Cellulose. Products containing fiber
The composition of any food product that is of organic origin includes so-called hollow fiber. Intertwined with each other, these fibers form compounds without which the human body could not exist and function at the proper level. Fiber is a plexus of such hollow fibers; in the medical literature it is also known as cellulose and granulosa.
It should be noted that the body requires a fairly long period of time to absorb fiber as such, since fiber is the rough part of plants that is not digested by the body. However, despite this fact, this “slow-acting” carbohydrate is extremely important for ensuring the normal digestion process. That is why it is so important to eat foods containing fiber - once it enters the body, it passes through all its systems in transit and, thus, simultaneously collects and removes all food debris, poisons, toxins, and excess fat. In other words, fiber of plant origin is the orderly of the gastrointestinal tract and, I must say, it copes well with the functions assigned to it.
It's no secret that the products that enter us have a direct impact on our health, our well-being and, naturally, our appearance. Together with them, these products bring vitamins, minerals and other useful substances that will undergo splitting, transformation and absorption by plasma. The situation is completely different when fiber enters the body. This element does not undergo either the stage of decomposition into useful components, or the stage of digestion by the stomach; in fact, it leaves our body in the form in which it entered it, however, it plays a primary role in maintaining order and balance in the body.
Fiber performs a number of very important functions, namely:
- Normalization of metabolism and restoration of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Products containing fiber initiate the process of rapid, but completely safe weight loss. Having eaten even a small portion of such foods, we feel full, and the hated extra pounds begin to evaporate;
- Normalization and reduction of blood sugar concentration;
- Peristalsis is activated and stimulated (the process of contraction of organs in order to move their contents to the exit);
- The lymphatic system is actively cleansed;
- Toxins, waste, intestinal and gastric mucus, excess fats come out;
- Cholesterol is reduced, and this is an excellent prevention of cardiovascular diseases;
- Active strengthening of muscle fibers occurs;
- According to some scientists, the risk of developing cancer is reduced.
Today, in pharmacies you can purchase a huge number of dietary supplements rich in fiber, however, it is still better to give preference to natural products and fiber of plant origin.
Properties of fatty tissue
There is such a thing as adipose tissue - this is a mesh layer of skin, which is penetrated by collagen fibers and is located immediately under the skin itself (dermis). This mesh contains special “lobules of fat” that form our animal or subcutaneous fat.
What is fatty tissue needed for? This is connective tissue that provides shock absorption and thermal insulation to the body. In some cases (at different stages of obesity), the weight of fatty tissue can be from 10 kg, and the localization is different in men and women. Women accumulate fatty tissue mainly in the thighs and buttocks, and men - in the chest and abdomen. According to statistics, this connective tissue reaches its greatest thickness (up to 5 cm or more) in the hips, and the smallest thickness occurs in the eyelids and genitals.
The properties of fatty tissue include the following features:
- Energy. Fat is an important source of energy reserves in the body. Fat reserves are used up during periods of intense energy expenditure or during fasting.
- Thermal insulation. Heat is lost slowly through fat, which is useful in cold climates. The thicker the layer of fat, the less a person freezes at low temperatures. However, in excess amounts, fat spoils the figure, lowers self-esteem, and, in addition, adds problems in the “heart” part. Excess weight is a prerequisite for coronary heart disease, hypertensive crisis, diabetes mellitus and even skeletal-deforming osteoarthritis.
- Protection. Fat protects all internal organs from overheating and also increases skin elasticity. Shifting in different directions, the dermis seems to “slide” over the subcutaneous fat and has much less damage.
- Accumulation. Fat is the body’s reserve for “hungry” times. In addition to the fiber itself, the body accumulates other useful substances in subcutaneous fat. For example, estrogen hormones, which are important for the sexual function of the body, as well as vitamins A, D and E.
- Production of hormones. In addition to natural accumulation, fatty tissue is capable of independently producing important hormones. For example, leptin, which is responsible in our body for the feeling of satiety, etc.
