The main differences between callanetics and Pilates
Both areas of fitness, with regular and persistent training, have a powerful healing effect on the body. Let's look at the features of each.
Features of callanetics
Callanetics is a system of physical training that includes a set of exercises for stretching and contracting muscles. The basic principle is alternating static load (holding body position in certain poses for 60-100 minutes) and stretching.
The creator of an unusual trend in fitness is American Callan Pinkney, who has suffered from musculoskeletal diseases since childhood. Doctors forbade her to play sports, but Callan developed a unique system of gymnastic exercises that helped her get rid of her ailments and get in good physical shape.
During a callanetics class, several major muscle groups work intensively at once, including deep-lying ones, which cannot be used in any other form of fitness. Their activation stimulates fat burning and allows you to correct your figure in a short time. After 2-3 months, any housewife will look like a ballerina: flexible, slender and graceful.
In just 1 hour of callanetics training, the muscles receive the same load as in 7 hours of training according to the classic shaping program.
Features of Pilates
Pilates is a dynamic type of training in which exercises are performed in a specific technique and sequence. Their goal is to develop joint flexibility, strengthen the muscle corset, improve posture and coordination of movements.
Pilates exercises involve the main motor muscles (flexors and extensors), as well as stabilizer muscles that keep the body in balance.
The author of the system is the German trainer Joseph Pilates. He developed a special technique for performing standard gymnastic exercises while in prison. They helped to maintain vitality and improve health in difficult conditions.
Basic principles:
- maximum concentration, focus on correct body position and breathing;
- smoothness of movements, absence of jerks, pauses between exercises;
- constant “search for the center” - the abdominal and pelvic muscles must be kept tight throughout the entire workout.
In Pilates, it is not the quantity, but the quality of movements that is important. There is no need to work up a sweat, doing the maximum number of repetitions in several approaches. Concentrating on the work of a specific muscle helps you feel the tension, getting the maximum effect.
Pilates was originally used to rehabilitate the disabled and wounded in the First World War. Later they began to use it to restore injured athletes and dancers.
Despite the fact that both Pilates and callanetics were created with the goal of promoting health and are similar in the effect they produce on the body, there are significant differences between these systems.
There are 5 fundamental differences.
- Nature of the load: dynamic in Pilates, static in callanetics.
- The main goal of Pilates is flexibility and correction of poor posture. Callanetics is aimed at stretching and strengthening muscles and losing weight.
- Pilates exercises involve a specific group of motor muscle fibers and stabilizer muscles. Callanetics involves superficial and deep-lying muscle layers.
- Pilates can be practiced by beginners in fitness; callanetics is more suitable for trained people and athletes.
- The Pilates method mainly strengthens the muscles of the back and abdominals, eliminating osteochondrosis and diseases of the spinal column. Callanetics develops the muscle corset of the whole body.
The frequency and duration of training for both types of fitness depend on the level of physical fitness, health status, and availability of free time. But to achieve results, Pilates should be practiced more often (at least 3-4 times a week). Callanetics training at the initial stage is carried out three times a week, later 1-2 times are enough.
Excursion into history
The creator of Pilates was Joseph Pilates, a native of Germany. From birth he was a sickly and weak child, and his peers made fun of him and bullied him because of this. He began to show interest in sports at the age of 10, and it bore fruit. Since his father was a gymnast, Josef started with this sport, and then also did boxing, swimming and wrestling. By the age of 15, he had a well-built, developed body and good health.
During the First World War, he was detained and placed in a camp in Great Britain along with other Germans. There were poor conditions there and because of this, many prisoners got sick, but Pilates continued training and developed his own method even in such conditions.
After the war, he briefly moved to Germany and then to the United States. There he saw that sports centers were beginning to gain popularity and decided to invest all his savings in his own studio. And I was right. The first to positively evaluate his system were ballet dancers, and over time, athletes and actors became interested in it. Within a few years, he opened branches in major US cities, but this technique gained worldwide popularity already in the 70s thanks to his students.
