A person who wants to achieve perfect abs often simply does not understand how to do it quickly and effectively. As a rule, in such cases you have to contact a specialist - a trainer in any gym club. Here, even in the first lesson, the trainer begins to explain the exercises, touching on complex terms - this is not clear to everyone, since most simply do not know the names of the muscles located at the abdominal level.
The abdominal muscles are accustomed to simply pumping according to the proposed sets of exercises, but if you know the internal structure of the body, you can independently draw up a scheme for strengthening. It is recommended to study not only the interaction system and possible strengthening of muscle fibers, but also the location and functions - this will help in quickly achieving the goal. The information presented below contributes to the accumulation of general knowledge of anatomy, and is also fundamental in strengthening the abdominal muscles.
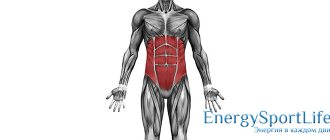
Abdominal muscle anatomy
A person who simply wants to look fit does not have the idea that the anatomical structure of the abdominal muscles is the main point in the question presented. But it is anatomy that helps trainers create a set of exercises - the client’s personal wishes to pump up the abdominal muscles directly or sideways are the starting point in subsequent training for men and women.
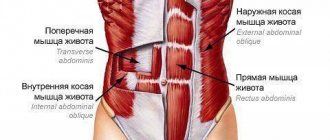
The abdominal muscles are conventionally divided into groups. The following types are subject to pumping:
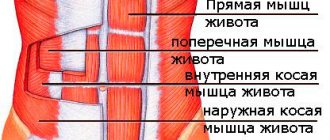
- The rectus muscle is the longest, located in front of the abdominal wall. It is this component that contributes to the formation of the famous cubes on the stomach - the tissue is “broken” by the transverse tendons.
- Transverse - attached to the inguinal ligament and ilium. Although this component is located close to the rectus muscle, it is quite difficult to pump it up.
- Internal oblique - located deep, attached to the iliac crest and cartilages of the lower ribs.
- External oblique - covers the outer surface of the ribs and is located under the skin. Subject to maximum pumping during training along with straight fabric.
You should study the structure and functions of the abdominal muscle fibers every time before deciding to start a specific complex. This is the only way to understand which group of abdominal muscles the proposed complex is designed for. As a rule, the name of the complex can answer the question, but only knowledge about the functionality will help determine whether it will be effective in a particular case.
The structure of the abdominal region
The location and functions of the abdominal muscles in humans are closely interrelated. This area is divided into four types:
- Rectus abdominis muscles. They are attached to the cartilaginous tissues of the 5-7 ribs, the pubic bone and the xiphoid process of the chest.
- The external oblique is attached to the pubic symphysis, the outer surface of the 5-12 ribs, and the iliac crest.
- The transverse is attached to the iliac crest and the lateral third of the ligament in the groin.
- The internal oblique muscle is attached to the iliac crest and the cartilaginous tissue of the lower ribs.
Now it’s worth considering each group separately, as well as why they are in the body.
Video
Rectus muscle
This long abdominal muscle belongs to the anterior abdominal cavity. It starts from the pubic crest and extends to the very top of the abdomen, where it is attached to the sternum with the ribs.
Please note: It is visible when pumping the press. The so-called “cubes” of the press are formed because these tissues are crossed transversely by tendon bridges.
These rectus muscles, in addition to the aesthetic load, are responsible for bending the torso forward and pulling the ribs down. They also lift the pelvis if the chest is fixed. These abdominal muscles, which form the abdominal press, are worked most often and are involved in the work when performing many exercises not only for the abdomen, but also for the hips and back.