We recommend reading: The benefits and harms of yeast-free bread for your figure, calorie content and recipes
It is important to know!

Foods rich in fiber have a beneficial effect on the health of the whole body, since the intestinal microflora depends on them. Fiber, the so-called ballast substances, is a complex carbohydrate that includes non-starch polysaccharides, resistant starch and/or cellulose.
In other words, these are fibers found in plants, namely stems, roots, fruits, leaves and stems. Most often, such substances are found in low-sugar plant foods, combining with other beneficial substances. One of the main properties of fiber is to slow down the absorption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, which is very useful for weight loss and excess weight gain. Many people wonder what foods contain fiber? When answering this question, you need to remember that this substance is not found in products of animal origin; it is found only in products of plant origin.
Digestive Health Support
Plant fiber is known for its ability to improve intestinal motility and counteract constipation, but its healing properties are also manifested in the case of other diseases of the digestive system.
For example, diverticulitis - inflammation of the intestines - is one of the most common age-related digestive disorders in the modern world.
According to a study published in the Journal of Nutrition, consuming foods rich in insoluble fiber reduces the risk of diverticulitis by 40%!

What is fiber
Fiber is the name given to plant fibers produced from certain parts of plants. Simply put, these are complex carbohydrates that make you feel full. The most common examples of fiber are plant grains, seed skins, cabbage leaves, and bean stems. All these components are not poisoned by enzymes of the digestive tract, but are delivered to the intestines for processing, or rather, to the beneficial microflora living in it.
A logical question arises: if fiber cannot be absorbed, why is it needed at all and what are its benefits? The main task of the plant component is to help the gastrointestinal tract digest and eliminate food faster. The fact is that the longer food remains inside the digestive tract, the more difficult and difficult it is for the body to get rid of it: bloating, flatulence, and gas formation appear. Fiber can speed up the process of eliminating food naturally, which is why it is primarily indicated for those who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Types of fiber
There are two main types of fiber:
- Soluble fiber.
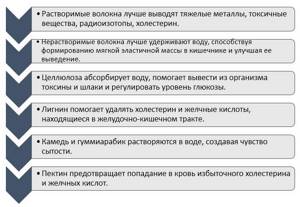
This includes lignin and cellulose. Dissolving in water, it leaves behind a stretchy mass that can reduce glucose and cholesterol levels. Contained in the following products: plantain, beans, oats, apples, peas, citrus fruits, carrots. The most famous representative of soluble fiber is pectin. It is able to absorb a fairly large amount of moisture and form a jelly-like composition. In addition to the listed properties, soluble fiber removes bile acids and “bad” substances from the body that interfere with its normal functioning. - Insoluble fiber.
The following type of dietary fiber is not digested by gastrointestinal enzymes and helps speed up the process of bowel movement. An ideal solution for those who suffer from constipation - in a short time the stool returns to normal. This fiber is found in flour, nuts, bran and some vegetables. Its work is similar to a sponge - it absorbs bile acids, cholesterol, radionuclides and even salts of heavy metals, then promotes their rapid removal from the body.
Different foods contain different amounts of dietary fiber, so to maximize their effectiveness, it is recommended to eat a varied diet.
Functions of fiber
Fiber performs a huge list of important functions, the main one of which is facilitating the passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract. Due to its composition, when it enters the intestines along with food, it forms a food lump. It easily passes to the “exit”, so heavy foods do not stay long in the digestive tract. It is due to the consumption of a sufficient amount of fiber that the human body works smoothly, without failures or difficulties. With a lack of plant fibers, the gastrointestinal tract begins to function like an avalanche, which is why undesirable symptoms appear over time.
