How much protein is in one egg?
To answer this question as accurately as possible, you need to know the weight of the egg. Depending on their weight, they are divided into the following categories:
- third category (35.0 – 44.9g)
- second category (45.0 – 54.9g)
- first category (55.0 – 64.9g)
- “O” selected (65.0 – 74.9g)
- “B” highest category (over 75g)
If you don’t have scales at hand, don’t rush to get upset. Just remember that the average egg weighs about 60 grams.
It takes up approximately 2/3 of the weight of the entire egg, 1/3 is the yolk, that is, the weight of the white in an average egg is 40 grams. But it is very important to remember that egg white contains about 90% water, so from 40 grams we will get only 4-5 grams of pure protein.
In order not to count every time how much protein we will get from an egg of a particular category, you can simply save this table for yourself:
Calorie content Boiled egg. Chemical composition and nutritional value.
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “Boiled egg”.
The table shows the nutritional content (calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) per 100 grams of edible portion.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 158.7 kcal | 1684 kcal | 9.4% | 5.9% | 1061 g |
| Squirrels | 12.828 g | 76 g | 16.9% | 10.6% | 592 g |
| Fats | 11.616 g | 56 g | 20.7% | 13% | 482 g |
| Carbohydrates | 0.707 g | 219 g | 0.3% | 0.2% | 30976 g |
| Water | 74.1 g | 2273 g | 3.3% | 2.1% | 3067 g |
| Ash | 1.01 g | ~ | |||
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin A, RE | 262.6 mcg | 900 mcg | 29.2% | 18.4% | 343 g |
| Retinol | 0.253 mg | ~ | |||
| beta carotene | 0.061 mg | 5 mg | 1.2% | 0.8% | 8197 g |
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.071 mg | 1.5 mg | 4.7% | 3% | 2113 g |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.444 mg | 1.8 mg | 24.7% | 15.6% | 405 g |
| Vitamin B4, choline | 253.54 mg | 500 mg | 50.7% | 31.9% | 197 g |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 1.313 mg | 5 mg | 26.3% | 16.6% | 381 g |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.141 mg | 2 mg | 7.1% | 4.5% | 1418 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 7.071 mcg | 400 mcg | 1.8% | 1.1% | 5657 g |
| Vitamin B12, cobalamin | 0.525 mcg | 3 mcg | 17.5% | 11% | 571 g |
| Vitamin D, calciferol | 2.222 mcg | 10 mcg | 22.2% | 14% | 450 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 0.606 mg | 15 mg | 4% | 2.5% | 2475 g |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 20.404 mcg | 50 mcg | 40.8% | 25.7% | 245 g |
| Vitamin K, phylloquinone | 0.3 mcg | 120 mcg | 0.3% | 0.2% | 40000 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 2.3214 mg | 20 mg | 11.6% | 7.3% | 862 g |
| Niacin | 0.192 mg | ~ | |||
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 141.41 mg | 2500 mg | 5.7% | 3.6% | 1768 |
| Calcium, Ca | 55.56 mg | 1000 mg | 5.6% | 3.5% | 1800 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 12.12 mg | 400 mg | 3% | 1.9% | 3300 g |
| Sodium, Na | 135.35 mg | 1300 mg | 10.4% | 6.6% | 960 g |
| Sera, S | 177.78 mg | 1000 mg | 17.8% | 11.2% | 562 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 193.9 mg | 800 mg | 24.2% | 15.2% | 413 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 157.58 mg | 2300 mg | 6.9% | 4.3% | 1460 g |
| Microelements | |||||
| Iron, Fe | 2.525 mg | 18 mg | 14% | 8.8% | 713 g |
| Yod, I | 20.2 mcg | 150 mcg | 13.5% | 8.5% | 743 g |
| Cobalt, Co | 10.101 mcg | 10 mcg | 101% | 63.6% | 99 g |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.0293 mg | 2 mg | 1.5% | 0.9% | 6826 g |
| Copper, Cu | 83.84 mcg | 1000 mcg | 8.4% | 5.3% | 1193 g |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 6.061 mcg | 70 mcg | 8.7% | 5.5% | 1155 g |
| Selenium, Se | 32.02 mcg | 55 mcg | 58.2% | 36.7% | 172 g |
| Fluorine, F | 55.56 mcg | 4000 mcg | 1.4% | 0.9% | 7199 g |
| Chromium, Cr | 4.04 mcg | 50 mcg | 8.1% | 5.1% | 1238 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 1.1212 mg | 12 mg | 9.3% | 5.9% | 1070 g |
| Digestible carbohydrates | |||||
| Mono- and disaccharides (sugars) | 0.707 g | max 100 g | |||
| Sterols (sterols) | |||||
| Cholesterol | 575.76 mg | max 300 mg | |||
| Saturated fatty acids | |||||
| Saturated fatty acids | 3 g | max 18.7 g | |||
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 4.077 g | min 16.8 g | 24.3% | 15.3% | |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 1.414 g | from 11.2 to 20.6 g | 12.6% | 7.9% | |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | 0.078 g | from 0.9 to 3.7 g | 8.7% | 5.5% | |
| Omega-6 fatty acids | 1.337 g | from 4.7 to 16.8 g | 28.4% | 17.9% |
The energy value of a boiled egg is 158.7 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.