The creator of callanetics, Callan Pinkney (real name Barbara), was also not in good health. For her mother it was a difficult pregnancy and childbirth, so the girl was born with physical disabilities. She had problems with her spine and legs. As a child, Barbara was distinguished by her fighting character and, despite her characteristics, she wanted to study at ballet school. Long and hard training had a beneficial effect on her body and improved her physical condition. While studying at the university, because of unhappy love, the girl decided to go on a journey that lasted 11 years, but after it she became seriously ill and, according to doctors, was to remain disabled for the rest of her life. But she was not going to put up with it and began her fight against the disease through training.
So she began to develop her own exercise system. Seeing its results, friends and relatives began to show interest in the technique, and over time, the first results appeared. Against the backdrop of success, Callan decided to write her first book about this technique, which she called callanetics, and began to promote it to the masses. Her first success came after participating in a local show, after which callanetics became more popular, and a year later everyone was talking about it, from glossy magazines to Oprah Winfrey.
Similarities between callanetics and Pilates
These two popular trends also have common features. The very fact that they were designed specifically for promoting health, and not for losing weight or gaining muscle mass, like most types of fitness, says a lot.
Both systems have a positive effect on all organs and systems of the body, develop flexibility, coordination, and improve posture. In addition, classes help relieve psychological tension and get rid of stress.
Callanetics and Pilates are similar in training organization:
- both sets of exercises can be performed at home;
- do not require additional equipment, equipment, special clothing or shoes; all you need is a mat and a little free space (4 sq.m.);
- you can learn the correct technique for doing the exercises on your own;
- training takes place at a smooth pace, there are no jumping, running, or sudden movements;
- there is no risk of injury.
Pilates and callanetics, like no other types of fitness, are suitable for people with cardiovascular diseases and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. You can exercise at any age, women and men.
What is better, stretching or yoga?
Many people asked this question before choosing a suitable sports direction for themselves. Yoga cannot be called just a sport, since it is a whole philosophy that includes physical and spiritual practices. Stretching and yoga, the difference between which is significant, are similar in the presence of stretching exercises performed at a slow pace. As for the popular spiritual practice, it uses various exercises supplemented by meditation. In addition, yoga is aimed at working out the whole body, and stretching stretches muscles individually.
Contraindications
Despite the healing effect for the body, there are a number of diseases and conditions for which callanetics or Pilates is contraindicated.
- Exacerbation of hernias, spinal protrusion.
- Influenza and ARVI in the acute period (high temperature, muscle weakness).
- Untreated injuries, fractures, sprains.
- Postoperative period (you can study one year after surgery or cesarean section).
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Pregnancy is not the best time to start training. But, if the expectant mother has already done Pilates or callanetics before, then the classes will even benefit her and prepare her body for childbirth.
If you have bronchial asthma, severe diseases of the musculoskeletal system, or varicose veins, you should consult your doctor before starting training. It is possible to draw up an individual lesson plan taking into account your health status.
Types of stretching
There are several classifications, so depending on the load on the muscles, soft and deep stretching are distinguished. The first option involves stretching the muscles to their usual length (one movement is performed for 40 seconds), and the second leads to their stretching to a larger size (one movement is performed for 1-5 minutes). There are types of stretching that differ in the way the exercises are performed:
- Static
. This option is intended for beginners, and it is aimed at relaxing the muscles. The exercises are performed slowly and smoothly. - Dynamic
. This type is simple and can be used by people who do not have serious physical training. During training, the muscles first tense and then relax. - Active
. When figuring out what stretching is, it is necessary to dwell on this option, which helps stretch muscles that are in a passive state. This type of training helps improve joint mobility. - Isometric
. Stretching, when using this type of training, occurs in several stages: tension, relaxation, stretching and fixation. To cope with it, a person must be physically prepared. - Ballistic
. This type of stretching is a development system that is the most unsafe, since the exercises are performed abruptly and at a fast pace. It is recommended to exercise only under the guidance of a trainer. - Proprioceptive neuromuscular
. This type is used to restore joint mobility after injury or surgery.
The benefits of these types of fitness
Callanetics and Pilates are designed to restore lost health, natural flexibility, and strengthen the body's muscular corset. The more persistently and for longer you do these types of fitness, the more health benefits you can get. After just a few weeks of regular training, the results will be noticeable:
- Posture will improve, the desire to slouch will disappear;
- back and neck pain will disappear;
- performance will increase;
- the muscles will become elastic.
