Your body needs omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in food.
Omega-3s are “essential” fatty acids because the body cannot produce them on its own. In this regard, we must consume foods containing Omega-3 fatty acids to replenish the body with these very beneficial substances.
There are three different types of Omega-3 fatty acids: ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), DHA (docosahexanoic acid) and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid). The priority species are DHA and EPA, which are found in seafood such as salmon and sardines. On the other hand, ALA is found in some plant-based foods, including nuts and seeds, as well as high-quality cuts of grass-fed beef.
To get the polyunsaturated fatty acids you need, I recommend including foods rich in Omega-3s and, in many cases, supplements. Even with this combination, make sure you're getting at least 1,000 milligrams of DHA and EPA per day, and about 4,000 milligrams of total Omega-3 (ALA/DHA/EPA combination).
What makes Omega-3 foods better than the rest?
The human body has the ability to convert ALA to some extent into beneficial DHA and EPA, but it is not as efficient if the body were to obtain these Omega-3s directly from foods that contain them. This is just one reason why nutritionists recommend eating wild fish several times a week, since many types of seafood have high levels of DHA and EPA.
While EPA and DHA are the preferred omega-3 sources, all other sources are healthy and encouraged, so add nuts and seeds to your breakfast, or cook fish for lunch. Even after extensive research, it is not entirely clear how well ALA is converted into EPA or DHA or whether it provides benefits on its own, but health authorities such as Harvard Medical School still consider all omega-3 resources to be essential in the diet.
Historically, people who eat the most foods rich in Omega-3s (such as people from Okinawa or Japan) have lived longer and are healthier than people whose diets are low in Omega-3s. The typical Okinawan diet - which consists of plenty of fish, sea vegetables and other fresh produce - contains 8 times more Omega-3 than our diet. This is the reason why the Okinawan population is considered the healthiest in human history.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids - what they are and how they are useful
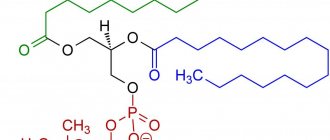
Vitamins, fats, proteins, carbohydrates and microelements are necessary for our body. Many of the substances we need are found in food. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are no exception. The name is based on the structure of the molecule. If an acid molecule has double bonds between carbon atoms, it is polyunsaturated. Please do not confuse PUFAs with polyunsaturated fats. The second are fatty acids paired with glycerol, they are also called triglycerides. They are the source of cholesterol and excess weight.
Alpha-linolenic acid is often found in dietary supplements and vitamins. In such compositions you can see docosahexaenoic and ecosapentaenoic fatty acids. These are omega-3 PUFAs.
In the composition of the preparations you can also see linoleic, arachidonic or gamma-linolenic acids. They are classified as omega-6. These elements cannot be synthesized in our body. That's why they are so valuable. They can come to us either through food or medications.
The foods you eat must contain PUFAs. If they are not there, symptoms of a lack of necessary substances will appear over time. I think you've heard about vitamin F. It is found in many vitamin complexes. So, vitamin F contains omega-3 and omega-6 acids. If you take vitamins, be sure to pay attention to its presence.
What is the value of these substances:
normalize blood pressure; lower cholesterol; effective in the treatment of acne and various skin diseases; promote weight loss by burning saturated fats; participate in the structure of cell membranes; prevent thrombosis; neutralize any inflammation in the body; have a positive effect on the reproductive system.
Omega-6 and omega-3 are best taken not separately, but together. For example, Eskimos consume these fats in equal proportions. Proof of this is the low mortality rate from heart and vascular diseases.
Most scientists agree that the optimal proportion of these fats is 5:1 (less is always omega-3)
If a person is sick, then 2:1. But since everything is quite individual, your doctor can recommend a different ratio just for you.
Omega-3 Foods: The Best vs. the Worst
Pay attention to any large supermarket and you will see that food labels are vying with each other to boast about Omega-3 content now more than ever. While Omega-3s are artificially added to a variety of processed foods—such as peanut butter, baby formula, oatmeal, and protein powder—it's best to get these nutrients from natural seafood, especially commercial seafood.
While natural Omega-3 resources are not always perfect, you can find foods that contain them to some extent through fortification: pasteurized dairy products, fruit juices, eggs (not organic or from cage-free chickens), margarine, soy milk and yogurt, bread, flour, weight loss drinks, baby food (since scientists discovered that Omega-3s help children's brains develop properly).
