Appetite suppressants
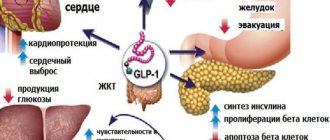
Anorexigenic drugs are a group of substances that suppress appetite by affecting the central nervous system. The brain has hunger and satiety centers. Drugs in this group have a stimulating effect on the satiety center, but at the same time inhibit the hunger center. The effect on the central nervous system occurs through the accumulation of serotonin and norepinephrine in the hypothalamus. Thanks to this, the feeling of hunger decreases.
Anorexigenic drugs that suppress appetite are divided into adrenergic stimulants, serotonergic system stimulants, and combination drugs.
Indications for use
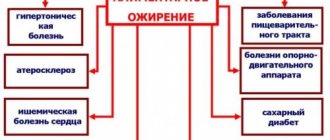
These types of drugs are taken for various types of obesity. These include:
- obesity associated with excessive food intake into the body (nutritional);
- weight gain due to hormonal imbalance (used in combination with other drugs);
- obesity with hypothyroidism;
- excess weight that cannot be treated with other means.
Appetite suppressants should be taken in accordance with a diet, using fasting days.
Symptoms of Anorexia Nervosa
Manifestations of eating behavior:
obsessive desire to lose weight, despite insufficient (or normal) weight; fatphobia (obsessive fear of excess weight, obesity); obsessions related to food, fanatical calorie counting, narrowing interests and focusing them on weight loss; regular refusal to eat, motivated by lack of appetite or recent consumption of food, limiting its quantity (argument - “I’m already full”); turning meals into a ritual, chewing especially thoroughly (sometimes swallowing without chewing), serving in small portions, cutting into small pieces; avoidance of activities related to eating, psychological discomfort after eating.
Other behavioral signs:
desire for increased physical activity, irritation if it is not possible to perform exercises with overload; the preferred choice of loose, baggy clothes (to hide your imaginary excess weight); rigid, fanatical type of thinking, incapable of flexibility, aggressiveness in defending one’s beliefs; tendency to avoid society, solitude.
Mental condition:
depressed state of mind, depression, apathy, decreased ability to concentrate, performance, withdrawal, obsession with one’s problems, dissatisfaction with oneself, one’s appearance and one’s success in losing weight; often – psychological lability, sleep disturbances; a feeling of loss of control over one’s life, inability to be active, futility of efforts; the anorexic does not believe that he is sick, refuses the need for treatment, and persists in refusing food;
Physiological manifestations
body weight is significantly (more than 30%) below the age norm; weakness, dizziness, tendency to frequent fainting; growth of fine and soft vellus hair on the body; decreased sexual activity, in women, menstrual cycle disorders up to amenorrhea and anovulation; poor blood circulation and, as a result, a constant feeling of cold.
Contraindications and side effects
Anorexigenic drugs should be used strictly as prescribed by the doctor, as these drugs are contraindicated for some people. Which patients should not take drugs from this group:
- with severe hypertension;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- history of heart attack or stroke;
- heart failure;
- circulatory disorders;
- glaucoma;
- status epilepticus.
Also contraindications are mental disorders and pathological processes in the central nervous system, liver and kidney failure, insomnia and pregnancy.
In case of an overdose of these drugs, weakness, nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, diarrhea or diarrhea, urination problems, increased excitability, dizziness, increased blood pressure, excessive sweating, allergic reactions such as urticaria or Quincke's edema may occur.
If such symptoms appear, the dose of the drug should be reduced. If the symptoms have not changed, you should immediately stop taking the medicine and consult a doctor to correct the course of treatment.
Treatment of Anorexia Nervosa
Borderline conditions in anorexics, as a rule, are caused by deep pathological disturbances of homeostasis, therefore emergency aid for persons admitted with signs of acute heart failure with significant exhaustion is the correction of the water-electrolyte state, restoration of ion balance (restoration of potassium content in the serum). Prescribe mineral and vitamin complexes, high-calorie foods high in protein. If food is refused, parenteral administration of nutrients is required.
However, these measures correct the consequences, but do not eradicate the psychological cause or treat anorexia itself. In order to begin psychotherapy, it is necessary to convey to the patient’s loved ones the seriousness of the disease and convince them of the need for treatment. A significant difficulty is convincing the anorexic person that he has a mental illness and the need for treatment. The patient must voluntarily implement measures to treat anorexia; forced therapy may be ineffective and simply impossible.
