Spice as medicine
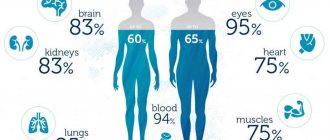
Turmeric contains a huge amount of vitamins and microelements. Therefore, it is used not only in cooking, but also serves as an effective medicine. It has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial properties, improves digestion, accelerates metabolism, removes waste and toxins from the body.
The spice is a natural antioxidant, reduces the risk of cancer and cardiovascular diseases, and is used to treat liver and stomach ulcers.
The spice is actively used in pharmaceuticals and is the basis of many medicines with proven effectiveness.
Beneficial features
Curcumin for the brain
Curcumin is a powerful anti-inflammatory substance that protects against a variety of degenerative diseases. Researchers have found that it can reduce anxiety, depression, stimulate neurite outgrowth, and promote neuroplasticity. []
Curcumin has been shown to increase brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) activity in preclinical studies. It is a vital factor that promotes the growth and strengthening of neural connections necessary for maintaining cognitive skills and memory. []
Helps with depression
Curcumin is believed to treat depression through multiple mechanisms. It is unclear whether one specific mechanism is responsible for the bulk of its antidepressant properties, or whether a mixture of neurophysiological effects contributes to the antidepressant response. Below is a list of possible ways curcumin supplements may improve your mood:
- Increase in BDNF . Research has shown that curcumin increases BDNF levels. Low BDNF causes many neurological disorders, including major depression. And its increase improves mental health, well-being and mood. []
- HPA axis modulation . In depression, there is an increase in the activity of the HPA axis (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal). Curcumin may modulate the HPA axis, thereby normalizing its function and improving symptoms of depression. []
- Neurotransmitter levels . In depression, there are abnormally low levels of serotonin (to the point of depletion), low levels of norepinephrine, and low levels of dopamine (in the prefrontal cortex). Taking curcumin eliminates these deficiencies. []
- Mitochondrial restoration . Mitochondria are like "power plants" in cells and are responsible for producing energy. With depression, their functioning is disrupted. Curcumin repairs mitochondrial damage, thereby correcting the dysfunction. []
- Reduced oxidative and nitrosative stress . Major depressive disorder is associated with abnormally low levels of important vitamins and antioxidants. Many speculate that one cause of depressive symptoms is a lack of antioxidant activity. Curcumin acts as an antioxidant, reducing both oxidative and nitrosative stress. []
Clinical studies have shown that it reduces depressive behavior even in cases of established patterns of depression. For example, 1000 mg of curcumin per day is good for improving mood and helping fight depressive symptoms. It is most effective in people with persistent depression. At the same dose of 1000 mg/day, boosted with bioperine, it reduced anxiety symptoms among obese people with depression and anxiety. There were no side effects reported in any of the trials, a stark contrast to modern antidepressants. The latter, in turn, cause agitation, weight gain, insomnia, sexual problems and increased suicidal tendencies. [, , , , ]
Helps with Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease is a neurodegenerative disease associated with loss of memory, cognitive skills and speech. This is the most common form of dementia. Despite its prevalence, there is still no effective therapeutic treatment.
Research shows that curcumin improves cognitive function in Alzheimer's patients. This is due to the following things [, , , ]:
- Disruption of insulin pathways . Abnormal insulin signaling pathways are common in Alzheimer's patients. Curcumin helps normalize these pathways, leading to improved cognitive function, spatial learning, and memory.
- Loss of synapses . Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the loss of synapses. Synapses are connections between cells through which signals are transmitted. Curcumin repairs damaged synapses while improving synaptic performance and structure. It also leads to improved spatial learning and memory.
- Oxidation and inflammation . The loss of synapses—and indeed entire brain cells—is largely caused by oxidation and inflammation. They occur when beta-amyloid plaque forms in the brain. Curcumin not only reduces brain inflammation caused by beta-amyloid plaque. But it also reverses its toxic effects on brain cells.
