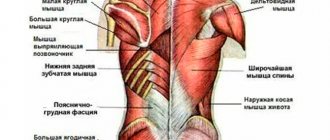
Back anatomy
A person is largely made up of muscles. Therefore, it is important to know the anatomy of the back before starting training. The basis of all human skeletal muscles is the back. The whole body rests on the back: hip joints, neck, arms.
The muscles of the body can be layered on top of each other in several layers, therefore the following types are distinguished:
- deep - located closer to the skeleton of the body;
- superficial - removed from the skeleton.
Functional purpose of the spinal muscles
It is generally accepted that the main task of a back corset is to support the body in an upright position. At the same time, they often forget. However, the tasks of the muscle corset are not limited to this. Correct position of the back (posture, stance, neck position), protection of the spine, inside of which the spinal cord is located, from external influences or damage, maintaining the position - all this work, every day, is performed by the muscle corset.
Muscle division into layers
Before you start training, you need to understand the structure of muscles in layers. All of them are divided into external and internal. The external ones are divided into the first layer, the second and the third. Intrinsic muscles consist of deep, middle and superficial layers.
The first layer of extrinsic muscles consists of the trapezius and latissimus muscles in the back. At the base of the second is a diamond-shaped (small and large). The third, more complex layer consists of the serratus muscles of the scapula, infraspinatus, supraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres.
In turn, the internal superficial ones consist mainly of the belt muscles of the neck and head. The middle ones are based on the extensor muscles of the back and the transverse spinalis. The deep muscles consist of the interspinous, intertransverse, lumbar multifidus, suboccipital and levator ribs muscles.
Who needs to pump up their back muscles?
Back training is important for many reasons: pumped up back muscles will immediately make you stand out from the crowd of athletes, because only a real bodybuilder can work out the “wings”! Your body will look harmonious and balanced.
There is nothing you can do in martial arts without a strong back: your stabilization depends on the strength of your muscle corset. The back is the frame that holds all the muscles and unites the efforts of the whole body. Weak back muscles cannot properly perform their stabilizing role, and problems may arise in maintaining an upright posture. In wrestling, pumped-up back muscles make it easier to perform throws with body extension.
Powerlifters also strive to effectively pump up their backs: in powerlifting, this is the key to success in performing deadlifts, one of the competitive disciplines of powerlifting.
Why is it not easy to work out your back?
In addition, by pumping up your back muscles, you will significantly make your daily life easier, because we perform most of the functional movements, for example, carrying heavy objects, on our backs. From a medical point of view, developed back and core muscles help maintain correct posture and spinal alignment, which has a positive effect on the vital organs of the abdominal cavity. You see how important it is to train your back, are you ready to train? If you are already in the gym and ready to start, we recommend 2 programs from our training videos. Further in the article you will find several more program options.
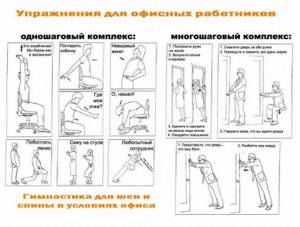
Therapeutic exercises for back pain
Often a person cannot tolerate back pain (musculoskeletal function is impaired, pain syndrome, sometimes the pain radiates to the internal organs). You can cope with simple diseases when your back hurts with the help of special exercises.
Consult your doctor before attempting any treatment at home. A professional doctor will help you create a set of gymnastic or rehabilitation exercises together with other treatment methods.
Forward bends
The legs are positioned slightly wider than the shoulders, the neck is elongated and the back is straight. Raise your hands up, bend down to touch the floor with your hands. Hold the position for a few seconds, feel your legs and back. Get up. For those who have back pain, the exercise is suitable due to muscle stretching.
Quantity:
10-15 reps.
Exercise kitty
In the all-fours position, the legs and arms are placed next to each other. Then the back arches up (convex, as in the image), down (a depression is formed in the lumbar region). This exercise stretches and strengthens the back corset. With its help, wrestlers strengthen their backs along with flexibility.
Quantity:
10-15 reps.