In addition to the sorbing function, fiber is also responsible for:
- improvement of stomach function;
- the appearance of a quick feeling of satiety while eating;
- reducing the risk of developing colon cancer;
- decreased appetite;
- intestinal motility;
- nutrition of beneficial intestinal microflora;
- intake of a sufficient amount of minerals, vitamins and microelements into the body;
- reducing blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Another beneficial property of fiber is that it prevents the rapid absorption of fats in the small intestine, which is why sugar enters the blood slowly, and not at lightning speed. This, in turn, does not increase insulin production, which is especially important for diabetics.
Important for maintaining a healthy weight
By increasing your fiber intake by just 14 grams per day, you can reduce your calorie intake by 10 percent and still feel full and satisfied.
Soluble fiber mixes with water in the intestines to form a gel-like substance. This gel slows down the absorption of sugar into the blood. It also activates receptors in the stomach, which send a signal to the brain that we are full. So, a person feels full after consuming the same amount of food, even if that food contains fewer calories.
Beneficial properties of fiber
Fiber is unique; it helps stabilize the body. No wonder it is recommended for use by both adults and children. In order for the body to function normally, we must not forget to include coarse dietary fiber in the diet. And these are not only fruits and vegetables, but also grain products. For example, wholemeal rye bread. Fiber helps digestion by absorbing harmful toxins, it pushes out the remains of undigested food, thereby improving intestinal function and peristalsis. Fiber or cellulose, which is found in plants, does not provide energy to the body, but it must be present in the diet.
Fiber has the following properties:
Stabilizes the body's urinary system and improves intestinal function. Including fiber in the diet relieves irritable bowel syndrome, constipation, and hemorrhoids; A diet balanced with fiber allows you to lose excess weight faster. You eat fewer calories and feel better; Fiber helps lower blood cholesterol levels, which in turn reduces the risk of cardiovascular pathologies, strokes, and heart attacks. For stable heart function, he recommends consuming foods with high levels of soluble fiber (rice, flax seeds, legumes, oat bran); Fiber contains active components that help lower blood sugar levels. Endocrinologists recommend using it for people suffering from diabetes. It is indicated for obesity and endocrinological pathologies of the body.
As you can see, simple fiber contained in vegetables, fruits, and cereals is an important component that maintains good health.
Why you should get your fiber from food rather than supplements
The shelves of pharmacies and health stores are replete with fiber supplements. Therefore, a reasonable question arises - why not get the right amount of it by taking supplements, rather than from food.
Fiber supplements usually contain only a small proportion of the required dietary fiber. And fiber sources are often suspect. Beware of taking any supplements containing methylcellulose (synthetic cellulose), calcium polycarbophil, or wheat dextrin as they have no nutritional value or nutrients and are synthetic.
Additionally, according to a study conducted at the University of Maryland Medical Center, people taking certain medications (diabetes medications, cholesterol-lowering medications, antiepileptic drugs, and some antidepressants) are not recommended to take fiber supplements because it may interfere with the absorption of these medications. medicines and some minerals.
Tags: Fiber
- Related Posts
- Vitamin D2 and D3: what's the difference?
- Shark liver oil: beneficial properties, uses, side effects
- 9 most important eye vitamins for improving vision: list
« Previous entry
Fiber requirement standards. Table by age
Everyone should get enough fiber daily.
It is recommended to get fiber from a variety of foods rather than overloading your body with monotonous foods.
The most important sources are legumes and grains, fruits and vegetables. For example, 1 piece of bread made from whole wheat contains 3 g of fiber, 200 g of oatmeal - 4 g, 200 g of boiled dark beans - 15 g.
If it is impossible to compensate for the body’s needs with usual food, it is necessary to include specialized biologically active food supplements or medications. Before treatment you should consult your doctor.
You should try to consume your daily amount of dietary fiber. They can be obtained from grains and legumes, vegetables, fruits, as well as by taking certain medications and dietary supplements.
The daily fiber requirement is approximately 25-30 g, but most people have no more than 15 g of this substance in their diet.
