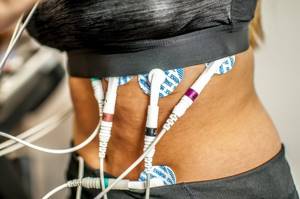
It is usually very difficult for residents of megacities to find time to take care of their health. It's no secret that the frantic pace of life in large cities leaves no chance for morning jogging, evening trips to the gym and wellness treatments. But there is a way out. In the 21st century, the latest achievements of medical science come to our aid. Thus, a procedure for healing the body, which has proven itself in space medicine, called electrical myostimulation of muscles (or simply myostimulation), has now become available to “earthly” residents.
Electromyostimulation (EMS) is an innovative procedure aimed at overall health improvement of the body, including the fight against excess weight. The technology is also used for problems with the musculoskeletal system and for the speedy rehabilitation of injuries. In our country, myostimulation was first used in the 60s. last century to restore muscle tone of astronauts after flights. And in many other countries, this procedure has long been used in sports medicine. For example, in Germany, myostimulation began to be used as a means of rehabilitation of athletes back in the 1970s.
How does the EMS suit work?

The history of electrical muscle stimulation begins in the 60s of the last century. In connection with human flights into space, a problem arose: in conditions of weightlessness, natural muscles could completely atrophy. Many astronauts, returning to Earth, suffered from weakness and pain. To prevent them from losing their shape in zero gravity, the first myostimulatory mechanisms were invented. Then one device was the size of a table and weighed up to a hundredweight.
Modern athletes and just people who want to lose weight and improve muscle tone will not have to purchase a machine of intimidating size and appearance. EMS developments are a priority in the sports industry, offering EMS suits to everyone. They have the following advantages:
- Small sizes. Modern EMS suits weigh no more than five to seven kilograms, allowing even fragile girls who want to reduce their waist size to train.
- High maneuverability. For a long time, athletes and bodybuilders were prejudiced against such developments, not least because the suits were bulky and uncomfortable. It was difficult to train in them with a barbell or on machines. New developments do not interfere with traffic.
- Suits are produced on the basis of special elastic fabric . In appearance, this sports equipment resembles diving equipment, but without a heavy oxygen cylinder on the back.
- Often, EMS suits are used not by one person, but by several. Therefore, manufacturers build in antibacterial properties along with a liquid drainage system. Thanks to these details, you can train in comfort, without sweat.
- Additionally, a control system is included in the form of wired or, in the latest developments, wireless devices, which control the intensity of electrical signals to certain areas of the body.
A person involved in sports can regulate the strength and intensity of electrical impulses. It is not difficult to guess that the more powerful the current passes through the muscles, the higher the load. At the same time, the sensations remain painless, only a slight tingling sensation is subjectively perceived, which many even call pleasant.
Why it's worth a try
EMS training is a rather unusual, yet effective form of fitness. Like any other type of physical activity, it promotes:
- general improvement in well-being;
- increasing concentration and performance;
- reducing stress levels;
- figure modeling.
In general, people who exercise regularly report an increase in energy levels: ordinary tasks are performed easily and do not require much effort. But you won’t be able to achieve a positive effect with training alone. It is also necessary to change eating habits, make the diet more healthy and nutritious. All this is long and hard work, which specialists will help you with.
But first, let’s look at the main reasons why you should try EMC classes.
Save time
The modern rhythm of life does not allow many people to conduct two or three full-fledged workouts weekly. A good solution is EMS-training, one lesson of which lasts about 20-30 minutes. Taking half an hour to improve your health and well-being is entirely possible. In addition, you can find a gym near your home or work - this will save additional time, since you won’t have to travel across the city.
Working on muscles that are usually difficult to train
Another advantage of training using the electrical stimulation system is that up to 90% of the muscles are worked out, even those that are only slightly involved when performing strength exercises. This means that more calories will be burned per session, and the body will become more sculpted, elastic, and toned over time.
The ability to diversify your workouts and increase their effectiveness
People who have been visiting the gym for several years usually become bored with their regular workouts. It seems that the world of fitness has nothing more to offer - the same exercises and complexes are everywhere. Then training using the EMS system will become a real salvation. They will allow you to diversify your usual activities, while increasing their effectiveness.
Recovery from injuries
Electrical muscle stimulation exercises may be prescribed as part of physical therapy for recovery from injury. As already mentioned, such training reduces the load on the spine and joints, which reduces the likelihood of injury.
How to train with an EMS suit

Any system of physical exercises implies regularity, a well-calibrated approach and an understanding of why this or that action is being performed. That is why many people recommend that you definitely resort to the services of specialist trainers in EMS training. An ordinary fitness specialist may not always know the nuances of the latest developments. However, there are general rules for training in an EMS suit:
- At the first stage, preparation is given, just like in a regular training session.
- At this point, an analogue of cardio training is assumed, therefore “real” exercises must correspond to the supply of impulses. The delivery of electrical stimulation is also more general, allowing all muscles to warm up.
- Next is the transition to the main set of exercises. You work out as usual, but using the settings you determine which muscle area is currently “problematic” and which you want to focus on.
- Just like in the cardio training mode, the approaches performed must correspond to the specific task. For example, you cannot overstimulate the shoulder girdle, but at the same time perform approaches to the calf muscles.
- The third stage is only for EMS training. You don’t go into the shower, but stay in your suit, lie down and switch to the lymphatic drainage massage mode. All excess liquid quickly disappears. This is why suits are popular among women who want to get rid of cellulite.
Training in modern suits, which take into account all the features of human anatomy and movements during active sports, will not cause inconvenience, so a person practically does not feel the difference.
Interesting fact: any exercise, although aimed at a specific muscle group, does not achieve the ideal effect. Many people know that if you are too eager to pump up your buttocks, you can “pump up” your thighs or calf muscles. Exercising in EMS equipment allows you to eliminate such undesirable consequences of training.
How is the lesson going?
The word “electromyostimulation” suggests that while you are blissfully idle, some kind of “stimulation” will occur in your body. That's right, except for one thing - you definitely won't have to be idle! If you go to such a class, then your body will have to work hard, otherwise EMS training will not bring you any visible effect.

