Nutrition in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy should be comprehensive and balanced in proteins, fats and carbohydrates, as well as micro- and macroelements and vitamins. With food, a pregnant woman’s body receives those substances that go into the formation of many organs and systems of the fetus, and some of them are consumed unchanged, and some, as a result of certain biochemical reactions, are prepared for consumption by the cells of the human body.
You should also try to gain weight in accordance with accepted standards, since excess weight in a pregnant woman is extremely undesirable, as it contributes to the formation of large children, who often cannot be born on their own, and surgical delivery is required. Therefore, the unshakable principle is that the diet for pregnant women in the 2nd trimester is the nutrition of the pregnant woman. This means that the quantity and quality of food consumed must be strictly controlled.
Basic Rules
The goal of rational nutrition in the second trimester is to supply the body with building materials, and since further normal growth of the fetus and the development of its organs requires more nutrients, the daily calorie content of food should increase by 300 Kcal.
In addition, the unborn baby requires more vitamins and minerals, therefore, their consumption by the mother should increase compared to the first 14 weeks.
In the second trimester, the brain actively develops, which requires magnesium, iodine, and phosphorus. The bone skeleton continues to form, which means you need more vitamin D.
The energy value of the daily diet in the second trimester of pregnancy is 2400-2800 kcal (2500 is enough for the average woman).
The mother's body's need for protein increases, up to 2g per kg of weight. The protein content should be 120–140 g, of which 60% is of animal origin, the fat content also increases to 85 g, and 80% should be of vegetable origin. But the amount of carbohydrates is reduced to 300 grams (upper limit).
Diet
Meals in the second trimester should be fractional, up to 5-6 times a day. The growing uterus puts pressure on both the stomach and intestines, and overeating or even eating the amount of food equal to “non-pregnant” food causes heartburn and disrupts intestinal motility, which leads to constipation.
In addition, frequent and small meals promote better absorption of nutrients. The last meal should be no later than 2 hours before bedtime.
Cooking
All dishes must be steamed or baked, but without crust. Cooking and stewing of foods is allowed. This culinary treatment allows you to preserve vitamins, which are very necessary for mother and baby in the second trimester.
In addition, fried foods increase the load on the liver and gallbladder, which are already working double duty.
Salt and liquid
The second trimester of pregnancy is a period in which gestosis of the second half often occurs. Therefore, it is worth giving up salty foods and limiting salt intake to 6 grams, maximum 10 grams per day. Salt retains fluid in the body, which leads to swelling.
The same goes for liquids. Fluid intake, including soups, should be no more than 1 liter per day. Drinking a lot of water increases the load on the kidneys, and they are already functioning in an enhanced mode.
Alcohol
Everyone knows about the dangers of alcohol, especially during pregnancy. In the second trimester, the brain, cardiovascular and other important systems actively develop, so drinking alcohol even in small quantities can lead to the birth of a disabled child. Beer “loads” the kidneys, and wine is not only allergenic, but also increases blood pressure.
Product distribution
It is advisable to consume protein foods (meat and fish) in the first half of the day, and lactic acid products and fiber in the second half. Protein foods stay longer in the digestive tract, so it should be given at the time of day when the intestines actively peristalt.
Vitamins in the second trimester
The second trimester of pregnancy is often accompanied by iron deficiency anemia, so the need for iron and vitamin C, which helps better absorption of iron, increases. It is necessary to give preference to foods rich in iron and ascorbic acid.
The same goes for calcium. In the second trimester, the fetal skeleton is actively formed, and if a woman does not want to lose a couple of teeth, she should pay attention to fermented milk products.
Iodine promotes the development of the thyroid gland in the fetus and is involved in the formation of the nervous system,
Potassium prevents miscarriage and improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system,
Sodium prevents the development of edema.
However, you need to be careful with the selection of microelements, since their excess in the body is also undesirable. Therefore, it is better to trust your doctor in this matter.
Essential vitamins:
- Vitamin C promotes better absorption of calcium and iron, which are necessary for fetal bones and prevent the development of anemia, and also stimulates the immune system.