Child's pose exercise
The legs are gently bent until the pelvis touches the heels, from a kneeling position. After your pelvis touches your heels, you need to spread your knees wide to the sides and tilt your pelvis towards the floor until you feel a stretch in the muscles of your back and pelvis. It is forbidden to lift the buttocks from the heels, but it is allowed to slightly round the neck and back. One approach is performed per day.
Quantity:
5-10 reps.
Osteochondrosis: “regret” or “pump up” your back?
Fig.1 Normal
Of course, having trained muscles surrounding the spine is better than weak ones, but there are a number of issues that allow us to look at this statement from a different angle. Firstly, why do those who engage in elite sports periodically get back pain? You cannot say about these people that they have “weak” muscles. Secondly, what should those who have back pain do, this is just another problem in a series of other diseases, especially heart disease, vascular disease, hypertension, thrombophlebitis? After all, any increase in the intensity of the load that accompanies strength training can lead to a worsening of the condition and exacerbation of the disease? And thirdly, how correct is it to associate back pain with the amount of stress exerted by physical exercise on the body?
Let's try to understand this problem and look at it from different angles. First of all, you need to know what causes pain, or as they say in medicine, etiology. The fact is that back pain can be a consequence of osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias, diseases of the joints of the spine, inflammation in muscles and tendons, tumors, or a consequence of problems of internal organs: heart, kidneys, etc. This list can be continued, more Moreover, in some cases, the localization of pain is perceived by people in the same way, but the root cause of its origin can differ significantly. Therefore, the first conclusion is: an accurate diagnosis by a specialist doctor is the basis for the choice of means and methods of physical activity.
One of the most common spinal problems in the age of high-speed Internet and space tourism is osteochondrosis. Scientific works and publications of scientists are replete with statistical data that almost every person after 30 years has osteochondrosis, not to mention professional athletes who, in pursuit of results, subject their musculoskeletal system to enormous tests, as a result of which they easily part with part of their health, exchanging it for medals, titles and certificates. Osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine, accompanied by structural changes in the intervertebral cartilage and vertebral bodies, followed by the formation of bone growths (osteophytes). Subsequently, the bone growths, increasing in size, cause a narrowing (stenosis) of the intervertebral canal and begin to put pressure on the nerve roots, which increases when the vertebrae are displaced relative to their anatomical position (Fig. 2.).
Rice. 2 Stenosis of the intervertebral canal due to the proliferation of osteophytes
It is at the moments when even a slight but sharp displacement of the vertebra occurs that the pressure on the nerve roots of the spinal cord increases, which, apparently, was not foreseen by the “creator,” since any compression of the cells of the nervous system (neurons) is regarded by the body as possible “ a threat to biological integrity,” and he is naturally forced to reflexively defend himself. An effective method that the human body uses that can quickly limit movement in any joint is pain.
According to physiologists, pain is a psychophysiological state of a person, reflecting the most important integrative function of the body, which mobilizes various systems of its protection from the effects of a damaging factor (Anokhin P.K., Orlov N.V., Erokhina L.G., 1976). Mild pain is a signal that some “part” in the body is malfunctioning. Acute, sharp pain is no longer a signal, but information that the “part” is close to a serious “breakdown”, or, even worse, has already “broken”. And the more this kind of “breakdown” occurs, the more, naturally, the pain is stronger and more noticeable. Thus, let’s make a second conclusion: pain is a signal that not everything is in order in the body, and constant, persistent pain is a reason to see a doctor. Another effective way the body uses to prevent further displacement of the vertebrae is by spasm of the paravertebral muscles, which creates a natural mobilization around the vertebrae.
This leads to the third conclusion: increased muscle tone around the spine is a sign of a violation of the anatomical position of the spinal segments and a harbinger of damage; the next signal may be pain. So, from the above it follows that a change in the anatomical position of the vertebrae can cause increased compression of the nerve roots by osteophytes formed as a result of osteochondrosis, and, accordingly, cause pain in the back, in the muscles and organs that are innervated by this root - the so-called pain of a neurological nature.
Consequently, ensuring the anatomical position of the vertebrae (stabilization) in everyday, work and sports activities is a necessary condition for the normal functioning of the entire body as a whole and the key to the absence of exacerbation of the disease.
