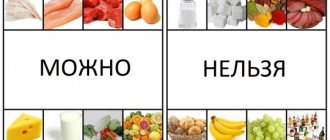
What is the essence of the weight loss method?
It is known that carbohydrates provide the body with energy. If the resulting energy is not consumed, it is stored in the form of fatty layers.
A low-carb diet allows you to effectively lose weight
Weight loss with a low-carbohydrate diet occurs due to the fact that the consumption of carbohydrates is reduced to a minimum, and the amount of protein in the diet increases. This starts the following processes. The body, having ceased to receive the necessary energy, begins to seek its new sources. In the first 2–3 days, the energy supplier is glycogen, which accumulates in the liver, muscles and fat layer. Then fats begin to be intensively broken down, as a result of which additional sources of energy are synthesized - ketones (these substances, in addition, can reduce appetite).
Thus, the diet is based on biochemical processes, as a result of which fats are actively burned and weight loss occurs, while in a week you can lose 3-5 kg of excess weight.
It should be noted that this diet is not just a method of losing weight, but a certain eating style that you can use throughout your life. Strict restrictions are imposed only in the initial phase, and then, to maintain and improve the result, you can take as a basis the rule of not consuming more than 3-5 g of carbohydrates per 1 kg of weight. At this rate, body functions are not impaired, and weight is guaranteed to be maintained and not to grow.
It will not be possible to lose weight locally in certain areas (abdomen, thighs, buttocks, etc.). Weight decreases evenly throughout the body.
It should be noted that carbohydrates are not completely excluded during the diet, since without them the normal functioning of the body cannot be carried out. The diet involves the consumption of not simple, but complex (slow) carbohydrates, which are absorbed gradually, and the body completely uses up the energy received from them.
Yolk diet for weight loss:
Video: balance of proteins, fats, carbohydrates
On a low-carbohydrate diet, the source of protein is mainly animal products. However, there is also a vegetarian option for low-carb weight loss. In this case, protein can be obtained from legumes and nuts.
General rules
In recent years, fat-protein diets with extremely low carbohydrate content have become very popular.
Let's consider the question of what a low-carbohydrate diet is, its features and purpose. Dietary systems with carbohydrate restriction are used for various purposes: for weight loss, for diabetes mellitus , for the treatment of obesity , for hypertension . Low-carbohydrate diets (the so-called keto diets ) are also indicated for athletes involved in a sport such as billballing, which uses a special nutrition system - drying, which allows you to quickly gain relief and expressiveness of the body by reducing the fat layer and increasing lean muscle mass. And each of the intended purposes of diets with a reduced carbohydrate component has its own rules and many nuances.
Carbohydrates are a large class of chemical compounds, including simple (monosaccharides) and complex (polysaccharides) carbohydrates, each of which has different effects on metabolism:
- simple carbohydrates - are quickly absorbed in the body and are broken down into monosaccharides (glucose/fructose) during metabolism. They are quickly absorbed in the body and, if they are supplied in excess, and there is no need for them, they are converted into intra-abdominal and subcutaneous fat. When they are utilized, the blood sugar level quickly rises, which provides a feeling of satiety, which passes just as quickly. Products containing simple carbohydrates include sugar, sweet fruits, honey, jam, preserves, confectionery, candies and other sweets;
- complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen , pectin , fiber, inulin ) are absorbed slowly in the body (the duration is 3-5 times longer). They have a complex structure and include many monosaccharides. They are broken down in the small intestine, and their absorption is slowed down by fiber. Complex carbohydrates increase blood sugar slowly, and therefore the body is saturated with energy evenly. Products containing complex carbohydrates (fiber, starch, pectin) include whole grain bread, white rice, cereals and cereals made from them, pasta, bananas, pineapple, dried fruits.