- Acetylcholinesterase . Curcumin inhibits acetylcholinesterase, which helps increase levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at synapses. This mechanism is present in almost all drugs against Alzheimer's disease. Acetylcholine is an important neurotransmitter that is directly involved in cognitive processes.
Helps with Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease severely affects movement and balance and carries a high risk of developing dementia. Like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease is caused by a buildup of toxic proteins, inflammation, and damage to dopamine-producing brain cells. []
Clinical studies have shown that curcumin increases cell survival, reduces cell death due to apoptosis, and improves mitochondrial function. These are all important actions that provide new life and renewed energy to the affected cells. It also reduces the behavioral manifestations of Parkinson's while increasing the amount of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Increasing dopamine levels is extremely important. It is its loss that leads to the loss of control over the motor system associated with this disease. , ]
Helps with stroke
An ischemic stroke occurs when blood flow is blocked from reaching part of the brain. This causes brain cells to become inflamed and die. After initial treatment, it is necessary to open the blocked area of the artery. However, due to inflammation and oxidative stress, this procedure may result in sudden return of blood and cause ischemic reperfusion injury. [, ]
Curcumin helps combat these types of injuries, thereby minimizing the damage caused by a stroke. It increases markers of cell repair, which indicates improved healing after acute stroke. It also reduces oxidative damage during the reperfusion phase. [, ]
During a stroke, which is caused by damage to brain cells, there is an increase in inflammation as the tissue heals. Administration of curcumin to rats prior to stroke was found to reduce inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction that typically occurs during the reperfusion phase of stroke. It also reduces the size of the infarct area (cell death) and significantly reduces the tissue swelling that occurs after a stroke. []
Overall, research suggests that using curcumin as a protective measure can significantly reduce any damage caused by stroke.
Additional neuroprotective effects
Curcumin has been shown to protect brain tissue from the effects of acute head injuries. Head trauma causes a sudden surge of oxidative stress and early inflammatory changes in the brain. It can combat these destructive effects. One study found that when rats were supplemented with curcumin before injury, they experienced dramatic reductions in oxidative stress levels and other signs of brain damage. []
It may also help protect against long-term brain damage associated with chronic alcohol abuse. This type of damage occurs as a result of oxidative stress, fat peroxidation in brain cell membranes, inflammation, and other mechanisms common to neurodegenerative diseases, strokes, and head injuries. Curcumin also counteracts these effects in the liver. Research also shows curcumin's protective properties against alcohol-induced brain degeneration. []
Stimulates neuroplasticity
Cognition, memory, spatial orientation, facial recognition, learning - all depend on the structure and function of the brain.
Curcumin can fight inflammation and oxidative stress. And this makes it a powerful tool for maintaining brain health. A 2021 study identified another mechanism underlying its neuroprotective and cognitive properties: stimulation of neuroplasticity. []
Neuroplasticity is the brain's ability to form, break, and remake connections between individual brain cells (neurons). This allows the brain to quickly adapt to changes in the environment, knowledge, and emotions. This process underlies learning, memory and cognition. One of the main factors supporting neural plasticity is the ability to produce neurites. They are tiny projections coming from brain cells. Neurites form branches called dendrites that connect our neurons. It is through these synaptic connections that nerve signals are transmitted. []
Preclinical experiments have shown impaired neurite outgrowth in models of neurodegenerative diseases, depression and stroke. The inability to establish connections between brain cells significantly reduces plasticity and ultimately reduces the ability to cognition, memory and skill development. [, ]
This new knowledge about improving communication between brain cells is what makes curcumin so attractive to researchers. It promotes active neurite growth and increases neuronal plasticity. These effects have been shown to counteract—and even reverse—the harmful effects of chronic stress and even traumatic brain injury on cognition, memory, learning, and plasticity. []
Curcumin for the Heart

One way to improve heart health is through exercise. One of the reasons why exercise is good for the heart is that it improves endothelial function. When the researchers compared exercise with curcumin supplements, they found that it was as effective as exercise in improving endothelial function.