The body will become more flexible, toned, joints will become more mobile, movements will become smooth and graceful. Self-confidence will increase and susceptibility to depression will decrease.
Nutrition during stretching
No matter what kind of sport a person does, proper nutrition is of great importance, otherwise discomfort and health problems may arise, and if the training is intended for weight loss, then there may be no result. Water balance is of great importance, so you need to drink at least two liters of liquid per day. In the information regarding stretching - what is it, it was stated that muscle elasticity is important, and for this you need to include in your diet fatty acids, which are found in fish, nuts, vegetable oil and avocado.
The menu should include foods rich in vitamins, and fresh vegetables and fruits are best suited for this purpose. It is recommended to minimize the amount of salt consumed, which makes the ligaments stiff. You also need to give up sugar, which can easily replace honey. Many people are interested in whether it is possible to eat after stretching, so trainers recommend eating no earlier than an hour after exercise.
What's best for losing weight?
Any type of physical activity, especially in combination with proper nutrition, has a positive effect on your figure. Pilates and callanetics also contribute to weight loss, but not in the same way.
Static loads activate the work of many muscle groups, which requires a large expenditure of calories. In 1 hour of training you can burn 300-350 kcal.
When performing static callanetics exercises, slow muscle fibers are activated, which activate the process of burning fat deposits. These muscles cannot be used during strength training or repetitive movements (as in Pilates).
You should not expect a quick weight loss effect when practicing callanetics, but the results will be long-lasting. If your body weight significantly exceeds the norm, you should add cardio exercise to the statics (in the absence of contraindications). This will speed up the weight loss process.
Review of callanetics
Callanetics is considered to be a specific set of exercises, which includes gymnastics and statics and uses all the muscles of the body. How is callanetics different from Pilates? For the first direction, yoga asanas serve as the basis. A 1 hour session is considered to be equal to 24 hours of simple aerobic exercise.
The main essence of the system is heavy static loads, since performing some elements requires the ability to hold a pose for 1.5 minutes. Not everyone can do this. Exercises tone not only the external muscles, but also those located inside. Many physical activities do not work the internal muscles, which over time leads to weakness. You will be able to see the first results in the fifth lesson.
What's better for your back?
Pilates is the most useful form of fitness for diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, poor posture) or previous back injuries. A set of exercises strengthens the muscular corset that supports the spine, normalizing its functioning.
Lesson after lesson, the spinal column will gradually return to the correct physiological position, blood circulation in the intervertebral discs will improve, and compressed nerve endings will be released.
Freed from “distortions” resulting from injuries or poor posture, the body will move as nature intended. The balance in the functioning of muscle groups will be restored, which will entail the normalization of the activity of the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems of the body.
If you have problems with the spine, it is advisable to consult a doctor and an experienced trainer who will select a set of exercises in accordance with the nature and location of pain in the back.
Comparison
History of creation
Pilates was developed in the early twentieth century by Joseph Pilates. The system's greatest success came at the beginning of the twenty-first century. Currently, over ten million people around the world practice this technique.
Callanetics was created in the early eighties of the last century by ballerina Callan Pinkney based on yoga asanas. She had serious knee and back pain. Conventional treatment methods did not help, so I had to develop my own system.
Distinctive features
As described earlier, Pilates is the smooth transition of exercises from one to another, and callanetics is tense and concentrated statics.
Pilates uses slow, wide-range exercises that require a high degree of concentration to fully engage the required working area, and a certain number of repetitions are performed. While callanetics uses 29 static exercises, where the emphasis is not on movement, but on stretching and contracting certain muscle groups.
If you compare Pilates and calanetics in terms of complexity, the first one is much simpler, since it does not require much flexibility initially, it helps you gradually “get used to it”, and is quite simple for beginners. But those who practice callanetics are required to have flexibility and the ability to work on a particular area as much as possible. The maximum possible position of body parts is achieved, so that the muscle is maximally loaded. Quite severe stretching exercises are also used here as auxiliary exercises.