In essence, a low-carbohydrate diet models metabolic processes in the body that are identical to fasting, when metabolism is reoriented to gluconeogenesis , in which the process of glucose formation occurs from non-carbohydrate components (glycerol, lactic/pyruvic acid, amino acids , fatty acids). In the initial period of fasting, the metabolism of amino acids (protein) increases, which reaches a certain level and persists for 25-30 days, and then the use of protein as “metabolic fuel” slows down sharply, since its reserves in the body can only decrease to a certain level. At the same time, the mobilization and oxidation of free fatty acids accelerates.
At this stage, under conditions of severe carbohydrate deficiency, energy metabolism switches from carbohydrate to lipid metabolism, in which the energy substrate is the oxidation of fatty acids with the production and accumulation of ketone bodies. Thus, a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet induces benign ketosis. And mobilization from the glycogen and the relatively rapid development of a feeling of satiety contributes to a faster rate of body weight loss.
When using diets of this type, it should be taken into account that the low content of carbohydrates and dietary fiber in the diet causes insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals into the body. Therefore, diets that suppress appetite against the background of rapid ketosis, even with the additional introduction of necessary components into the diet, can be prescribed for a limited period. When following low-carbohydrate diets, it is important to remember that the mechanism of formation of ketosis bodies is triggered by limiting carbohydrates in the diet to 100 g/day.
Hypocarbohydrate diet for weight loss
It is based on a sharp restriction in the diet of the amount of foods containing predominantly simple carbohydrates and, to a lesser extent, foods high in complex carbohydrates. At the same time, the protein content in the diet corresponds to the physiological norm, and the fat consumption rate is moderately reduced. Accordingly, the total calorie content of the daily diet is reduced to 1700-1800 Kcal/day. Limiting carbohydrates in weight loss diets below 120-130 g is not recommended or acceptable when using fasting diets for a short period. The choice of products - sources of carbohydrates is determined by the required degree of reduction in the energy value of the daily diet, the duration of the diet and the specified goal.
In the diet, sugar and sugar-containing products, confectionery products, sweet drinks, honey, ice cream are excluded, bakery and pasta products made from premium flour, polished rice, semolina are limited, and in cases where it is necessary to further reduce the energy value of the diet (up to 1000- 1200 kcal/day) excludes other cereals, potatoes, some fruits and berries (grapes, bananas,) dried fruits. The main source of carbohydrates should be products containing vitamins and minerals, rich in dietary fiber - dietary types of bread with the addition of bran and crushed grains, ground or wholemeal bread, legumes, cereals, preferably whole grains or partially retaining the shell (unpolished rice, buckwheat, barley/oatmeal porridge), vegetables, non-sweet fruits and berries.
It is important to understand that an anti-carbohydrate diet with the exclusion/limitation of sugar and sugar-containing foods in the diet does not mean that sugar contributes more to weight gain/ obesity than other carbohydrates. The presence of sugar in the diet is not important for reducing body weight in cases where the energy value of the diet is less than energy expenditure. The point of choosing carbohydrate sources is that products containing complex carbohydrates have a higher nutritional value (create conditions for the natural activity of intestinal microflora, stimulate the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract, adsorb toxic compounds, cholesterol ) and allow for more stable and long-lasting satiety than sugar-containing ones. products.
Low-carbohydrate diet - table of foods with quantitative carbohydrate content
To create a low-carbohydrate diet, it is important to understand the quantitative content of carbohydrates in certain foods. This information is reflected in the table below.
| Product name | Carbohydrate content |
| Bagels | 58 |
| Boiled pasta | 25 |
| Wheat porridge | 27 |