Endothelium is the inner layer of cells lining arteries. It secretes a variety of signaling molecules that control cell growth, blood vessel tone (relaxed or constricted), blood clotting function, and platelet and leukocyte adhesion—all of which are closely linked to vascular health and atherosclerosis.
Impaired endothelial function has been associated with a wide range of age-related disorders, including atherosclerosis, hypertension, heart failure, ischemia (insufficient blood flow), Alzheimer's disease, and other conditions.
Curcumin combats many other risk factors for heart disease, including suppressing chronic inflammation, reducing the effects of high glucose levels, and normalizing blood lipid profiles. As a result, curcumin may mitigate the cascade of events that lead to heart attacks, heart failure, strokes, and even the microvascular complications seen primarily in people with diabetes.
The main factor in the development of cardiovascular diseases is metabolic syndrome. It is a combination of abdominal obesity, hypertension, glucose intolerance and lipid metabolism disorders. Together, these factors contribute to chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, which set us up for atherosclerosis, reduce blood flow to vital organs, and increase the risk of heart attack or stroke. []
Metabolic syndrome and obesity increase the risk of developing type II diabetes, a condition in which damage caused by high blood sugar quickly accelerates, worsening blood vessel health.
Curcumin has several modes of action to improve cardiovascular health:
- It reduces inflammation.
- Restores lipid profile.
- Prevents and reverses cardiovascular effects in diabetics.
- Controls the harmful effects of glucose.
Anti-inflammatory properties
One of the reasons obesity and metabolic syndrome are so harmful is that they promote chronic inflammation, which exposes tissues to constant low-level oxidative stress. Inflammation also threatens the integrity of cellular DNA, proteins, and other essential structural and functional molecules required for healthy biological activity.
Simply put, chronic inflammation is an age-accelerating process.
That's why one of the best ways to protect your heart is to suppress inflammatory changes. This allows the tissue to heal naturally and restore lost function, which ultimately helps slow down the aging process itself.
In a 2015 randomized controlled trial, subjects with metabolic syndrome took either a placebo or one gram of curcumin per day containing bioperine, a natural compound added to improve absorption. After 8 weeks, those taking the supplement experienced a significant reduction in chemical stress markers while enhancing natural protective enzyme systems. The end result was a reduction in overall inflammation levels. []
Other recent studies have confirmed that taking one gram of curcumin per day, boosted with bioperine to improve bioavailability, results in significant reductions in the levels of numerous inflammatory cytokines (signaling molecules) that mediate many of the damaging effects of chronic inflammation. [, ]
Lipid profiles
Another defining feature of metabolic syndrome is abnormal lipid profiles, especially elevated triglyceride levels and decreased protective HDL cholesterol ("good cholesterol"). High cholesterol increases the risk of atherosclerosis, which increases the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Curcumin supplements have a beneficial effect on lipid profiles.
One study found that adding one gram per day of the drug curcumin-bioperine resulted in significant reductions in LDL (“bad cholesterol”) and total cholesterol, a decrease in triglyceride levels, and a significant increase in HDL cholesterol. []
Curcumin achieves these benefits because it affects almost every pathway by which cholesterol enters the bloodstream and damages blood vessels, including absorption from the diet, removal of cholesterol from the liver, transport of cholesterol from cells, and removal of cholesterol from tissues throughout the tissue. []
Additionally, curcumin's ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species reduces the risk of oxidative damage to lipids, thereby limiting the resulting inflammatory damage that contributes to early plaque formation and narrowing of arteries that restrict blood flow.
Curcumin also improves the oxidative stress-resistant properties of beneficial HDL cholesterol molecules, increasing their health benefits. []
Curcumin for Diabetics
Diabetes places enormous amounts of oxidative and inflammatory stress on the heart muscle and blood vessels. People with diabetes are two to three times more likely to die from cardiovascular disease than people without diabetes. []
Curcumin may prevent—and even reverse—many of the harmful steps that contribute to cardiovascular disease in diabetics.