I would like to note that the process of rehabilitation of a person with diseases or injuries implies not only the maximum restoration of the anatomical integrity and functions of systems and organs, but also the restoration of quality of life. Moreover, in situations where it is not possible to completely restore structure and function, conservative means and methods aimed at minimizing factors that contribute to repeated exacerbations of the disease and aggravation of the problem come to the fore. A system called “Back School” has long been widespread abroad, the participants of which acquire skills in everyday physical activity in the face of existing spinal problems.
Thus, the problem of physical activity in general, and the necessary physical exercises in particular, in case of osteochondrosis, must be looked at from the following positions: Physical activity and physical exercises should help maintain a normal level of functioning of all body systems for the full implementation of the life tasks facing a person within his household, work, sports activities, i.e. his society.
What are aerobic and strength training, stretching, etc. traditionally used for? However, when implementing these programs, it is necessary to take into account a number of rules: During physical activity, it is necessary to limit or eliminate impact loads on the spine, such as running, jumping, etc., since the repeated impact force on the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc will squeeze it to the side, that in conditions of degenerative changes in the intervertebral cartilage itself can lead to protrusions and intervertebral hernias.
For the same reason, when performing physical exercises, it is necessary to limit or eliminate - depending on the condition of the spine - axial loads on the spine of more than 3 kg, for which starting positions are used: lying, sitting, reclining on an inclined surface, exercises in water, etc. During exercises aimed at developing mobility in the joints, it is necessary to limit excessive flexion, extension and stretching of the spine, since this kind of exercise (bridge, plow, free hangs on the bar, etc.) promote stretching of the paravertebral ligaments and, as a result, destabilization of the vertebrae relative to each other.
In the case of existing pain, the physical exercise program should include a number of special exercises, developed strictly individually and aimed at eliminating the consequences of compression of the nerve roots. For example, post-isometric relaxation of spasmed muscles, unloading and traction of the spine on special devices, reflex-segmental massage, which helps improve the trophism of tissues and organs innervated by this root. Teaching a person the skills to stabilize the spine in the face of external and internal forces that can lead to displacement of the vertebrae, increased compression on the nerve roots and, consequently, the appearance or increase in pain. Based on the above, we can conclude that a person who “sorries” his back, instead of increasing the quality of life, on the contrary, reduces it, acquiring poor blood supply to the muscles surrounding the spine, reducing their functionality, etc.
On the other hand, training the superficial muscles of the flexors and extensors when “pumping” them is of an amplitude nature, which will also aggravate the problem, since this kind of movement is not possible without displacement of the vertebrae. Where is the solution to the problem? In the formation and consolidation of the skill of stabilizing the anatomical position of the spine by improving intermuscular coordination, with its subsequent transfer to physical activity in everyday life, work, and sports. Testing To understand what stabilization skill is, try a test to assess spinal stabilization skill under isometric tension. To do this, lie on your back with your knees bent at an angle of 90 degrees. Place your feet on the floor shoulder-width apart. Hands lie on the floor along the body. Place the folded cuff of a conventional mechanical blood pressure monitor under your lower back (Fig. 3 A).
Assessment of spinal stabilization skills during isometric tension.
Rice. 3 A
Inflate the pillow to 40 mmHg. Art. and while exhaling, tense the muscles of the whole body with an intensity of 60-80% of the maximum possible, gradually increasing the tension. The criterion for achieving tension above 60-80% is holding your breath. Maintaining pressure in the pillow in the range of 30-50 mm Hg. during tension, indicates the presence of skill in stabilizing the spine (Fig. 3 B).
Rice. 3 B
If there was an increase in pressure on the pillow, which was expressed in the shift of the pressure gauge needle to a greater value of 40 mm Hg. Art. side, this means that during the tension there was a flattening of the lumbar lordosis. In this case, we can talk about the presence of functional muscle asymmetry due to the lack of intermuscular coordination between the rectus abdominis muscle and the spinal extensor muscles or due to reduced tone of the spinal extensor muscles (Fig. 3 B).