| White sugar | 105 |
| Armenian lavash | 56 |
| White bread | 51 |
| Bread Borodinsky | 39 |
| Green peas | 12 |
| Milk chocolate | 62 |
| Boiled white rice | 30 |
| Marmalade | 70 |
| Honey | 77 |
| Buckwheat | 29 |
| Dates | 68 |
| Peanut | 15 |
| Shortbread cookies | 58 |
| Hazelnut | 15 |
| Sunflower seeds | 18 |
| Sesame seeds | 20 |
| Walnuts | 11 |
| Watermelon | 9 |
| Eggplant | 5 |
| Cornflakes | 75 |
| Parsley | 8 |
| Tomatoes | 4 |
| Sour cream | 3 |
| Sweet pepper | 5 |
| Boiled potatoes | 16 |
| Boiled beets | 7 |
| Fruit kefir | 5 |
| Whole milk | 12 |
| Banana | 22 |
| Milk ice cream | 25 |
| Cashew | 25 |
| Carrot | 5 |
| Grape | 15 |
| Raspberries, strawberries | 5 |
| Tangerines, oranges | 7 |
| Apricot compote | 23 |
| Pear compote | 15 |
| Apples | 10 |
| Red/black currant | 7 |
| Cherry | 12 |
| Dried rose hips | 26 |
The main principles of a low-carb diet are:
- Reducing the diet of carbohydrates (mostly simple) to 120-130 g/day with a physiological norm of protein content and moderate restriction of fats (up to 70-75 g/day), mainly due to the reduction of solid animal fats. The ratio of complex and simple carbohydrates should be approximately 95 to 5. At least 50% of the protein in the diet should be provided by animal products: eggs, lean fish, meat, cottage cheese, seafood. The calorie content of the daily diet should vary between about 1700-1800 Kcal/day.
- The main intake of complex carbohydrates should be in the first half of the day. At dinner, you should give preference to protein foods.
- Limiting the consumption of salt and salty foods.
- Meals are split, no snacks between meals.
- Prepare food using dietary culinary methods for processing foods - boil, steam, stew, bake. Frying food is not allowed.
- Drink at least 2 liters/day of free fluid.
To increase the effectiveness of a low-carbohydrate diet, it is recommended to practice fasting days, since they accelerate the mobilization of fat from the depot and contribute to the restructuring of metabolism.
However, it is necessary to understand that the energy value of fasting days varies at the level of 500-700 kcal/day and has a limited range of products, which leads to a deficiency of essential food nutrients . Therefore, fasting days can be used no more than 1-2 times a week. There are extremely many options for fasting days - mainly protein (meat, kefir, fish, cottage cheese), carbohydrate (fruit and vegetable), combined - relatively close in the composition of nutrients and products to a balanced diet.
Below are some options for fasting days:
- Kefir-curd diet - 50 g of low-fat cottage cheese and 200 ml of yogurt or 1% fat kefir, 5 times a day;
- Meat (fish) diet - 50-70 g of boiled lean meat (fish), 5 times a day and 100-150 g of vegetables (cucumbers, cabbage, tomatoes) 5 times a day.
Vegetable and fruit diets have a particularly low energy value (250-300 kcal), which can be recommended both for adult men and women with a regular diet, and for vegetarians.
- Salad diet - 250 g of raw fresh vegetables in the form of salads 5 times a day, if necessary, with the addition of 10 g per day of vegetable oil or 10% sour cream.
- Cucumber diet - 300 g of fresh cucumbers, 6 times a day (1.5 kg).
- Apple diet - 250 g of raw or baked apples 6 times a day (total 1.5 kg).
On fasting days, you are allowed to drink still mineral water, rosehip decoction without sugar, and tea. Salt is limited to 2-3 g/day. On fasting days, it is mandatory to take one tablet of multivitamin-mineral preparations ( Vitrum , Complivit , Multimac , Vitamax , Vitaspectrum , Unicap , Multitabs , Teravit and others).
Low carbohydrate diet for diabetes
For diabetes mellitus, a low-carbohydrate diet is included in a complex of therapeutic measures. Such patients are prescribed a therapeutic diet, Table No. 9 according to Pevzner (with normal weight). The diet provides for a reduction in carbohydrates in the diet, but the overall decrease in the carbohydrate component is not so pronounced and amounts to 3.5 g per 1 kg of the patient’s weight (on average 300-350 g/day). The energy value of the diet is 2500 kcal. The menu is limited mainly to simple carbohydrates with a physiologically normal content of proteins (95-100 g/day) and fats (75-80 g/day).