In a randomized controlled clinical trial, subjects with type II diabetes took either capsules containing 1.5 grams of curcumin per day or a placebo for six months. Those who took this supplement experienced significant improvements in their arterial stiffness scores. People who took curcumin also saw reductions in insulin resistance, triglycerides, uric acid, as well as visceral fat (abdominal fat that accumulates around organs and is particularly inflammatory) and total body fat levels—all representing significant reductions in cardiovascular health risk. []
Another cardiovascular complication of diabetes is damage to tiny blood vessels, or microangiopathy. It contributes to diabetic complications such as swelling of the limbs, as well as diseases of the retina, kidneys and heart. Curcumin improves blood flow and helps relieve many of these complications.
Curcumin for cancer

It reduces the survival rate of cancer stem cells and increases their sensitivity to chemotherapy, making tumors more vulnerable to treatment. When applied directly to human brain cancer cells, curcumin induced cell death. This works in six important ways:
- Survival alarm . Early cancer cells develop the ability to proliferate and survive in conditions that do not normally support cell replication. Curcumin modulates multiple survival signals through multiple pathways, thereby stopping uncontrolled replication.
- Apoptosis . It is programmed cell death that eliminates dysfunctional cells. Cancer cells lose their ability to die naturally. This plays a major role in the development of cancer and its resistance to conventional treatment. Curcumin switches back to the apoptosis signaling pathway, encouraging overproliferating cells to die rather than continue to grow and spread.
- Growth factors . A wide range of growth factors and other molecules can promote cancer cell replication. Curcumin directly inhibits many of these molecules, stopping cancer growth in a multi-target manner.
- Inflammation . Low-level inflammation is a powerful stimulator of cancer cell growth and survival. Curcumin blocks pro-inflammatory processes at several different points. This reduces the overall state of inflammation and slows down the development of cancer. By blocking the inflammatory master molecule NF-κB, curcumin blunts cancer-causing inflammation.
- Cancer stem cells . Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are an unusual population of cells in tumors. These cells, like all stem cells, can develop into many other types of cells, including new cancer cells. CSCs are responsible for both the formation of new tumors and the failure of traditional chemotherapy. Because they are able to survive with the help of drugs that kill normal cancer cells. Curcumin has been shown to inhibit the growth of CSCs in numerous laboratory studies.
- The immune system . A healthy immune system constantly patrols the body, searching for and destroying emerging cancer cells. With age, however, the immune system becomes less functional, in a process called immunoscence. Curcumin supports the body's immune system by preventing the loss of tumor-destroying immune cells.
Curcumin as an antioxidant
When the body responds to physical injury, a series of changes occur that release free radicals. These free radicals, or “oxidants,” protect the body from external influences such as infection. However, in the process of killing offending bacteria, oxidizing agents can also harm our cells. Such oxidizing agents may include superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radicals and lipid peroxides. Over time, as our cells continue to be exposed to these free radicals or oxidants, the organs begin to degrade. The result can be diseases and conditions such as chronic inflammation, heart disease, accelerated aging, and erratic cell growth that leads to cancer.
The body has built-in defense mechanisms to protect itself from the effects of free radicals, but eventually aging and disease reduce the body's ability to keep oxidants away. Research shows that curcumin can inhibit or even reverse this process by removing or neutralizing free radicals and breaking their subsequent oxidative chain reaction. Numerous studies have shown that curcumin inhibits lipid peroxidation, superoxides and hydroxyl radicals. [, , ]
Curcumin reduces weight
First, it reduces the efficiency with which cells process nutrients. This causes them to produce a smaller balance of chemical energy per unit of food. With less chemical energy balance, the body must use its fat reserves. This happens to maintain the vital activity of vital cells. Thus, it must burn fat deposits.
Secondly, it reduces insulin resistance. When cells are resistant to insulin, they do not consume normal amounts of food energy. Consequently, normal amounts of chemical energy are not released for use by other tissues. By reducing insulin resistance and restoring physiological stability, curcumin allows cells to process more nutrients. When the cell absorbs more nutrients and subsequently processes them, a person loses weight faster. []
For people who are overweight and suffer from metabolic disorders, curcumin can be a life-changing and even life-saving treatment.
