Types of exercises and technique
Here we come to the most interesting part! Here I will talk about the main and effective exercises for pumping up your arms. They are divided into 2 groups: basic and insulating.
Basic
Basic exercises are our everything! They provide a heavy load, use several muscles and form the basis of the workout.
To the delta
- Barbell Chest Press
I.p.: sitting on a bench, feet resting on the floor, bar lying on the chest, grip shoulder-width apart.
Squeeze the barbell upward until your arms are fully straightened. Do not lean your body forward or backward; your arms and torso remain perpendicular to the floor.
- Barbell row to the chin
IP: standing, grip slightly narrower than shoulder width.
Bend your elbows and pull the barbell up. Your goal is to raise your shoulders parallel to the floor.

Tip: If you feel discomfort in your wrists, use a curved barbell.
For biceps
- Barbell curls (picture on the left)
IP: feet shoulder-width apart, elbows pressed to the body and slightly forward.
Raise the barbell up without lifting your elbows from your body. Hold at the top point and take an i.p.
Tip: Don't lift the bar too high, otherwise you will take the tension off your biceps.
- Reverse close grip pull-ups (picture on the right)
IP: grip slightly narrower than shoulders, palms facing yourself. Elbows pressed to the body.
Try to make the movement come from your hands; do not help yourself with your whole body, otherwise the load will be redistributed.

For triceps
- Dips
Keep your body absolutely straight. Don't lean forward. At the top point, fully straighten your arms.
Tip: If your gym has V-shaped bars, use a narrow grip.

- Close grip bench press
IP: lying on a bench, legs bent at the knees and resting on the floor. The lower back is arched. The grip is closed, shoulder-width apart or narrower. Arms are straightened, palms facing away.
As you inhale, slowly lower the barbell to your lower chest. With effort, return to the rep position, squeezing the barbell upward.

Tip: do not move your elbows away from your body, otherwise the load will transfer to the pectoral muscles.
Insulating
Isolation exercises are aimed at working one specific muscle. They form the desired relief and polish the result.
On the shoulders (delta)
- Dumbbell flyes in a standing position (picture on the left)
IP: standing, arms with dumbbells slightly bent at the elbows. Stretch your arms out to the sides so that they are parallel to the floor. Elbows tend to the ceiling, turn your hands so that at the top point the little finger is higher than the thumb.
- Arnold press (picture on the right)
IP: sitting. Bend your elbows, hold the dumbbells at your neck, palms facing you.

Press the dumbbells upward, rotating your arms so that your palms are facing away from you at the highest point.
- Dumbbell flyes lying on an incline bench face down
The technique is the same as the standing fly, only this time you are lying on. Extend your arms out to your sides until they are parallel to the floor. Do not throw your arms down, maintain tension until the end of the approach.
- Raising dumbbells in front of you
I.p. standing, hands with dumbbells are lowered along the surface of the thigh. Grab with your palms facing you.
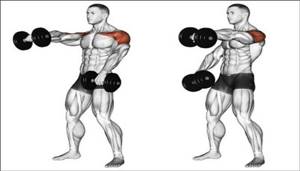
Lift one dumbbell at a time until your arm is parallel to the floor. The movement is carried out by the muscle, try not to jerk or help yourself with your body.
For biceps
- Scott Bench Curl
IP: fix your hands so that they rest firmly on the bench. Take the barbell with a narrow grip.
As you exhale, lift the barbell up, hold for 2-3 seconds, and smoothly lower the barbell down.
Advice: do not jerk, concentrate on the execution technique.
- Upper pulley to chest
Usually this exercise is used to work the back, but by changing the technique, we can transfer the load to the biceps.
IP: sit on the block bench and straighten your body, do not lean back. The grip is slightly narrower than the shoulders, the cable should look down at mid-thigh level.

As you exhale, pull the cable down and toward you, bending your elbows. Slowly return to i.p.
Tip: in this exercise the moment of returning to the i.p. is more important than traction, so it is important not to drop the line.
- Curling your arms on a block
I.p.: grab the cable of the lower block, straighten up and press your elbows to the body.
As you exhale, pull the cable toward you and toward your chest, bending your elbows.
Tip: Do this exercise at the end of your workout. It requires a large number of repetitions and therefore “clogs your hands.”
For triceps
- French bench press (picture on the left)
IP: lying on a bench, legs bent at the knees and resting on the floor. The grip is slightly narrower than shoulder width, the arms are straightened and slightly tilted from the vertical towards the head.
As you inhale, bend your arms and smoothly release the barbell towards your head. As you exhale, return to i. P.