The diet provides for a limited content of sodium chloride (up to 10-12 g/day), extractives and cholesterol . The content of foods containing lipotropic substances and dietary fiber increases (seafood, beef, veal, cottage cheese, whole grain cereals, wholemeal bread, lean fish, vegetables/fruits). If you are overweight, the carbohydrate content in the diet is reduced to 120 g per day, and the caloric content of the diet is reduced to 1700 kcal ( Table 9A ). The diet is fractional with an even distribution of carbohydrates.
Opinion of nutritionists
Since during the period of an immediate low-carbohydrate diet (7 days or a month), daily carbohydrate intake does not exceed 40–60 g, most nutritionists are wary of such types of weight loss. A deficiency of carbohydrate products and an excess of protein products can cause unwanted disturbances and side effects in the body.
Experts recommend adhering more to a proper and balanced diet, in which the intake of carbohydrate foods is also controlled. This eating behavior, combined with moderate physical activity, is guaranteed to ensure weight loss. It will not be as fast in speed, but without harm to health.
Healthy and harmful low-carb foods
You may be wondering what contains carbohydrates and what does not. Let's be clear: Even if a food or dish is low in carbs, that doesn't mean it's a healthy food! In many cases, the quality of carbohydrates you eat is more important than the quantity. I recommend staying away from packaged low-carb foods, such as most store-bought protein bars or quick snacks, to avoid processed or synthetic ingredients in your diet. Yes, they will provide you with fats and protein, yes, they are low in carbohydrates, but on a global scale they are still harmful because they contain processed protein powders, refined oils and artificial sweeteners.
If you're wondering what to take with you for a quick snack on the run, it's best to make your own. You can make low-carb snacks at home using ingredients like nuts, seeds, humus, coconut flour and coconut oil, protein powder (whey or bone broth), oatmeal and cocoa powder energy bites, kale sprouts, and even low-carb ones. sweets” like cookies, muffins or donuts. The quickest way to do this is to make a low-carb protein shake.
As you look to clean up your diet and embrace new low-carb recipes, you'll also want to get rid of "diet" or "comfort" foods that contain low-fat artificial ingredients. To achieve lower fat content, these products typically use more flour or carbohydrates, thickeners, emulsifiers or artificial sweeteners. And although they may not have much carbohydrates or cane sugar, I would still avoid foods with trans fats or hydrogenated oils, because in essence they are the same fast food or shelf-stable food.
Contraindications
Since with a low-carbohydrate diet the balance of proteins-fats-carbohydrates is disturbed, there are some restrictions under which this method of losing weight cannot be used:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- age under 18 years;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, gastritis);
- period of exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Basic rules of a low-carb diet
- During weight loss, you can only consume approved foods. During the entire period of losing weight, it is strictly forbidden to consume:
- sugar;
- bread and other baked goods;
- confectionery;
- White rice;
- pasta;
- vegetables that contain a lot of starch;
- fruits high in sugar (bananas, grapes, dates, etc.);
- carbonated drinks;
- alcoholic drinks.
- Allowed foods should be boiled, steamed or baked.
- Carbohydrate intake should not exceed 100 g per day.
- When losing weight, be sure to follow a drinking regime: you need to drink 2 liters of clean water per day.
- The diet requires five meals a day, and the last meal should not be later than 2-3 hours before bedtime.
- You should sleep at least 7 hours a day.
- During the period of weight loss, it is necessary to consume vitamin complexes.
- During the diet, moderate physical activity is recommended. This will improve the final result and preserve muscle mass.
- The duration of a low-carbohydrate diet with strict carbohydrate restriction should not exceed 30 days.
- The daily calorie intake for women should be at least 1200 kcal, and for men - at least 1500 kcal.
Table: ratio of BZHU with a low-carbohydrate diet for women and men
| Daily norm | ||
| Women | Men | |
| Calories | 1200 kcal | 1500 kcal |
| Squirrels | 120 g | 150 g |
| Fats | 46.7 g | 58.3 g |
