4.7
(6)
Vitamin B12, or cyanocobalamin, is a substance involved in many vital processes. Therefore, you should know what vitamin B12 is, what foods it contains, and what the consumption rate is.
- Salmon
The important role of vitamin B12 in the body
The vitamin is involved in DNA synthesis and maintains the general condition of the body. Additional intake of cyanocobalamin is recommended for the prevention of many diseases.
Benefits of B12:
The role of cyanocobalamin (B12) for the human body.
- Prevents the development of cancer. In combination with vitamin B9, it stops damage to the cell’s deoxyribonucleic acid chain. This damage can cause some types of cancer to develop.
- Improves brain activity. Taking the vitamin is recommended for older people to prevent Alzheimer's disease. It is also necessary to improve memory, attentiveness, and eliminate signs of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- Helps cope with depression. With the participation of cyanocobalamin, a hormone is produced, which affects mood changes. With a lack of B12, depression occurs 2-3 times more often than in the absence of vitamin deficiency.
- Prevents anemia. The vitamin is involved in the production of healthy, mature red blood cells.
- Replenishes energy reserves. Nutrients are converted into energy needed by the body with the help of vitamin B12.
The consequence of a lack of cyanocobalamin can be the appearance of psychological problems, decreased performance, fatigue, paralysis due to damage to nerve cells.
Causes and symptoms of deficiency

The body excretes cyanocobalamin in bile. Its destruction takes a long time.
A lack of vitamin B12 occurs with a long-term refusal of foods containing it - meat, liver, fish, milk, eggs. The preservative E200 can also cause the destruction of cyanocobalamin.
The reason for the deficiency is a violation of its absorption in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - atrophic gastritis, enterocolitis, helminthic infestations.
Regular deficiency for 5-6 years is the cause of the development of B12 deficiency anemia. The pathological condition disrupts the formation of deoxyribonucleic acid, the metabolism of fatty acids, reduces the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin, and affects the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system. This type of anemia causes diseases of the liver, kidneys, and blood.
Other causes of B12 deficiency anemia are taking medications for seizures, birth control, and excessive consumption of foods containing yeast.
Diseases of the stomach, biliary tract, and intestines cause secondary vitamin deficiency due to a decrease in the production of cyanocobalamin by intestinal microflora.
Even with a sufficient intake of foods containing vitamin B12, it is poorly absorbed if the body does not produce enough intrinsic factor (Castle factor) - an enzyme that interacts with the inactive form of cyanocobalamin from food and converts it into the active (digestible) form.
In old age, Castle factor is practically not produced due to reduced synthesis of acids in the body. In this case, the doctor prescribes injections instead of cyanocobalamin tablets. Including acidic plant foods - berries, fruits, vegetables - in the diet helps maintain the required level of acid production in the body.
Some vitamins are antagonists. Therefore, you cannot mix vitamins B12 and B1, B2, B6, and ascorbic acid in one syringe - they are destroyed by the cobalt ion, which contains the cyanocobalamin molecule.
The following signs indicate vitamin B12 deficiency:
- increased fatigue, drowsiness, depression;
- headache, dizziness;
- irritability;
- lack of appetite;
- numbness of the limbs;
- weakening and hair loss;
- grayish or yellowish complexion.
Daily requirement
Daily norm:
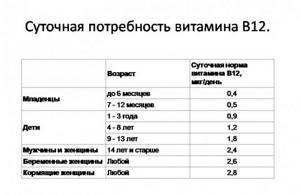
Daily intake of vitamin B12.
- adult - 3 mcg;
- child - from 0.5 to 1.5 mcg;
- nursing woman - from 2 to 4 mcg;
- infant - 0.4 mcg.
Cyanocobalamin is required in greater quantities when taking medications to normalize sleep, tablet contraceptives, smoking and alcohol abuse.
Plant products (vegetables and fruits) do not contain cyanocobalamin, so vegetarians are recommended to take multivitamins.
Useful properties of Vitamin B12
The main task of the vitamin is the formation of red blood cells, and it is also involved in the process of cell division and DNA formation.