- French press sitting or standing (picture on the right)
IP: standing or sitting. The grip is narrow, the bar is extended above the head.
Lower the barbell behind your head while holding the weight in your hands. Do not place the projectile on your shoulders.
Tip: you can replace the barbell with a dumbbell, lift it with both hands or with one hand alternately.
- Extension of arms on a block
IP: straight grip, narrower than shoulder width. Press your arms towards your body. Legs slightly bent.
As you exhale, pull the cable down, straightening your arms; as you inhale, bend your elbows.
Tip: watch the amplitude, the larger it is, the greater the load on the triceps
Examples of training programs
These programs are a template for what arm training might look like. But it is worth understanding that for each person, this or that exercise can give a different effect. Therefore, training should be tailored to the athlete individually, using trial and error. But if it’s still difficult for you to do this, then you can safely take these examples and train on them.
Hand training for beginners
We are talking about athletes who are just starting their training journey. The main task for them is to master the technique and gain muscle mass. Therefore, they do not need to perform separate exercises for the arm muscles. We will already work our biceps and triceps by performing heavy basic movements. But after a month or two, you can add one exercise for each muscle group. The workout will look like this:

Chest + triceps
- Warm up 5 minutes
- Exercises for the pectoral muscles
- Dips (if difficult, then reverse push-ups) 3 sets of 8-10 reps. In this case, the first approach should be a warm-up.
- Stretching and calming exercises for 5-10 minutes.
Example workout
Let's now put together a complex for the hands to understand how it will look in the gym.
Training for beginners
- Barbell curls - 3 sets (15, 12, 12).
- Scott Bench Curl – 3 sets (15, 12, 12).
- Dumbbell curls - 2 sets (12, 12).
Advice: don’t try to take on a lot of weight right away. During dumbbell curls, perform the first set of simultaneous curls of both arms, and the second of alternating ones.
Mass training
- Barbell curls - 4 sets (8, 8, 10, 10).
- Dumbbell curls on a Scott bench alternately - 3 sets (8, 8, 10).
- Dumbbell flyes lying on an inclined bench face down - 3 sets (12, 12, 15).
- French press sitting or standing - 3 sets (10, 10, 12).
- Bending arms on the lower block - 3 sets (10, 10, 12).
Tip: Use the reverse pyramid method, gradually reducing the working weight with each approach. Short intervals between sets are necessary for muscle growth. Rest of 30 seconds is the best option.

You can train your arms quite often, as the muscles here recover quickly. To maintain tone, one workout per week is also suitable, and if you are focused on active arm growth, two workouts per week (once every 3-4 days).
Attention! Don't discount warming up before exercise and stretching after. This will prevent you from injuries and discomfort in the gym.
Bodymaster.ru recommends Fitness Trainers:
If your arms are your weak point, you can train them once a week, or set aside a separate day for training them.
- The workout should not last more than an hour. This time is enough to completely work out the target body part. If you exercise longer, it means you should be less distracted during your workout.
- Keep the intensity high by shortening the rest between sets, performing supersets, negatives and drop sets. After training, you should feel tired in your arms.
- Set specific goals.
- Use safe weights.
It should also be taken into account that the arm muscles are small and work mainly through isolation movements, which do not increase their size due to the limitation of working weight.

Give your arms secondary load with a variety of compound movements. Incorporate a variety of isolation exercises to prevent adaptation and keep the intensity high.
Warm-up for arms
You can always include the following exercises without changing your current workout. To work the biceps, focus on the biceps muscle: perform rowing exercises and pull-ups supinated, i.e. reverse grip (wrist turned towards the face). To put it simply, pull-ups can be done in a gravitron or with rubber loops, or replaced with pull-ups to a barbell with a reverse grip.
Exercise "Rowing"

Reverse grip pull-ups

Pull-ups

Common mistakes in arm training
- Race for record weight
First, it can cause serious injury. Secondly, if the weight is too heavy, the exercise technique is disrupted, and as a result, you will not get the desired result. Thirdly, some exercises with light weights can significantly work the muscle due to a wide range of motion.
- One grip, one hand placement
Experiment with grip and positioning, so over time you will work all the muscles in your arms, which will have a positive effect on your appearance.

