06/12/2016 Training
To train your back more effectively, learn which muscles, bones and joints work during exercise. Train your back with a scientific approach!
Often, people who are just starting to train, first of all, work on the large and impressive-looking muscles in the front of the body. The muscles of the arms, chest and abs look great in the mirror, so many novice athletes neglect to work on their back muscles. However, the back is just as important as the front of the body when it comes to aesthetics, strength and performance.
People who are serious about building their physique know that a broad back will set them apart from other athletes. Understanding your body's anatomy and movement system will make your workouts more effective. I want to tell you everything you need to know to build a great back.
Muscular anatomy
The back consists of many muscles. We won't be able to talk about each one individually, so I want to focus on those that play the most important role in the training process. Here's what you need to know to build an amazing back.
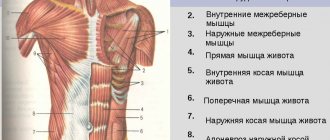
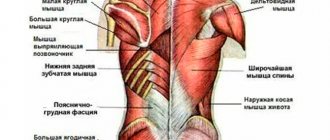
Latissimus muscles
Biomechanics of the latissimus dorsi muscle. Full FAQ. Exercises, misconceptions, myths
The latissimus dorsi muscles are perhaps the main muscles that most people start working on if they want to build up their back. These muscles originate from the humerus (the bone of the upper arm) and extend to the shoulder blade, lower thoracic spine, and thoracolumbar fascia, which is the membrane covering the deep muscles of the back. Since the latissimus muscles occupy a large part of the upper back, they play an extremely important role in building massive and broad muscles.
Trapezius muscles
The trapezius muscles are much larger than you probably realize. Trapezes are divided into 3 parts. The upper part begins at the base of the skull, goes down and attaches to the collarbone. The middle one originates at the top of the spine and is attached to the shoulder blade. The lower one begins in the middle part of the spine and is also attached to the shoulder blade.
Rhomboid muscles
The rhomboids are deep muscles that are located under the trapezius. They are located at an angle and run from the thoracic spine to the shoulder blades. Even though these muscles are not on the surface, you should work on them, as this will have a positive effect on the proportions of your body.
What about the lower back?
This article will focus on the muscles of the upper back. We cover many of the muscles in the lower back in our Ab and Core Workout video.
How does the back muscle corset work?
The back muscles, covering the space from the neck to the tailbone, are functionally responsible for the extension of the spine and shoulder movements. These muscles facilitate movement by attaching to the spinous processes of the vertebrae, ribs or shoulder blades. Many also attach to the back of the pelvis.
The back muscles perform the following functions:
- protects the spinal cord;
- supports the head and body in an upright position;
- regulates the movement of limbs.
Structurally, the back consists of the spine and various muscles, external and internal. Because the spine determines the shape of the back, as well as the structure that gives rise to many of the spinal muscles, it is the most important component of back anatomy.
It extends from the base of the skull to the pelvis and consists of 33 stacked bones called vertebrae. These include the cervical, thoracic in the upper and middle back, lumbar in the lower back and the vertebrae that are part of the pelvis. All this makes up the axial skeleton along with the rib cage and skull.
While the rib cage functions to protect the thoracic organs and facilitate breathing through the action of the thoracic diaphragm muscle, it also serves as the attachment site for many muscles. These include groups that straighten the spine and those that expand, rotate and flex it.
The shoulder blades are considered part of the shoulder girdle. Therefore, they are closely related to the movements of the arms in the shoulder joint. Many movements are initiated by the muscles of the back, and the muscles that attach directly to the shoulder blades.
Numerous muscles, ligaments and tendons support the spine, providing it with flexibility and a wide range of motion. They are classified and arranged according to their function.
The muscle corset is the musculature responsible for correct body posture and maintaining the spine in an upright position.
Skeletal anatomy
The spine plays an important role in almost every movement of the body, but when training your back, you must also understand other bones and joints.
Thoracic spine
The thoracic region is the upper part of the spine. It is made up of 12 bones and runs from the base of the neck to the lower back. A well-developed upper back is essential for safe and effective training.
shoulder blades
The shoulder blades are triangular bones that connect the humerus and the collarbone. They participate in traction horizontal movements.
Shoulder joint
The shoulder joint plays an important role in pulling movements. This is a kind of hinge that allows the hand to be mobile. Because it allows the arm to move and rotate so much, this joint is quite fragile. Remember this and be careful while training.
Possible pathologies
The complex anatomy of the human back muscles suggests the occurrence of various pathologies:
- inflammatory processes that may be symptoms of other diseases;
- atrophy of the spinal muscles;
- injuries.
The most common disease in this area is myositis, a pathological condition based on the occurrence of spasm or inflammation. The primary symptom is severe pain resulting from a pinched nerve. Possible causes of the disease are: stress, hypothermia, infectious infections, prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position, bruises, fractures. Myositis that has become chronic does not cause symptoms.
Important! Common types of myositis: polymyositis and dermatomyositis.
Polymyositis is an inflammatory lesion of several muscle groups at the same time. It is characterized by the following symptoms: mild pain, weakness in the body, shaking, constant fatigue. The danger of this disease lies in its consequences. If you do not notice the disease in time, you can get tissue atrophy, arthritis of the joints, and swelling.
Dermatomyositis mainly affects the female half of humanity at a young age. The exact cause of the pathology cannot be determined; it is presumably caused by a pathogen virus or a hereditary factor. Symptoms:
- skin rash, purple or red, on the face, arms, stomach, back, neck;
- swelling;
- weakness in the body;
- weight loss;
- chills, sweating.
The rate of development of the disease depends on the individual characteristics of the person. The disease is characterized by the appearance of severe complications in the form of accumulation of salts and calcium in the subcutaneous tissues.
The spinal muscles perform many important functions at the same time, so they are subject to extreme stress. There are a large number of nerves around the spine, which causes severe pain during inflammation.
Functions of the back muscles
Once you learn more about muscles, bones and joints, you will understand how they create movement. And movements, as you all understand, are the basis of training. By understanding how these movements occur, we can build a strong upper back as well as maintain healthy shoulder joints.
Latissimus muscles
The latissimus muscles are responsible for the movement of the shoulder joints. Thanks to them, you can move your shoulders back and forth, as well as rotate them. Strong lats are especially important when performing pull-ups, deadlifts, and other heavy lifting exercises.
Trapezius muscles
The trapezius is also involved in shoulder movement. As you extend your arms forward, your upper and lower trapezius and serratus muscles work together to lift your shoulder blades upward. The trapezius muscles are also involved in bringing the shoulder blades together and lowering them down. You also engage them when you shrug.
Rhomboid muscles
The rhomboid muscles are responsible for retracting the shoulder blades as well as rotating them.