Real reviews agree on one thing - such an activity in 20-30 minutes will weaken you no less than a “real” sentry in the hall. You will be put on a suit similar to a diving suit, made of thick rubberized fabric that fits tightly to the body. You can leave your training uniform at home, you will only need underwear, and even then not in all gyms. Some sports facilities will give you a disposable set of underwear before training. After putting on, the suit will be slightly moistened for better conductivity of the electrical impulse.
If you are not a fan of group training, then you will definitely like the EMS class - you will be one on one with the trainer, and all his attention will be directed to you. Special suction cups are attached to the suit, which will stimulate muscle tissue.
The activity is not at all static - you will have to walk, swing your arms and legs, bend over and squat. It would seem, why is it so complicated? It’s just that under the influence of electrical stimulation you will no longer feel the body in the usual way. Some people experience tingling, others feel like their muscles are stiff. One way or another, simple movements will be difficult. After training, you will have a strange feeling - it seems like you didn’t do anything, but at the same time you are tired and sweaty no less than after a class at the fitness center.
You will truly understand that the training was not in vain, in the evening or in the morning, during the regeneration of muscle tissue. According to reviews, after the first lessons it is even difficult to walk and sit. But this only speaks in favor of EMS training.
Pros and cons of EMS suits
Exercises with additional electrical stimulation seem ideal for anyone who wants to improve their appearance, build muscle in certain areas of the body without affecting others, get rid of cellulite and achieve great shape. Despite the endorsement of EMS training by the International Sports Association, some people continue to have doubts. Indeed, there are objective pros and cons, the first are the following advantages:
- reduction of training time - electrical stimulation allows you to achieve a similar effect, not in an hour, but in 20 minutes;
- the necessary muscles are activated, the load is directed to the necessary areas;
- fewer contraindications - for example, you can exercise with injuries;
- EMS training is indicated for clinical obesity, if conventional training is prohibited due to the risk of stress on the joints;
- special applications will accurately track effectiveness.

Disadvantages belong to two groups - contraindications and “unjustified” hopes. They can be listed in the following details:
- “doing nothing” won’t work—strength training will not be cancelled;
- the effect may appear more slowly than you would like if you have been practicing for a long time;
- There are contraindications - some skin diseases, the presence of a pacemaker.
Some trainers still consider EMS training a “publicity stunt” and a “waste of money.” Such an opinion is more likely to indicate retrograde thinking and inertia than competence. However, you shouldn’t expect miracles - an EMS suit is an excellent assistant for an athlete, but not a substitute for other loads.
Features of EMS training and EMS rehabilitation
The video shows the EMS training process. Its essence lies in the fact that a certain exercise is done, and the impulse supplied to a specific muscle strengthens your own, which leads to increased contraction and tension of the trained muscle. The greater the tension in a muscle, the more microdamage it receives, and as it adapts and recovers, it strengthens and becomes larger.
So, what are the features of EMS training?
EMS means “electromyostimulation”, that is, muscle stimulation with electric current. For this, a device is used - a stimulator, which delivers electrical impulses through electrodes attached to the body, thereby causing muscle contraction.
Another special feature is that, in accordance with your goals, you can select exercises and install electrodes in specific places that need to be stimulated. For example, after surgery on the knee ligaments, when rapid atrophy of the quadriceps femoris muscle occurs, we can do the necessary restorative exercises on the legs and strengthen the work of the leg muscles by additionally influencing them with electrical impulses. And this is, indeed, a good solution for possible pain, swelling or inflammation (but in moderation), muscle contractures, weakness and psychological fear of full loads on muscles and joints. Naturally, such training, and even ordinary ones with weights, can be started only after a certain period of time after injuries or operations.
The leg muscles themselves are very strong, they work non-stop and the load on them is significant. As an example, it is very difficult for athletes to pump up the calf muscles - it is a very strong muscle, so to grow it you need to do a lot of exercises with heavy weights.
But when a joint is injured and the ligaments are damaged and in the process of healing, we cannot put a huge weight on them. What to do? Either do various tension exercises every day 3-4 times in 4 sets of 20 times, as provided by rehabilitation programs, or somehow take advantage of new technologies. Electrical stimulation and EMS training will be an excellent addition to a rehabilitation program developed by a rehabilitation physician.
Take the traffic rules knowledge test for a cyclist!
Time limit: 0
Navigation (job numbers only)
0 out of 15 tasks completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
Information
To be able to obtain rights, please click Next
You have already taken the test before. You can't start it again.
The test is loading...
You must log in or register in order to begin the test.
You must complete the following tests to start this one:
results
Correct answers: 0 out of 15
Your time:
Time is over
You scored 0 out of 0 points (0)
Categories
- No category 0%
- Please write in the comments if you liked the test.
Should things like this be added to the site? What would you like to see on the site? Thanks in advance for your feedback!
maximum of 15 points
| Place | Name | Recorded | Points | Result |
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data | ||||
Your result has been recorded in the leaderboard Loading
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- With answer
- With a viewing mark
- Task 1 of 15
1.
Workout program for weight loss
Preliminary preparation plays a big role in obtaining the expected result.
General recommendations for the training program include:
- The need to train under constant supervision and guidance of a professional trainer with a sufficient level of qualifications. Attempts to save money and practice on your own often end in serious health problems and the need for long-term rehabilitation.
- The training schedule is adjusted to the needs of the trainee: his daily employment at work and the availability of free time are taken into account. Before classes, the trainer takes into account height, body weight, usual daily physical and motor activity - the collected information helps to eliminate excessive stress on the body and avoid accidental injuries.
- The schedule takes into account the time the body needs to recover. Overload of weak ligaments and tendons can lead to their ruptures and sprains.
The trainer conducts at least 3 joint training sessions over 1-2 weeks. During this period, he examines information about the trainee and, based on the data received, draws up a schedule for future classes.
Are the Rules broken in the situations depicted?
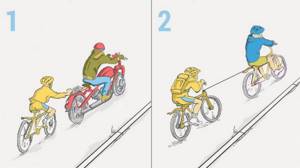
Correct 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.6. A cyclist is prohibited from:
d) while driving, hold on to another vehicle;
f) tow bicycles;
Wrong 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.6. A cyclist is prohibited from:
d) while driving, hold on to another vehicle;
f) tow bicycles;
2.
Which cyclist doesn't break the rules?

