One of the two main components of milk, whey, is made from the liquid part of milk that is separated from the curds (the second main component) during the cheese making process. Whey contains proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals.
Because it is rich in amino acids and easy to digest, whey is perhaps the most popular sports nutritional supplement. Whey protein has been scientifically shown to be essential for accelerating muscle protein synthesis, sustainably burning fat, and strengthening the immune system. Also, whey improves insulin sensitivity and significantly reduces appetite. In addition, whey protein concentrate accelerates the production of glutathione, our bodies' No. 1 antioxidant.
Types and differences of whey proteins
There are several types of whey protein: concentrate, isolate and hydrolysate.
They differ in the content of protein, carbohydrates (lactose), biologically active substances, protein form, etc.
These differences are a consequence of different degrees of technological processing of the raw material - milk whey.
Whey is a by-product of the cheese and yogurt making process. It makes up 80-90% of milk volume and contains about 50% of milk's nutrients: protein, lactose, vitamins and minerals.
The protein content of whey is low, so the process of making whey protein begins with its concentration.
Whey must be processed immediately after it is separated during cheese making, as bacteria begin to multiply very quickly in it, destroying protein and producing lactic acid, increasing its concentration 1.
We recommend : Is it possible to eat eggs while losing weight? Which is better: raw, boiled or fried?
1 Whey Protein Concentrate
Whey contains a large amount of water, which, when removed, produces whey concentrate, which has a much higher protein content.
As for other nutrients (fats and carbohydrates (lactose)), their amounts can vary significantly in different types of concentrate (see table below).
Processing occurs at low temperature and low acidity, which helps preserve the biological value of 90-96% of the original protein .
Those. the degree of damage to the protein is very low and almost all of it, when consumed, will be used for its intended purpose and will not be flushed down the toilet.
Please note: the paragraph above does NOT indicate the amount of protein, but its biological value, i.e. how completely it is absorbed. 100% corresponds to complete absorption.
Whey protein concentrate can be obtained even at home by simply evaporating the whey at a low temperature and then drying the dehydrated whey mass. True, the fat and carbohydrate content in it will be higher, and the protein content will be low.
Depending on the degree of concentration, the amount of protein in the concentrate can vary from 35% to 80% of the weight of 1.
Content of other nutrients per 100 g of product (for concentrate with 80% protein, which is most often used in sports nutrition):
- ~4 g fat;
- ~3 g of carbohydrates (the proportion of carbohydrates varies from manufacturer to manufacturer);
- 6-7 g lactose (as opposed to 1 g in whey protein isolate).
If a technology without strong heating is used in production, the concentrate retains beneficial biologically active substances - the same ones that are responsible for the health benefits of whey protein.
For those who are lactose intolerant, it is important to keep in mind that the lactose content in whey protein concentrate can be up to 7%, i.e. its consumption by such people (like whole milk) can cause gastrointestinal disorders.
Whey protein isolate does not have this problem because its lactose content is kept to a minimum.
Share with us your experience of losing weight or gaining muscle mass!
Whey protein concentrate is the cheapest form of this protein, since, unlike isolate and hydrolyzate, it requires fewer production resources during production.
| Differences between different types of whey protein concentrates 1 | ||||
| Type of whey protein concentrate | 35% protein | 50% protein | 65% protein | 80% protein |
| Protein, % | 29.7* | 40.9* | 59.4* | 75.0* |
| Moisture, % | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| Lactose, % | 46.5 | 30.9 | 21.1 | 3.5 |
| Fat, % | 2.1 | 3.7 | 5.6 | 7.2 |
| Lactic acid, % | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 1.2 |
*The difference in the mass fraction of protein in the name of whey protein concentrate and in the composition is explained by the fact that the name reflects the value calculated based on the total nitrogen content in the product (protein): not all the nitrogen in its composition is part of the protein molecules.
The main difference between whey protein concentrate compared to isolate and hydrolyzate is a smaller amount of protein, lower price and preservation of biologically active substances beneficial to health.
We recommend : Casein or Cottage Cheese? When is the best time to eat cottage cheese for weight loss and muscle gain? Is it possible for the night?
2 Whey protein isolate: differences from concentrate
Whey protein isolate has gained particular popularity in bodybuilding due to its high concentration of protein and low concentration of fats and carbohydrates, which are considered undesirable.
Whey protein isolate has a significantly higher protein concentration of all types of whey proteins - over 90%.