EPA and DHA resources in fortified foods are typically obtained from microalgae. In their natural form, they add a fishy odor to food, so these processed foods must undergo intensive chemical cleaning to mask their taste and odor. This reduces or alters the fatty acids and antioxidants in foods, making them less healthy than foods that have not been processed.
In addition, Omega-3 is now being added to animal feed to increase its content in dairy, meat and poultry products. As food manufacturers know that consumer awareness of Omega-3 is growing, we will continue to see more and more products fortified with this supplement.
What are the dangers of shortages and excesses?
If the diet is improperly formed (vegetarianism, diets, fasting) or there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract, there is a high risk of developing EFA deficiency . The easiest way to recognize a deficiency is by the following symptoms:
- pain in muscles, tendons and joints;
- dandruff;
- feeling of thirst;
- increased fatigue of the body, decreased performance;
- hair problems (fragility and hair loss);
- the appearance of a rash on the skin, peeling, drying out;
- apathetic and depressive states;
- deterioration of the condition of the nail plates, decrease in their density;
- problems with stool, which manifest themselves in the form of constipation;
- disruptions in wound healing processes;
- gradual increase in blood pressure;
- weakening of the immune system, increasing the risk of colds and viral diseases;
- deterioration of memory and attention, excessive absent-mindedness;
- decreased vision;
- delay in the processes of mental development and growth;
- slowing down recovery processes.
If you do not know which foods contain Omega-3 fatty acids and do not saturate your diet with them, then the appearance of the described symptoms is a reality. In addition, a deficiency of useful elements over a long period of time leads to the development of problems with the central nervous system and neuropsychiatric diseases.

An excess of the substance in question is a rare phenomenon , which is often associated with uncontrolled use of drugs containing a high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, an overdose of a substance is no less dangerous than a deficiency. The problem manifests itself as follows:
- Loose stools, diarrhea.
- Reduced blood clotting, which leads to prolonged bleeding. This is possible even with minor cuts. The greatest danger comes from internal hemorrhages - in the stomach or intestines.
- Malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Gradual decrease in pressure level.
The dangers of Omega-3 deficiency
Omega-3 rich foods are thought to help reduce the risk of heart disease due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
They are necessary for the normal functioning of the nervous system, protection of cell membranes, good mood and hormone production. That's why Omega-3 foods are considered sources of "healthy fats" that form polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAS), better known as ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). Although most people consume adequate amounts of other types of fatty acids known as omega-6s (found in modified edible oils such as canola oil, sunflower oil, and some nuts), most people have low levels of omega-3s and may allow yourself to increase your consumption of foods rich in this substance.
Research shows that a low ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 is more desirable to reduce the risk of many chronic diseases that have become epidemic in most Western societies. For example, researchers from the Washington, D.C. State Center for Genetics, Nutrition and Health found that the lower the Omega-6/Omega-3 ratio in women, the lower the risk of developing breast cancer. The 2:1 ratio reduces inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and the 5:1 ratio has beneficial effects in patients with asthma.
The average person suffers from Omega-3 deficiency because they do not include Omega-3 foods in their weekly diet such as fish, sea vegetables/algae, flaxseeds or grass-fed meats. Depending on who you ask, these numbers may vary, but I insist that the ideal ratio of Omega-6 foods to Omega-3 foods should be approximately equal, or at least around 2:1.
What could be the risks of consuming too little Omega-3 (plus too much Omega-6)?
- Inflammation (sometimes severe)
- Increased risk of heart disease and high cholesterol
- Indigestion
- Allergies
- Arthritis
- Pain in joints and muscles
- Psychological disorders such as depression
- Poor brain development
- Decreased cognitive abilities
Benefits of consuming natural Omega-3 products:
Many studies show that omega-3 fatty acids provide support: (6)
- Cardiovascular health (by reducing blood pressure, cholesterol levels, plaque buildup in the arteries, and the likelihood of a heart attack or stroke)
- Stabilizing blood sugar levels (prevents diabetes)
- Reducing muscle, bone and joint pain by reducing inflammation)
- Helping regulate cholesterol levels
- Improving mood and preventing depression
- Improving mental abilities and helping to focus and learn
- Boosting immunity
- Treating eating disorders like ulcerative colitis
- Reducing the risks of cancer and preventing the occurrence of metastases
- Improving appearance, especially skin condition
There is currently no set recommendation for how much Omega-3 we should consume each day, so the amount ranges from 500 to 1,000 milligrams per day depending on who you ask. How easy is it to get the recommended amount of Omega-3? To give you some idea, for example, over 500 mg of Omega-3 is found in a can of tuna and a small serving of salmon. Below we will tell you in detail which foods contain omega-3 and where it is more abundant.