- Vitamin A is responsible for the genetic makeup and development of the retina in the fetus.
- Vitamin E prevents miscarriage.
- Vitamin D is essential for skeletal development.
- Folic acid, as well as magnesium and phosphorus, affect the development of the nervous system.
Are there any special hygiene features in the second trimester?
There is no point in discussing daily hygiene: you need to take a shower every day, since human skin actively secretes all unnecessary substances through sweat and performs respiratory and metabolic functions. During pregnancy, it is important to keep your entire body clean. Normally developing pregnancy - you can periodically visit the bathhouse and sauna, but only at a comfortable temperature, without overusing the steam room. Too high a temperature can cause high blood pressure, miscarriage and premature birth. You should be careful when visiting the bathhouse.
Prohibited Products
The list of prohibited foods includes those that increase gas formation and putrefaction in the intestines, since the longer the pregnancy, the more problems with stool.
In addition, dyes, preservatives and other chemical additives are potentially harmful to the growing fetus.
You should avoid spicy, smoked and salty foods; they irritate the gastrointestinal tract, contribute to heartburn and can provoke gestosis.
You should not get carried away with animal fats, so as not to overload the gallbladder, as well as simple carbohydrates, which lead to rapid weight gain and can affect the weight of the fetus.
You should pay special attention to allergenic products; allergies will not bring pleasant sensations to the mother, and in the future it may also appear in the child.
Heavy and difficult-to-digest foods contribute to constipation, so you should also avoid them.
List of prohibited products:
- fresh pastries, white bread, culinary products, cakes and pastries, pancakes and pancakes;
- fast food, semi-finished products;
- sweet carbonated drinks (simple carbohydrates and gas);
- legumes;
- chocolate, cocoa, strong tea and coffee (cause constipation and excite the nervous system);
- sausages, smoked meats, lard;
- marinades, pickles, mustard, horseradish, pepper;
- strawberries, nuts (hazelnuts and peanuts), honey – allergens;
- ice cream, milkshakes, condensed milk;
- canned meat and fish;
- mushrooms in any form (hard to digest);
- fatty meat, fish, poultry;
- yolk (excess cholesterol), raw and fried eggs;
- limit butter, fatty sour cream;
- red and black caviar;
- blue cheeses (risk of infection), sharp and fatty cheeses;
- raw meat and fish (sushi, stroganina) are sources of salmonella and toxoplasma.
How much weight can a woman gain during pregnancy?
Doctors “allow” a woman to ideally gain 10-13 kg of weight during pregnancy. In the first three months, body weight increases by 2 kg, then weight increases by 1.5-2 kilos per month. The first trimester is characterized by low fetal weight gain, while from the second trimester of gestation the baby grows rapidly, as does the uterus itself, the volume of amniotic fluid, and fatty tissue. The woman’s total blood volume also increases, and all the numbers added together form such a large weight gain.
Of the 10-13 kg increase, adipose tissue normally accounts for up to 4 kg, no more. Consumption of fatty, high-calorie foods during pregnancy causes an increase in the proportion of adipose tissue and the development of obesity, which threatens problems for the baby . For the pregnant woman herself, obesity is also fraught with various troubles:
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Pain in the back/lower back, development of osteochondrosis;
- Varicose veins;
- Arterial hypertension.
Authorized Products
Dishes consumed by a woman in the second trimester of pregnancy should not overload the gastrointestinal tract, ensure regular bowel movements and be easily digestible.
It is especially important to consume as much plant fiber as possible, which prevents constipation and contains a large amount of vitamins.