Correct 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.6. A cyclist is prohibited from:
b) move on highways and roads for cars, as well as on the roadway if there is a bicycle path nearby;
Wrong 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.6. A cyclist is prohibited from:
b) move on highways and roads for cars, as well as on the roadway if there is a bicycle path nearby;
3.
Who should give way?

Correct 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.5. If a bicycle lane crosses a road outside an intersection, cyclists must give way to other vehicles traveling on the road.
Wrong 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.5. If a bicycle lane crosses a road outside an intersection, cyclists must give way to other vehicles traveling on the road.
4.
What loads is a cyclist allowed to carry?

Correct 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.4. A cyclist may only carry such loads that do not interfere with the operation of the bicycle and do not create obstacles for other road users.
22. Cargo transportation
22.3. Transportation of cargo is permitted provided that it:
b) does not interfere with the stability of the vehicle and does not complicate its control;
Wrong 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.4. A cyclist may only carry such loads that do not interfere with the operation of the bicycle and do not create obstacles for other road users.
22. Cargo transportation
22.3. Transportation of cargo is permitted provided that it:
b) does not interfere with the stability of the vehicle and does not complicate its control;
5.
What do the doctors say?
In most statements by doctors, ems fitness, the effectiveness of which is not disputed, is recognized as a safe method of promoting health and maintaining physical fitness. In a positive way, minor stress is noted for the heart and blood vessels, joints and spine.
Doctors, noting the effectiveness of ems training for the body, in reviews urge you to remember what contraindications exist. That is why they insist on consulting a doctor and working under the supervision of an experienced trainer. This is especially true for those who are obese, because in addition to fat, this category of visitors also has concomitant diseases. Systemic control is also necessary for varicose veins.
Compliance with the rules and recommendations of specialists will help you improve your health and acquire an athletic body.
Which cyclists violate the Rules when transporting passengers?
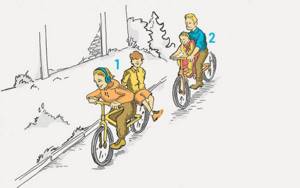
Correct 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.6. A cyclist is prohibited from:
e) carry passengers on a bicycle (except for children under 7 years old, transported on an additional seat equipped with securely fastened footrests);
Wrong 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.6. A cyclist is prohibited from:
e) carry passengers on a bicycle (except for children under 7 years old, transported on an additional seat equipped with securely fastened footrests);
6.
In what order will vehicles pass through the intersection?
Correct 16. Driving through intersections
16.11. At an intersection of unequal roads, the driver of a vehicle moving on a secondary road must give way to vehicles approaching this intersection of carriageways on the main road, regardless of the direction of their further movement.
16.12. At the intersection of equivalent roads, the driver of a non-rail vehicle is obliged to give way to vehicles approaching from the right. Tram drivers should follow this rule among themselves. At any unregulated intersection, a tram, regardless of the direction of its further movement, has an advantage over non-rail vehicles approaching it along an equivalent road.
16.14. If the main road at an intersection changes direction, drivers of vehicles moving along it must follow the rules for driving through intersections of equivalent roads. This rule should be followed among themselves and by drivers driving on secondary roads.
Wrong 16. Driving through intersections
16.11. At an intersection of unequal roads, the driver of a vehicle moving on a secondary road must give way to vehicles approaching this intersection of carriageways on the main road, regardless of the direction of their further movement.
16.12. At the intersection of equivalent roads, the driver of a non-rail vehicle is obliged to give way to vehicles approaching from the right. Tram drivers should follow this rule among themselves. At any unregulated intersection, a tram, regardless of the direction of its further movement, has an advantage over non-rail vehicles approaching it along an equivalent road.
16.14. If the main road at an intersection changes direction, drivers of vehicles moving along it must follow the rules for driving through intersections of equivalent roads. This rule should be followed among themselves and by drivers driving on secondary roads.
7.
Riding bicycles on sidewalks and pedestrian paths:
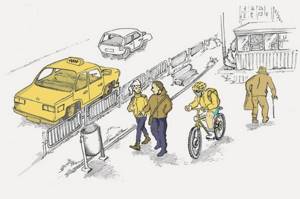
Correct 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.6. A cyclist is prohibited from:
c) move on sidewalks and pedestrian paths (except for children under 7 years old on children's bicycles under the supervision of adults);
Wrong 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.6. A cyclist is prohibited from:
c) move on sidewalks and pedestrian paths (except for children under 7 years old on children's bicycles under the supervision of adults);
8.
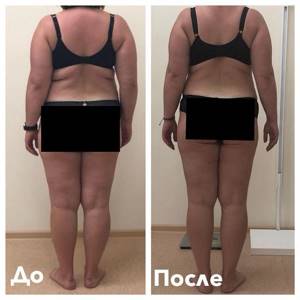
Result before and after: photo