Callanetics
In Pilates, it is not large muscle groups that are trained, but individual underdeveloped ones. Particular attention is paid to the spine, its correct position in space and strengthening muscle tone. In addition, the so-called “center of strength” is strengthened: the abdominals, lower back, hips and buttocks. This type of physical exercise helps eliminate pain in the spine that is caused by osteochondrosis.
In callanetics, attention is mainly paid to the abdomen, buttocks and thighs, but very little is given to the spinal muscles.
In Pilates, breathing should be chest costal, and in callanetics, shallow.
You can do Pilates both in special fitness centers and on your own at home, but callanetics is best done under the guidance of only an experienced trainer who can correct mistakes.
Which is better to choose?
To summarize, let’s summarize in a table all the similarities and differences between both types of fitness, their goals and results.
| Criterion | Pilates | Callanetics |
| Who is it suitable for? | For beginners in fitness, people with injuries, diseases of the musculoskeletal system or lovers of quiet workouts | For those with experience in fitness, athletes recovering from injuries, who want to lose weight and tighten their body |
| primary goal | Strengthen your back muscles, improve your posture, gain mental balance and body control | Strengthen the muscle corset of the whole body, improve flexibility, stretching, lose weight |
| Necessary equipment | Rug or mat, you may need a fitball | Mat, some exercises use a chair |
| Does it help you lose weight | Minor weight loss effect | Effective for weight loss |
| Breathing technique | Constant control of breathing: inhale through the nose, exhale through the mouth | Calm nasal breathing throughout the workout |
| Do I need an instructor? | Possibility of self-teaching the basics | It is advisable to have a trainer's supervision at the initial stage. |
| Load nature | Dynamic | Static |
| Results from training | Improving posture and general health, gaining mental balance | Strengthening the muscle corset of the whole body, losing weight, increasing self-esteem |
We hope that our comparative analysis of callanetics and Pilates will help you choose the appropriate type of training.
Whatever choice is made, it is important to understand that only regular exercise for at least several months will lead to the desired result.
It may be worth trying both types of exercise. Practice will show what suits you best.
How is stretching useful?
Stretching has a number of beneficial properties, which makes this discipline popular. Regular training helps you develop flexibility, become slimmer and more flexible. Posture, lymph and blood circulation improves. The benefits of stretching for women include toning muscles and slowing down the aging process. Special exercises have a relaxing effect on the muscles, helping to cope with pain and tension. Stretching is used to prepare the body for intense physical activity and, conversely, to relax after training.
Conclusions website
- Pilates is a dynamic set of exercises, while callanetics tends to be static.
- In Pilates, special attention is paid to the spine and the “center of strength”, while callanetics is mainly aimed at the abdomen, buttocks and thighs.
- Pilates provides less stress on the body, unlike callanetics, which requires complete dedication.
- In Pilates, breathing is thoracic and costal, and in callanetics it is superficial.
- Pilates is not based on ancient practices, and callanetics is based on yogic asanas.
- Pilates, as a simpler system, is accessible to many and can be practiced independently, but callanetics requires sensitive coaching guidance.
For an untrained person, the difference between Pilates and callanetics is hardly noticeable. You need to have experience as a trainer or good training skills to pay attention to important details and characteristic differences. Therefore, the question of choosing between Pilates and callanetics for weight loss is often asked, and this is the right position - there is no point in switching to a new technique or mastering it on your own! What is the difference between callanetics and Pilates?
Sample workout program at home
At the end of each exercise in callanetics, you should slowly, without sudden movements, return to the starting position. Don't forget about breathing.
For beginners
- Exercise 1. Place your feet shoulder-width apart, place your hands on your belt, look forward. Bend your knees slightly and, raising your right arm up, stretch as high as possible (make sure that your shoulder does not rise), put your left hand on your thigh and, tightening your buttocks, swing your pelvis forward and up. Try to extend your right arm as much as possible, while slowly bending slightly to the side.
The neck and upper shoulder girdle should be relaxed. To return to the starting position, move your right arm to a position in front of you, bend your knees, bend forward and, without bending your arm, turn your arm and torso to the left. Pull up your buttocks, move your pelvis forward and upward and straighten up. Now everything is the same in the other direction.