Oblique muscles
The oblique muscles of the peritoneum are located on both sides of the human body. They are responsible for turns. They are divided into internal and external. The internal ones are located deep and stretch from the sternum to the pelvis. The external ones are located directly under the skin above the internal ones. Thanks to them, the body bends and twists (accordingly, oblique exercises are called twisting). Moreover, their action is symmetrical. That is, for example, when twisting to the left side, the left external and right internal abdominal muscles work. Based on the name, it becomes clear that their arrangement is oblique. Together with the rectus abdominis muscles, the obliques help stabilize the spinal column by increasing intra-abdominal pressure. Therefore, the spine remains healthy and functions normally. Also, the lateral press helps maintain the internal organs in the desired position.
Obliques are also called stabilizers (as are lumbar). By strengthening them, you can maintain or correct your posture and return your spine to its natural position. Any complex movement begins with the work of the lateral press, and only after that the activity moves to other departments. Strengthening the oblique abdominal muscles is a must to keep them in good shape. Otherwise, asymmetry occurs in the waist area, an imbalance in the development of this muscle group.
Please note: When the goal is to get beautiful abs, you need to remember that not only pumping is important in this matter. If the fat layer is more than 1.5 cm, then the results will not be visible. Therefore, all loads should be not only for hypertrophy of the oblique and rectus muscles, but also for the reduction of fatty tissues located under the skin.
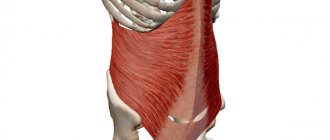
The external oblique muscles are the largest muscles visible in the abdominal region. They are responsible not only for twisting and bending, but also for carrying and lifting heavy objects. They are the only ones in continuous activity, even when a person is standing, responsible for maintaining balance. They provide support to the lower back and spinal column during a variety of movements. The internal oblique muscles, when contracted bilaterally, flex the spine.
Video
If the contraction is one-sided, then either the body is rotated or the ribs are lowered. The attachment of the oblique muscles occurs on the intermediate line at the iliac crest, the area of the lumbothoracic fascia and on the inguinal ligament (its lateral part). The lower beams are directed both down and up. they become a wide aponeurosis along a contour drawn to the pubic bone from the cartilage on the rib. The lower bundles of this muscle in men are included in the spermatic cord, responsible for raising the testicle.
Transversus muscle
The transverse is the third and deepest layer of the peritoneal musculature. The bunches of this group are arranged horizontally, passing from behind and forward, going around the waist. When it contracts, it helps reduce the size of the peritoneal cavity by retracting the abdomen and pulling the ribs toward the midline.

Functions of abdominal fibers
Where the muscles are located is only part of achieving attractive and toned abs. Structure is important, but now you need to determine what functions this or that muscle tissue performs - in fact, this will help pump up and reduce a certain part of the abdomen and waist.
The abdominal muscles perform the following functions:
- The rectus abdominis muscles are the basis for supporting the spine when bending the body forward or backward.
- The external oblique muscle is the basis for turning the body, bending and carrying weights in the hands. Unlike the straight muscle, oblique muscle tissue is constantly in motion and tension. In fact, they simply keep the body in a straight position while walking or sitting.
- The internal obliques help in flexing the spine and also help support and move the ribs. Internal obliques also provide invaluable assistance in supporting the internal abdominal organs.
Not only the internal components have a holding function. All abdominal muscles that form the abdominal press should be strengthened - this will help avoid prolapse of internal organs, as well as the formation of hernias.
Video
It should also be noted that with prolonged sitting, the tone of the straight and oblique muscle fibers decreases - this contributes to an increase in abdominal volume and the development of numerous diseases of the internal organs.
Rule for pumping up your abs No. 1
You can know by heart the structure of the abdominal muscles, as well as how they need to be trained, but remember once and for all: if you do not change your diet, then you can forget about beautiful cubes forever. Also, don't think that working out your abdominal muscles will help you get rid of excess belly fat. Reducing body fat also depends on what kind of food you eat, and abdominal training plays a secondary role in these processes.

Description and functionality
Now we should talk about the features of all types of muscles - this will answer numerous questions and also help solve some problems.