The content of lactose, fat (0.4% compared to 7% in concentrate) and cholesterol is significantly lower than in concentrate.
There are two technologies for producing whey protein isolate: ultrafiltration and ion exchange.
Both produce a powder with very good consumer qualities: solubility, foaming, formation of emulsions and gels, and are pleasant to the taste.
However, in terms of beneficial properties, the isolates obtained using these two technologies differ.
Using ultrafiltration technology, in which the whey is not heated or chemically treated, the isolate retains important bioactive components that enhance immune function and provide other health benefits.
Ion exchange technology, on the contrary, destroys almost completely biologically active fractions .
Also, a large proportion of the protein becomes unusable , which reduces its effectiveness for gaining mass.
Isolate has a significantly higher concentration of BCAA amino acids compared to concentrate. These amino acids play a critical role in creating muscle fibers, restoring them after exercise, and protecting them from breakdown.
If you think what we do is important, support our project!
YES!
The rate of digestion and absorption of whey protein isolate is the same as that of concentrate.
Whey protein isolate, in contrast to concentrate, has a significantly higher protein content, less lactose, fewer biologically active substances, and in some of its varieties, a higher relative proportion of damaged protein. It also costs more
We recommend : The benefits and harms of milk: expert reviews
3 Distinctive properties of whey protein hydrolyzate
The protein molecules in whey protein hydrolyzate are pre-broken into chains of several amino acids, eliminating the need for digestion. Therefore, its absorption rate is even higher than that of concentrate and isolate .
It is often recommended for use immediately AFTER and DURING bodybuilding training - when the body's need for nutrients is maximum.
Scientific research supports the superior muscle-building benefits of whey protein hydrolyzate when taken during and after exercise.
This is explained primarily by the faster absorption time and greater availability of amino acids when taken immediately after training.
Hydrolysates are less allergenic compared to non-hydrolyzed types of milk proteins.
One of the disadvantages of hydrolyzed whey protein is the lack of a thermic effect : it requires significantly less energy to digest.
This is one of the properties that makes protein and protein foods in general beneficial for weight loss. Therefore, whey protein hydrolyzate is less beneficial for weight loss than concentrate and isolate.
Also, during hydrolysis due to exposure to high temperature, beneficial protein fractions - biologically active substances - are destroyed.
This type of protein is most often the basis for making protein bars.
Isolates, hydrolysates and other purified forms of proteins tend to be more expensive than concentrates because the technology for making them is more complex.
Whey protein hydrolyzate has the highest absorption rate (~20 min), is less useful for weight loss, contains fewer biologically active substances, and the protein in its composition is often highly damaged
We recommend : Protein bars: benefits and harm. Reviews from doctors and scientists
Regimen and dosage regimen
When consuming protein isolate, you should follow a certain regimen and dosage.
Depending on the purpose of use, the rules of administration will vary:
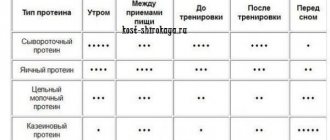
- To build muscle mass, isolate is taken at 2-4 grams per 1 kilogram of weight. For heavy loads, this amount can be increased to 8 grams. It is better to divide the total amount of proteins into several doses during the day. Suitable time for use is in the morning, between meals, 1.5 hours before training and after exercise.
- To lose excess weight, it is enough to take 1-2 grams of isolate per 1 kilogram of weight. The total amount of proteins can be divided into two doses - in the morning and after active physical exercise.
Isolate helps you get the right amount of protein.
When losing weight, isolate helps to quickly saturate the body and reduce the number of calories consumed by reducing fats and carbohydrates in the diet.
But you should not replace the entire daily amount of protein with it. It is important to get at least half of your daily requirement from food.
This applies to athletes who are gaining muscle mass and want to lose excess weight.
Table of differences between different types of whey proteins
| Differences between different types of whey proteins | |||||
| Protein | Carbohydrates (lactose) | Fats | Price | Peculiarities | |
| Whey Protein Concentrate | 35-80% | a lot of | a lot of | low | the most pleasant taste, the highest content of biologically active substances, the proportion of destroyed protein is low |
| Whey Protein Isolate | > 90% | few | few | high | the content of biologically active substances depends on the method of technological processing, suitable for those with lactose intolerance, the proportion of destroyed protein can be high |
| Whey Protein Hydrolyzate | > 90% | few | few | the tallest | fastest absorption time, low content of biologically active substances, suitable for those with lactose intolerance, the proportion of destroyed protein may be high, less useful for weight loss |
Rating of the best brands
Many companies are engaged in the production and sale of sports supplements. It's easy to get confused in such diversity.
