Hello, dear readers! If you go to the clinic about pancreatitis, atherosclerosis or gastritis, the doctor is unlikely to prescribe therapeutic fasting. He, as taught, will send you for tests and examinations and, based on the results, will give you a list of medications. Theorists and practitioners of fasting-dietary therapy do not consider fasting a medicine, characterizing it as an element of a healthy life, a way to make nature work to strengthen vitality. However, the range of indications for this popular healing method is quite wide.
What is fasting?
To begin with, let’s agree that fasting means eating nothing at all and drinking only water.
To function normally, the body needs proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, which it receives from food. When there is no food, internal savings come into play, and when they run out, self-production of what is needed from internal reserves begins. The body primarily uses ballast (sick) cells as consumables. From a hungry shake, all internal systems are activated and begin to work at full capacity. This is the healing mechanism of fasting.
But, let's take it in order.
Scientists have discovered how intermittent fasting affects your health
A group of scientists from the University of Graz (Austria) observed 60 volunteers for four weeks who were on a special diet - intermittent fasting. According to a study published in Science, the effect of the experiment confirmed the scientists' expectations.
Intermittent fasting, or periodic, cyclical, intermittent fasting, has recently become extremely popular. There has been indirect evidence that it not only provides health benefits, but may also prolong life. However, these statements were mostly based either on hypotheses or results of this kind were obtained from animal studies. Whether these results could apply to humans to the same extent was still an open question.
The essence of this diet is to limit the time of meals, i.e. When creating your diet and menu, you need to create periods when you can’t eat.
To gain more clarity on this issue, Austrian scientists invited volunteers for a four-week “pilot” project. According to the conditions of the experiment, 60 participants, middle-aged men and women, were slightly overweight but healthy, and were neither vegans nor vegetarians. Half of them (the control group) had to maintain their previous eating habits, while the other half ate according to a specific intermittent fasting technique.
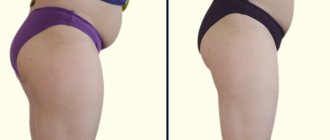
After four weeks of the experiment, each of them lost an average of 3.5 kilograms, while the subjects in the control group lost only about 200 grams.
Among other positive effects, the following were noted: lowering blood pressure; improvement of metabolic processes; an increase in the concentration of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the blood - substances that, according to a number of observations, reduce the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular diseases.
The study participants had "no side effects even after 6 months of the diet," the article says, and the diet overall improved "physiological and molecular markers of aging in healthy, non-obese individuals."
However, due to methodological shortcomings, the study by Austrian scientists, one of the pioneers in this matter, cannot draw clear conclusions on the exceptional benefits of this diet, writes NZZ.
But meanwhile, there are a number of studies confirming the benefits of intermittent fasting. For example, American scientists recently showed that one-day fasting leads to a reduction in inflammatory processes in the body without weakening the immune system.
While 48-hour fasting already had a negative effect on the body's defenses.
Thus, not every type of intermittent fasting is equally beneficial. Therefore, it is all the more important to carefully study the benefits and risks of each type of diet.
Day one - fats burn in the flames of carbohydrates
The body does not immediately switch to self-sufficiency - an endogenous diet; first it deals with easily accessible accumulations. We create these accumulations ourselves by consuming more food than we need.
Glycogen - glucose stored in the liver and muscles - plays the role of fuel when burning fat. When the supply of “firewood” for 1-2 days runs out, the combustion process does not go through completely - oxidation products remain - butyric acids and acetone, which poison the body and cause temporary attacks of poor health - weakness, nausea, headache.
Exit

You need to be able to get out of it no less competently. If you immediately rush to food after unloading, you may end up in the hospital with serious intestinal disorders. Please follow these rules.
- The exit is organized exactly at the same time that the entry was made.
- If it was dry fasting, you should start with a glass of warm water, which you need to drink in small sips. You can start eating only after half an hour.
- The first meal should be as light and low-calorie as possible: liquid porridge with water or boiled vegetables.
- During the day, you need to carefully select foods so as not to overload your stomach: portions should be small, overeating is excluded.
- The basis of the diet is boiled or baked vegetables, cereal porridge, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, a little hard cheese, low-fat chicken or fish broth.
- From the next day, you can gradually introduce other foods: fruits, fresh vegetable salads, eggs.
In the recommendations scattered across the Internet on how to break a one-day fast, you can also find anti-advice (for example, start with an enema, laxatives or emetics). Carefully analyze the information and be able to filter out such teachings that can provoke serious gastric disorders.
Acidosis triggers endogenous nutrition
The remains of fat combustion are acidic products, the process of their accumulation, which has reached its highest point, is called acidotic (from Latin acidum - acid) shift, it occurs on the 6-8th day of fasting.
The smart body understands that it is impossible to accumulate fat waste further and turns on the endogenous nutrition regime - it begins to produce the missing fuel (sugar) from the existing internal reserves of fat and protein. Everything returns to normal, the symptoms of intoxication gradually disappear.