Cooked protein content
It is believed that the healthiest way to prepare an egg is boiling. But everyone knows that during heat treatment the weight of products decreases. What happens to the protein? It all depends on how exactly we prepare it:
- A hard-boiled egg contains about 12 grams;
- Soft-boiled – 13 grams;
- The “bag” method, as in the previous case – 13 grams;
- Melange – 12 grams;
- A fried egg retains approximately 14 grams.
There are also cooking methods that bring the egg to a semi-finished state. Among them are:
- Egg powder;
- Dried egg white.
With this processing method, 50% of the protein mass is lost.
General concepts about calorie content and categorization
A chicken egg contains 12 vitamins, and in terms of vitamin D content, the product is second only to fish oil. It is also rich in vitamins E, A and B. But this is not the only advantage. An important plus is the quality and complete digestibility of the elements contained in a chicken egg. BJU (proteins, fats and carbohydrates) are in an optimal ratio, which guarantees that the basic needs of the body are covered.
When calculating the calorie content of a product, consider the product labeling. If we consider the current Russian standards, then it is worth highlighting the following markings:
- D - dietary (must be sold within a week);
- C is a table product, the sale of which is given 25 days.
A second character is placed next to the letter. Here the values are as follows:
- “3” – 3rd category. Weight - 34-44.9 g .
- “2” – 2nd category. Weight - 45-54.9 g .
- “1” – 1st category. Weight - 55-64.9 g .
- “O” - selected type, which weigh 65-74.9 g .
- “B” is a product of the highest category. This includes those weighing from 75 grams .
When calculating calories, consider weight and quality. In addition, the method of preparation is also of great importance. Thus, the product can be eaten raw, boiled (including soft-boiled) and fried. Let's take a closer look at the composition of a chicken egg (proteins, carbohydrates, fats) and calorie content for each option.
The effect of protein on the body
American scientists have concluded that for the normal functioning of the body, you need to consume the following amount of this element per day:
- Women - 46 grams;
- Men - 56 grams.
An insufficient amount of it can lead to such consequences as:
- Deterioration of immunity,
- Loss of muscle mass,
- Problems with the cardiovascular system.
But, of course, everything should be in moderation. An overdose of protein products also negatively affects the body.
Briefly about the composition and beneficial properties
Since the discovery of cholesterol in eggs, attitudes towards it have changed dramatically. Many people who emphasized healthy eating stopped taking the product or reduced their consumption. But in those days, few people understood the features of cholesterol and its effect on the body. There was no division into two categories yet - “harmful” and “good” cholesterol.
Over time, scientists conducted a series of experiments that made it possible to identify an important element for the body - lecithin. The latter, in some way, “neutralizes” cholesterol and makes eating eggs practically safe for humans (with moderate consumption). In addition, it was possible to prove the benefit of the product in the treatment of atherosclerosis and for the prevention of this disease.
The energy value of a chicken egg is sufficient to cover the body's protein needs and provide energy. In this case, the benefits of the product are considered from two perspectives:
- Protein is almost no different in quality and properties from similar elements contained in meat or milk. Dozens of studies have shown that the product is quickly absorbed and saturates cells with a significant set of amino acids. In addition, regular protein consumption is a chance to strengthen the body and accelerate muscle growth. It is also useful for children who need material for growth.
- The yolk is a substance that contains choline, biotin and lecithin, and vitamins - tocopherol, retinol and B vitamins. The yolk also contains microelements - iron, phosphorus and potassium.
The composition of the egg (proteins, fats and carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) causes the following effect on the body :
- Protects the optic nerve and prevents cataract formation.
- Helps renew blood. The product contains elements that accelerate and optimize hematopoietic processes.
- Stimulation of the immune system, acceleration of weight loss processes.
- Improving performance and strengthening memory.
- Renewal of body cells, preservation of youth. This is possible due to the presence of tocopherol in the composition.
- Helps in the preservation of bones and teeth (explained by the presence of phosphorus in the composition).
Chicken eggs, consumed in moderation, are beneficial for the body. It is recommended to eat boiled foods containing fewer calories. In addition, they are absorbed faster and do not pose a health risk. It is allowed to take eggs (raw and boiled) during the diet.
About the benefits of egg white
The properties of egg whites are legendary. So why is it useful?