For normal intestinal functioning, EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) recommends following the following consumption standards:
| Age | Floor | Daily requirement | |
| 1-3 years | boys and girls | up to 14 g | |
| 4-7 years | 17-19.5 g | ||
| 8-12 years | 22-25 g | ||
| 13-18 years old | boys and girls | 25-31 g | |
| 19-30 years old | 22-35 g | ||
| 30-50 years | men | 40 g | with a non-standard diet 14 g per 1,000 kcal |
| women | 25 g | ||
| over 50 years old | men | 30 g | |
| women | 21 g | ||
To prevent organ pathologies, as well as type 2 diabetes, it is necessary to include in the daily menu more dishes and foods rich in fiber - the volume of its consumption should be at least 30 g every day. Experts give a similar recommendation to people with cancer and obesity.
Daily Fiber Value
The norm of fiber for our body per day is an extremely controversial indicator. Doctors in the field of nutrition recommend consuming the substance in amounts of 5 to 25 g. This is what Western medicine says. Russian nutritionists claim that our Slavic ancestors in the distant past received much more - from 25 to 60 g of fiber, and their body always worked like a clock.
The compromise solution is the golden mean of 35 g. This is the amount of fiber that should be supplied daily to the body of a modern person with a variety of foods.
Thus, it is possible and necessary to introduce fiber into your diet not only in order to cleanse the gastrointestinal tract of toxins, improve the peristalsis of the small and large intestines, and also reduce cholesterol, but also help your body lose weight to its own norm and permanently consolidate the effect of lightness and harmony your body.
Source
More articles from the section “Benefits and harms of products”

The benefits and harms of lard, composition, how many calories

Green buckwheat: benefits and harms, calorie content, beneficial properties

Pumpkin juice - beneficial properties and contraindications for women, men and children

What kind of grain is couscous, benefits and harms, calorie content
Why is excess dangerous?
Everything is good in moderation. Fiber is no exception.
Excess fiber entering the body can lead to a number of dyspeptic disorders (increased gas formation, cramping pain in the lower abdomen).
The symptom complex is caused by the activation of enzymatic processes and the retention of food particles in the lumen of the digestive tube.
It is recommended to meet the body's daily requirement for dietary fiber in order to avoid consequences such as flatulence and abdominal pain.
Fiber-rich foods - benefits and contraindications
Why doesn't our body want/can't digest fiber?
The answer is simple: it will take a lot of time to process the rough parts of plants, but their transit through the body ensures cleansing of food waste, waste and toxins, and the presence of carbohydrates is necessary for a feeling of fullness.
For this reason, dietary fiber can be considered the intestinal orderlies and the best friends of a thin waist.
Unlike food, which goes through a long process of digestion, fiber is excreted in its original form, however, it can be soluble and insoluble.
What does this mean: in a healthy intestine with balanced microflora, bacteria live that can destroy hard dietary fiber.
With their help, soluble compounds are formed in the large intestine. They take on a jelly-like state and are partially absorbed.
Fiber is found in vegetables and fruits
The degree of solubility can be determined by the peel of the fruit - the thinner and softer it is, the more the fibers are broken down.
The soluble group consists of resins, alginates, and pectins. Insoluble - cellulose, lignin, hemicellulose.
What fibers do
- stimulate metabolic processes, accelerate metabolism;
- control insulin levels, preventing the development of diabetes;
- reduce the risk of developing intestinal pathologies and cancer;
- reduce the amount of food consumed, filling the stomach - this gives a feeling of fullness and helps control weight;
- have a laxative effect, removing harmful substances.
There are two types of fibers in nature – soluble and insoluble. The former are needed to control glucose levels. Insoluble is the same “brush” for the body that helps our intestines regularly cleanse themselves of toxins and absorb nutrients. There is a lot of such fiber in vegetables, nuts, seeds, bran and other plant foods.
What to do for vegetarians
Meat, fish, milk and other foods of animal origin do not contain this complex carbohydrate at all. But animal products contain many essential amino acids. Therefore, switching to one type of diet without correcting the lack of microelements with the help of nutritional supplements is a wrong approach that can affect your health.
