Chemical composition of oil
The main component of natural butter is milk fat. When churning the butter, the fat droplets join together, and the plasma of the original, more liquid emulsion (cream) is released in the form of whey.
The oil contains the following nutrients:
- vitamin A (50–65% of the daily value for an adult in 100 g of product);
- vitamin D3 (13% of normal);
- vitamins E and K (6–7% of normal);
- cholesterol (170 mg).
The calorie content of the product is 570 kcal, 662 kcal or 750 kcal per 100 g, and the fat content is 62.5%, 72.5% or 82.5%, respectively. In ghee the proportion of milk fat is about 99%.
From a chemical point of view

p, blockquote 3,0,0,0,0 –>
Butter is a water-in-fat emulsion. Formed during whipping cream, when droplets of milk fat join together, pushing away excess plasma - “throwing away whey.” The resulting product contains almost no protein (0.5 g per 100 g) and carbohydrates (0.8 g), but it contains 82.5 g of fat (or 72.5 g, in “peasant” butter). Therefore, it can be safely consumed by people both allergic to cow’s milk proteins and those with lactase deficiency.
p, blockquote 4,0,0,0,0 –>
The calorie content of butter is 748 kcal per 100 g, and therefore at a time when the nutritional value of any product was determined primarily by the number of calories, it was considered a very healthy product. Then the compass needle turned in the opposite direction, calories became the enemy, cholesterol was declared the cause of all cardiovascular ills, and as a result, a healthy and tasty product acquired a bad reputation for a long time.
p, blockquote 5,0,0,0,0 –>
Fortunately, medicine is constantly evolving, and the value of butter is not determined by calories alone.
p, blockquote 6,0,1,0,0 –>
p, blockquote 7,0,0,0,0 –>
Beneficial features
Butter has the following beneficial properties:
- Saturates the body with retinol (vitamin A) and increases its absorption from other products. Retinol is necessary for the normal function of the hematopoietic system, the health of the eyes, skin and other organs. 100 g of oil contains more than half the daily requirement of vitamin A, but few people who are losing weight consume it in such quantities. A more important property is its ability to increase the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins from lower-calorie sources (tomatoes, carrots, peppers, etc.). In the absence of fats, vegetables containing beta-carotene significantly lose their usefulness.
- Ensures the absorption of vitamin D3 and participates in its metabolism. From a nutritional point of view, low-fat dairy products are less beneficial for the body than low-fat dairy products. This is due to the fact that calciferol (vitamin D3) is well absorbed in the presence of milk lipids. The starting material for endogenous D3, which is formed in the body when exposed to ultraviolet radiation, is cholesterol, which is found in animal fats. Calciferol is responsible for the health of teeth and bone tissue, normal gene expression and immune function.
- Normalizes the function of the gastrointestinal tract, softens the mucous membrane of the inflamed stomach and intestines. The enveloping properties of the oil are useful for gastrointestinal ulcers, gastritis and intestinal inflammation. Fat-soluble vitamins supplied with oil stimulate the regeneration of damaged mucous membranes and relieve minor inflammation.
- Promotes normal production of sex hormones. Sex hormones (estrogens, testosterone), like vitamin D3, are synthesized on the basis of cholesterol. They are responsible not only for sexual function, but also for the health of skin and bone tissue, psycho-emotional state, endurance and level of physical activity. This means that low-fat diets often lead to lethargy, depression, menstrual irregularities, decreased libido, skin inflammation and other complications.
- Provides long-term satiety and high performance. The oil is rich in saturated fatty acids, which are a good source of energy. 1 g of milk fat gives the body 9.1 kcal, so porridge or a sandwich with a small piece of butter will be a healthy and satisfying breakfast.
- Stimulates the immune system. Low-density lipoproteins, which serve to deliver cholesterol into cells, play an important role in stimulating the immune response and antibody synthesis. Lauric acid, contained in butter and cream, reduces the likelihood of the spread of fungal infection and the development of generalized candidiasis. According to some data, a number of saturated fatty acids contained in this dairy product have an antitumor effect and reduce the likelihood of the formation of secondary cancer foci (metastases).
- Improves cognitive functions. Brain tissue is the most cholesterol-rich structure in the body. This substance is used to synthesize new cells of the central nervous system, maintain the integrity of myelin sheaths and create connections between brain cells. Lack of cholesterol causes mood disorders, deterioration of concentration and memory, and decreased speed of thinking. The work of brain tissue is also stimulated by unsaturated arachidonic acid, which enters the body with oil.
- Relieves pain. To soften and heal the inflamed mucous membrane of the throat during a cold, a drink made from milk, honey and butter is used. The fatty emulsion is not beneficial for those losing weight, but it effectively lubricates the throat and reduces pain.
The butter contains virtually no milk sugar or protein, so it can be added to the diet of people who are allergic to casein (cow's milk protein) and lactose intolerant.