Rice. 3 V
If there was a decrease in pressure on the pillow, which was expressed in the shift of the pressure gauge needle to less than 40 mm Hg. Art. side, this means that there was an increase in lumbar lordosis. In this case, we can talk about the presence of functional muscle asymmetry due to the lack of intermuscular coordination between the rectus abdominis muscle and the extensor muscles of the spine or due to reduced tone of the rectus abdominis muscle (Fig. 3 D).
Rice. 3 G
After this, try repeating the test with pressure gauge control. If you manage to maintain the pressure within 30-50 mmHg. when visually monitoring the pressure gauge dial, this means: you have the so-called “skill” of stabilizing the spine, the presence of which will significantly reduce the time it takes to acquire stabilization skills.
How important is it?
The fact is that if a situation arises when a simultaneous isometric tension of the muscles of the secondary stabilizers occurs, for example, when trying to maintain balance on a slippery surface, the lack of intermuscular coordination will not allow maintaining the physiological bends and individual segments of the spine in the anatomical position, which is ensured in the presence of neurological diseases spine, as mentioned earlier, is an important factor for ensuring quality of life and preventing exacerbation of the disease.
Conclusions:
Of course, stabilization exercises will not cure osteochondrosis, as, indeed, other physiotherapeutic means, but they will give the opportunity to live fully and enjoy the opportunity to move.
Author: Dmitry Erdenko - specialist in physical rehabilitation and physical therapy, head of the methodological office of the Department of Exercise Therapy, Massage and Rehabilitation of the Russian State University of Physical Culture and Technology, methodologist in physical therapy at the Research Institute of Rheumatology.
Back strength exercises for girls in the gym
Other muscles of the body are often worked along with the back (legs and arms). This is due to the lack of sufficient time to fully work out the spinal muscles. However, there are effective exercises for training a group of spinal muscles that require little time. You can do this with dumbbells and a barbell. The exercises below will help you figure out how to properly pump your back on the exercise machine.
Deadlift
Straighten your back, relax and lower your shoulders, tighten your abs. Dumbbells in hands, lightly touching hips. Bend your knees slightly, squat down lightly, and push your pelvis back until your upper back is parallel to the floor. It is important to lower and raise the dumbbells along your legs so that the tension on the muscles is correct. To prevent back damage, you should not use dumbbells that are too heavy (it is better to start small and gradually increase the weight). This exercise with dumbbells can be performed at home.
Quantity:
10-15 reps, 3-4 sets.
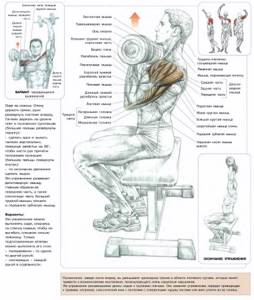
Bent-over row
The exercise can be performed with dumbbells and a barbell. First tilt your torso forward a little and sit down. We place our feet shoulder-width apart so that the stance is stable. The barbell or dumbbells are taken with a straight grip. Then, they rise as high as possible, while the position of the remaining parts of the body should be rigidly fixed (only the hands work). If you perform this exercise correctly, you can pump up the latissimus dorsi muscles along with the abs and arms.
Quantity:
10 reps, 3-4 sets.
Raising and abducting arms in an inclined position
This exercise applies to training with dumbbells at home or in the gym. Get into the starting position (feet shoulder-width apart, knees bent, lean your body forward). The dumbbells are held in your hands, slightly bent, with a neutral grip. The arms are raised up to a position parallel to the floor, then slowly brought down. The elbow bend is maintained constantly.
Quantity
: 10-15 reps, 3-4 sets.
The exercise is useful because it can be performed at home without dumbbells. You can use plastic water bottles instead. This will allow you to train every day when it is not possible to go to the gym.
When training in the gym, you can ask the trainer for advice by asking the question: How to pump your back with dumbbells at home. Home workouts will help you build better muscles when used in conjunction with exercises at the gym.
It should be remembered that training with a herniated disc or other back diseases is strictly contraindicated. In this case, it is better to consult a specialist doctor. He will conduct the necessary examinations and find the reason why your back hurts.