| Carbohydrates | 75 g | 93.8 g |
Varieties
A more strict type of diet for weight loss includes the low-carbohydrate diet according to Khairullin . Its peculiarity is that in the diet the amount of fat and protein foods is not limited with a sharp restriction of carbohydrates: no more than 6-8 g per day in the first days with a gradual increase in their content to 20-40 g. The course of dietary nutrition is divided into 4 stages , each of which is aimed at solving certain problems, not only at losing extra pounds, but also at consolidating the result.
- The stimulating stage involves a sharp reduction in carbohydrates to 0-10 g per day. Its duration is 14 days. The main task is to launch the ketosis mechanism and the fewer carbohydrates contained in the diet, the faster the goal is achieved. At this stage, drinking plenty of fluids (up to 3 liters per day), taking a vitamin-mineral complex and dietary fiber are recommended.
- Stage of ongoing weight loss - the weekly diet provides for an increase in the daily carbohydrate component by 5 g. At the same time, the rate of weight loss will slow down. Gradually increase the daily amount of carbohydrates to a level at which weight loss slows down a little, but does not stop at all. As a rule, in different people this occurs at a level of consumption of 20-40 g of carbohydrates per day. When you stop losing weight, reduce carbohydrates, thereby activating the process of ketosis. You must determine for yourself exactly at what level of carbohydrate consumption the weight loss process continues and at what level it stops. For some, this level will be 15-30 g per day (15 g - you continue to lose weight, 30 g - weight loss stops), and for others - 40-60 g.
- Pre-maintenance stage - begins when about 3-5 kg remains before the set goal. At this stage, the weight loss process must be slowed down, which is achieved by increasing the carbohydrate content in the daily diet by 10 g each and maintaining this rate of weight loss (1.5-2 kg per month) for 2-3 months. At the same time, you must determine at what level of carbohydrate intake weight loss stops and at what rate of weight loss is minimal. At this stage, you should clearly know at what level of carbohydrate intake you stop losing weight and at what level you begin to gain weight.
- The maintenance stage is nutrition at the level of carbohydrate consumption that does not lead to weight gain, on average it is from 50 to 100 g of carbohydrates.
In principle, it is not necessary to use the entire system; you can stay in the first, stimulating stage until you reach the weight you need. Once you reach your goal, begin gradually increasing your carbohydrate intake by 5 grams per week.
Authorized products
A low-carb diet is characterized by a variety of foods, so you don’t have to go hungry during the diet. The table shows the main products that are used for weight loss.
Table: permitted products
| Indicators per 100 g of product | ||||
| Calories, kcal | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | |
| Chicken breast | 116 | 19,6 | 4,1 | 0,3 |
| Turkey | 194 | 21,6 | 12 | 0 |
| Beef | 224 | 34,72 | 8,37 | 0 |
| Veal | 89 | 20,4 | 0,9 | 0 |
| Lean pork | 172 | 30,46 | 4,62 | 0 |
| Lean fish (hake) | 86 | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0 |
| shrimps | 87 | 18,3 | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| Mussels | 77 | 11,5 | 2 | 3,3 |
| Champignon mushrooms) | 27 | 4,3 | 1 | 0,1 |
| Cottage cheese 5% | 145 | 21 | 5 | 3 |
| Low-fat kefir | 40 | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| Low-fat cheese (cheddar, colby) | 173 | 24,35 | 7 | 1,91 |
| Egg | 157 | 12,7 | 11,5 | 0,7 |
| Brown rice | 112 | 2,32 | 0,83 | 23,51 |
| Buckwheat | 92 | 3,38 | 0,62 | 19,94 |
| Oat bran | 40 | 3,21 | 0,86 | 11,44 |
| Cabbage | 28 | 1,8 | 0,2 | 4,7 |
| cucumbers | 14 | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,5 |
| bell pepper | 26 | 1,3 | 0,1 | 4,9 |
| Apples | 52 | 0,26 | 0,17 | 13,81 |
| Orange | 43 | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 |
| Grapefruit | 35 | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 |
| Green tea | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0,3 |
The table data shows that the main suppliers of protein are meat products, fish and eggs. Cereals, vegetables and fruits provide the body with the necessary slow carbohydrates.
Gallery: foods allowed on a low-carb diet