- Exercise 2. Place your feet shoulder-width apart, extend your arms to your sides at shoulder level, with the inside of your palms facing the floor. Bend your knees slightly, tighten your buttocks, move your pelvis forward and lift it up. Turn your palms, making sure your thumbs are facing up. Slowly place your hands behind your back and raise them as high as possible. Pull your shoulders and head back. Connect and separate your hands back and forth at a short distance. Now bend your elbows and lower your arms.
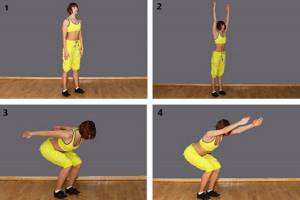
- Exercise 3. Take a chair. Turn the feet of your joined legs outward, stand with your back straight and your shoulders straightened towards the back, and lean against it without making much effort. Rise on your toes, connect your heels and turn your knees to the sides. Without changing your position, bend your knees slightly, lower yourself 3-5 cm, rounding your buttocks and lower back. Return your pelvis to the starting point, bend your knees and lower yourself a little more. Move your pelvis forward and upward, rounding the bottom again.
- Exercise 4. Leave a chair in front of you with the back facing you, and place your straightened left leg on it. The foot of the straightened right leg should be slightly turned outward. Slowly raise both arms as high as possible. Without stopping to stretch, slowly bend forward, parallel to your leg. When you can no longer stretch, bend your arms and cross them over your shins, with your elbows pointing in opposite directions. Slowly lean towards your leg just a little bit. Initial position. Do the same with the other side.
- Exercise 5. Place a chair in front of you and grab it with your hands. Bend both legs: put the left one in front of you, take the right one back. Place your right hand on your thigh, lift your right foot and lower leg, bending your pelvis and torso forward. Place your hand back on the support and, relaxing your shoulders, slightly raise your right knee. Without changing my position, slowly move your leg to a position in front of you, then take it back. Do the same with the other side.
- Exercise 6. Place a chair in front of you and grab it with your hands. Bend your right leg and place it in front of you, straighten your left leg and extend it to the side. Left hand on the hip, move the pelvis and thigh of the left leg forward. Put your hand back on the support, tilt your torso and shoulders to the right. Raise your left leg a little, slowly raising and lowering it a short distance. Do the same with the second side.
For advanced
- Exercise 1. Lie on your back, bring your bent legs together, press your feet to the floor. Place your hands on your inner thighs and spread your elbows out to the sides in an upward direction. Slowly lift your head off the floor and lower it so that your nose looks at your chest. Rounding your shoulders and neck as much as possible, stretch your arms along your body parallel to the floor and slowly move your arms back and forth over a short distance.
- Exercise 2. Sit on the floor with your legs spread as far apart as possible, rest your hands on the floor behind you. Slowly raise your arms, slowly bend your torso forward to reach the floor with your hands. Bend your arms, place your forearms and elbows on the floor. In this position, slowly bend down a little.

- Exercise 3. Bend your legs under you, place your buttocks on your heels. Slowly raise your straightened arms up, form a lock with your hands, and pull your body up a few centimeters. In the same position, slightly raise your pelvis above your heels, slightly spread your hips and move your pelvis forward and upward as much as possible. Without changing position, slowly rotate your hips to the right and left with a small amplitude.
- Exercise 4. Kneel, bend your legs under you, place your buttocks on your heels, rest your hands on the floor behind you. Tighten your buttocks, move your pelvis forward and lift up. Then lift the torso and pelvis up and bend as much as possible, but without reaching the point of pain. Raise and lower the pelvis smoothly, with an amplitude of no more than a centimeter.
- Exercise 5. Sit with your legs extended and your back straight in front of a chair (you can use a table). Press your feet against the legs of the chair, round your shoulders. Tighten your hips and squeeze the legs of the support with your feet. Then relax the muscles and squeeze again.
For pregnant
- Exercise 1. Sit on a sports mat with your legs crossed. Place your hands on your shoulders and alternately raise them as much as possible. Try not to swing and reach as high as possible, but don't try too hard.
- Exercise 2. It is recommended to perform this exercise after the 4th month of pregnancy. It can be done while leaning against a wall or lying on a mat with your legs bent. As you exhale, press your back to the surface, while lifting your pelvis. Then, relaxing all your muscles, take a deep breath.