The internet is replete with before and after photos, whether you can trust them or not. It is worth understanding that EMS is not at all a miraculous device that can turn you into a Thumbelina without any effort. Most likely, many hours of work in the gym are behind most of these photos.
Who has the right of way when crossing a bike path?
Correct 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.5. If a bicycle lane crosses a road outside an intersection, cyclists must give way to other vehicles traveling on the road.
Wrong 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.5. If a bicycle lane crosses a road outside an intersection, cyclists must give way to other vehicles traveling on the road.
9.
What distance should be between groups of cyclists moving in a column?

Correct 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.3. Cyclists traveling in groups must ride one after another so as not to interfere with other road users. A column of cyclists moving along the roadway must be divided into groups (up to 10 cyclists in a group) with a movement distance between groups of 80-100 m.
Wrong 6. Requirements for cyclists
6.3. Cyclists traveling in groups must ride one after another so as not to interfere with other road users. A column of cyclists moving along the roadway must be divided into groups (up to 10 cyclists in a group) with a movement distance between groups of 80-100 m.
10.
The impact of EMS on the physical performance of athletes: team sports
Hockey professional
The participants in the study were 17 hockey players of the second division of the French hockey league. They were randomly assigned to two groups (first - EMS, second - control), classes were held three times a week for three weeks. The purpose of the study was to examine the effects of a short-term EMS training program on skating speed, knee extensor muscle strength, and vertical jump height.
Result: After three weeks, hockey players from the EMS group showed a significant improvement in skating speed at a distance of 10 m (time improved by ~5.8%), skating speed at a distance of 30 m remained unchanged. It was measured using an infrared photovoltaic system. The isokinetic strength of the knee extensor muscles was determined using a Biodex dynamometer: it increased by 18–25%. At the same time, the jump height deteriorated by ~6.1%. There were no changes in representatives of the control group.
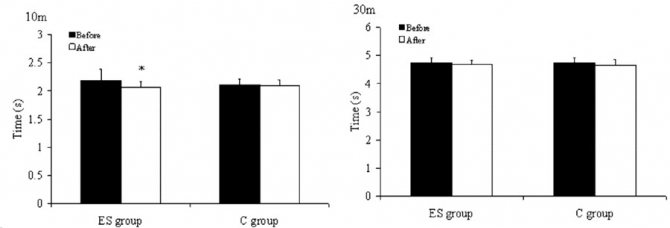
The time it took the subjects to cover 10m and 30m, respectively. (ES) - EMS group, (C) - control group.
The scientists who conducted the study note that exercises to develop jump height are not included in the mandatory training program for hockey players, and in terms of importance, 10-meter sprints are significantly superior to 30-meter sprints in game situations.
Amateur hockey
A similar study was conducted among hockey fans. 30 hockey players took part in it, who were randomly divided into two groups. EMS sessions took place once a week for 12 weeks with a four-week break. There was no control group: all hockey players followed a single program using EMS equipment. At the same time, the training itself was not aimed at working specific muscles, but included complex exercises for the whole body.
The purpose of the study was to determine the effect of EMS on skating sprint speed at a distance of 10 m, snap force, knee extensor muscle strength and jump height.
Result: After 12 weeks of training, representatives of both groups increased their jump height by 5.15% (although this factor is not significant for playing hockey), skating time at a distance of 10 m decreased by 5%, and the maximum isokinetic strength of the quadriceps increased by 7%. At the same time, the force of the click remained practically unchanged. This is largely due to the fact that the strength of the click is primarily influenced by the execution technique.
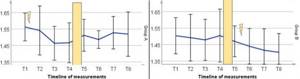
Average change in sprint times for group A and group B. The lightning bolt shows each corresponding period of EMS training - the first 6 weeks were static EMS training, the second 6 weeks dynamic.
The study demonstrated the high effectiveness of EMS technology in improving the athletic performance of players in amateur hockey leagues, even when used infrequently and without focusing on specific muscles.
Football
The study involved 20 football players from a French amateur league, who were divided into two groups of 10 people each: a group that used EMS equipment to perform quadriceps exercises, and a control group that performed the same exercises but without EMS. Both groups worked out 12 minutes a day, three times a week for five weeks, and also played soccer for an average of five hours a week.
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the effects of EMS training on jump height, 10-meter sprint speed, and ball-striking power. The athletes' performance before the experiment was compared with the performance they demonstrated after three and five weeks.