- Is it possible to lose weight by being a vegetarian?
How much should you eat per day
For normal functioning of the whole body, fiber intake should be in the range of 25 to 50 grams per day. Men need a little more, from 35 grams, but within the same limits. Most people consume about half the normal amount of complex carbohydrates - this is evidenced by the increase in the number of digestive diseases.
To get into the norm, you need to eat oatmeal for breakfast, vegetables throughout the day and a few fruits for a snack. There are many variations, but this is the basis of proper nutrition.
Let's see how much fiber is found in different types of foods
| Fruits, berries and dried fruits rich in fiber: | ||||||||||
| Raspberries | 5,1 | Black currant | 3,0 | Gooseberry | 2,0 | A pineapple | 1,2 | |||
| Strawberries | 4,0 | Dried apricots | 3,2 | Quince | 1,9 | Avakado | 1,2 | |||
| Dates | 3,5 | Figs (fresh) | 3,0 | Olives | 1,5 | Peaches | 0,9 | |||
| Banana | 3,4 | Red Ribes | 2,5 | Orange | 1,4 | Apricots | 0,8 | |||
| Raisin | 3,1 | Cranberry | 2,0 | Lemon | 1,3 | Grape | 0,6 | |||
| Vegetables, roots and greens rich in fiber: | ||||||||||
| Corn | 5,9 | Rhubarb (stalks) | 1,8 | Pumpkin | 1,2 | Sorrel | 1,0 | |||
| Dill | 3,5 | Radish | 1,5 | Carrot | 1,2 | Cauliflower | 0,9 | |||
| Horseradish | 2,8 | Sweet green pepper | 1,4 | White cabbage | 1,0 | Cucumbers (ground) | 0,7 | |||
| Parsley root | 2,4 | Sweet red pepper | 1,4 | Celery | 1,0 | Green onion | 0,9 | |||
| Parsnip | 2,4 | Turnip | 1,4 | Potato | 1,0 | Radish | 0,8 | |||
| Fiber-rich beans, nuts and seeds: | ||||||||||
| Peanut | 8 | Chestnut | 6,8 | Peas | 5,7 | Lentils | 3,7 | |||
| Brazilian nut | 6,8 | Sunflower seeds | 6,1 | Beans | 3,9 | Coconut | 3,4 | |||
| Fiber-rich breads, pasta and cereals: | ||||||||||
| Oat groats | 2,8 | Oat flakes “Hercules” | 1,3 | Pearl barley | 1,0 | Millet. bread flour 1 tsp. | 0,2 | |||
| Corn bread | 2,5 | Buckwheat porridge kernel | 1,1 | Rice porrige | 0,4 | Supreme pasta varieties | 0,1 | |||
| Corn grits | 1,8 | Rye bread | 1,1 | Wheat porridge | 0,7 | Wheat flour 1 tsp. | 0,2 | |||
| Barley grits | 1,4 | Peas | 1,1 | Semolina | 0,2 | Pasta 1 s. | 0,2 | |||
The effectiveness of fiber in losing weight
A huge number of people suffer from excess weight problems. But there are effective ways to correct your figure. You can try a lot of new-fangled diets, but simple fiber, when consumed correctly, helps you lose excess weight naturally. This is a natural remedy, the effectiveness of which has long been tested by time.

The structure of fiber promotes the absorption and elimination of substances unnecessary for the body. Even a small amount of fiber, swelling in the stomach, turns into a kind of gel-like mass, which gives a feeling of fullness and creates soft conditions for digestive activity. This applies to soluble fiber. Insoluble fiber passes through the gastrointestinal tract unchanged and has a moderate laxative effect. Thanks to this, weight stabilization occurs.