- Exercise 3. Sit in a comfortable position with your eyes closed. Inhaling slowly, turn your neck to one side, and exhaling, lower your head forward. Repeat on the other side.
The essence and meaning of training
Everything in callanetics is done very slowly, with deep breathing. The pose is held for 60 to 100 seconds. The meaning of callanetics is that muscle stretching occurs gradually, without sudden loads. Thus, the muscles more easily remember what state they need to remain in, and as a result of practicing callanetics, we get a flexible, freely moving, hardy body, a healthy spine, accelerated metabolism and the absence of fat on the stomach and sides.

The callanetics course is not focused specifically on burning fat, but since classes lead to an acceleration of metabolism, fats will no longer be able to remain on your waist with impunity, and the muscles will have beautiful outlines.
Yoga for health, peace and harmony
Yoga is a set of spiritual, physical and mental practices with which you can cleanse karma and achieve enlightenment by merging with the Absolute. No one knows exactly when yoga appeared. The first mention of it is found in the ancient collection of hymns “Rigveda”. In a word, it was a very, very long time ago.
But we will consider yoga not as a spiritual practice, but as performing asanas and short meditations at the end of the class.
We take yoga, cleanse it of all spiritual practices, virtues and meditations and get a set of asanas and breathing exercises.
Asanas and breathing exercises
An asana is a static body position, a pose that you maintain for a certain time, usually 30-60 seconds. Precise execution of asanas - with an elongated spine, no kinks in the neck, correctly distributed load - helps get rid of some health problems and strengthen the body.

Amy/Flickr.com
In everyday life, we use strictly defined muscle groups, while others are rarely used and lose tone. This is a problem not only for sedentary people, but also for athletes who play one sport and neglect stretching.
An equally common problem is muscle tension. When you maintain an unnatural body position for a long time, for example, sitting at a computer, some muscles are tense all the time. Constant muscle tension in the wrong position affects both bones (problems with joints, spine) and internal organs, creating pressure where there should not be any.
While performing asanas (provided they are done correctly), strictly defined muscle groups are tensed, including those that are rarely used in everyday life. The remaining muscles that are not involved in a particular asana are relaxed, so you do not waste energy on them.

Terri-Jane/Flickr.com
Correct execution of asanas helps to rebuild the body, bring it to a normal state, without clamps and “distortions”.
Stretching for a flexible body and injury prevention
In short, stretching is stretching. You can do stretching as a warm-up and cool-down, or separately from other loads, using it as an independent workout to develop flexibility.

Earl McGehee/Flickr.com
Stretching includes dynamic and static exercises aimed at increasing the elasticity of joints, muscles and ligaments. This includes stretches to strengthen the spine, splits, and exercises to increase joint mobility.
At the same time, stretching does not have a specific sequence of movements, as in Pilates, or difficult poses to perform, as in yoga. If you want to stretch specific muscle groups before training, there is nothing stopping you from choosing four or five stretching exercises, and leaving the rest for a cool down or not doing them at all.
Also, in stretching there is no special emphasis on breathing. While stretching, it is important not to hold your breath, but to take smooth and deep breaths. But this is where, as a rule, breathing recommendations end.
And another difference between stretching and yoga and Pilates is the presence of paired exercises, when several participants stretch each other.
Who is stretching suitable for?
You will like stretching if:
- you want to improve flexibility and joint mobility;
- you need a good stretch after training;
- you don't want to spend a lot of time stretching.
You won't be impressed by stretching if:
- you already do yoga or Pilates;
- you are looking for an integrated approach to developing flexibility, endurance, muscle strength;
- you want to lose weight and have chosen stretching for this.
What should you wear for stretching?
Since training involves stretching muscles, it is important to choose the right clothing. It should not only be comfortable, but also not interfere with movement. Clothes for stretching should have good stretch; for this, pay attention to the composition, which may include 80-90% natural thread and 10-20% elastin or polyester. As for shoes, they should be soft, for example, they could be ballet flats, slippers or sneakers, but you can just exercise in socks.