The meat of young calves is recommended for weight loss, as well as for elderly and sick people.

Low calorie content and high protein content are the main qualities of shrimp.

The advantage of vegetables is not only their low calorie content, but also that they contain a lot of fiber, which is what cleanses the body.

Qualified nutritionists recommend eating apples for weight loss

Buckwheat is not just a source of carbohydrates, but also a medicine and a beauty product

The benefits of tea for human health are undeniable, since a cup of this drink contains many of the microelements we need

Cottage cheese is widely used in diets in the treatment of liver and heart diseases, hypertension and atherosclerosis.

The benefit of grapefruit is that its fruits are an effective means of combating excess weight. Of all the known varieties of rice, the healthiest is brown rice, which ranks 17th in the ranking of healthy foods for humans.

Eggs are a food product high in protein, vitamins and mineral salts.

Chicken is a dietary product. It is much lower in calories than other types of meat. It also contains a lot of polyunsaturated fatty acids. This is important for people suffering from cardiovascular diseases

Eating champignons helps restore memory and improve human brain activity.

White hake meat is lean and very tender. This fish has practically no small bones, and its fillet is quite easily separated from the spinal bone
Fish and seafood
Fish and other seafood are generally very nutritious and healthy.

They are especially high in vitamin B12, iodine and omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids, which are elements that many people lack in their diets.
Like meat, almost all fish and seafood contain almost no carbohydrates.
Salmon (zero)
Salmon is one of the most popular fish among health-conscious people, and for good reason.
It is an oily fish, which means it contains significant reserves of heart-healthy fats, in this case, omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids.
Salmon is also rich in vitamin B12, D3 and iodine.
Carbohydrates : zero.
Trout (zero)
Carbohydrates : zero.
Like salmon, trout is a type of fatty fish rich in omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids and other important elements.
Sardine (zero)
Sardine is a fatty fish that is usually eaten almost entirely, bones and all.
Sardine is one of the most nutrient-dense fish on the planet, and contains almost everything the human body needs.
Carbohydrates: zero.
Shellfish (4-5% carbohydrates)
Unfortunately, shellfish find their way into our daily diet much less often than they deserve. However, they are on a par with the healthiest products in the world, and in terms of nutritional richness they can compete with meat from internal organs.
Shellfish typically contain small amounts of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates : 4-5 grams of carbohydrates per 100 grams of shellfish.
Sample menu for the week
The presented menu can be used for a diet lasting 7 days. This menu can be taken as the basis for low-carb weight loss. Various variations of dishes from permitted products are allowed.
Recent Entries
Is it possible to give a mirror: how to protect yourself from bad omens It became known about the influence of cell phone towers on human health Is it possible to eat bananas bought in Russia?
Low-calorie diet for weight loss:
Table: sample menu of a low-carb diet for 7 days
| Day | Breakfast | 2 breakfast | dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| 1 day | Cottage cheese casserole - 150 g, tomato or cucumber - 1 pc., unsweetened tea - 200 ml | Kefir – 100 ml | Stewed fish - 150 g, cabbage salad - 150 g, bread - 1 pc. | Grapefruit - 1 pc. | Brown rice porridge with vegetables - 200 g |
| Day 2 | Omelette of two eggs, boiled chicken - 150 g | Low-fat cottage cheese - 100 g | Mushroom soup with low-fat sour cream - 200 g, bread, unsweetened tea - 200 ml | Kefir with chopped cucumber and herbs - 200 ml | Boiled beef - 150 g, cucumber and tomato salad - 150 g |
| Day 3 | Stewed vegetables with grated cheese - 150 g | Milk – 100 ml | Vegetable soup with chicken broth - 200 g | Apple - 1 pc. | Boiled breast - 200 g, stewed cabbage - 100 g |
| 4 day | Oatmeal with apple – 150 g | Grapefruit - 1 pc. | Veal or chicken stew with vegetables - 200 g | Low-fat cottage cheese - 150 g | Buckwheat porridge - 150 g, beet salad - 100 g |
| 5 day | Cheese - 50 g, boiled eggs - 2 pcs., unsweetened tea - 200 ml | Apple - 1 pc. | Pea soup with chicken broth - 150 g, vegetable salad - 100 g, beef cutlet - 50 g | Kefir – 100 ml | Boiled brown rice - 150 g, mussels - 100 g |
| Day 6 | Cheese - 50 g, boiled egg - 1 pc., unsweetened tea - 200 ml | Natural yoghurt – 100 ml | Baked meat - 150 g, vegetable salad - 150 g | Kiwi - 1 pc. | Stewed vegetables - 200 g |
| Day 7 | Milk buckwheat porridge – 150 g | Low-fat cottage cheese - 100 g | Fish baked with vegetables - 200 g | Kefir – 100 ml | Baked breast - 150 g. |
For a longer period of low-carb diet (for example, 30 days), the amount of complex carbohydrates can be increased to normal levels every 5-6 days. This will prevent a slowdown in metabolism, which is typical for all types of diets.
Vegetables
Most vegetables contain almost no carbohydrates, especially leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables, since almost all of their carbohydrates are found in fiber.