List of permitted products:
- whole grain or bran bread, yesterday's bread, dry biscuits (biscuits, crackers);
- porridges: buckwheat - protein and iron, oatmeal and millet - magnesium, all porridges are a source of fiber;
- carrots and juices from them - vitamin A, cranberries, lingonberries, currants, citrus fruits (with caution) - vitamin C, herbs and green vegetables - folic acid;
- rose hips, sea buckthorn, nuts, apricots and dried apricots - fiber and vitamin E;
- fish – polyunsaturated fatty acids, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin D;
- boiled lean meat and poultry are a source of protein;
- low-fat fermented milk products – calcium, improve intestinal motility;
- freshly squeezed juices, green tea, rosehip decoction;
- figs, seafood (shrimp, mussels, squid, seaweed) - a source of iodine;
- egg white omelettes;
- vegetable oils – normalize intestinal function, sources of vitamin E;
- liver, pomegranates, green apples are sources of iron;
- cottage cheese, mild and low-fat varieties of cheese.
If a woman treats pregnancy responsibly and adheres to proper nutrition, she will avoid digestive problems (heartburn, constipation, flatulence), and will also significantly reduce the risk of developing pregnancy complications (preeclampsia, diabetes mellitus, gestational pyelonephritis). In addition, a sufficient amount of vitamins and microelements will ensure normal development of the fetus.
Menu

Diet during pregnancy 2nd trimester - sample menu for the week (breakfast, second breakfast, lunch, afternoon snack, dinner):
Monday:
How to avoid obesity and regain an erection at any age?
- Oatmeal with dried fruits;
- 2 apricots;
- Chicken soup with pieces of poultry meat. 2 slices of bran bread;
- A glass of kefir;
- Buckwheat. Fish meatballs. Grated carrot salad.
Tuesday:
- Pumpkin porridge with milk;
- Pear;
- Fish soup with pieces of fish. 2 slices of rye bread;
- A handful of walnuts;
- Rice. Baked salmon steak. Greek salad".
Wednesday:
- Cottage cheese seasoned with yogurt and raisins;
- Apple;
- Creamy spinach soup with croutons. Boiled chicken breast;
- Prunes stuffed with nuts;
- Vegetable stew. Veal meatballs in tomato sauce.
Thursday:
- Buckwheat porridge with milk;
- Berry juice;
- Borscht with beef and sour cream. 2 slices of whole grain bread;
- A glass of fermented baked milk;
- Bean puree. Cod liver. Cucumber and tomato salad.
Friday:
- Cheesecakes with raisins and sour cream;
- Tomato juice;
- Pea soup with croutons. Boiled turkey fillet;
- A cheese sandwich;
- Pilaf with seafood. Beet salad.
Saturday:
- Muesli with dried fruits and nuts;
- Fruit salad;
- Broth with croutons. Fish soufflé;
- A glass of curdled milk;
- Spaghetti with cheese. Baked pike perch with spinach.
Sunday:
- Omelette of 2 eggs with tomato;
- Apple-celery juice;
- Cream of broccoli soup. Steamed beef cutlets;
- A handful of almonds;
- Mackerel baked with vegetables. Green bean salad.
In between meals during a diet during pregnancy in the second trimester, you can snack on fruits, seeds, nuts, dairy and fermented milk products.
“Space diet” by Sergei Sivokho: without denying himself anything, the comedian lost 42 kg in 3 months
How to replace cottage cheese during pregnancy
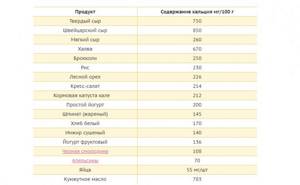
If there are no contraindications from the body, but you just don’t really like cottage cheese, you can try to diversify the taste of the product by adding dried fruits, honey or yogurt. Or try preparing some dish based on cottage cheese (cheese pancakes, casserole, cottage cheese soufflé or pudding). If you really don’t want cottage cheese during pregnancy or for health reasons you cannot include this product in your diet, use alternative sources of useful elements (including calcium and protein). There are quite a lot of products that are not inferior to cottage cheese in terms of the content of these elements. The following table will tell you which ones.
What to do with nipples that are inverted or flat?
Some women have naturally flat or inverted nipples, which will greatly interfere with feeding the baby. The baby will not be able to latch on to the nipple on his own, so the mother is forced to bottle-feed him. But even if you have flat nipples, you can straighten them a little if you start training before giving birth.