Curcumin for eyes
It helps in the treatment of certain eye diseases and pathologies. One of them is known as chronic anterior uveitis (CAU). This is an inflammatory disease of the vascular layer of the eye, in particular the area entering the diaphragm. Curcumin is as effective as corticosteroid therapy, the only currently available standard treatment for chronic anterior uveitis. It also effectively inhibits chemically induced cataract formation. [, , ]
Curcumin repairs muscles
Muscle regeneration is a complex phenomenon. Curcumin works in part by altering the arrival time and status of chemical messengers known as cytokines. Cytokines appear on the scene early and have a powerful effect on inflammation and cell growth. For example, a cytokine known as IL-6 (interleukin-6) causes muscle cells to multiply. Another, called TNF (tumor necrosis factor), prevents cells from growing and developing. By suppressing one and enhancing the other, curcumin can speed up the recovery process. []
How much curcumin is in turmeric?
It is thanks to the curcumin contained in turmeric that the spice has all those unique properties. Curcumin is a chemical compound contained in the rhizomes of the plant that can fight inflammation of various origins at the molecular level.
However, it should be noted that the curcumin content in the root of the spicy plant, as well as in the powdered seasoning itself, is only 3%. This is what you should use as a starting point to determine your daily intake of spices.
How safe is turmeric?
The thousand-year history of the use of turmeric in India and a number of other countries, as well as many studies conducted to study the medicinal properties of curcumin, confirm its safety when consumed in small quantities.
At the same time, you need to understand that, due to its properties, turmeric can have a strong effect on the body that is comparable and sometimes even stronger than the effect of some medications. Therefore, its use in therapeutic doses is contraindicated for a number of diseases, as well as in combination with certain medications.
Note that when they talk about the side effects of turmeric and contraindications to its use, they usually talk about taking its active ingredient - curcumin in high doses. Any sane person understands that taking medications in doses exceeding those indicated in the instructions for use will not only not help get rid of the disease, but will also cause harm to the body. Also with turmeric, taking it in large quantities can have extremely negative consequences.
Large doses of curcumin can be harmful even to healthy people, not to mention those who suffer from diseases for which turmeric is completely contraindicated or its use is possible only with constant monitoring.
To get the desired effect from the numerous beneficial properties of the spice and not cause harm to the body, do not exceed the recommended doses.
Below is a list of contraindications for taking turmeric, as well as precautions and cases when it can be used only with constant monitoring of the body's condition.
How much can you consume per day?
Various sources contain recommended doses of spice consumption for the treatment of various ailments. But today there is no official confirmed information on the amount of spice taken to treat certain diseases.
It is not known for certain how much turmeric powder should be taken to treat the liver, what the daily intake of the spice should be for the prevention of cancer, etc.

In this case, we can only be guided by the official recommendation: experts from the World Health Organization on food additives working under the UN have determined a safe daily dose of 3 mg of curcumin per 1 kg of human body weight.
As mentioned above, the spice powder contains 3% curcumin. Therefore, 1 teaspoon of turmeric (which is equal to 4.40 grams of the spice) contains 132 mg of curcumin.
For example, a safe daily dose of turmeric for a person weighing 70 kg is 210 mg of curcumin, which is equal to approximately 1.5 teaspoons of the spice.
Due to the absence of other official recommendations, you should not exceed the specified spice consumption limits. After all, when treating any disease, you must adhere to the main principle “Do no harm.” Moreover, considering that on average you can consume 1-3 tablespoons of spice powder per day, which you will agree is not so little.
Taking turmeric does not exclude treatment prescribed by a doctor and can only be used as part of complex therapy.
And despite the fact that studies using large doses of the substance have not revealed toxic properties or serious side effects of curcumin, it is recommended to adhere to the specified dose.
It is recommended to divide the amount of seasoning consumed into several doses (2-3 times a day).