“By understanding how these movements are generated, we can build a strong upper back as well as maintain healthy shoulder joints.”
Treatment
To prescribe treatment and make an accurate diagnosis, you must visit a doctor and undergo a full examination. Therapy for myositis depends on the cause of the disease. Treatment of inflammatory processes in the back brace usually begins with massage.
In cases where the cause of inflammation of the back muscles is infection with helminths, anthelmintic drugs are prescribed. If the causative agent of the pathology was an infectious disease, then the doctor prescribes therapy with antibacterial drugs. The purulent form of myositis involves surgical treatment with pumping out putrefactive contents.
Note!
Painkillers are prescribed to all patients without exception, most often they are NSAIDs or painkillers ointments that relieve tension from the affected area.
In addition to doctor’s prescriptions, it is important to adjust your diet, walk more in the fresh air, and after pain symptoms are relieved, you need to gradually begin doing physical exercise to strengthen your back corset.
Basic exercises for back muscles
You should not train your back by performing jerky movements that force it to bend or rotate. You must use your muscles, bones, and joints to make smooth but effective movements. These exercises will give a load to all the back muscles, ensuring their maximum development.
It is also important to know how your body works during different movements. Each of these exercises will develop muscles in different ways, resulting in a proportionate physique and increased overall fitness levels.
Exercise No. 1 Pull-ups
Pull-ups work the latissimus dorsi muscles. This seemingly simple exercise may take time to master the correct technique. Once you can do high reps with your bodyweight, make the exercise more challenging by adding weights.

When doing pull-ups, make sure you move through a full range of motion. Increase your time in the lower phase to stretch the muscles, and in the upper phase, try to pull your chest towards the bar. This technique will help to better pump the lower trapezius and mid-back.
Exercise No. 2 Bent-over dumbbell row
This horizontal row is a great exercise for working the rhomboids, mid-trapezius, and proportionate development of the arm muscles. This is a fairly simple exercise, but its effectiveness can easily be reduced to zero if you do not follow the technique and work with too much weight.