How to eat air and where proteins come from
Acidosis, which is generally believed to be a companion to painful conditions, turns into a healing factor that initiates the process of nutrition from the air.
A person, like a plant, begins to absorb carbon dioxide (CO2), which, dissolving in the blood, activates the synthesis of nucleic acids and amino acids - the building material for protein production.
Additionally, the body produces protein by processing internal protein trash - degenerative tissue - tumors, foci of infection, edema and adhesions.
It turns out that by giving up food for a while, you can:
- cleanse the body of ballast reserves of fats, proteins and carbohydrates,
- launch recovery and rejuvenation processes due to enhanced protein synthesis,
- obtain controlled autolysis (self-digestion) of pathological neoplasms, including oncology.
Hunger only under control
Despite the apparent simplicity of the procedure, it is impossible to fast without medical supervision. An exception is one-day fasting, but this method also requires certain skills and theoretical training. You can learn more about how to fast properly at home by reading the article: “Are there any benefits to one-day fasting?”
It is not for nothing that the concept of “therapeutic fasting” in medical practice has been replaced by the term “fasting-dietary therapy” (RDT). This is a set of measures - not only food abstinence itself, but also everything that happens in parallel, as well as before and after:
- preparation or entry—pre-cleaning (enemas, taking laxatives),
- controlled refusal of food,
- accompanying cleansing procedures (sauna, enemas),
- contrast procedures (sauna, dousing, winter swimming),
- increased physical activity (running, walking),
- breathing practices (yoga, according to Buteyko),
- recovery (exit),
- subsequent diet and proper nutrition.
Changes in metabolic processes should be under constant monitoring. To avoid intoxication and other complications, the doctor must monitor how test data (blood, urine) and other types of diagnostics change and carry out therapy flexibly. Each stage of therapy and the appointment of procedures are carried out in accordance with the patient’s condition.
Who should not fast?
There is a category of people for whom fasting is strictly contraindicated. Among them are children, the elderly, pregnant and lactating women. And:
- oncological diseases of 3 and 4 degrees;
- paralysis;
- recovery period after surgery or heart attack;
- tuberculosis in the active phase or hepatitis in the acute stage;
- underweight more than 15% of normal BMI;
- blood diseases, thrombophlebitis.
In some cases, a positive effect from therapeutic and health-improving abstinence from eating may be observed, but a doctor must assess the risks in each specific case.
Therapeutic fasting - what diseases can it help with?
One should speak with caution about fasting as a way to cure all diseases. I repeat, this is not a medicine, but a way to activate our internal reserves. The quantity and quality of reserves are individual for each person; they depend on age, standard of living, and state of health. The degree of the disease itself can also vary.
In addition to general health benefits , the therapeutic effectiveness of RDT is confirmed by reviews from patients who have recovered from diseases of the digestive and endocrine systems, allergies, hypertension, angina pectoris, atherosclerosis, and nervous disorders.
A little about ways and methods
The boom in the topic of fasting in Russia was associated with the appearance in the mid-80s of the book “The Miracle of Fasting” by the American healthy lifestyle promoter Paul Bragg. The Bragg fasting method is weekly daily fasting on distilled water with a gradually increasing period of time up to 30-40 days and a hard fast on raw vegetable salads.
Much earlier than Bragg, at the beginning of the 20th century, Alexey Alekseevich Suvorin studied ancient healing systems in Russia. Having emigrated to Yugoslavia after the revolution, he ended up in prison, where he went on a long hunger strike and stayed on it. The disappearance of several chronic diseases was the impetus for the development of our own system of home 40-day fasting.
In the wake of the popularity of the topic, folk healer Gennady Malakhov proposed cascading cycles of dry food abstinence for 5 days for 1-2 months.
Therapist Mavra Ohanyan recommends not eating for up to 2 weeks, but not drinking water, but complex herbal decoctions.
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Yuri Sergeevich Nikolaev proposed a balanced flexible scheme of unloading therapy in a hospital setting. The system is deeply scientific, combining previously accumulated experience, research results and knowledge of modern medicine.

Entrance
You need to know how to prepare for a one-day fast so as not to break down and complete the task. If you properly organize the entrance to it, the risk of complications will decrease and the effectiveness of the event will increase.
3 days before:
- give up fatty meat, fish, fast food, snacks, baked goods, sweets, alcoholic, carbonated and energy drinks;
- the basis of the diet is low-fat dairy products, cereals, vegetables and fruits, juices;
- Boil, bake, steam dishes, but do not fry.
For 1 day:
- give up dairy products, mushrooms, nuts, legumes, coffee, tea;
- the basis of the diet is vegetables, fruits, herbs, berries, juices, fresh juices, herbal infusions;
- It is advisable to eat everything fresh;
- no smoking;
- Give a cleansing enema in the evening.
The best time to enter is in the morning, when you are allowed to eat your last meal. This could be a small portion of porridge with water, unsweetened fruit, a glass of freshly squeezed juice diluted with water (recipes) or whole grain bread with a slice of hard cheese. Why is it better to choose breakfast? The next day, when you leave at exactly the same time, you will have a whole day ahead of you to enjoy food and drink.
If you enter in the evening, exit will be more difficult, since it is not recommended to overeat at night; you will have to limit yourself to a light dinner and then fast all night. Most often, this ends in a breakdown: before going to bed, a person fills his stomach, which at the end of the fasting day turns into a blow to the gastrointestinal tract.