Back muscle workout #1
Deadlift
- 5 sets of 15,12,10,8,6 repetitions
- Body part: Quadriceps Equipment: Barbell
Pull-ups
- 1 set of 25 reps
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Bodyweight
Note: If you can do that many pull-ups in one set, do two sets of 25 reps. Use a wide overhand grip and full range of motion
Bent-over barbell row
- 3 sets of 12 reps
- Body Part: Press Equipment: Barbell
Note: Use a weight that you can lift for 8 reps. Rest and then complete the set.
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
To properly tone your back muscles with this workout, remember this: your deadlift should be sharp and active, but completely controlled, and slow on the downward movement. Use a full range of motion when doing pull-ups, concentrating only on your back and not your biceps. Remember that your biceps are just hooks, nothing more.
We pump our back at home
We figured out the question: why pump your back. However, the question: how to properly pump your back at home yourself remains open (what exercises will be effective?). There is a lot of material on this topic on the Internet. However, the back (in particular the spine) is a very important and fragile part of the body, so we have collected only the most proven exercises. So, how to properly train your back muscles at home?
Arm rotation from plank position
Stand in a plank position, but instead of elbows, rest on your palms. Spread your legs slightly to the sides, tighten your lower back and abs to a slight tension. The palm is lifted off the floor, then a circular motion is performed.
Using the plank, we work the lower back, mid-back, abs, and latissimus dorsi muscles in the area of the shoulder blades.
Quantity:
10-15 reps, 2-3 sets per arm.
Swimmer exercise
The swimmer exercise helps to strengthen your back muscles at home without additional equipment. Lie on your stomach, stretch your arms out in front of you, palms down. Then lift your face and upper back off the floor. We pump up the upper back by simultaneously lifting the back and legs as high as possible. Quantity:
10-15 reps, 4-5 sets.
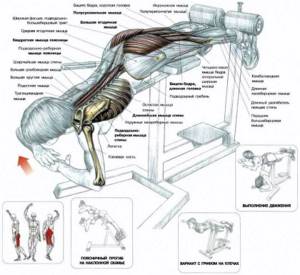
Strengthen your back with push-ups
Lying push-ups are the most popular exercise without sports equipment, allowing you to pump up your back muscles at home. Good for strengthening the spine. Works your back and chest at the same time. Often, the trainer advises girls to train their backs with push-ups.
During the exercise, the abdominal muscles tense, which leads to tension in the back. Thus, it works well on the lower back. Also, the latissimus dorsi muscles are worked at home without additional equipment. Back push-ups, like other muscles, can be trained quickly.
Place your palms on the floor, bring your legs together and stretch them back. Bend your elbows and lower yourself until your elbows are bent at a 90-degree angle. Then, straighten your arms. By performing this exercise regularly, you will quickly pump up your back with push-ups.
Quantity:
10-15 reps, 3-4 sets.
Strengthening exercises for the back muscles
Exercise “Strong back”. Gives strength to the spinal muscles and is preventive in nature against ailments of the spinal regions.

Lie on your back and place a flat pillow in the form of a cushion under your lumbar region. Bend your legs and spread them slightly hip-width apart. Pressing your heels into the floor, try to pull your toes and point them towards you. The arms are slightly bent, the palms are tensely turned towards the shoulders.
Raising the back of your head as much as possible, pull your chin towards your chest. This should create a feeling of stretching in the neck muscles and spine. Freeze for a few moments, then release the tension and lie quietly.

Exercises for a thin waist and flat stomach. TOP 20 best solutions + instructions with photos and videos!
How to pump up your abs in a week at home? The best exercise system for beginners! Exercises for girls and men

How to run to lose weight - a review of the most effective methods to lose weight in your legs and stomach. Instructions with photos and videos!
The next exercise for the back and abs is best done in the gym, since you will need a body bar with two discs, each weighing 1 kg.
Sitting on the floor with your legs bent, take the bodybar with your hands and fix it in the chest area. Gently lean back until tension appears in your abdominal muscles. Rotate the bodybar in the form of rowing with oars.