What foods contain trans fats?
At home, the main source of trans fats is margarine. But that's not the worst thing. Margarine is easy to avoid.
The worst thing is that the food industry runs on trans fats. So the answer to the question “where are those terrible trans fats?” will sound like this: wherever possible. They are easy to find in any industrially prepared product. It could be cookies, or sausage, ketchup or a frozen casserole.
Therefore, if you want to protect yourself from the toxic effects of trans fats, you should not only eliminate margarine from your diet, but also forget about all prepared foods, from frozen dough to sausages.
Oil damage
A natural product can only be considered harmful to health if the recommended intake is regularly exceeded. Depending on the state of a person’s health, this norm can range from 10–15 g (for gastrointestinal dysfunction, excess weight, high cholesterol) to 35–40 g (for healthy people) per day.
The benefits and harms of oil depend on its composition. You should stop using the product if one or more of the following signs are present:
- the presence of hydrogenated vegetable or palm oil;
- absence of a list of ingredients on the packaging or indication that the product has been reconstituted;
- violations of the oil structure (presence of lumps, foreign inclusions, etc.);
- the smell of margarine.
Use is strictly limited or excluded for the following indications:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which are responsible for the digestion of fats (pancreatitis, cholecystitis, hepatitis);
- acute disorders of cerebral and cardiac circulation (heart attack, stroke);
- atherosclerosis;
- obesity;
- hormone-dependent tumors of the genitals and other organs.
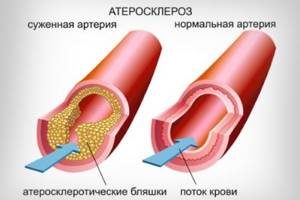
In these cases, regularly consuming full-fat dairy products may increase the risk of complications or relapse of the disease.
Vegetable fats are more dangerous than trans fats
Spenders are terrible. However, regular vegetable oils can be even worse. In this case, the drama of the situation also lies in the fact that, unlike trans fats, the harm of which is widely known, vegetable oils are an enemy whose existence few people realize, and therefore do not think about defending against.
Of course, what has been said does not apply to all vegetable fats without exception, and you can always answer the question of which vegetable oil is the healthiest. Everything is determined by its composition, and the influence of this composition on the human body.
Is it possible to use butter on a diet?
Limiting the amount of fat is the easiest way to significantly reduce your overall caloric intake. Reducing lipid levels by 10 g reduces the nutritional value of food by 91 kcal, while the same restriction of carbohydrates provides only -40 kcal.
Daily fat intake during the diet is 30–50 g, depending on the initial and desired weight, body type, chosen method of losing weight and other factors. The share of saturated fatty acids from animal products should be about 40% of this norm.
Eating eggs and natural butter is one of the healthiest ways to ensure you get enough saturated fat because... dietary meat and dairy products have a minimal percentage of fat content.
The complete exclusion of dairy butter from the diet is typical for vegetarian, vegetable and fruit diets, low-fat diets, mono-diets and other express weight loss methods. It is not advisable to follow them for longer than a week, because... A lack of essential nutrients and cholesterol negatively affects the health and well-being of those losing weight.
The principles of balanced diets and proper nutrition allow for the regular consumption of butter from cream, provided that a quality product is chosen and the daily norm is observed.
In some exotic weight loss methods, oil is used as one of the necessary components of the menu. These include the Berlin diet and the bulletproof coffee diet - coffee with butter.

Daily limit
How much oil should you consume per day? Forty grams of cream per day is enough, relative to vegetable - the numbers can be double, or even triple. This quantity is the required minimum.
Everyone knows that both butter and vegetable oil contain a large concentration of fats in their pure form. And when getting rid of excess fat reserves, that is, when losing weight, it seems logical to many to exclude this product from consumption at least for the duration of the diet.
But in fact, everything turns out to be not so simple, so you must adhere to the minimum norm recommended by doctors. Based on this, diets are chosen. Since all oils contain beneficial substances, it is unacceptable to completely abandon them for a long time.
More on the topic >> Is it really necessary to eat pearl barley to lose weight? But as?
Basic principles of use
To get maximum benefit from the product without harming your figure, you must adhere to the following principles of its use:
- Include oil in your breakfast or lunch menu. Eating fatty and carbohydrate foods in the morning and afternoon allows you to spend all the calories you receive during the period of increased metabolism. In the evening, those losing weight are advised to limit themselves to low-fat sources of protein and non-starchy vegetables.
- Combine the product with vegetables. It is most useful and advisable to combine full-fat dairy products not with bread, but with red and orange vegetables: this allows you to prolong satiety and increase the digestibility of beta-carotene. The combination of butter with porridge, rye and whole grain bread is also acceptable.