Rectus abdominis muscle
Pumping up the rectus muscles only at first glance refers to the formation of outwardly attractive abs. As it turns out, the rectus muscles are the main ones in preventing the formation of hernias. Of course, there is no need to start professional and labor-intensive strengthening, but you should still perform simple exercises.
Video
Rectus muscle tissue, as mentioned above, has transverse ligaments - each person has different numbers and distances between them. This feature explains the fact that pumped up abdominals look different for everyone. In women and men, the rectus abdominal muscle is slightly different - in women, the lower part is more elastic, and accordingly, they have to pump the lower abdomen longer and more intensely. Increased elasticity of the abdominal fibers is necessary for bearing a child - the muscle stretches during the enlargement of the uterus.
This is interesting: The straight muscle tissue “narrows” towards the bottom, which makes the fibers much smaller. It is the elongated fibers located above the navel that are easier to pump up. Performing exercises to pump up the lower abdominals turns out to be more difficult.
A dangerous point in the violation of the structure of the rectus muscle is the divergence of the white line - the separator into the right and left sides. Normally, the line should be no more than 2 cm wide. The discrepancy indicates the need for surgery, since the natural retention of internal organs ceases. This happens during pregnancy in women, during heavy stress on the abdominal muscles or during obesity.
Oblique external
Oblique outer components help rotate the body and keep it level. The fibers of these muscles belong to the group of the most important broad abdominal components. The anterior parts of the fibers develop into tendons, covering the rectus muscle. The end of the oblique external component is an attachment to the aponeurotic vagina. The oblique external muscle fibers of the abdomen help a person not only hold the body, but also bend to the sides, stimulating the movement of the ribs.
Please note: As a rule, a person does not need to specifically pump up the oblique fibers of the abdomen, but the lack of appropriate tone will lead to an increase in waist size. Women who want to “make” their waist should focus all their efforts on pumping up the external oblique muscles.
Internal obliques
The internal oblique components are located under the external fibers, running from the pelvis to the diaphragm. The attachment of the oblique fibers is determined from the cartilage to the pubic bone.
Transverse
The deepest, located under the straight and oblique muscle tissue. In fact, the transverse fabric covers a person's waist. In front, an aponeurosis is formed in the area of the white line.
Functions of the abdominal press
Experts highlight the fact that it is important not how the muscles are divided into what groups, but what function they perform.

According to existing anatomy, the abdominal muscles are responsible for the following functions:
- maintain intrauterine pressure in the abdomen;
- are the basis in the process of air entering the human lungs;
- help remove urine and feces from the body;
- abdominal fibers act as the main element in a woman’s labor.
This is important: Experts say that pumping the abdominal press is mandatory in order to avoid any disturbances in their functionality. A prolonged sitting position leads to a decrease in tone in the abdominal muscles - this leads to the development of health problems, which include constipation, shortness of breath and other troubles. In women, weak tone leads to the development of diastasis during pregnancy - separation of the white line of the abdomen.
From all of the above, it should be concluded that the structure of the abdomen is fundamental, both in physical and aesthetic health. Only high-quality strengthening can achieve attractive forms. Constant and low-intensity loads ensure the appropriate and normal functionality of the internal organs and the entire body as a whole.
Abdominal muscles: female anatomy
This topic is also one of the most discussed. It’s worth saying right away that the structure of a woman’s abdominal muscles is practically no different from the structure of a man’s abdominal muscles. But despite this, there are still several biological features that we would like to talk about.
With the onset of menopause, the female body experiences a decrease in the production of natural estrogen, which ultimately disrupts the hormonal balance. When estrogen levels decrease, the female endocrine system, so to speak, begins to behave like a man. This leads to an uneven distribution of fat deposits: more and more fat begins to form in the abdominal area. For the same reason, with the onset of menopause, representatives of the fair sex need to focus their attention on training the abdominal muscles in order to reduce the effect of redistribution of fat deposits.