Fiber, among other things, when it enters the stomach, increases significantly in volume, and a person begins to feel full. And this feeling does not leave a person for quite a long time. You eat less, feel full quickly and lose weight. Don't expect instant results from fiber. The body will gradually get used to the new diet and adapt to it. But the result will definitely be good, since you will not only be able to lose weight, but also cleanse your body of harmful substances accumulated in it. This type of eating behavior guarantees longevity and health; it is recommended by many leading nutritionists.
Products with dietary fiber and rules for reasonable weight loss
Regular consumption of foods high in fiber helps you lose extra pounds and maintain a healthy weight. A sufficient amount of dietary fiber can speed up metabolism at rest, that is, when a person burns some calories without engaging in sports or other physical activity.
Most foods high in fiber (fruits, vegetables, greens) are low in calories. Those who want to lose weight need to eat more of these foods to feel and look healthy. They quickly saturate the body, which helps eliminate excess weight and maintain excellent physical shape.
The rules for losing weight with dietary fiber dictate the following points:
- You need to consume 20 g of fiber daily. This volume is provided by 800 g of vegetables and fruits eaten with peel;
- pearl barley, buckwheat, oatmeal, as well as brown rice will provide up to 5-7 g of fiber in the diet;
- 100 g of whole grain bread contains up to 6 g of dietary fiber;
- 2 times a week it is necessary to introduce into the diet dishes prepared with the addition of lentils, beans or peas;
- Every day you need to consume up to 6 tbsp. l. steamed bran;
- confectionery sugar must be replaced with dried fruits;
- During snacking periods, you should eat nuts or seeds.
To lose weight, you need to eat fiber-rich foods in the morning. Also, nutritionists do not recommend drinking water with food.
The menu should be compiled according to the following principle:
- salads – 25% of the diet;
- fruits – 25% of the diet;
- fresh or cooked vegetables - 25% of the diet;
- cereals and legumes – 10% of the diet;
- nuts – 10% of the diet;
- vegetable fats – 5%.
Most products of plant origin contain dietary fiber, but the following are considered the best (in descending order of the amount of fiber they contain per 100 g of product):
- Wheat bran – 46.6 g.
- Chia seeds – 34.4 g.
- Flax seeds – 27.3 g.
- Dried porcini mushrooms – 26.2 g.
- Poppy seeds – 19.5 g.
- Buckwheat grain – 14.0 g.
- Beans – 12.4 g.
- Lentils – 11.5 g.
Dietary fiber is an essential part of a healthy human diet. When calculating the daily menu, it is advisable to use a table of the content of these substances in food products. In this case, it will be possible to say with confidence that the body will receive a sufficient amount of fiber for its normal functioning.
Fiber as the “elixir of youth”
We hear a lot about the power of superfoods, their ability to prolong life and keep us in great shape. Fiber may be the best of them all!
The results of the analysis, published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, show how powerful the impact of consuming fiber is on our health. Scientists analyzed 17 studies involving nearly a million people and found that every 10 grams of fiber consumed per day reduced the risk of premature death by 10 percent.
What fibrous foods are allowed during pregnancy?
Dietary fiber in food consumed daily brings undeniable benefits to the body. This is especially important for women carrying a child. It is important for them to compose their menu in accordance with the tables of fiber content in products so that it is as balanced as possible.
The daily diet of pregnant women must include fresh fruits and vegetables.
They help normalize stool and regular bowel movements, and also help maintain stable blood glucose levels. They are recommended to eat up to 2 kg of vegetables and fruits daily. At the same time, apples, pears, apricots and peaches should be consumed with the peel, since it contains the most dietary fiber.
The main sources of fiber for pregnant women are whole grain products. Rice, rye and wheat bran are high in dietary fiber. However, their excess in the body prevents the normal absorption of other nutrients obtained from their food.
In addition, nutritionists recommend adding peas and lentils to your diet. In addition to their high dietary fiber content, they are sources of iron, calcium, zinc, and phosphate.
It is especially useful to enrich the diet with foods rich in fiber for pregnant women in the last trimester. During this period, the fetus begins to put pressure on the organs of the digestive system, which causes problems with digestion of foods.