Result: The force of hitting the ball was measured using 44 special radars. The shots were taken from nine meters. Measurements showed that the ball speed at impact without a run-up increased compared to the starting indicators in the third (by ~8.7%) and fifth (by ~10.6%) weeks. Running ball speed increased in week five (5.6%). There were no changes in football players from the control group. Vertical jump height was monitored using the Optojump system. After five weeks, it increased by an average of 6.3%, while the interim results of the third week showed no increase. In the control group - no changes. Sprint speed was measured using infrared photocells and controlled by TAC software. No significant changes were found in any of the groups.
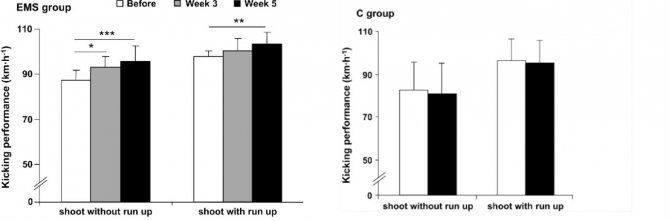
Comparison of ball speed between the EMS group (left) and the control group (right). The indicators of impact without a run-up and with a run-up obtained before the start of the experiment, after 3 and 5 weeks, respectively, are presented.
Volleyball
The study involved 10 professional male volleyball players. The training was conducted three times a week for four weeks and consisted of combined plyometric programs using EMS. Each session consisted of three parts: knee extensor exercises (48 contractions), EMS exercises for the plantar muscles of the foot (30 contractions) and 50 plyometric jumps.
Subjects were tested before the start of the study, in the second week and after completion of the four-week training program, and after two weeks of regular training at the end of the experiment.
Result: In the second week, the maximum voluntary muscle contraction increased compared to the initial level: knee extensors - by 20%, plantar flexors - by 13%. After four weeks, an increase in the height of the half-squat jump was recorded by 8–10%, and an increase in the squat jump by 21% (relative to the initial values). The gains were maintained after an additional two weeks of volleyball training.
Another study involved 12 volleyball players who combined EMS training with their traditional training. The training took place three times a week for four weeks and included EMS sessions with exercises for the knee extensors and plantar muscles of the foot for a total duration of 12 minutes.
Result: 10 days after completion of training, vertical jump height increased by 4–6.5%, and scientists concluded that sports activities using electrical stimulation help the central nervous system react faster and better control the muscles of the body.
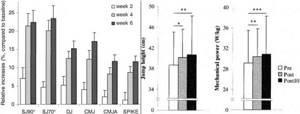
The graph on the left (first study) shows the relative percentage increase in vertical jump height for different jump types between baseline and week 2 (white bars), baseline and week 4 (gray bars), and baseline and week 6 (black bars). The graph on the right (Study 2) shows the average vertical jump height in cm and average strength during continuous CMJ (hands-free jumping from a standing position) before and after a 4-week EMS training program and 10 days after the last EMS session.
Basketball
10 basketball players participated in the study. The training took place three times a week for four weeks and included leg extension exercises using EMS equipment.
Testing was conducted before the start of training, in the fourth week, and four weeks of regular basketball training after the end of the study.
Result: After four weeks, an increase in isokinetic and eccentric leg muscle strength was recorded by 29–37 and 30–43%, respectively, as well as an increase in the height of the squat jump by 14%, and a jump from a vertical position without using hands (countermovement jump) remained unchanged. Measurement after the next four weeks showed that the vertical jump increased by 17%, while the progress in the squat jump was fully maintained. The study has proven the high effectiveness of electrical myostimulation in terms of increasing the strength of the knee extensor muscles and, as a result, improving vertical jump performance, even within a short strength training program.
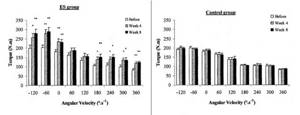
Torque/angular velocity ratio of the knee extensors in moment. On the left is the graph of the EMS group (ES group), on the right is the graph of the Control group for the control group (bottom graph).
Rugby
The study was conducted among 25 professional rugby players, randomly assigned to two groups: 15 people in the EMS group and 10 in the control group. EMS training focused on the muscles - knee extensors, gluteal muscles and foot flexors. Classes were held three times a week for six weeks and then once a week for the next six weeks.
The purpose of the study was to determine the effects of EMS training on leg muscle strength, scrum efficiency (teams' starting position before the ball is thrown into play), full squat strength, sprint speed and vertical jump height.
Result: After the first six weeks of EMS training, squat strength significantly improved (+8.3%), and after another six weeks it increased to 15% of the initial values. The vertical jump height increased by 10%, but the athletes’ performance in grappling and sprinting did not change. No significant changes were detected in representatives of the control group.