In most cases (not counting the early stages, without severe exhaustion), anorexia is treated in a hospital setting, the first task is to restore normal body weight and metabolism. Freedom of action and movement in the hospital for anorexics is very limited and patients receive additional incentives in the form of walks, meetings with relatives and friends as a reward for following a diet and gaining weight. Patients themselves, in agreement with the attending physician, determine these reward measures based on their attractiveness and their interest in receiving rewards. The technique of such rewards is considered quite effective for moderately severe anorexia, but in severe advanced cases this method may not have an effect.
Basic therapy for anorexia - psychological help, support, correction of obsessive states, distracting the psyche from fixation on appearance, weight and food, getting rid of feelings of inferiority, developing personality and self-respect, the ability to accept oneself and the world around. Family therapy is recommended for adolescents.
The drug "Meridia"
The price of this product seems attractive to many. After all, 700-800 rubles is inexpensive compared to other similar drugs. These tablets are an effective way to lose weight and have a quick effect. The medicinal substance belongs to the group of anorexigenic drugs and increases the feeling of satiety. It blocks the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, causing the therapeutic effect of the drug. It is used for obesity in the absence of concomitant pathology, in the presence of lipid metabolism disorders and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
"Meridia" is available in gelatin capsules of 10 and 15 mg, 14 pieces in 1 pack. Contraindications to taking the drug are drug intolerance to this group, nervous and mental disorders, hormonal imbalance in the body, heart and vascular diseases, pathologies of the kidneys, liver, and thyroid gland.
You can reduce body weight by taking 1 capsule of 10 mg daily. If the drug is well absorbed, the daily dose can be increased to 15 mg. The course of treatment should be no more than 1 year. Meridia tablets, the price of which is about 700 rubles for 14 capsules, can be purchased with a doctor’s prescription.
Self-torture
Naturally, the body still tries to fight hunger, and girls, despite taking medications, have “breakdowns.” What they call “gluttony,” but which is essentially an attempt to eat a normal portion of ordinary food - after all, after a long fast, eating more than the usual portion is problematic. It hurts.

Motivator from the “40 kg” community
And failures always come with punishment. That is, self-torture. Posting photos of yourself with the caption “I’m fat” is the mildest possible punishment. You can also post the photo in an album for criticism and receive a dose of insults. You can punish yourself with a dry fast. Dry means you can’t even drink. No food, no water.
When obsessive thoughts about food arise, anorexics are advised to imagine something terrible instead of food: worms, rotting corpses or excrement. Do unpleasant things. Punish yourself with hard physical work.
And the last method is cuts. Anorexics cut themselves (mostly their legs, many then post photos of cuts on their thighs online). In fact, the problem of self-harm is not the problem of anorexia. Self-harm is an unhealthy attempt to relieve emotional pain, intense anger and frustration. It can bring short-term relief both on an emotional and physical level: on the one hand, there is a feeling of control over one’s own body, on the other, the cut provides a surge of adrenaline, which, in turn, makes past experiences unimportant. But not for long. Then the feeling of guilt, shame and the return of previously experienced emotions comes again.
"Reduxin"
This is a combined drug that simultaneously inhibits the hunger center due to metabolites and activates the satiety center. The medicine is used 1 capsule per day. The dose is prescribed individually, depending on the degree of obesity and the general condition of the body. Most often it is 10 mg. Reduxin tablets should be taken without chewing and washed down with plenty of water.
Indications for their use: obesity in the absence of concomitant pathology, in the presence of lipid metabolism disorders and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Reduxin tablets should not be used by pregnant and lactating women or people with pathologies of certain organs. In this case, mandatory consultation with a specialist is required. The drug is prescribed in compliance with the daily regimen and nutrition.

Lose weight to death: 3 scary methods used by anorexics
Anorexia nervosa is a serious disease that is difficult to treat. At the same time, a huge number of girls strive to get it. The online public “40 kg” alone has more than 5 million subscribers, and hundreds of thousands more - for the publics “Typical Anorexic”, “Ana Loves You” and the like. In search engines, along with the word “anorexia,” they often search for the phrase “how to get sick.” Get sick and lose weight. Sometimes - to death. We learned all about 3 scary ways that girls who dream of becoming “fragile butterflies” lose weight.