Omega-6 - benefits and harms
How do you know if you don’t have enough PUFAs or if you have too much of them? Inflammatory diseases may indicate an excess of polyunsaturated fats. Repeated depression and thick blood also indicate this. If you find an excess of these fatty acids, try to exclude from your diet: walnuts, vegetable oils, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds.

It wouldn't hurt to consult a doctor. After all, it may be that the above symptoms are not related to omega-6. With a lack of this substance, as well as with its excess, thick blood is observed. Also, high cholesterol. With excess and deficiency of acids of this type, similar symptoms can occur. A lack of these polyunsaturated fats may be indicated by:
- loose skin;
- obesity;
- weak immunity;
- infertility in women;
- hormonal disorders;
- joint diseases and problems with intervertebral discs.
It is difficult to overestimate the benefits of this type of fat. Thanks to them, our body accelerates the removal of toxins. The functioning of the heart and the condition of blood vessels improves. The risk of mental illness is reduced. Brain activity increases. The growth of nails and hair and their appearance improves. An adult should consume at least 4.5-8 g of this PUFA per day.
What are the best Omega-3 foods?
Below are the top 15 foods that contain the most Omega-3 (percentages based on a daily intake of 4,000 milligrams of Omega-3):
- Mackerel: 6,982 milligrams in 1 cup cooked (174 percent DV)
- Salmon fish oil: 4.767 milligrams in 1 tablespoon (119 percent DV)
- Cod liver oil: 2,664 milligrams in 1 tablespoon (66 percent DV)
- Walnuts: 2,664 milligrams per 1/4 cup (66 percent DV)
- Chia (Spanish sage) seeds: 2,457 milligrams in 1 tablespoon (61 percent DV)
- Herring: 1.885 milligrams in 3 ounces (47 percent DV)
- Salmon (farmed): 1,716 milligrams in 3 ounces (42 percent DV)
- Flaxseed meal: 1,597 milligrams in 1 tablespoon (39 percent DV)
- Tuna: 1,414 milligrams in 3 ounces (35 percent DV)
- White fish: 1,363 milligrams in 3 ounces (34 percent DV)
- Sardines: 1.363 milligrams per can/3.75 ounces (34 percent DV)
- Hemp seeds: 1,000 milligrams in 1 tablespoon (25 percent DV)
- Anchovies: 951 milligrams per 1/2-ounce can (23 percent DV)
- Natto: 428 milligrams per 1/4 cup (10 percent DV)
- Egg yolks: 240 milligrams per 1/2 cup (6 percent DV)
What foods should you avoid even though they are advertised as being high in Omega-3? These include traditional animal meats (that are not grass-fed), farmed fish (salmon is especially common), regular and pasteurized dairy products, and sea krill oil supplements (which are made from krill, deep-sea molluscs, which are usually contaminated).
Remember that farmed fish is inferior to wild caught fish in terms of both pollution levels and nutrient and omega-3 content. Farmed fish typically contains high concentrations of antibiotics, pesticides, and low levels of nutrients such as vitamin D. There is also evidence that farmed fish has more Omega-6 fatty acids and less Omega-3 fatty acids.
Below is a table of what omega-3 contains and in what quantities per 100 grams of product.