To purchase high-quality protein and not waste money, you need to focus on time-tested brands of supplements. It is worth choosing products that have been sold for many years and have positive reviews from athletes.
This isolate is one of the most popular among athletes and those losing weight. It contains only protein and no carbohydrates. A serving of the supplement provides 28 grams of pure protein and only 106 kcal.
Numerous reviews contain positive ratings and evidence of the effectiveness of the product. An additional advantage is the absence of an unpleasant aftertaste.
This is a protein from a French manufacturer.
It is a highly purified product and is used for the production of sports and baby food. The isolate contains 95% protein and 1% carbohydrates.
This isolate is made from whole milk, not whey.
Due to this, high nutritional value is maintained. Thanks to special cleaning, the risk of an allergic reaction is reduced. It can be consumed by people with lactose intolerance.
Syntrax Nectar
This isolate is loved by many customers for its variety of flavors.

At the same time, its tastes are pleasant and do not give off excessive chemicals or a metallic aftertaste. Each serving of the supplement contains 24 grams of protein and a minimum of fat and carbohydrates.
Be sure to read:
Isotonics: what is it, what is it for, the best companies, how to take it, how to make it yourself
Many reviews indicate strong foaming and poor solubility as disadvantages. But these two characteristics are signs of the quality of a good protein.
This is a popular brand of sports supplements. You can find many positive reviews about this isolate; it is sold in all sports nutrition stores.
It contains a mixture of isolate and concentrate, and the amount of fat and carbohydrates is reduced to a minimum. The line of flavors is represented by 22 variants of different combinations, as well as 3 natural additives without sweeteners.
Among the advantages, consumers note good solubility without lumps, even in a regular bottle.
Zero Carb by VPX
In the production of this isolate, cross-flow filtration is used, which ensures a high quality product without a single gram of fats and carbohydrates.
The powder contains 20 grams of protein per serving. Several flavor options help diversify your diet.
Rice protein
This protein powder is made by grinding brown rice into a fine powder and adding enzymes to break down and separate the carbohydrates and fiber from the protein portion of the whole grain, which is then filtered. Most rice proteins provide about 90% protein. Rice protein is fast digesting, rich in branched chain amino acids and contains more arginine than whey, casein, eggs or soy.
Recommended intake time: Rice protein is recommended to be taken before and after workouts. It normalizes the arginine content in whey shakes and is also suitable for vegetarian bodybuilders. Optimal protein mixes combine the muscle-building effects of whey and casein and the muscle-restoring effects of soy protein.
Harm and side effects
Taking protein supplements helps improve body condition and increase muscle mass. But their uncontrolled use can have side effects and even harm health.

Taking protein supplements helps improve body condition and increase muscle mass
Supplements cannot completely replace all meals.
If overused, the following complications may occur:
- Impaired kidney and liver function. An athlete needs about 2 grams of protein per 1 kilogram of weight per day. When consuming a large amount of isolate, this norm is exceeded. As a result, the load on the excretory system and disruption of the kidneys and liver increases.
- Lack of nutrients. Although proteins are rich in minerals and amino acids, they cannot fully provide the body with all the necessary substances. As a result, a deficiency of substances occurs and disruption of the functioning of the entire body.
- Toxin poisoning. Some additives contain traces of hazardous substances (mercury, lead, cadmium, etc.). Their volume is very small and with moderate protein consumption they do not have a negative effect on the body. But if they are consumed excessively, poisoning occurs.
Compliance with dosages and rules for taking isolate helps to avoid such complications.
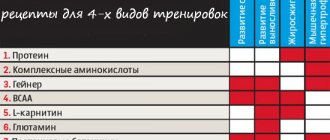
Fast protein[edit | edit code]
Fast protein
is a protein with a high absorption rate from the gastrointestinal tract. Fast proteins include whey proteins - concentrate, isolate and hydrolysate with the highest absorption rate; meat and fish proteins are also classified as fast proteins, but they are used extremely rarely. Fast protein is ideal for gaining muscle mass, as it quickly creates a high concentration of amino acids in the blood and muscles, which is especially important after training, and also provokes the secretion of the anabolic hormone insulin. For maximum effect, it is recommended to combine with BCAA.