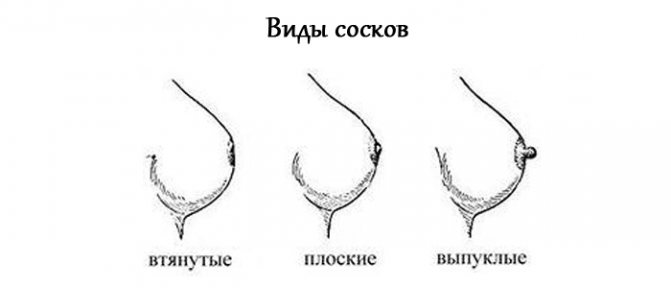
Exercises should be done several times a day, starting from the second trimester. After washing, they must be carefully pulled out and rolled between the thumb and forefinger. These exercises are done in the absence of the threat of interruption.
There is a connection between the breasts and the uterus, and excessive stimulation of the nipples can lead to contractions of the uterus. Therefore, if the uterus often comes into tone, then it is better to postpone the exercises to a later date.
Read also: How to prepare your breasts for feeding your baby (flat or inverted nipples)
Thrush and how to deal with it?
By the end of the second trimester, thrush (candidiasis) occurs in a huge number of pregnant women. It directly depends on the state of immunity, and in a woman it is greatly reduced so that the body does not “decide” to reject a foreign body - the fetus. Reduced immunity is fertile ground for the active proliferation of Candida fungi, which provoke an inflammatory disease. Another factor that increases the risk of developing thrush is a change in hormonal levels, which affects the change in pH in the genitals.
Treating candidiasis is a complex process, and the trouble is that there are no effective medications that can be used during pregnancy. And it must be treated, even if it does not occur without symptoms. It is especially important to get rid of thrush before childbirth, because the baby, when passing through the birth canal, can be infected with pathogenic fungi. All medications are prescribed only by a doctor, and it is better not for the expectant mother to use folk remedies !
Effect on the body
A proper diet has the most beneficial effect on a woman’s body. Her body systems work harmoniously, and it is possible to avoid eating disorders, poisoning, and intestinal infections.
The woman’s body receives the necessary vitamins and minerals, and she feels great. Eliminating fatty, unhealthy foods from your diet helps prevent obesity.
Healthy nutrition for the mother helps the baby develop and grow. It receives the necessary substances that allow the small organism to form correctly.
If the mother refuses junk food and does not have bad habits, the occurrence of any pathologies can be prevented. Proper nutrition is the key to the health of mother and child.
Recipes
Fruit salad for breakfast

Ingredients:
- tangerines – 2 pieces;
- kiwi – 1 piece;
- bananas - 1 piece;
- apple - 1 piece;
- drinking yoghurt – 100 ml.
Peel the banana and cut into thin slices. Apple, kiwi, tangerines are washed and peeled, cut into small cubes. Pour the prepared ingredients into a deep bowl and pour yogurt over it. You can decorate with raisins or raspberries.
Milk porridge with pumpkin

Ingredients:
- pumpkin - half a kilo;
- millet – 1 tbsp.;
- milk – 3 tbsp.
- butter - to taste;
- salt, sugar - to taste.
The pumpkin is thoroughly washed and cut into small cubes. Wait for the milk to boil in the pan, place the vegetable there, add salt and wait for it to boil again. The millet is washed several times. Combine with milk and pumpkin and cook under a closed lid for 10-15 minutes. At the end add a piece of butter. The porridge is transferred to ceramic pots. Be sure to cover with lids and place in a room heated to 130 degrees. oven for half an hour.
Broccoli soup

Ingredients:
- cabbage – 1 piece;
- potatoes - 3 pieces;
- salt - to taste.
Wash and peel the potatoes, cut into small cubes. Broccoli is divided into inflorescences. Place everything in a pan, pour boiling water over it and cook until the vegetables are ready. Drain the water, grind the contents of the container in a blender to a homogeneous consistency. You can dilute it a little with water from the pan. Place on plates and eat warm.