To perform dumbbell rows, get into any position that is comfortable for you and brace your upper back. Pull the dumbbell by bending your elbow and pressing your shoulder blade toward your back. Don't do too many repetitions or use momentum.
Exercise No. 3 Pullover with a dumbbell
This is a great exercise for isolating the lats. It will also help you develop core strength and shoulder mobility.

To get the most benefit from this exercise, lie on your back and take a deep breath. Keep your abs tight to help stretch your lats. Since you will be moving the dumbbell behind your head, you will have to work hard to maintain proper body position. If you arch your back too much, you won't be able to stretch your lats. So remember to keep your core muscles engaged.
Exercise No. 4 Pull-down block to the face
This exercise will take you out of your usual movements and also add some variety to your training. The face pulldown is a great way to build upper and mid back muscles.

When performing the exercise, hold onto the rope with your thumbs on top of the handles. This grip is more comfortable for shoulder movement. If you use a normal grip, the rotator cuff will not move as actively. Fix the position of your upper back, watch the movements of your elbows and bring your shoulder blades together. Stop in the positive phase of the exercise when your elbows are in line with your body.
Myositis of the back muscles is a possible disease of the back muscles
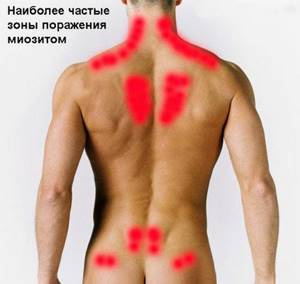
Myositis is inflammation of the muscles of the neck, chest, hip or back. The disease affects one or more muscles at the same time. Myositis causes pain and leads to the formation of nodules in the muscles.
Without proper treatment, the disease enters the chronic stage. Myositis is inflammation of the muscles of the neck, chest, hip or back. The disease affects one or more muscles at the same time. Myositis causes pain and leads to the formation of nodules in the muscles. Without proper treatment, the disease enters the chronic stage.
What is myositis
Myositis is an inflammatory process in skeletal muscles. The most common myositis occurs in the muscles of the back, shoulders and neck. If the disease affects not only the muscles, but also the skin, the doctor diagnoses dermatomyositis.
Depending on the number of muscles affected, local myositis and polymyositis are distinguished. One muscle group suffers from local myositis. Polymyositis affects several muscle groups.
Myositis has two stages: acute and chronic. Acute myositis occurs suddenly, after injury or heavy physical exertion. Without treatment or with improper treatment, myositis becomes chronic and regularly bothers a person: muscles ache during hypothermia, changes in weather, or prolonged exercise.
Causes of myositis
The disease occurs due to muscle overstrain or injury, severe muscle cramps, hypothermia, and intense training. Inflammation of the back muscles develops due to infectious diseases: influenza, ARVI, chronic tonsillitis, sore throat, rheumatism.
Other causes of myositis include: metabolic disorders, gout, diabetes mellitus, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, scoliosis, osteochondrosis.
Myositis occurs due to fungal and bacterial infections, parasites, and diseases of the immune system. The cause of the disease can be exposure to toxic substances, for example, alcoholism or cocaine addiction. Purulent myositis appears if a person gets an infection in an open wound or receives an intramuscular injection without following the rules of hygiene.
Myositis affects people who work in a certain position and strain the same muscle group: pianists, violinists, drivers, programmers.
Types of spinal muscle myositis