This back exercise requires a fitball and dumbbells. Lie on it with your back, place dumbbells in your hands and hold them in front of you. Place your feet on the floor at a 90-degree angle. Spread your hands and bring them together again.
Recommended for strengthening the area between the shoulder blades.
- similar to the previous exercise, but the arms are moved alternately. For balance, you can lean on a chair. This movement involves the middle dorsal muscles.
- standing straight with a load in your hands, raise your shoulders up and down without straining your arms. This way the muscles of the neck and back will be involved.
- Lie on the fitball with your back up and your feet against a vertical surface. Raise and lower your torso, while the muscles of your lower back actively work. To make it more difficult, raise your legs higher. In addition to the spinal muscles, the gluteal and femoral muscle sections are also involved.
Using exercise machines to train your back
Some people have various back exercise machines at their disposal. With their help, it is possible to organize proper training. In this section of the article you will get the answer to the question: How to properly pump your back on a simulator
so as not to rip it off.
Also, what exercises to do
to get maximum results.
The main rule of any training
Training will be beneficial only if the athlete adheres to the following rules:
- Training should be regular. so that the body gets used to the stress;
- The increase in loads should be gradual (a sharp increase in load will lead to injury);
- Before training, be sure to do a warm-up to warm up your muscles.
It doesn’t matter whether you train your back muscles at home or in the gym under the supervision of a trainer - always remember these rules and follow them.
What equipment to use for training
There is a myth: If you use expensive modern equipment, your training will be effective. For some, a crossbar is enough for training, while others need professional training equipment.
Pull-up exercise on the bar
A universal exercise that is widely popular among men. The exercise is popular due to its versatility. You can use it to pump up your biceps. When you pump your abs, your oblique abdominal muscles become stronger.
To perform this exercise, you need to hang on the bar by your hands. Then bend your elbows until your chin rises above the bar. Thus, on the horizontal bar, the athlete lifts himself using the muscles of the back, arms, shoulders and forearms.
Quantity:
5-10 reps, 3-4 sets.
How to pump up a girl's back muscles
Girls are advised not to pay as much attention to stress as men. After all, the body is quite fragile, so the chance of getting any injury is much higher.
Girls are better off doing warm-up exercises with dumbbells or training at home on a fitball.

To make your muscles look beautiful, it is enough to stick to short but periodic workouts.
Girls are advised to seriously monitor their protein diet, since most often the problem lies precisely in unhealthy eating.

Eat right, exercise occasionally, and you won't have to sweat a lot to maintain your results.
When training your back muscles, never bend your back - this is the key to all your success.

Under no circumstances should you give up on training, distribute the load correctly, eat well, and then the results will not keep you waiting.
Beginners are advised to do more sets with fewer repetitions; later the load can be increased.
Is it possible for a man to pump up his shoulders on his own?
You can train your shoulders in the gym using barbells and exercise machines. However, not everyone can regularly visit the gym, asking questions:
- How often should you train at home?
- What and how best to pump up your back muscles?
- Is it possible to combine training of other muscle groups with the back in one day?
How many times a week do you train?
How many times a week you need to pump your back is up to everyone to determine for themselves. If you train your back in the gym, the optimal frequency is 2-3 times a week. This frequency of training is due to the fact that back training in the gym takes place under additional loads (back training with kettlebells and other exercise equipment). The men's gym has a lot of additional equipment.
Back training at home is usually done in a more gentle manner. The most common stretching exercises performed are back exercises and push-ups. Sometimes, at home they train their back with a barbell. Therefore, you can do workouts at home a little more often than in the gym (3-4 times a week).
What to pump your back with?
For greater benefits from training, back exercises are often alternated with other muscle groups. For example, you can train a wide back with your legs or arms. Sometimes they combine the back and shoulders in one workout. If you have a barbell or crossbar, such training is easy to organize. However, the question: what to pump your back with remains open.
When choosing a barbell for home, pay attention to the thickness of the bar. It should be such that you can completely wrap your arms around it. Then back training with a barbell will be enjoyable. It will be pleasant to play sports.