In addition, it affects the condition of the blood, immune system, gastric and intestinal mucosa. In addition, it participates in the formation of nerve fibers and improves metabolism. Just like vitamin C, it fights the appearance of anemia, reduces irritability and maintains a healthy nervous system, improves memory and concentration.
It follows from this that without vitamin B12, our body will not have an easy time, since its lack has a negative impact on health and well-being.
List of foods that contain the most vitamin B12
The substance is found in large quantities in products obtained from animals.
Vitamin B12 content table:
| 100 g of product | B12, mcg |
| Beef liver | 60 |
| Pork liver | 30 |
| Kidneys | 20 |
| Chicken liver | 16 |
| Beef heart | 10 |
| Goose eggs | 5,1 |
| Beef tongue | 4,7 |
| Rabbit meat | 4,1 |
| Mutton | 3 |
| Beef | 2,6 |
| Chicken | 0,5 |
| Chicken eggs | 0,5 |
| Dairy | |
| Swiss cheese | 1,5 |
| Low-fat cottage cheese | 1,3 |
| Milk | 0,4 |
| Kefir (fat content 1%) | 0,4 |
| Fish and seafood | |
| Octopus | 20 |
| Pacific oyster | 16 |
| Herring | 13 |
| Far Eastern mackerel | 12 |
| Ocean sardine | 11 |
| Trout | 7,4 |
| Chum salmon | 4,1 |
| Sea bass | 2,4 |
| Cod | 1,6 |
Animal liver and kidneys
The highest content of nutrients is in the liver and kidneys. Of particular value is lamb liver, which contains 1500% of the recommended intake of the vitamin (RNI). Beef liver contains 990% of the RNP.
Shellfish
Soft-bodied vegetables are sources of vitamin B12, copper, and phosphorus. In 190 g of soft-bodied meats, 3130% of the RNP is present.
Lots of B12 in canned soft shell broth. From 100 g of such vitamin broth, the body can receive up to 14 mcg of the nutrient.
Sardines
Sardines are rich in vitamins, both fresh and canned. Their nutritional value is high; sardines contain almost all the substances that the body requires.
Sardines contain omega-3 fatty acids. Together with vitamin B12, they help strengthen the cardiovascular system and eliminate inflammation.
Beef
Beef has an increased concentration of B12, iron, protein, phosphorus, and zinc. You should eat low-fat meat, 100 g of which can replenish about 60% of the RNI. This meat product must be boiled or baked and consumed in moderation.

The benefits of beef meat for vitamin B12 deficiency.
Breakfast cereals fortified with vitamin B12
Fortified breakfast cereals are suitable for people who prefer to eat only fruits and vegetables. If the daily diet consists of a 240 ml portion of fortified cereals, which contains about 5 mcg of B12, then in 2 weeks the level of its concentration in the body increases.
Nutritionists recommend choosing cereals with a minimum amount of sugar and a high content of whole grains or fiber.
Atlantic mackerel
100 g of fish contains 790% of the RNP. This type of fish also contains omega-3 fatty acids, which speed up metabolic processes, reduce appetite, and strengthen joints.
Tuna
Tuna contains a high concentration of protein and minerals. The highest concentration of B12 is in the dark meat of fish, which is located just under the skin. 100 g of tuna contains about 160% of the RNPV.
Canned tuna is also healthy. A can of canned fish contains 85% of the RNP.
Trout
Rainbow trout contains many useful substances. A 100g serving of rainbow trout provides 125% of the ER.

Vitamin B12 content in mackerel.
Animal liver and kidneys
Organic animal products are some of the most nutritious foods available. Liver and kidneys, especially those from lamb, are rich in vitamin B12. A 100-gram serving of lamb liver supplies the body with an incredible 1,500% of the RDA for vitamin B12 ().
While lamb liver contains significantly more vitamin B12 than beef or veal liver, the latter two contain about 990% of the RDA per 100g (, ). Lamb liver is also very rich in copper, selenium and vitamins A and B2 ().
Lamb, veal and beef kidneys also contain vitamin B12, providing about 1,300% of the RDA per 100g serving. They also provide more than 100% of the RDA for vitamin B2 and selenium ().
