fats or carbohydrates.

- Try to eat home-cooked meals and avoid processed foods.
- Eliminate sugar and refined flour.
- Eat more vegetables and drink more clean water.
- Try to focus on foods that have been minimally processed.
Have you ever been on a diet?
Found a violation? Report content
Are carbohydrates converted into fat?
With the help of LJ blogger Znatok-ne, Lyle McDonald and several scientific studies, we tell you whether carbohydrates, so disliked by many after the era of protein diets, turn into fat.
When we eat in a surplus, the body's fat reserves can actually be replenished, both directly from fats and from “non-fat precursors”: mainly from carbohydrates. However, this is only possible as a result of a process called De novo lipogenesis (DNL), which is, to put it mildly, difficult to implement: the daily diet should contain no more than 10% fat + you need to eat a huge amount of carbohydrates (about 700 g). Among other things, the energy efficiency of DNL is very low because the body needs to spend too much energy on this process.
In a number of studies conducted to study DNL, an excess of carbohydrates in the diet provoked weight gain mainly due to an increase in glycogen stores and the water it attracts (you know that every 0.5 kg of carbohydrates in the body retains an additional 1.5 kg of water), and not because fat was synthesized.
Considering all of the above, the contribution of DNL to our adipose tissue is considered extremely insignificant. Even with a calorie surplus, the majority of carbohydrates are oxidized, and almost all the rest is stored as glycogen. In this case, about 5% can go to DNL (and only if the conditions listed at the beginning of the article are met: very little fat + a lot of carbohydrates).
Why then do we get fat on a calorie surplus with little fat?
Nutritionist and fitness expert Lyle McDonald writes the following in his book How We Get Fat:
“Carbohydrates are rarely converted into fat and stored that way. When you eat more carbs, you burn more carbs and less fat; eat fewer carbs and you will burn fewer carbs and more fat. An excess of carbohydrates increases the amount of carbohydrates burned, reducing the amount of fat burned; more of the fat eaten per day is stored in fat reserves.”
When the goal is to reduce the amount of fat, this is done largely by reducing carbohydrates, just so that the body uses the existing fat for life support.
If there are plenty of carbohydrates, it takes energy from them and not only does not touch the already accumulated fat layer, but also stores the fats consumed daily. If carbohydrates are scarce, it uses up reserves.
In this case, giving up fat seems very tempting: however, we must not forget that reducing it too much will lead to both the possibility of DNL and many health problems. (You can read about the benefits of fats in our material “Why eat fats”).
Less carbohydrates - less kilograms?
Throughout 2021, low-carb diets have been popular again. Fast carbohydrates in foods such as white bread, candy and chocolate are instantly absorbed into the bloodstream and cause a surge in insulin, which ultimately leads to hunger and changes in energy. Nutritionists advised reducing the amount of carbohydrates to make weight loss easier. In this case, your body will use stored fat instead of carbohydrates, which are usually used for fuel.
Edinson Cavani suspended for 3 matches for Instagram post
9 fathers who agreed to be a model for their daughters, but did not regret it
The personal life of the Game of Thrones star, Maisie Williams, in photos
The keto diet requires not only a reduction in carbohydrates, but also an increased intake of fats. Some experts believe that they keep you fuller longer and do not affect your blood sugar levels.

The study examined whether different amounts of carbohydrates could affect how the body uses energy. Among 164 participants, it was found that those who ate a low-carb diet burned more calories than those who maintained a high-carbohydrate diet. At the same time, the weight of the participants remained stable.
David Ludwig, a leading expert at Boston Children's Hospital, said he suggests limiting carbohydrates for people who want to maintain a low weight after finishing the diet. He also noted that this approach is great for people with diabetes because it minimizes spikes in blood sugar.
However, David noted that this study does not examine the long-term effects of such a diet, so people who are planning to follow it should definitely consult a specialist before they take action.
Proteins on the way to fat burning
Moreover, it is not only carbohydrates that inhibit fat burning. Squirrels also get in the way, to quote Lyle MacDonald:
“Here's what happens mechanically and how it makes you fat:
– excess dietary fat is directly stored in reserves;
– an excess of carbohydrates increases the amount of carbohydrates burned, reducing the amount of fat burned;
– a larger amount of fat eaten per day is stored in fat reserves;
Brief conclusions
- However, an excess of carbohydrates helps the existing fat remain intact and the fats received daily are stored in the form of new subcutaneous reserves.
- Excess protein helps exactly the same.
The advantages of carbohydrates are not limited to the fact that in 99% of cases they are not converted into fat: they also give us energy, help maintain immunity, participate in the normal functioning of the hormonal system, in the construction of enzymes and cell membranes. (Full guide to carbohydrates here).
We will not tire of repeating: the diet must be balanced, include each of the macronutrients in an adequate volume consistent with your goals. Only in this case everything will be fine both with your health and with achieving your fitness goals.
Dairy

Everyone knows that when losing weight, you should include cottage cheese and kefir in your diet, preferably low-fat. Dairy products contain easily digestible protein and calcium. Thanks to them, you can lose weight and speed up metabolic processes. But you should approach their choice more than responsibly. Read the label carefully. Choose products without sugar, flavors or artificial sweeteners. Also, don’t get carried away with low-fat foods, they are not at all as good as you think. Calcium from dairy products is absorbed much better with milk fats. And low-fat products are often rich in additives that are harmful to the figure, which give them taste.
Content
Carbohydrates
(saccharides) is the general name for a broad class of natural organic compounds. The name comes from the main components: “coal” (carbon) and “water”. Carbohydrates are the most important nutrient in the diet. To achieve different sports goals, an individual calculation of carbohydrate needs is required.
Carbohydrate calories:
4.1 kcal in 1 gram.
From a bodybuilding perspective, carbohydrates provide a source of easily accessible energy. However, carbohydrates present in the body constitute only 2% of its total energy reserves, while 80% of the energy reserve is contained in fat deposits and the remaining 18% in proteins (skeletal muscle).
Since every gram of carbohydrates is stored in the body along with 4 grams of water, whereas fat storage does not require water, the body stores fat more easily and relies on it as its main reserve source of energy.