Key role in cancer prevention
Plant fiber is an important part of our excretory system. It constantly eliminates toxins and carcinogens before they have a chance to affect the body. For example, it prevents the development of colorectal cancer by reducing the transit time of the intestines - literally sweeping out all the harmful residues.
In a National Cancer Institute study called Polyp Prevention, published in the Journal of Nutrition, participants were placed on a high-fiber diet (lots of fruits and vegetables). Scientists have focused on studying recurrent colorectal adenomas (polyps).
According to the test results, it turned out that the appearance of relapses of adenomas was directly related to the amount of beans consumed by the experimental subjects. The scientists believe that beans were the largest source of dietary fiber for most study participants.
However, dietary fiber not only reduces the risk of colorectal cancer. Fiber can also protect us from other forms of cancer, including breast, prostate (prostate), mouth and throat cancer.
Every 10 grams of plant fiber we consume is associated with a 10 percent reduction in the risk of colorectal cancer and a 5 percent reduction in the risk of breast cancer, according to a study published in the Annals of Oncology.
Another study published in the Official Journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics found that women who ate 28 grams of fiber per day had a 24% lower risk of developing breast cancer before menopause compared to women who ate only 14 grams per day.
Women who consumed more dietary fiber also reduced their lifetime risk of developing breast cancer by 16%.

Recommendations for dietary fiber consumption
Knowing the list of foods high in fiber, you can change your diet.
It is best to eat fruits and vegetables raw. A significant amount of fiber is lost during cooking. It is recommended to stew or lightly fry vegetables.
Fiber is not able to be destroyed during peeling of fruits or vegetables. You should know that fiber is not completely preserved in juices. Therefore, when drinking orange juice or an orange, it is better to eat the fruit.
Instead of sweets, it is recommended to eat fruits or dried fruits.
A healthy person needs to take about 30 grams per day. fiber. You can get it by eating foods rich in fiber.
It is advisable to cook porridge for breakfast every day. It supplies the body with vitamins, microelements and minerals. Porridge helps keep the body in good shape. In addition, eating porridge will charge you with energy and a feeling of fullness for a long time. One serving of oatmeal contains 5 grams. fiber. To increase the daily dose, you can add any fruit or dried fruit to it.
When consuming fiber, you should drink plenty of fluids. If you do not follow the drinking regime, then dietary fiber will inhibit or block the exit of food from the intestines.
Some types of fiber can be harmful if you have digestive difficulties. Eating large amounts of fiber in old age may cause digestive problems. Elderly people may complain of increased gas formation, stool upset, etc.
In this case, you need to be careful when consuming fiber.
Excess fiber in the body can cause diarrhea. Eating hard-to-digest foods should be done slowly and gradually to achieve the required fiber levels.
People who suffer from certain gastrointestinal diseases should monitor the amount and type of fiber they consume.
If you have irritable bowel syndrome, you should be careful. Excessive consumption of plant fibers contributes to exacerbation of disease symptoms.
For chronic diseases, doctors usually recommend strict diets. You should consult with a specialist in advance to avoid further problems. It is necessary to reduce the amount of foods containing fiber for ulcers, colitis and individual intolerance.
In therapeutic and healthy nutrition, fiber is an indispensable component. To improve your well-being and stay healthy, you should include dietary fiber in your diet every day.
Controlling Blood Sugar and Fighting Type 2 Diabetes
Dietary fiber has a unique ability to regulate blood sugar levels. This is why nutritionists recommend that diabetic patients consume beans and legumes. These fiber-rich energy sources help slow the absorption of glucose and also regulate blood sugar levels over time.
In a study published in NutritionJournal, researchers tested the glycemic response of traditional beans in rice dishes compared to plain rice.
Seventeen men and women with diabetes were divided into groups, one of which was fed regular white rice, and the other was fed white rice and beans. The researchers measured the participants' blood glucose levels after 90, 120 and 150 minutes. The results showed that the group that ate beans with rice had better control over their blood sugar levels.