Table 1
| Fish (serving 100 g) | Amount of Omega-3 fatty acids (g) | Amount of Omega-6 fatty acids (g) | Omega-3: Omega-6 |
| Caviar black and red | 6,789 | 0,081 | 1 : 0,01 |
| Fresh Atlantic mackerel | 2,670 | 0,219 | 1 : 0, 08 |
| Atlantic sea salmon | 2,586 | 0,172 | 1 : 0,06 |
| Farmed Atlantic salmon | 2,506 | 0,982 | 1 : 0,39 |
| Fresh Pacific herring | 2,418 | 0,192 | 1 : 0,07 |
| Fresh tuna | 0,243 — 1,664 | 0,010 -0,068 | 1 : 0,006 – 1 : 0,40 |
| Pacific mackerel fresh | 1,614 | 0,116 | 1 : 0,07 |
| Atlantic sardines | 1,480 | 0,110 | 1 : 0,07 |
| Canned salmon | 1,323 | 0,152 | 1 : 0,11 |
| Fresh trout | 1,068 | 0,224 | 1 : 0,21 |
| Swordfish | 0,825 | 0,030 | 1 : 0,03 |
| Oysters | 0,740 | 0,032 | 1 : 0,04 |
| Fresh halibut | 0,669 | 0,038 | 1 : 0,05 |
| Fresh conger eel | 0,653 | 0,196 | 1 : 0,30 |
| Shrimps | 0,601 | 0,028 | 1 : 0,05 |
| Flounder | 0,563 | 0,008 | 1 : 0,2 |
| Sea shellfish | 0,396 | 0,032 | 1 : 0,08 |
| Scallop | 0,396 | 0,004 | 1 : 0,01 |
| Pacific cod | 0,221 | 0,008 | 1 : 0,04 |
PUFAs during pregnancy

Polyunsaturated lipids are the most important nutrients for expectant mothers, as they reduce the risk of premature birth and alleviate the manifestations of toxicosis. In addition, the elements are “responsible” for the formation of the peripheral nervous system in the growing embryo. Considering that fats make up 70% of the retina and 30–40% of brain lipids, vitamin F controls the ontogenesis of the visual apparatus and brain in the developing fetus.
During pregnancy, the mother “gives” 2.5 grams of PUFAs to the child, so the daily need for essential fats doubles. The daily requirement of vitamin F for pregnant women is 15 grams (omega-3 – 2 grams, omega-6 – 13 grams).
Other effects of taking PUFAs during pregnancy:
- They potentiate the release of prostaglandins and eicosanoids, which improve the child’s immune status.
- Participate in the mechanisms of building the cardiovascular system of the embryo.
- “Control” the proper formation, maturation and functioning of the placenta (metabolism and blood supply).
- Prolongs pregnancy.
- Prevents the development of toxicosis in the third trimester (gestosis).
- Prevents the development of thrombophilic disorders, and as a consequence, placental insufficiency.
- Reduces the likelihood of developing postpartum depression by 50%.
- Increases the tolerance of the birth act by the embryo.
To replenish the daily requirement for fats, flaxseed or camelina oil, nuts, fish, vegetables, and fruits are introduced into the daily menu. However, a balanced diet, in 90% of cases, does not cover the daily requirement of the substance. Therefore, it is advisable for expectant mothers to use biologically active complexes, which include omega-3 acids.
Consider the list of drugs containing essential fats:
- Premium Omega-3 fish oil (Madre Labs, USA). 1 capsule contains 180 milligrams of eicosapentaenoic acid, 120 milligrams of docosahexaenoic acid and 1000 milligrams of fish oil.
- Rx Omega-3 Factors (Natural Factors, USA). The drug contains fish oil (1170 milligrams in 1 tablet) and a concentrate of polyunsaturated fats ω-3 (600 milligrams in 1 capsule).
- Novomegin (Art-life, Russia). The biocomplex consists of a concentrate of omega-3 polyunsaturated lipids (150 milligrams per 1 capsule), flaxseed oil (200 milligrams per tablet), lipoic acid, vitamin E, dihydroquercetin, organic selenium.
- Prenatal DHA (Nordic Naturals, USA). Organic tablets include: eicosapentaenoic acid (102.5 milligrams), docosahexaenoic acid (220 milligrams), cholecalciferol (200 IU), fish oil (500 milligrams).
- Omega-3 (Solgar, USA). The dietary supplement contains a concentrate of polyunsaturated fats extracted from the muscles of cold-water fish of the northern seas. 1 capsule of the drug contains 900 milligrams of omega-3, 1500 milligrams of fish oil.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
To normalize the psycho-emotional background of a woman during pregnancy, along with taking these complexes, it is advisable to drink 15 milliliters of flaxseed oil per day.
Other Natural Sources of Omega-3
- Omega-3 Nuts and Seeds - In addition to walnuts, chia, flaxseeds, California nuts, Brazil nuts, cashews, hemp seeds and tree nuts have omega-3 in the form of ALA (although walnuts, flaxseeds and chia definitely , are the best sources).
- Vegetables - Many vegetables, especially green leafy ones, are good sources of ALA. Although ALA omega-3 foods are not as good as those containing EPA and DHA, they should still be present in your diet considering how much fiber and other nutrients they contain. Some of the vegetables with the highest omega-3 content are: Brussels sprouts, kale, spinach and watercress.