- Cervical myositis. The most common type of disease. Occurs due to a cold, overstrain of the neck muscles or being in an uncomfortable position for a long time. The pain is felt on one side of the neck, the person cannot turn his head freely.
- Myositis of the back muscles. The pain is localized in the lower back, so the disease is often confused with lumbago. With myositis, the pain is not so sharp, aching. It does not go away at rest and intensifies with movement and palpation of the lumbar muscles. Inflammation of the back muscles often occurs during pregnancy due to increased stress on the lower back.
- Infectious non-purulent myositis. Occurs due to enteroviral diseases, influenza, syphilis, tuberculosis and brucellosis. Accompanied by severe muscle pain and general weakness.
- Acute purulent myositis. The disease often becomes a complication of a chronic purulent process - for example, osteomyelitis. The patient feels pain in the muscles, they swell, the temperature may rise, and chills may appear.
- Myositis ossificans. It affects the muscles of the shoulders, hips and buttocks. It develops after injury, but can also be congenital. During illness, calcium salts are deposited in the connective tissue. The muscles become denser and atrophy, and the pain is mild.
- Dermatomyositis. More often occurs in young women after stress, colds and hypothermia. Red or purple rashes appear on the arms, face, back and chest. The person feels weak, has chills, and the temperature rises. Calcium salts accumulate under the skin and muscles shorten.
- Polymyositis. The most severe form of myositis. The disease affects several muscles. Accompanied by pain and weakness in the muscles. At first it is difficult for the patient to climb stairs, then from a chair.
Symptoms of myositis
- pain in the neck radiates to the shoulders, forehead, back of the head, ears;
- aching pain in the chest, back, lower back, calf muscles;
- pain intensifies when moving or feeling muscles, in the cold;
- the pain does not go away after rest, the muscles hurt even at rest, when the weather changes;
- the muscles swell, become dense, tense, nodules can be felt in them;
- a person cannot turn his head, straighten up, or bend over;
- the skin over the painful area becomes hot and swelling appears;
- Due to pain, muscle weakness may develop, and rarely, muscle atrophy.
Why is myositis dangerous?
Myositis causes muscle weakness. It is difficult for a person to climb the stairs, get out of bed, or get dressed. As the disease progresses, a person has difficulty raising his head from the pillow in the morning and holding it upright.
The inflammatory process can invade new muscles. Cervical myositis is a serious danger: it affects the muscles of the larynx, pharynx and esophagus.
In severe cases, it is difficult for a person to swallow, coughing attacks appear, and muscles atrophy. Shortness of breath occurs due to inflammation of the respiratory muscles.
If myositis is not treated promptly, the muscles will atrophy and muscle weakness may persist for life.
Diagnostics
Myositis is easily confused with other diseases. Symptoms of lumbar myositis and cervical myositis can be mistaken for an exacerbation of osteochondrosis. In addition, aching pain in the lower back may be a sign of kidney disease. To accurately determine the cause of the pain, consult a specialist.
The doctor at the Health Workshop clinic in St. Petersburg will conduct a comprehensive examination and make an accurate diagnosis. He will conduct a survey and examine the painful area. You will help the doctor if you clarify the nature of the pain and remember under what circumstances it appeared. Our doctors use the following diagnostic methods:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination);
- ECG (electrocardiogram);
- Laboratory research.
Treatment of myositis
Conservative treatment relieves muscle pain and heals the body. In case of acute myositis and exacerbation of chronic myositis, it is better for a person to stay at home and avoid physical activity.
The doctor individually prescribes a course of treatment for the patient. The doctor selects procedures depending on the type and form of myositis, age and characteristics of the patient’s body. The course includes 5 different procedures, the patient undergoes them 2-3 times a week. Treatment for inflammation of the back muscles lasts from 3 to 6 weeks. Muscle pain will go away after the first week of treatment.
The course consists of the following procedures:
- Resonance wave UHF therapy;
- Acupuncture
- Fermatron injections
- Rehabilitation on a simulator
- Blockade of joints and spine, etc.
The specialist penetrates deeply into the dense muscle. This helps well with cervical myositis. Conservative methods relieve tension and restore the functioning of damaged muscles, normalize blood pressure, strengthen the immune system and improve the patient’s well-being.
Acupuncture sessions relieve pain, inflammation and muscle spasms. Physiotherapy restores muscle tone, their ability to contract, and improves blood circulation.
After completing the course of treatment, the doctor will give the patient a list of exercises that can be performed at home to consolidate the effect. The doctor will advise what else to do to prevent myositis.
Prevention of myositis

To protect yourself from myositis, dress appropriately for the weather, avoid hypothermia, drafts, injuries, and intense training. Do not sit on metal or cold benches while waiting for the bus. Do not suffer infectious diseases on your feet; treat influenza, sore throat, colds, and acute respiratory viral infections in a timely manner. It is better not to lean against a cold wall for a long time and not to sit with your back to the window, even if it is closed.
Play sports: swimming, running, yoga, cycling and skating. If you work in the same position, take breaks and warm up: bend in different directions, make circular movements with your shoulders. Do not smoke while driving with the window open, otherwise you risk getting cervical myositis.