Barbell squat performance (kg) for the EMS group and control group before the start of the experiment (white bar), after a 6-week period (gray bar) and after a 12-week period (black bar). (Fig. 1) Contraction values (kg) for EMS and control groups before, after 6 weeks and 12 weeks of training. No changes were found between groups.
Based on the results of the study, it was concluded that EMS training can significantly improve some strength indicators of rugby players in a relatively short period of time.
Vehicles will pass through the intersection in the following order
Correct 16. Driving through intersections
16.11. At an intersection of unequal roads, the driver of a vehicle moving on a secondary road must give way to vehicles approaching this intersection of carriageways on the main road, regardless of the direction of their further movement.
16.13. Before turning left and making a U-turn, the driver of a non-rail vehicle must give way to a tram in the same direction, as well as to vehicles moving on an equivalent road in the opposite direction straight or to the right.
Wrong 16. Driving through intersections
16.11. At an intersection of unequal roads, the driver of a vehicle moving on a secondary road must give way to vehicles approaching this intersection of carriageways on the main road, regardless of the direction of their further movement.
16.13. Before turning left and making a U-turn, the driver of a non-rail vehicle must give way to a tram in the same direction, as well as to vehicles moving on an equivalent road in the opposite direction straight or to the right.
11.
What Research Shows About EMS Training
Despite the obvious excitement of some athletes, as well as flashy, intrusive advertising, scientific research shows that it is not so rosy at all. If there are no direct contraindications, electrical myostimulation is beneficial. For example, to prevent critical loss of muscle mass in sick people, the method turned out to be effective, but only in combination with proper and competent medical care. This option is also suitable for older people for whom regular training is contraindicated.
However, the effectiveness is questioned by scientists. This type of training is most suitable for weakened or untrained people and bedridden patients. In fact, there are no studies that prove that EMC allows you to build perfect abs, biceps or triceps without effort.
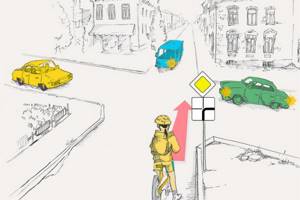
A cyclist passes an intersection:

Correct 8. Traffic regulation
8.3. Traffic controller signals take precedence over traffic light signals and road sign requirements and are mandatory. Traffic lights, other than flashing yellow ones, take precedence over priority road signs. Drivers and pedestrians must comply with the additional requirements of the traffic controller, even if they contradict traffic lights, road signs and markings.
16. Driving through intersections
16.6. When turning left or turning around when the main traffic light is green, the driver of a non-rail vehicle is obliged to give way to a tram in the same direction, as well as to vehicles moving straight in the opposite direction or turning right. Tram drivers should follow this rule among themselves.
Wrong 8. Traffic control
8.3. Traffic controller signals take precedence over traffic light signals and road sign requirements and are mandatory. Traffic lights, other than flashing yellow ones, take precedence over priority road signs. Drivers and pedestrians must comply with the additional requirements of the traffic controller, even if they contradict traffic lights, road signs and markings.
16. Driving through intersections
16.6. When turning left or turning around when the main traffic light is green, the driver of a non-rail vehicle is obliged to give way to a tram in the same direction, as well as to vehicles moving straight in the opposite direction or turning right. Tram drivers should follow this rule among themselves.
12.
The effect of EMS training on weight loss

Advertising proves that myostimulating training helps you easily and without any effort or dietary restrictions to bring your weight back to normal. In fact, this is not true.
How many calories are burned after EMS training?
During the experiments, it was possible to find out that in the current state the consumption is about 60-65 kilocalories, and even with the most intense stimulation mode it reaches only 70-76. For comparison, it is worth noting that one medium-sized apple contains approximately 45-55 kilocalories.
Therefore, we cannot talk about the effectiveness of EMS training for weight loss. However, a similar technique may well be used as an additional tool. True, you should not expect great results, and everyone must decide for themselves whether it is necessary to purchase often very expensive equipment in order to burn an additional 15-20 kilocalories. After all, even regular walking, for example, brings many times more benefits and allows you to burn much more fat mass in the same period of time.
Flashing red signals of this traffic light:
Correct 8. Traffic regulation
8.7.6. To regulate traffic at railway crossings, traffic lights with two red signals or one white-lunar and two red ones are used, having the following meanings:
a) flashing red signals prohibit the movement of vehicles through the crossing;
b) a flashing white-lunar signal indicates that the alarm system is working and does not prohibit vehicle movement.
At railway crossings, simultaneously with the prohibitory traffic light signal, an audible signal may be turned on, additionally informing road users that movement through the crossing is prohibited.
Wrong 8. Traffic control
8.7.6. To regulate traffic at railway crossings, traffic lights with two red signals or one white-lunar and two red ones are used, having the following meanings:
a) flashing red signals prohibit the movement of vehicles through the crossing;
b) a flashing white-lunar signal indicates that the alarm system is working and does not prohibit vehicle movement.
At railway crossings, simultaneously with the prohibitory traffic light signal, an audible signal may be turned on, additionally informing road users that movement through the crossing is prohibited.
13.
Reviews, real results from EMS exercises in terms of weight loss
Despite the fact that the effectiveness of EMS for weight loss has been proven by medicine, negative reviews about such training prevail on the Internet. How can this be? Everything is explained very simply.

EMS classes are not very different in complexity from the training we are used to in the gym, but as for the cost, it is several times higher. In fact, one EMS class can cost you more than a monthly membership to a good gym.
If you go to the EMS simulator once or even five times, you will not lose weight or gain significant strength! In addition, after such a workout, you will feel an increased feeling of hunger, just like after a regular workout. Increasing your caloric intake will definitely not contribute to weight loss. It turns out that EMS training does not have any declared effectiveness? Reviews say no, but in reality, students approach the training process ineffectively and ultimately do not get the expected result.