Iron prevents anemia.
The human body uses iron to produce hemoglobin, a protein in blood cells that carries oxygen to organ tissue. Iron also makes you more resistant to stress and illness, and prevents fatigue, weakness, irritability and depression.
During pregnancy, a woman's total blood volume increases. In this way, the body “adapts” to the new physiological situation, and the child’s circulatory system also starts up. As a result, the expectant mother's need for this mineral doubles.
When iron is deficient, a pregnant woman may experience fatigue and be more prone to infections. In addition, a lack of this element is also dangerous for the fetus: the risk of premature birth and low birth weight of the child increases.
How much is needed: 20 mg per day.
Best natural sources: liver, lean red meat (especially beef), poultry, fish, whole grains, eggs, legumes, buckwheat, pomegranate, apples, beets, peaches, apricots.
Is it possible or not?
Cottage cheese is essentially a dairy product. This is the thickened part of sour milk, which is freed from the liquid component - whey. The product can and should be eaten by pregnant women if the woman herself wants it. But you shouldn’t force yourself, despite all your dislike for cottage cheese, to eat this product. And here's why - the benefits of cottage cheese as a storehouse of calcium are somewhat exaggerated . Judge for yourself - 100 grams of product contains about 120 mg of calcium. And the daily requirement of a pregnant woman for this element is on average from 1500 to 2000 mg.
It turns out that in order to cover the daily requirement for calcium, a pregnant woman needs to eat more than a kilogram of cottage cheese. In such quantities, a fermented milk product is unlikely to be beneficial. That is why cottage cheese is a voluntary activity. If you want, eat, if you don’t want, don’t force yourself. There are foods that are also rich in calcium and may well be sources of the element in the diet, for example, fresh greens, certain types of fish, in particular sardines, Parmesan cheese and sesame seeds.
The need for calcium when carrying a baby is great. It is especially important that a woman consumes enough of it in the middle of pregnancy, when the process of mineralization of the baby’s bones is underway. But whether this need will be satisfied with the help of cottage cheese is not significant.
It is important to include foods high in calcium in your diet.

What dishes are excluded
From the 4th month of pregnancy the following is removed from products:
- all very fatty types of meat;
- any sausages;
- fried, pickled, smoked and overly salted dishes;
- sausages;
- cream confectionery;
- hot sauces and spicy seasonings;
- garlic, onion;
- alcoholic drinks.
Be careful when including citrus fruits and strawberries on the menu because of the risk of the baby developing allergies in the future.
How to avoid food allergies in your unborn child
In Russia, about 20% of children in the first year of life suffer from food allergies. The reasons are heredity (more often develops in children whose parents themselves suffer from allergies), maternal smoking during pregnancy, frequent viral infections and poor nutrition (excessive consumption of allergenic foods during pregnancy or a strict hypoallergenic diet). List of allergenic foods that you should eat less or less often from the second trimester:
- Milk - no more than 300 ml/day (if it is very difficult to refuse, it is better to drink goat milk), since most often children under one year old develop a food allergy to cow's milk protein.
- Chicken eggs – 1 pc. 2-3 times a week, it is better to eat yolks without proteins, because they are an allergen, avoid chicken meat.
- Nuts (walnuts are more useful, peanuts and hazelnuts are more allergenic), it is better to eat them dried, since vitamins are lost during frying, you can only 100 g and no more than 1-2 times a week.
- Eat cocoa and chocolate no more than once a week.
- Fruits, berries and vegetables with a “bad” reputation - strawberries, raspberries, citrus fruits, mangoes, peaches, tomatoes.
- It is better to exclude honey completely, or eat 1 spoon for a cold or insomnia.
- Packaged food containing preservatives, thickeners, stabilizers, color, taste and aroma enhancers can be completely excluded.
Red fish, crabs and shrimp – no more than once a week.