Conclusion:
A 100g serving of lamb, beef or veal liver contains up to 1500% of the RDA for vitamin B12, while the same serving of kidney contains up to 1300% of the RDA.
Chinese study
Many substances can be obtained from plants or animals, but neither has the ability to produce B12. Only some bacteria living in the earth can synthesize it.
The habit of thoroughly washing fruits and vegetables before eating is thought to contribute to B12 deficiency in vegetarians, so vegetarian foods are fortified with the vitamin.
Salmon
This fish is rich in vitamins D and B12. A 100g serving of salmon contains 2.8 mcg of cyanocobalamin, or 116% of the RNAV.
Eating salmon strengthens the skeletal system, reduces the risk of fractures, and helps slow down the aging process.
Soy, almond, rice milk fortified with vitamin B12
Plant milk does not contain the necessary vitamin. For vegetarians who refuse goat's or cow's milk, vegetarian milk undergoes a fortification process.
Soy milk in a volume of 240 ml can provide 45% of the RNI.
Dairy
240 ml of milk contains 18% of the RNI, in full-fat yogurt - 23%, in one slice of cheese - 16%.
Studies have shown that vitamin absorption from dairy products is better than from meat, seafood, and eggs.

Eggs are a rich source of vitamin B12.
Eggs
You can include eggs from different birds in your diet: eggs of duck, chicken, goose, quail. All of them enrich the body with iron, protein, vitamins A, B, D. The yolk contains 2 times more B12 than the white. 2 eggs contain 53% of the RNP.
Should You Take Vitamin B12 Supplements?
Vitamin B12 supplements are recommended for people who are at risk of deficiency. These include older people, pregnant or breastfeeding women, vegetarians and vegans, people with bowel problems and those who have had stomach surgery.
Vitamin B12 found in fortified foods and supplements is synthetically manufactured, making it suitable for vegans (). Vitamin B12 supplements can be found in many forms. You can swallow, chew, drink, inject them intramuscularly, or place them under your tongue.
Research has shown that vitamin B12 taken orally and intramuscularly are equally effective in restoring vitamin B12 levels in people with deficiency (, ,).
In fact, a study found that people with low levels of vitamin B12 replenished their stores to normal levels after 90 days of either taking supplements or taking injections ().
Conclusion:
Vitamin B12 supplements are recommended for people who avoid eating animal products or have trouble absorbing it. They can be found in different forms, and doses range from 150 to 2000 mcg.
a brief description of
Strictly speaking, vitamin B12 (synonym - cyanocobalamin) is of a non-vitamin nature. This is a collection of substances of bacterial origin.
Special microorganisms - actinomycetes - live in the human intestine and produce cyanocobalamin . For its successful synthesis, bacteria need the microelement cobalt.
Theoretically, provided that the intestines are absolutely healthy and there is a sufficient amount of cobalt in food, the vitamin produced by the body could be enough.
But in practice, the synthesis of cyanocobalamin in the intestine is insufficient , so a constant supply of B12 from the outside is required, in the form of medications and with food.
It is important to know which foods contain vitamin B12, where it is found most, and how to adjust your diet to increase its supply.
Tea leaf
Slightly more cobalamin (0.1–1.2 mcg/100 g dry weight) in tea leaves. Moreover, the amount of vitamin varies depending on the production method (~“color of tea”). Below is a table with the B12 content in different types of tea.
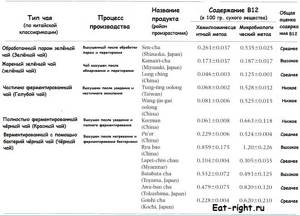
⚠ For complete understanding, I’ll add that fully fermented black tea - exactly what is sold in our stores - is considered “red tea” according to the Chinese classification. And the champion in vitamin B12 content is black tea according to the Chinese classification. It is obtained through additional bacterial fermentation of tea leaves. This is a rather unusual and rare type of tea. A distinctive feature of this tea is a large number of branches. When fermented by bacteria, they act as a kind of “disintegrant” for blocks of compressed tea leaves. By the way, Puer tea can also be classified as black tea according to the Chinese classification.