- Oils – Many oils contain some degree of omega-3, usually in the form of ALA. These include mustard oil, walnut oil and hemp oil. A newer vegetarian oil called algae oil is gaining popularity because early research shows it is easily converted into DHA in the body compared to other vegetarian omega-3 foods.
table 2
Physical properties
The lower liquids are volatile liquids with a pungent odor, the middle ones are oils with an unpleasant rancid odor, and the higher ones are solid crystalline substances that are practically odorless.
Only formic acid (see), acetic acid (see) and propionic acid are mixed with water in all respects; in higher members of the liquid acid series, the solubility quickly decreases and finally becomes equal to zero. J. compounds are highly soluble in alcohol and ether.
The melting points in the homologous series of liquid crystals increase, but unevenly. Liquid crystals with an even number of C atoms melt at a higher temperature than the following liquid crystals, which have one more C atom (Table 2). In both of these series (with an even and odd number of C atoms), the difference in the melting temperatures of two successive members gradually decreases.
This peculiar difference between liquid compounds with an even and odd number of C-atoms in the molecule is manifested not only in the melting points, but to some extent in the chemical properties. and even in their biol, properties. Thus, acids with an even number of C-atoms disintegrate, according to G. Embden, during hemorrhage in the liver to acetone, but acids with an odd number of C-atoms do not decompose.
Liquid crystals are strongly associated and even at temperatures exceeding their boiling point, they show twice the mol. weight than their formula suggests. This association is explained by the occurrence of hydrogen bonds between individual liquid molecules.
Omega-3 and Omega-6 content in fats and oils
| Fats and oils, 100 g | Omega-6, g | Omega-3, g | Omega-3 : Omega-6 |
| Coconut oil | 1,800 | 0 | no Omega-3 |
| Macadamia oil | 2,400 | 0 | no Omega-3 |
| Cocoa butter | 2,800 | 0,100 | 1 : 28 |
| Kuban sunflower oil (oleic acid content 70% and above) | 3,606 | 0,192 | 1 : 19 |
| Palm oil | 9,100 | 0,200 | 1 : 46 |
| Olive oil | 9,763 | 0,761 | 1 : 13 |
| Hazelnut oil | 10,101 | 0 | no Omega-3 |
| Avocado oil | 12,531 | 0,957 | 1 : 13 |
| Flaxseed oil | 12,701 | 53,300 | 1 : 0,2 |
| Rapeseed oil | 14,503 | 9,137 | 1 : 1,8 |
| Saffron oil (high oleic acid) | 14,350 | 0 | no Omega-3 |
| Mustard oil | 15,332 | 5,900 | 1 : 2,6 |
| Almond oil | 17,401 | 0 | no Omega-3 |
| Peanut butter | 31,711 | 0 | no Omega-3 |
| Rice bran oil | 33,402 | 1,600 | 1 : 21 |
| Sesame oil | 41,304 | 0,300 | 1 : 137 |
| Soybean oil | 50,293 | 7,033 | 1 : 7 |
| Cottonseed oil | 51,503 | 0,200 | 1 : 257 |
| Walnut oil | 52,894 | 10,401 | 1 : 5 |
| Corn oil | 53,510 | 1,161 | 1 : 46 |
| Wheat germ oil | 54,797 | 6,901 | 1 : 8 |
| Sunflower oil (regular) | 65,702 | 0 | no Omega-3 |
| Grape seed oil | 69,591 | 0,100 | 1 : 696 |
| Saffron oil (regular) | 74,615 | 0 | no Omega-3 |
Table 3
Omega-3 and Omega-6 content in nuts and seeds
| Product (portion 28g) | Omega-3 ALA (g) | Omega-6 (g) | Omega-3 : Omega-6 |
| Almond | 0 | 0.5 | no Omega-3 |
| Walnuts | 2.6 | 10.8 | 1 : 4 |
| Flax seedsChia seeds | 1.84.9 | 0.41.6 | 1 : 0.221 : 0.33 |
| Pecans | 0.3 | 6.4 | 1 : 21 |
| Pistachios | 0.1 | 3.9 | 1 : 39 |
| Pumpkin seedsSunflower seeds | 0.10 | 5.410.4 | 1 : 54no Omega-3 |
| Sesame | 0.1 | 6.7 | 1 : 67 |
Table 4
Omega-3 and Omega-6 content in green leafy vegetables
| The product's name | A portion | Omega-3 ALA (g) | Omega-6 (g) | Omega-3 : Omega-6 |
| Spinach (cooked) | 1/2 cup | 0.1 | Footprints | 1 : 0 |
| Fresh green salad leaves | 1 glass | Footprints | Footprints | 1 : 0,5 |
| Fresh red lettuce leaves | 1 glass | Footprints | Footprints | 1 : 1,5 |
| Fresh Boston salad | 1 glass | Footprints | Footprints | 1 : 1,5 |
| Stewed chard leaves | 1/2 cup | 0.0 | Footprints | no Omega-3 |
| Turnip leaves, steamed | 1/2 cup | Footprints | Footprints | 1 : 0,5 |
| Dandelion leaves, steamed | 1/2 cup | 0.1 | Footprints | 1 : 0,8 |
| Cale, lethargic | 1/2 cup | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.: 0,9 |
| Poached beet tops | 1/2 cup | Footprints | Footprints | 1 : 4 |
| Collard kale, stewed | 1/2 cup | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1 : 0,8 |
| Mustard leaves, steamed | 1/2 cup | Footprints | Footprints | 1 : 0,5 |
How do different types of Omega-3 fish oil compare?