So, if you have diabetes, prediabetes, or simply want to have more stable blood sugar levels, feel better, and have more energy, you need to eat a fiber-rich, low-sugar, plant-based diet (legumes, chia seeds, flax).
Our clients with type 2 diabetes report that simply adding chia seeds (1 tablespoon per day - about 5 g of fiber) to their daily diet, after just a week, reduced their blood sugar levels from 11 to 5.5-7 mmol/ l.

How to take fiber correctly
There is another, pharmaceutical variety of dietary fiber, which is sold in dry form. It is suitable for those who, due to constant employment, cannot maintain their usual diet.
To properly take fiber in this form, you need to follow these rules:
- We start with ½ spoon per day and gradually increase the dosage. To avoid unwanted consequences, the permissible amount is 2 tbsp. l. It is recommended to divide it into several doses.
- The right time is 30 minutes before meals, adding dry powder to some liquid: juice, fermented baked milk or yogurt.
- In between doses, it is recommended to drink as much water as possible.
It is important to understand that fiber is not a panacea for all gastrointestinal diseases. This product, of course, has a beneficial effect on the body, but cannot in any way heal it from existing pathologies. That is why before you start taking plant fibers, you should definitely consult with a specialist. After all, there are diseases for which fiber is strictly contraindicated: enterocolitis, stomach ulcers, infectious etiologies, chronic gastritis of unknown origin.
To improve your overall health, in addition to enriching your diet with fruits and vegetables, start moving more, drink more water and give up bad habits. And the result will not take long to arrive, believe me!
Can fiber be harmful?
Possible harm from fiber can be reduced to zero if you consume it in moderation and not on an empty stomach. It is best to consume foods containing fiber along with some liquids, for example, if you eat oat porridge, then the first course of this meal should be vegetable soup.
We recommend reading: Health benefits of quince, benefits and harms, features of use
Note! The only contraindication when introducing fiber into your diet is intolerance to this substance or acute attacks of gastrointestinal diseases, for example, stomach and duodenal ulcers.
Summarize
- Dietary fiber (fiber) has long been recommended for digestive problems such as constipation, but it also plays many other important roles in your body.
- For example, the dietary fiber in plant-based foods can promote optimal gut health, help you manage your weight, and even reduce your risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Unfortunately, most people do not consume enough of this important nutrient.
- Luckily, high-fiber foods are easy to add to your diet. Eating healthier whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds is an easy and delicious way to increase your fiber intake and improve your health.
Sources
- https://www.oum.ru/yoga/pravilnoe-pitanie/produkty-soderzhashchie-kletchatku/
- https://violetnotes.com/?p=694
- https://dietologiya.info/komponenty/45-kletchatka.html
- https://trenirofka.ru/all/v-kakih-produktah-bolsoe-soderzanie-kletcatki.html
- https://quickdiets.ru/pischevye-volokna-v-produktah-pitaniya.html
- https://WikiFood.online/nutrients/kletchatka-rastvorimaya-i-nerastvorimaya.html
- https://ya-krasotka.com/1320815907005270864/20-produktov-bogatyh-kletchatkoj/
- https://edaplus.info/food-components/cellulose.html
- https://www.magicworld.su/o-poleznom/1046-pishchevye-volokna-chto-eto-takoe-chem-polezny-spisok-produktov.html
[collapse]
Food allergies and fiber
If you suffer from food allergies, getting enough fiber from certain foods can be a challenge. You will have to look for appropriate products that do not cause allergies. Therefore, getting the required amount of dietary fiber daily may be a little more difficult for you than for people without allergies. Pharmacies can help solve the problem. They sell dietary fiber in the form of supplements that are added to food or taken as a meal on its own.
High fiber foods that may cause allergies:
- apples
- pears
- fresh melons
- broccoli
- potato
- carrot
- swede
- green bean
- zucchini
- pumpkin