To calculate a safe dose of turmeric per day for your weight, multiply your weight in kilograms by 3 (1 kg weight per 3 mg curcumin). And determine the number of teaspoons based on the fact that 1 teaspoon contains 132 mg of the biologically active compound.
How to use turmeric correctly?
When taking turmeric for medicinal purposes, it should be taken into account that the spice itself has low bioavailability and is poorly absorbed. The spice does not dissolve in water, is not absorbed in the intestines and is quickly eliminated from the body.
To absorb the spice and get the benefits from taking it, you need to use turmeric correctly:
- In combination with black pepper, its digestibility increases by 2 thousand times. It is recommended to use it in a 4:1 ratio (4 parts spice to one part pepper).
- Curcumin is fat soluble. When consumed with oils and natural fats (olive, sunflower, butter), it is better absorbed in the intestines. It is also useful to consume the spice with milk.
- When the spice is heated, active beneficial substances are released. Therefore, before use, it is recommended to pour boiling water over it, or better yet, boil it.
Composition and beneficial qualities of turmeric
The plant contains many useful substances: curcumin, vitamins, antioxidants, minerals, essential oils.
People who regularly consume turmeric can boast of good health, because thanks to such a rich composition, the plant has valuable medicinal properties that effectively affect the body:
- activates the immune system;
- improves blood circulation;
- regulates metabolism;
- promotes recovery of the body after operations;
- cleanses the body of pathogenic bacteria;
- controls pain and spasms;
- Suppresses free radicals that can cause cancer;
- produces serotonin, which promotes vigor and improves mood;
- relieves flu and cold symptoms;
- prevents memory disorders;
- promotes protein absorption;
- regulates intestinal microflora;
- strengthens the walls of blood vessels;
- refreshes and smoothes the skin.
In medicine, dried turmeric root powder is used, as well as extracts, syrups, essential oils and tinctures from it. For better absorption by the body, it is recommended to warm the powder a little before use or take it as part of warm drinks.

Choosing Turmeric Supplements
Turmeric supplements are preparations containing concentrated curcumin (95 – 97%). Biologically active drugs are obtained by emulsifying curcuminoids into a highly digestible form. The choice of drugs is large: from Russian Evalar to American Solgar, NOW Foods.
If you choose a drug containing curcumin, you need to consult your doctor to determine the dose of the drug, duration of use and the possibility of treatment.
Who should not take turmeric?
Although turmeric is considered safe for most people, some people may need to avoid it.
These conditions require special caution:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding : There is not enough research to determine whether turmeric is safe for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Gallbladder disease : Turmeric may cause the gallbladder to shrink and worsen symptoms ().
- Kidney stones : Turmeric contains high levels of oxalates, which can bind with calcium and cause kidney stones ().
- Bleeding : It can slow your blood's ability to thicken, which can make bleeding problems worse ().
- Diabetes mellitus : Turmeric can cause low blood sugar levels, which can be dangerous if taken simultaneously with blood sugar-lowering medications ().
- Iron deficiency : Turmeric may impair the absorption of iron ().
Additionally, turmeric supplements may interact with certain medications, such as anticoagulants (blood thinners) and diabetes medications (,).
However, turmeric appears to be safe for these conditions in amounts commonly consumed.
Summary:
Turmeric supplements are dangerous if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have certain medical conditions. Supplements may also interact with anticoagulants and diabetes medications. However, turmeric appears to be safe when used as a spice in food.
Taking turmeric every day
The spice is absolutely safe and, in the absence of contraindications and individual intolerance, provided that it is consumed daily in a dose recommended by the World Health Organization, it will not cause harm to health.
Turmeric can be taken daily; in this case, the safest way would be to consume the spice with food. Introduce spice into your diet by seasoning your favorite dishes. It is also useful to consume the spice with honey and add it to tea.

But moderation is important everywhere. If you use turmeric every day, after 1-2 months of regular use of the spice, it is recommended to take a break for the same period of time.