- Follow the daily norm. When limiting fat intake to 40 g, the permissible amount of saturated fatty acids (SFA) is about 16 g. 1 egg, 200 g of chicken breast and a glass of low-fat kefir, which can be included in the menu as dietary sources of protein, contain about 6 g of saturated fat . The remaining 10 g of EFAs are contained in 10–15 g of oil. With a less strict diet or weight maintenance, the amount of product can be increased to 25–35 g per day.
- Avoid products that contain butter and cream. It should be taken into account that junk food (fast food, fatty meat pates, sauces and cream pies) may contain oil as a base or additive. In order not to exceed the daily norm of EFAs, you need to be careful when choosing a menu and consume unhealthy foods only on cheat meal days, if they are included in the diet.
In order not to be deceived by the dietary content of foods and not to exceed the recommended amount of calories (1200–1400 kcal), you should consider the calorie content of the diet and the balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. For this, there are special applications that will show the deficiency or excess of nutrients for a particular menu composition.
From a culinary point of view

p, blockquote 20,0,0,0,0 –>
The norm for butter consumption is 10-30 grams per day.
p, blockquote 21,0,0,0,0 –>
In order for butter to retain all its beneficial properties, it should not be subjected to heat treatment, heating above 140 degrees. That is, you can melt the product, but using it in dough or for frying, from the point of view of health benefits, is completely pointless.
p, blockquote 22,0,0,0,0 –>
Those who want something exotic can try a very popular drink in America: coffee with butter. They are used as a breakfast replacement for those who want to lose weight. The inventor of the drink, while traveling in Tibet, tried traditional Tibetan tea with buffalo butter and decided to transfer it to Western soil. Caffeine gives you energy and speeds up metabolism, while the oil saturates you with energy.
p, blockquote 23,0,0,0,0 –>
To prepare a weight loss drink, pour 1-2 tablespoons (15-30 grams) of butter with freshly brewed (in no case instant!) coffee. Beat well until smooth.
p, blockquote 24,0,0,0,0 –>
Fans of this drink claim that its calorie content is only 122 kcal, and it provides enough energy and a feeling of fullness until lunch. Reviews about the taste are contradictory - from “the most delicious coffee I’ve ever tasted in my entire life” to “terribly disgusting.” Those interested can check: the drink will definitely not do any harm, and, as you know, there is no arguing about tastes.
How to replace butter
There are several healthy alternatives to butter that will allow you to reduce your consumption during the diet. These include:
Avocado guacamole paste saturates with healthy omega fats
- Avocado and herb paste. Avocado contains a large amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which have a choleretic effect, reduce cholesterol in the blood, improve the condition of the skin and hair, and stimulate brain function. To prepare the pasta you will need 1 peeled avocado, 2 boiled eggs or low-fat soft cheese, spices, a little lemon juice and natural yogurt. Avocado paste is suitable for sandwiches and holiday canapés.
- Hummus. Thick puree made from chick peas, sesame paste, olive oil, lemon juice and garlic has a pleasant taste and rich chemical composition. It can be used for breakfast and dietary snacks, combined with vegetables or whole grain bread.
- Ricotta and other soft cream cheeses. Low-fat cream cheese (8–20% fat) is suitable for making sandwiches and dietary variations of popular dishes with butter (for example, chicken Kiev). To prepare low-fat sauces, it is better to use unsweetened yogurt rather than soft cheeses.
- Vegetable oil. Coconut, refined olive and sunflower oils are good substitutes for butter in baked goods (muffins, soft cakes, etc.). Ready-made baked goods are allowed in small quantities for those losing weight: despite the absence of cream, they will have a high calorie and fat content.
- Peanut butter enriched with omega-3 acids. The calorie content of this delicacy is 608 kcal/100 g, and the fat content is 54%. Despite the amount of fat, nut butter is a healthy component of the diet menu. It is rich in plant proteins, B vitamins, vitamins E and K, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, manganese, zinc and copper. A 15 g serving of fortified pasta contains 15-16% of the daily value of omega-3 acids. Whole grain bread or bran toast with a thin layer of peanut butter is a healthy and dietary snack.
- Fruit puree and starch. Vegetarians, raw foodists and those losing weight on strict diets prepare sweets based on fruit puree (for example, banana or apple) and a small amount of starchy jelly, which provides the structure of the finished dish.
What should not be substituted for butter during a diet:
- Cream with a high fat content. Natural cream obtained from farms has a convenient thick consistency and could be a good alternative to butter for a morning sandwich. However, their fat content is 50–60%, so replacement will not be a significant help for those losing weight.
- Mayonnaise. The share of EFAs in mayonnaise is no more than 16–17% of all fats it contains. However, when dieting, it is recommended to completely abandon mayonnaise and sauces based on it: this will reduce the overall fat content and calorie content of the diet.
- Spread and margarine. Products containing hydrogenated vegetable fats should be excluded from the menu, because their consumption is much more dangerous for the cardiovascular system and figure than including butter and cream in the diet. The ban applies to spread-based chocolate butter, instant breakfasts and sweets containing confectionery fat.