The driver of which vehicle will cross the intersection second?
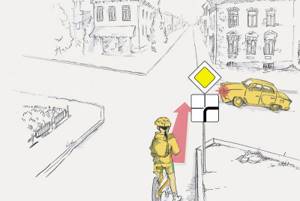
Correct 16. Driving through intersections
16.11. At an intersection of unequal roads, the driver of a vehicle moving on a secondary road must give way to vehicles approaching this intersection of carriageways on the main road, regardless of the direction of their further movement.
16.14. If the main road at an intersection changes direction, drivers of vehicles moving along it must follow the rules for driving through intersections of equivalent roads.
This rule should be followed among themselves and by drivers driving on secondary roads.
Wrong 16. Driving through intersections
16.11. At an intersection of unequal roads, the driver of a vehicle moving on a secondary road must give way to vehicles approaching this intersection of carriageways on the main road, regardless of the direction of their further movement.
16.14. If the main road at an intersection changes direction, drivers of vehicles moving along it must follow the rules for driving through intersections of equivalent roads.
This rule should be followed among themselves and by drivers driving on secondary roads.
14.
Cyclist:
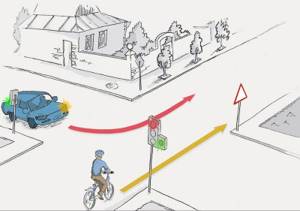
Correct 8. Traffic regulation
8.7.3. Traffic light signals have the following meanings:
A signal in the form of an arrow that allows a left turn also allows a U-turn if it is not prohibited by road signs.
A signal in the form of a green arrow(s) in the additional section(s), switched on together with the green traffic light signal, informs the driver that he has priority in the direction(s) of movement indicated by the arrow(s) over vehicles moving from other directions;
f) a red signal, including a flashing one, or two red flashing signals prohibit movement.
A signal in the form of a green arrow(s) in the additional section(s), together with a yellow or red traffic light signal, informs the driver that movement is permitted in the indicated direction, subject to the unhindered passage of vehicles moving from other directions.
A green arrow on a sign installed at the level of a red traffic light with a vertical arrangement of signals allows movement in the indicated direction when the red traffic light is on from the rightmost lane (or the leftmost lane on one-way roads), subject to the provision of priority in traffic to its other participants moving from other directions to a traffic light signal allowing movement;
16 Driving through intersections
16.9. While driving in the direction of the arrow turned on in the additional section simultaneously with a yellow or red traffic light, the driver must give way to vehicles moving from other directions.
When driving in the direction of the green arrow on the table installed at the level of the red traffic light with vertical signals, the driver must take the extreme right (left) lane and give way to vehicles and pedestrians moving from other directions.
Wrong 8. Traffic control
8.7.3. Traffic light signals have the following meanings:
A signal in the form of an arrow that allows a left turn also allows a U-turn if it is not prohibited by road signs.
A signal in the form of a green arrow(s) in the additional section(s), switched on together with the green traffic light signal, informs the driver that he has priority in the direction(s) of movement indicated by the arrow(s) over vehicles moving from other directions;
f) a red signal, including a flashing one, or two red flashing signals prohibit movement.
A signal in the form of a green arrow(s) in the additional section(s), together with a yellow or red traffic light signal, informs the driver that movement is permitted in the indicated direction, subject to the unhindered passage of vehicles moving from other directions.
A green arrow on a sign installed at the level of a red traffic light with a vertical arrangement of signals allows movement in the indicated direction when the red traffic light is on from the rightmost lane (or the leftmost lane on one-way roads), subject to the provision of priority in traffic to its other participants moving from other directions to a traffic light signal allowing movement;
16 Driving through intersections
16.9. While driving in the direction of the arrow turned on in the additional section simultaneously with a yellow or red traffic light, the driver must give way to vehicles moving from other directions.
When driving in the direction of the green arrow on the table installed at the level of the red traffic light with vertical signals, the driver must take the extreme right (left) lane and give way to vehicles and pedestrians moving from other directions.
15.
Who is not suitable for EMS training?
- If you are not ready to spend a significant amount. EMS training will cost you a little more than visiting a regular gym.
- If you don't want to stress and expect no stress. EMS training is often called “fitness for the lazy,” but this is not true. External impulses will make your muscles (including small and deep ones) literally tremble, so performing even the most basic exercises will not seem so easy to you.
- If you are a follower of classical training and trust only the weight of the barbell. Some people may enjoy the very process of regular exercise in the gym, but electrical stimulation, on the contrary, may cause discomfort. Exercising in wet uniforms and a tight vest is also not the most pleasant feeling.
READ MORE: Reverse dumbbell press lying on a horizontal and inclined bench
Contraindications
Low-frequency stimulation does not harm health; the restrictions are the same as for normal physical activity. Among the categorical contraindications is only a prosthesis in the heart. If you have cardiac disease or have a pacemaker installed, be sure to consult your doctor.
It is better to refrain from EMS training for pregnant women, since to date there has been no research in this area, but after the birth of a child it is an excellent way to quickly restore the pelvic muscles.
What do you think about the future of fitness? Write in the comments.
Can a cyclist turn left?
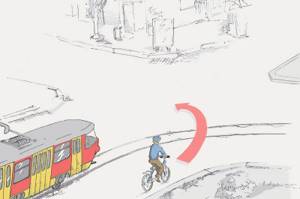
Correct 11. Location of vehicles on the road
11.14. Movement on the roadway on bicycles, mopeds, horse-drawn carriages (sleighs) and horseback riders is permitted only in one row in the rightmost lane as far to the right as possible, except for cases when a detour is in progress. Left turns and U-turns are permitted on roads with one lane in each direction and no tram tracks in the middle. Driving on the side of the road is permitted if this does not create obstacles for pedestrians.
Wrong 11. Location of vehicles on the road
11.14. Movement on the roadway on bicycles, mopeds, horse-drawn carriages (sleighs) and horseback riders is permitted only in one row in the rightmost lane as far to the right as possible, except for cases when a detour is in progress. Left turns and U-turns are permitted on roads with one lane in each direction and no tram tracks in the middle. Driving on the side of the road is permitted if this does not create obstacles for pedestrians.
( 6 ratings, average: 4.83 out of 5)
The influence of EMS on the physical qualities of athletes: individual sports
Swimming
The study involved 14 male professional swimmers. They were divided into two groups of seven people. The first was trained using EMS equipment, the second (control) performed the same exercises, but without electrical myostimulation. Swimming training took place three times a week for three weeks.
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the effects of EMS training on latissimus dorsi muscle strength. Peak torques recorded during arm flexion and extension were determined using an isokinetic dynamometer at different speeds (−60 to 360 degrees).
Result: After three weeks, representatives of the first group recorded an increase in isokinetic arm strength by 10–15% and, as a result, an increase in freestyle swimming speed at distances of 25 and 50 meters. Swimmers in the control group showed no changes.
Another study involved 24 national-level swimmers, who were divided into three groups (eight people each). Each devoted 20 hours a week to swimming. At the same time, the first group used EMS equipment three times a week for 15 minutes to train the latissimus dorsi muscle, the second additionally trained on land five days a week for 40 minutes, and the third was a control group and did only swimming.
Result: At the end of four weeks, participants in the first (EMS) and second (additionally trained on land) groups improved their results in swimming at a distance of 50 m by 1.7–2%, and also increased isokinetic arm strength by 11.2–16.9 %. It is worth noting that, compared to those who trained on land, athletes from the EMS group spent four times less time on additional training. No changes were detected in representatives of the control group.