- Contains a large amount of vitamins E, B and D. In terms of the amount of the latter, it is inferior only to fish oil;
- Amino acids, the amount of which is quite large in this product, improve brain function and cell regeneration;
- Can reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, which improves heart function and reduces the load on blood vessels.
And in general, this is a unique product! After all, only egg white combines such qualities as low calorie content and one of the main sources of protein.
How many proteins are in 1 egg (white + yolk)
A significant part of the composition of the egg is made up of proteins - about 13 g per 100 g of product. In 1 piece first category, weighing 50 g - about 6.5 g. The amount of this nutrient in the protein and yolk is different. The yolk contains fewer amino acids, it has more calories, and the protein content does not exceed 16%. The main protein components in the yolk are phosphovitin, livetin, and vitellin.
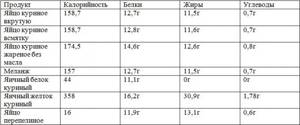
When cooked, the product does not lose its beneficial properties. Protein content in a boiled egg: 1 pc. – 6 g, in 100 g – 12 g.
The protein contains a protein called ovalbumin (
68% of the protein composition), which has antibacterial and restorative properties, the rest is made up of avidin, conalbumin, ovomucin and ovoglobulin. Thanks to a large number of useful amino acids, the product is perfectly absorbed by the body. The protein content of egg whites is 13%, the largest part being water – about 80%.
Dietary value
Most nutritionists advise introducing eggs into your diet as a breakfast. Why? This product is rich in nutrients and is easily absorbed by the body. Therefore, two eggs for breakfast will keep us feeling full for a long time. But at the same time they have very low calorie content. More specifically:
Accordingly, the lowest calorie cooking method is hard-boiled or soft-boiled. Doctors say that our body best digests eggs prepared using the latter method.
How many minutes does it take to boil eggs →
Chicken egg: proteins, fats and carbohydrates in 1 piece

| Food component | Contents of 100 g of raw egg | Contents in raw egg, 1 pc. (50 g) | Protein content (28 g) | Contents in yolk (16 g) |
| Squirrels | 12,6 | 6,3 | 3,7 | 2,6 |
| Fats | 12 | 6 | 0 | 6 |
| Carbohydrates | 0,68 | 0,34 | 0,18 | 0,16 |
| Water | 70 | 35 | 24 | 7 |
Chicken eggs are a fairly healthy food product that is present in the diet of almost every person. The composition is rich in amino acids, minerals and vitamins of different groups.
Eggs in bodybuilding
There is no point in talking about the importance of protein in the process of building muscle mass, because this has long been a well-known fact. In this regard, it is logical that a bodybuilder's diet should contain more protein than the average person's diet. Important: protein must be high in amino acids, which help the body absorb it.
After reading this article, we can safely say that eggs are an important and integral part of a bodybuilder’s diet. But very often, people who want to build muscle mass make one serious mistake: they eat exclusively whites, neglecting the yolks. But in vain, because the yolk contains all the fats and half the protein that can be obtained from an egg. It also contains most of the vitamins and minerals that are important for athletes.
Well, let's sum it up? Eggs are one of the lowest calorie sources of protein that can help solve many problems, both with health and with your figure. The main thing is to be able to use it correctly.
Amount of fat in eggs
As for fats, not everything is so rosy here. 100 grams of eggs contain about 11.5 grams of fat , which is not so little. However, not all fats in eggs are extremely harmful to the body. Let's figure it out!
And so, most of the fats in an egg are actually healthy monosaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which allow the body to keep cholesterol within normal limits and not accumulate it beyond measure. These fats also reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes because they regulate the amount of insulin and help stabilize blood sugar levels.
However, along with healthy fats, eggs also contain harmful ones, albeit in slightly smaller quantities.
Among them are low-density lipoproteins and cholesterol . The last one from this short list, in case of metabolic disorders, can accumulate in the body and be deposited on the walls of blood vessels, reducing their lumen. As a result, this leads to atherosclerosis and increased blood pressure, which in turn can provoke hypertension. However, this entire chain of changes applies to a greater extent to older people or people with impaired metabolism, while the vast majority of athletes under 30 almost never experience high cholesterol levels .
However, if the result of a medical study reveals that cholesterol levels are elevated, you should not give up eggs, but you can simply eliminate the yolk, which contains all the fats in the egg. And so, now you know how many carbohydrates are in an egg and why you shouldn’t be afraid of their quantity at all. As for proteins, due to their large quantity and rich amino acid set, eggs can certainly be considered one of the best foods for athletes gaining muscle mass. As for athletes during the drying period, in this case it is recommended to limit themselves only to proteins, since a large amount of fat from the yolks will not be useful here. The same applies to older athletes prone to high cholesterol levels.
carbohydrateseggs