On the other hand, starchy root vegetables such as potatoes and sweet potatoes are rich in carbohydrates.
Broccoli (7%)
Broccoli is a delicious cruciferous vegetable that can be cooked or eaten raw. It's high in vitamin C, vitamin K, fiber, and contains powerful plant compounds that may help prevent cancer.
Carbohydrates : 6 grams per cup or 7 grams per 100 grams.
Tomatoes (4%)
Technically, tomatoes are berries, but they are classified as vegetables. They have a lot of vitamin C and potassium.
Carbohydrates: 7 grams in a large tomato or 4 grams per 100 grams.
Onion (9%)
Onions are one of the tastiest vegetables on earth and add a vibrant flavor to dishes. It contains a lot of fiber, antioxidants and various anti-inflammatory components.
Carbohydrates: 11 grams per cup or 9 grams per 100 grams.
Brussels sprouts (7%)
Brussels sprouts are an incredibly nutritious vegetable, a relative of broccoli and regular cabbage. Rich in vitamin C, K and many other beneficial elements.
Carbohydrates: 6 grams per half cup or 7 grams per 100 grams.
Cauliflower (5%)
Cauliflower is a tasty and versatile vegetable that can be used to prepare varied and interesting dishes. It is rich in vitamins C, K and folate.
Carbohydrates : 5 grams per cup and 5 grams per 100 grams.
Kale (10%)
Kale or kale is very popular among health-conscious people. It is rich in fiber, vitamins C, K and carotene antioxidants. Among other things, kale in general has incredible health benefits.
Carbohydrates: 7 grams per cup or 10 grams per 100 grams.
Eggplant (6%)
Eggplant is another fruit that is often mistaken for a vegetable. It is rich in fiber and very varied in consumption.
Carbohydrates: 5 grams per cup or 6 grams per 100 grams.
Cucumber (4%)
Cucumber is a common vegetable with a mild flavor. Consists mainly of water with a small amount of vitamin K. [goes well with lard - approx. transl.]
Carbohydrates: 2 grams per half cup or 4 grams per 100 grams.
Bell pepper (6%)
Bell pepper is a well-known vegetable with a distinct, pleasant taste. It is high in fiber, vitamin C and carotene antioxidants.
Carbohydrates : 9 grams per cup or 6 grams per 100 grams.
Asparagus (2%)
Asparagus is a surprisingly tasty spring vegetable. It's loaded with fiber, vitamin C, folate, vitamin K, and carotene antioxidants. It also has a lot of protein compared to other vegetables.
Carbohydrates: 3 grams per cup or 2 grams per 100 grams.
Green beans (7%)
Green beans are technically a member of the legume family, but they are cooked and consumed as a vegetable.
Each bite contains a huge amount of nutrients, as well as fiber, protein, vitamin C, K, magnesium and potassium.
Carbohydrates: 8 grams per cup or 7 grams per 100 grams.
Mushrooms (3%)
Mushrooms, generally speaking, are not plants, but for simplicity, edible mushrooms are classified as vegetables. They contain significant amounts of potassium and some B vitamins.
Carbohydrates : 3 grams per cup and 3 grams per 100 grams (ceps).
What you can cook during weight loss: delicious recipes
Chicken fillet in a slow cooker
Ingredients:
- fillet - 250 g;
- water - 150 g;
- salt, ground pepper - to taste;
- bay leaf - 1 pc.
The chicken fillet should be washed, salted, peppered and placed on the bottom of the multicooker bowl. Pour water and add bay leaf. Set the “Extinguishing” mode for 1.5 hours.
100 g of dish contains:
- calories - 103 kcal;
- proteins - 12.5 g;
- fat - 5 g;
- carbohydrates - 0 g.