Because there is controversy over water contamination with toxins and contaminants like mercury, many people find it difficult to get enough omega-3s from eating fish alone. This is one reason why some people prefer fish oil supplements to complement Omega-3 products.
The difference between "fish oil" and "cod liver oil" can be confusing. Fish oil and cod liver oil are actually two different oils, although they are similar on a molecular level and both are extracted in the same way. The reason they are different lies in their sources: fish oil is extracted from tuna, herring, cod or other deep sea fish. Cod liver oil is extracted only from the liver of this fish.
How do they compare nutritionally? Fish oil is a huge source of Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, but it does not have enough vitamin A or D. Cod liver oil, on the other hand, has much lower levels of Omega-3, but very high levels of vitamins A and D.
According to some sources, cod liver oil contains about 8% EPA and 10% DHA, much less than fish oil, which has about 18% EPA and 12% DHA.
Because of its concentration of vitamins, cod liver oil has traditionally been given to young children since the 1960s because it helps the brain function and develop properly. Since many people today suffer from vitamin D deficiency, cod liver oil has come back into fashion. Many people who take cod liver oil rely on it during the winter, when they spend less time outdoors, to keep their vitamin D levels high.
What is the best type of fish oil if you want to supplement your diet? I believe the best form of Omega-3 in fish oil contains astaxanthin (a powerful antioxidant that also helps stabilize fish oil), so I would choose wild Pacific salmon fish oil, which has high levels of DHA/EPA and astaxanthin.
How to properly consume fatty acids?
- Season fresh salads with vegetable oils - when frying, they lose their beneficial properties.
- Do not store oils in the light, or even better, find a dark container for them.
- When purchasing, give preference to raw rather than frozen fish.
- Pay attention to walnuts - several kernels contain the daily requirement of fatty acids.
If you approach the preparation of your diet thoroughly, the fatty acids contained in the food will be enough to provide the entire body with them. A child needs one and a half to two times less polyunsaturated acids than an adult, it is also important not to forget about this.
Ideas for cooking with Omega-3 products
Salmon pies recipe
Cooking time: 15 minutes
Servings: 1-2
INGREDIENTS:
- 1 can Alaskan salmon
- 2 eggs
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- ¼ onion, chopped
- ¼ package Mary's Gone crackers, crumbled
PREPARATION:
Place all ingredients in a bowl and stir. Form the pies. Fry each side for five minutes.
Spicy baked fish recipe
Cooking time: 40 minutes
Number of servings:6
INGREDIENTS:
- 6 white fish fillets, such as mahi-mahi, sea bass, or golden snapper
- sea salt and black pepper to taste
- garlic clove, finely chopped
- 1/2 cup finely chopped onion
- 3 tablespoons coconut oil
- 1 tablespoon onion powder
- 1 tablespoon lemon pepper
- 1/2 teaspoon paprika seasoning
- 1 can (8 ounces) roasted tomatoes, diced
- 4 tablespoons parsley
- 1 tablespoon apple cider vinegar
- 3 tablespoons grated raw cheese
- 3 tablespoons almond flour
PREPARATION:
- Preheat oven to 350 degrees.
- Sauté the onion and garlic in a small skillet in coconut oil over medium-low heat until the onion is translucent and soft.