The drug "Fepranon": instructions for use
This is an anorexigenic drug, the active substance of which is amfepramone. Activates the satiety center, inhibits the hunger center, enhances the elimination of unnecessary substances and reduces weight. The activity of the drug appears after 1 hour, it lasts up to 8 hours, and penetrates well through the blood-brain and placental barriers.
Indications for prescribing the drug are alimentary obesity and lipid metabolism disorders due to hormonal imbalances. For thyroid pathology, it is used in combination with thyroid medications.
1 tablet of the drug contains 25 mg of active substance. You need to consume about 80 mg per day, that is, 1 tablet 2-3 times a day. You need to drink them half an hour before meals. The maximum duration of treatment is 2 months, the course can be repeated after 3 months. The drug is available only with a doctor's prescription.
An overdose of Fepranon may cause rapid heartbeat and breathing, hallucinations, and collapse. If you take the drug for epilepsy, you can provoke seizures, so for this type of disease you should limit your use.

The drug "Slimia"
This is a weight loss product whose medicinal effect is achieved thanks to the active substance sibutramine. The effect on the body occurs by activating the satiety center, reducing the feeling of hunger and subsequently eating less food. The drug also helps to increase metabolism and more quickly remove toxic substances from the body.
“Slimia” is used for nutritional obesity, obesity due to diabetes mellitus and lipid metabolism disorders. The drug is contraindicated in the following cases:
- for nervous and mental disorders;
- obesity associated with hormonal imbalances;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- pathologies of the liver, kidneys, thyroid gland;
- drug addiction or alcoholism;
- for people under 18 years of age;
- pregnant and lactating women.
“Slimia” is not very well tolerated by the body. Reviews from those losing weight show that the drug has side effects in the form of indigestion, headaches, drowsiness, and dizziness, most often at the beginning of the course of treatment. If you have such symptoms, you should consult a specialist about discontinuing the drug.
“Slimia” is available in tablets of 10 and 15 mg, the dosage of the drug is 1 tablet per day. The course of treatment begins with 10 mg; if the effect is positive, then the dose of the drug can be increased to 15 mg and a positive effect can be achieved in a shorter time.
Risk factors for anorexia
The presence of various chronic diseases of organs and systems can contribute to the development of anorexia. This:
endocrine disorders (pituitary and hypothalamic insufficiency, hypothyroidism, etc.);
diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, pancreatitis, hepatitis
and cirrhosis of the liver, appendicitis); chronic renal failure; malignant neoplasms; chronic pain of any etiology; prolonged hyperthermia (due to chronic infections or metabolic disorders); dental diseases.
Iatrogenic anorexia can occur as a result of taking drugs that act on the central nervous system, antidepressants or tranquilizers, with the abuse of narcotic and sedatives, amphetamines and caffeine.
In young children, anorexia can be caused by violation of the feeding regime and rules, persistent overfeeding. Anorexia nervosa is most common among women (the vast majority are young girls). The combined influence of fear of excess weight and noticeably reduced self-esteem contributes to the development of psychological aversion to food and persistent refusal to eat it.
Subconsciously, anorexia becomes the most obvious way to get rid of fears of excess weight and loss of attractiveness. The teenage psyche, which is prone to instability, fixes the idea of losing weight as overvalued, and the girl loses her sense of reality and ceases to perceive herself and the state of her health critically.
Anorexic girls can, even with an obvious lack of body weight up to complete exhaustion, consider themselves fat and continue to deny the body the necessary nutrients. Sometimes patients are aware of their exhaustion, but, experiencing a subconscious fear of eating, they cannot overcome it. During anorexia, a vicious circle arises - the lack of nutrients depresses the brain centers responsible for regulating appetite, and the body stops demanding the substances it needs.
Eating disorders, which include anorexia, are one of the most common psychosocial diseases, since many people use the satisfaction of the satiety instinct as a sublimation of missing positive emotions. Food becomes the only means of obtaining psychological benefits, and it is also blamed for psychological failures, going to the other extreme - refusing to eat.
Behavior in anorexia nervosa can be of two types (and the same person can act in both ways at different times):
strong-willed, strict adherence to diets, fasting, various types of fasting techniques; against the background of attempts to regulate nutrition, attacks of uncontrolled overeating (bulimia) occur, followed by stimulation of cleansing (vomiting, enemas).
As a rule, excessive physical activity is practiced until muscle weakness develops.