When combining your back and shoulders in one workout, you need to remember that most back exercises simultaneously work your shoulders. Especially exercises on the simulator. You can find a lot of equipment in the gym for girls and men. Therefore, everyone can choose what to pump their muscles with.
How to pump up your back muscles with dumbbells
In order to pump up your muscles with dumbbells, you must place your hands on a flat surface and perform exercises in the plank, with your feet on the floor, one hand resting on the bench, and the other lifting the dumbbells.

Keep your back straight. It is important to understand that this way the load will be distributed to the right places. It's quite difficult, but practice and you will succeed
Spend enough time a day lifting dumbbells and do several approaches. We perform lifts with both the left and right hand; the broad muscles of both sides of the back will be involved.

You shouldn’t think about how to pump up the rhomboid back muscles, since it’s quite difficult to pump up all muscle groups with dumbbells at once - you simply won’t have enough energy, especially if pumping up your back is only part of the complex of the entire workout.

Workout for the broad back muscles No. 3
Pull-ups
- 1 set of 30 reps
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Bodyweight
Note: 30 reps for as many sets as needed. If you can do that many pull-ups in one set, do two sets of 30 reps. Use a wide overhand grip and full range of motion
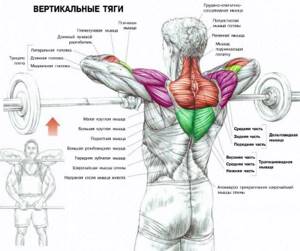
Pull-down of the upper block behind the head
- 2 sets of 8 reps
- Body part: Lat Equipment: Block
Smith Machine Bent Over Row
- 3 sets of 12 reps
- Body part: Middle back Equipment: Exercise
Standing dumbbell shrugs
- 4 sets of 12,10,10,8 repetitions
- Body part: Trapeze Equipment: Dumbbells
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
As you deadlift, pull the barbell toward your upper chest. In this and the next exercise, maintain continuous tension for the best back training. Pause and contract the muscles at the peak of the movement, counting to 3. When doing the T-bar row, move up sharply, move down slowly and in a controlled manner.
Workout for thickening back muscles #4
Deadlift
- 6 sets of 15,12,10,6-8,6-8,4 repetitions
- Body part: Quadriceps Equipment: Barbell
Bent-over dumbbell row
- 3 sets of 8-10 reps
- Body part: Middle back Equipment: Dumbbells
Bent-over barbell row
- 3 sets of 8 reps
- Body Part: Press Equipment: Barbell
Pull-ups
- 3 sets of 10 reps
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Bodyweight
Shrugs with a barbell
- 3 sets of 15 reps
- Body part: Trapeze Equipment: Barbell
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
When deadlifting, use a heavier weight than usual. Move up sharply, stay at the peak for three counts, and only then slowly lower down. In the bent over dumbbell row the pattern is similar. The features of pull-downs and push-ups here are as follows: maintain constant tension, and count to 5, hold at the peak. Stop with these two exercises halfway through each repetition and pause briefly for another 5 counts.
Back muscle training No. 2
Deadlift in a power rack
- 5 sets of 15,12,10,8,6 repetitions
- Body part: Lower back Equipment: Barbell
Smith Machine Bent Over Row
- 3 sets of 8 reps
- Body part: Middle back Equipment: Exercise
Pull-ups
- 4 sets of 10 reps
- Body Part: Lat Equipment: Bodyweight
Attention: 2 of these approaches are with a medium wide grip on top, and 2 with a wide grip
Shrugs with a barbell
- 4 sets of 12,10,8,6 repetitions
- Body part: Trapeze Equipment: Barbell
Note: All are working, so use a weight that will allow you to complete the required number of repetitions.
Add to Calendar * Add to My Workouts * Print Workout
* — The service is in beta testing
Power cleans are a sharp exercise. Be sure you understand this feature of the exercise and always keep your reps under control. The cable row should be performed with continuous tension: contract the muscles and count to 3 as you lower the weight to your chest. Whenever possible, reverse the movement for a count of 4. Use the same repetition method for lat pulldowns. When performing shrugs, pull your shoulders up towards your ears, pause and contract the muscles, work this way in any workout, not just when pumping up your back muscles.