- Grind the fried tomatoes in a blender.
- Add the garlic/onion mixture to the blender with the tomatoes and other herbs.
- Place the fish in a baking tray coated with coconut oil.
- Generously pour the tomato sauce over the fish.
- In a small bowl, combine flour and cheese.
- Sprinkle the fish with the cheese mixture and bake for about 30 minutes.
Oatmeal with chia seeds
Cooking time: 15-20 minutes
Number of servings:2
INGREDIENTS:
- 2/3 cup oatmeal
- 2 cups coconut milk
- 1/2 teaspoon vanilla extract
- 1/2 cup pumpkin puree
- 1/2 tablespoon chia seeds
- a pinch of salt
- 1/2 teaspoon cinnamon
- 1/4 teaspoon ginger
- 1/8 teaspoon nutmeg
PREPARATION:
- In a small saucepan, bring the oats and coconut milk to a boil.
- Reduce heat to low and add pumpkin puree and chia seeds.
- Cook over low heat for 5-7 minutes.
- Add the remaining spices, stirring regularly.
- Cook over low heat for another 5-7 minutes.
Are there side effects from eating Omega-3 foods?
Omega-3s are considered safe and effective when taken up to 20 grams at a time, but some people experience mild side effects when taking omega-3 fish oil supplements. Some side effects that may occur from taking fish oil include:
- "Fishy burps" or a fishy taste in the mouth (this is by far the biggest complaint, but it shouldn't happen if you're taking a high-quality supplement)
- Stomach pain or nausea
- Problems going to the toilet (diarrhea)
- Risks of excessive bleeding if you take more than 3 mg Omega-3 per day
- Allergic reactions
- Changes in blood sugar (or complications from diabetes medications)
Although most people do not experience any side effects when they eat plenty of Omega-3 foods and take supplements daily, talk to your doctor about side effects you experience when taking larger doses than recommended. The only thing you need to remember is that you should not take omega-3 fish oil supplements if you are allergic to most types of fish, as there is a high risk of a serious reaction.
Source
The effect of Omega-3 acids on cholesterol levels
Omega-3 is a group of essential fatty acids. Their synthesis in the body is not possible, which is why they are called “essential”.
Depending on the number of double bonds between carbon atoms, PUFAs are divided into two types:
- Monounsaturated – one bond;
- Polyunsaturated – two or more bonds.
Omega is a polyunsaturated acid.
The most important acids included in the composition:
- Alpha-linolenic (ALA). Main source: vegetable oils;
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). A small amount is found in plant foods;
- Docosopentaenoic acid (DPA). Can be transformed into any of the forms;
- Docosohexaenoic acid (DHA). Contained in the fat of sea fish and shrimp.
A study on the prevention of cardiovascular disease conducted in Japan included 18,645 patients. Before the start of the experiment, tests were taken to measure cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. The interpretation of the tests showed a value of 7.1 mmol/l and 1.7 mmol/l - triglycerides.
People were divided into 2 groups and given for 5 years:
- one subgroup of omega-3 600 mg 3 times a day in combination with statins in the amount of 5-10 g 1 time a day;
- the second part of the people took only statins.
By the end of the study, it was found that patients in the first group had a 24% reduction in the risk of angina pectoris. In both groups, total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels decreased by 19% and 25%, and in the first group triglycerides decreased by 9%, while in the second group only by 4%.
The study shows that taking Omega-3 with high cholesterol in conjunction with statins reduces the amount of triglycerides and LDL. If their content in the body is increased, this can lead to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and the development of atherosclerosis.
Sedimentation of atherogenic fractions of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels, which is prevented by regular consumption of Omega-3.
Regular consumption of foods or medications containing Omega-3 acids has a positive effect on the body:
- The number of high density lipoproteins increases. They help remove fat deposits from the walls of blood vessels, transfer them to liver cells - hepatocytes for conversion into bile acid and subsequent removal from the body.
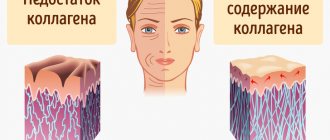
- The collagen structure is restored.
- Inflammation processes in the body are reduced.
- Unsaturated acids are involved in the construction of cell membranes.
- Blood sugar levels are regulated.
- Acids help to quickly cope with skin diseases.
PUFAs are also involved in the synthesis of the hormone serotonin, which is called the hormone of happiness. During pregnancy, the risk of toxicosis and miscarriage is reduced.