Stewed breast - a nutritious and tasty dish
Meat with cheese in the oven
Ingredients:
- veal - 400 g;
- feta cheese - 100 g;
- milk - 100 ml;
- vegetable oil - 1 tbsp. l.;
- salt, pepper, spices - to taste.
The veal should be washed in cold water, cut into pieces and beaten. Grease a baking tray with oil, place meat in it and pour milk. The prepared dish must be placed in an oven preheated to 180 °C and left for 1 hour. After this, the meat should be salted, peppered, and spices added. Cut the cheese into thin slices and place it on top, put it back in the oven and bake for another 30 minutes.
100 g of the finished dish contains:
- calories - 129;
- proteins - 15.5 g;
- fat - 6.4 g;
- carbohydrates - 0.7 g.

Veal with cheese will appeal to many people
Oat bran soup
Ingredients:
- turkey - 150 g;
- water - 1 l;
- onions - 1 pc.;
- egg - 1 pc.;
- oat bran - 1.5 tbsp. l.;
- chopped dill - 1 tbsp. l.;
- green onions - 2 arrows;
- salt, pepper - to taste.
Cut the turkey into pieces and boil for 20 minutes. Add dill, green onions and raw egg to the broth and cook for 5 minutes. Then add bran.
100 g of dietary soup contains:
- calories - 38 kcal;
- proteins - 4.3 g;
- fat - 2 g;
- carbohydrates - 0.1 g.

Bran soup allows you to gently cleanse the intestines
Salad with Chinese cabbage and fruits
Ingredients:
- medium Chinese cabbage – ½ piece;
- apple - 1 pc.;
- orange or grapefruit - 1 pc.;
- green onions - 2 arrows;
- lemon juice - 1 tbsp. l.;
- salt - to taste.
Peel the orange or grapefruit (cut out the pulp from the walls of the grapefruit, as they are very bitter). Cut all the fruits into cubes and combine with shredded cabbage. Add chopped green onions, salt and lemon juice to the salad. Mix everything thoroughly.
Sports diet for girls:
100 g of salad contains:
- calories - 33 kcal;
- proteins - 2.7 g;
- fat - 0 g;
- carbohydrates - 6.6 g.

Salad of Chinese cabbage, apples and citrus fruits has a spicy taste
Quitting the diet
To prevent the pounds from returning after a week-long or month-long marathon of a low-carb diet, certain rules must be followed:
- the number of calories consumed should be increased gradually to the daily norm, adding 50 kcal every week;
- Do not exceed the recommended amount of carbohydrates consumed per day (3–5 g per 1 kg of body weight);
- It is recommended to do a low-carb day once a week and use the menu from the proposed diet;
- We must not forget about the drinking regime - 2 liters per day of clean water;
- It is better to boil, cook in the oven and steam;
- Do not eat later than 2-3 hours before bedtime;
- It is recommended to do physical exercise.
Pitfalls of a low-carb diet
Lack of carbohydrates and increased protein intake can lead to some unwanted effects.
- Malfunctions of the liver and kidneys. These organs remove toxins from the body, including those formed during the breakdown of protein. Thus, the more protein products are consumed, the more toxic substances are synthesized, and the load on the liver and kidneys increases several times, which can lead to inflammatory processes.
- The risk of developing atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease and other diseases of the cardiovascular system. This is facilitated by an increase in the level of “bad” cholesterol in the blood during a protein diet.
- The occurrence of constipation and, as a result, hemorrhoids.
- Headaches, low mental activity, irritability and nervousness. These symptoms develop against the background of carbohydrate starvation.
- Deterioration of skin condition. Dry skin occurs due to insufficient fat.