Gymnastics
The study was conducted among 16 young female gymnasts to study the effect of EMS on leg muscle strength and vertical jump height. The athletes were divided into two groups and performed identical knee extension exercises three times a week for 20 minutes for the first three weeks and once a week for the next three weeks. Also, both groups did gymnastics according to the same program, while the first used EMS equipment, and the second was the control.
Result: After three weeks, gymnasts from the EMS group showed an increase in isokinetic leg strength by 35–50%, and after six weeks, the result in the vertical jump improved by 14–20%. A month after stopping EMS training, the jump performance was measured again and it was found that the result was maintained. This indicates the high effectiveness of combining EMS training with classical gymnastics.
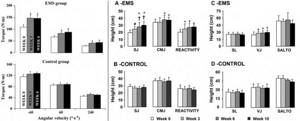
Right knee extensor torque and angular velocity relationships for the electrically stimulated (EMS) and control groups at week 0, week 3, and week 6. (Figure 1) Vertical jump performance in the EMS and control groups; SJ: squat jump; CMJ: counter movement jump; SL: split jump; VJ: vertical jump after handstand; SALTO: backflip. (Fig.2)
Athletics
The study involved 98 track and field athletes (51 men and 47 women, with an average age of 18 years), randomly assigned to four groups. The purpose of the study was to examine the effects of eight-week (two days per week) training periods combining plyometric exercises with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on jump height in young athletes.
Result: In those groups where athletes performed plyometric exercises using EMS equipment, an increase in jump height of 4–28% was recorded. There were no fundamental changes in athletes from the control group.

Table of results of the experiment, in which there are 3 EMS groups (G1, G2, G3) and a control group (Control)
Tennis
The study involved 12 professional tennis players (five men and seven women). Three times a week for 16 minutes for three weeks, they performed EMS exercises for the quadriceps (quadriceps femoris muscle), integrating them into their usual tennis training.
The researchers saw their goal as assessing the effectiveness and impact of EMS training included in tennis classes on the anaerobic performance of athletes during pre-season training. Participants were tested before the study began and their performance was tracked weekly for four weeks after the study.
Result: Thanks to electromyostimulation, it was possible to reduce the time in the 2 × 5 m shuttle sprint by 3.3% and increase the jump height by 6.4%. Maximal isometric quadriceps strength increased throughout the experiment: during the first three weeks of EMS training, it increased by ~27% and continued to increase over the next three weeks, when no EMS equipment was used. In the fourth week after the end of the experiment, the isometric strength of the quadriceps began to decrease.
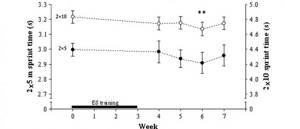
Time associated with the 2 x 5 m (open diamonds) and 2 x 10 m (filled diamonds) shuttle sprints before (week 0) and after the electrical stimulation (ES) program (weeks 4-7)
The study demonstrated the effectiveness of combining a short-term EMS training program with game-based practice, just as has been proven in hockey, volleyball, football and other sports (see below). Since the effect of increasing anaerobic performance disappeared a month after the cessation of training with EMS equipment, scientists suggested supporting it with additional training during the preparatory and competitive season of tennis players.