- Low intensity - long duration
I often notice people in the gym who work out for an hour, or even more, without putting much strain on themselves. In fact, short, intense workouts are much more effective.
- Lack of diversity
Muscles respond best to different types of load. Make sure your program is not too bland and, if necessary, add exercises that were previously neglected.
Sports nutrition
Sports nutrition will help speed up the process of gaining high-quality muscle mass: proteins, BCAA, vitamins and glutamine, as well as creatine for better results. These supplements are specially designed for athletes and fitness-active people of different fitness levels. Such drugs are completely safe, and their effectiveness has already been proven.
| BCAAs | Allows muscle fibers to recover faster and provides building material for the growth of lean muscle mass. |
| Creatine | Participates in energy metabolism in muscle and nerve cells. Widely used to increase strength, muscle mass and short-term anaerobic endurance. |
| Vitamin-mineral complex | During intense physical activity, vitamins and minerals are consumed by the body faster. They are also responsible for protein synthesis and are the engine of metabolic processes. |
| Glutamine | An essential amino acid that is part of protein and is necessary for muscle growth and support of the immune system. |
Warm-up and stretching
Attention! Don't discount warming up before exercise and stretching after. This will prevent you from injuries, sprains and discomfort in the gym.
Warm-up
Warm-up is needed to warm up your joints and muscles.
- Start with the neck - careful turns and tilts of the head forward, backward, left and right.
- Then roll your shoulders back and forth.
- Move to the elbow joint, making circular movements with your forearms.
- Twist your brushes clockwise and counterclockwise.
- Rotations of the pelvis, legs, knees and feet will prepare the lower body for the workout.
- Finish by spending 8-10 minutes on the treadmill or elliptical machine. Keep it at an easy pace.
Stretching
Stretching is the key to a successful workout. She logically completes the set of exercises. It is especially important to stretch for girls and women; it allows them to develop flexibility and achieve beautiful shapes.
Let's look at the main rules of stretching:
- You need to pull the muscles smoothly, gradually, without sudden movements or excessive pressure.
- A little pain in the stretched muscle is acceptable, but sharp pain is a signal to stop stretching immediately.
- Each pose must be held for 20-30 seconds.
- Don't forget to breathe deeply and freely, muscles need oxygen.
- Focus on the muscle group you just trained.
- The result will not be visible immediately, please be patient. Soon you will notice how you become more flexible and flexible.
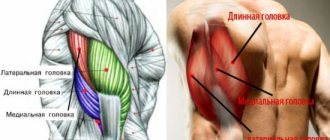
Biceps
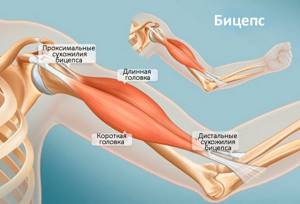
Biceps brachii
- Tendons connect the biceps muscles to the arm bones.
- The biceps brachii muscle consists of two heads: long and short.
- The long head is on the outside of the arm and makes up the majority of the biceps brachii muscle.
- The short head is on the inside of the arm.
- Forms the overall size of what is called the biceps. Most exercises are aimed at causing hypertrophy of this muscle.
Brachialis muscle
- Located deeper than the biceps brachii muscle.
- This muscle does not play a major role in functional movements, helping the biceps brachii muscle to flex the arm at the elbow joint.
- Even though the brachialis muscle is not a significant part of the arm, it is still important in balancing muscle size. By adding exercises aimed at this muscle to your arm training program, you can further increase the volume of your arms, getting a more holistic and harmonious picture. Your arms will look as strong as those of professional bodybuilders.
Triceps
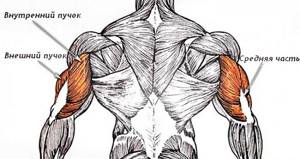
Triceps brachii
- Consists of two sections or heads that form the famous horseshoe shape and make up the entire back of the arm.
- An important muscle for stabilizing the shoulder joint.
- The triceps makes up one third of the total arm size. If you want to build massive arms, then you should pay attention to exercises that cause maximum triceps hypertrophy.
- Undertraining the triceps can lead to overuse of other muscles, increasing the risk of muscle strains and tears. It is very important to train the triceps with the same frequency and load as the biceps.