Fiber and protein in which products. Foods Rich in Fiber and Protein
Now let's move directly to the question of what foods contain fiber and protein.
Foods containing proteins and fiber include fruits and vegetables. They are a source of almost all the nutrients needed by humans. They contain many vitamins. Bananas, avocados, spinach, and asparagus are considered the healthiest fruits and vegetables containing proteins and dietary fiber. Nuts and seeds are also high in protein and fiber. Include pumpkin seeds, almonds, walnuts, hazelnuts and peanut butter in your diet. For example, 1 cup of cashews contains 21 grams of protein and 4 grams of fiber. 50 grams of nuts per day is enough.
Daily menu rich in fiber and proteins
We recommend preparing meals that simultaneously include foods with dietary fiber and proteins. An excellent dish to support this diet is a warm salad with chicken or beef with the addition of cucumber, tomato and lettuce. Eating one serving will give you 3.5 grams of fiber and 43 grams of protein.
Breakfast might look like this: 2 fried or boiled eggs, avocado and tomato salad, 100 grams of raspberries. This way you will enrich your body with 12 g of protein and 12 g of fiber.
Lunch: brown rice, smoked salmon, salad of leafy and green vegetables or salad of sprouted grains, herbs, tuna. That's about 25 grams of protein and 8 grams of dietary fiber.
Dinner: turkey with vegetables, 2 egg omelette or fish with a slice of rye bread.
For snacks, use nuts, fruits, dates, whole grain bread with peanut butter.
Reviews and results
Reviews among people who have practiced this diet vary significantly. Despite good tolerance and the absence of a pronounced feeling of hunger, the results differ for everyone and amount to 2-3 kg per week.
- “... I practiced this diet for 14 days. True, I started it in the winter before the New Year, and since vegetables and especially fruits are quite expensive during this period, I used fiber purchased at the pharmacy. I add 1.5-2 tablespoons of fiber to a serving of porridge or a glass of kefir 2 times a day. My health improved somewhat, but I lost only a little weight - 2.7 kg in two weeks”;
- “... I liked the diet because I really love vegetables and fruits and increasing their content in my diet was not difficult for me. At the same time, I removed all fatty, salty and smoked foods from my diet. I was on a diet for 1.5 months. The result is 5.8 kg.”
What is fiber for? What does the body need: benefits
Fiber is essentially, or to be more precise, simply dietary fiber or ballast substances. This means that, like water and mineral salts, fiber does not provide the body with energy, but at the same time plays an important role in its life. So how is it good for the body?
Dietary (plant) fiber, which is found primarily in low- or very low-sugar plant foods, is usually combined with other nutrients.
By the way, in a study by Pilar Buil-Cosiales, it was found that consuming fiber-containing fruits reduces the risk of mortality from cardiovascular diseases by 41%.
So we hope that opponents of fruits (and there are such people, and their names are legion) will come to their senses, read the article about fructose and conquer their raging fear of bananas, apples and pears.
Types and where many are found
Dietary fiber comes in two main types: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber is the pulp of fruits and vegetables, while insoluble fiber is the peel and husk. Both types are useful and necessary for our body.
Most plant foods contain these two forms of fiber simultaneously. We will tell you more about each of them, how they are eaten, and also what they contain:
- Soluble dietary fiber

They turn into a viscous gel in the intestines, which slows down the movement of food contents and significantly inhibits the enzymatic processing of carbohydrates. What is the list of vegetables rich in this type of fiber:
- Pectin. It is found in large quantities in apples, carrots, citrus fruits, cabbage and, oddly enough, in native potatoes. Pectin helps lower cholesterol levels and slows down the absorption of sugar, which makes it indispensable for diabetics.
- Gum. Contained in oatmeal and dried beans (peas, beans, beans, lentils). Like pectin, this type of fiber affects the digestibility of food.
- Lignin. It is found in greatest quantities in cereals (oats, rye, barley). Another source of lignin is stale vegetables (this does not mean spoiled, but slightly wilted products).
Also, soluble fiber is found in some fruits: prunes, raisins, avocados, berries, bananas, quince and peaches peels.
According to dietetics, with proper nutrition, the total amount of soluble fiber should be at least 3/4 of the total amount.
Insoluble dietary fiber

This is the so-called a coarse, large type of fiber, which, on the contrary, accelerates the movement of food contents through the gastrointestinal tract, has a laxative effect (used to prevent constipation), modulates pH in the colon, and is also a prebiotic (restores microflora).
Which vegetables and fruits have a lot of this fiber?
To begin with, we note that insoluble dietary fiber is divided into: cellulose and hemicellulose. Where there is a lot of them: bran, unprocessed grains (buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley, bulgur), legumes, nuts, seeds, green beans, cauliflower, broccoli, greens, peels of fruits and vegetables.
Advantages and disadvantages
If you follow the diet for a long time (about three months), you can lose up to 30 kg of excess weight. Such results will especially please obese people. In addition, you may notice that after a long period of restricting portion sizes, your appetite gradually decreases. Even after leaving the diet, it will be much easier to adhere to the principles of proper and fractional nutrition.
An undoubted advantage of fiber is its ability to sanitize the intestines. Like a sponge, it collects all the “garbage” that has accumulated over the years and removes it with ease. As a result, there is an improvement in well-being and appearance. Another advantage of the diet is the nutritional value. Maintaining a balance of fats, proteins and carbohydrates will allow you to lose weight with the help of fiber for a long time and without harm to your health. In addition, many are attracted by the flexibility of the diet and the absence of strict restrictions.
The disadvantage of the diet can be considered the discomfort that some people experience at the very beginning of the course. Excess fiber causes increased gas formation, abdominal pain and even diarrhea. After a week, symptoms usually go away. However, for any chronic or acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, consult your doctor before starting the diet.
Rate this article: 4.5 4.5 out of 5 (4 Votes)
Protein and fiber for dinner. The benefits of fiber for weight loss
The program is based on the consumption of plant-based products. They contain fiber - dietary fiber that is beneficial for the body. Plant cells are resistant to gastrointestinal enzymes. If we consider the chemical composition of cells, they represent a heterogeneous group of substances, which includes lignin and polysaccharides. Fiber includes:
- pectins;
- alginase;
- cellulose;
- hemicellulose;
- gum;
- chitin;
- alginates;
- phytin;
- protopectins.
It is important to know that fiber for weight loss can be soluble and insoluble. The features of these varieties are:
- Soluble – quickly saturates and cleanses the body of heavy metals. To saturate your body with useful substances, consume peas, legumes, flax seeds, oatmeal, apples, citrus fruits, nuts, red and orange vegetables, barley, brown rice, and seafood.
- Insoluble – promotes bowel movements, removal of toxins and waste, prevents the development of colon diseases. Contained in vegetables, seeds, nuts.
A diet based on the consumption of the insoluble type promotes effective weight loss. When food enters the stomach, it does not dissolve, swells and fills it, resulting in a feeling of fullness. To maintain nutritional balance, quickly lose extra pounds, and feel good, it is recommended to consume both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Keep in mind that if there is a lack of fiber of any origin, constipation appears in the body, problems with the skin of the face arise, and cancer and cholelithiasis develop. Thanks to the timely entry of such substances into the body, the following occurs:
- maintaining the necessary intestinal microflora;
- normalization of cholesterol and blood sugar levels;
- improvement of the cardiovascular system;
- eliminating the possibility of gallstones forming;
- removal of waste and toxins;
- breakdown of fat cells;
- acceleration of the bowel movement process;
- saturation with the necessary nutrients.
Fiber helps speed up the fat burning process, helps quickly get rid of rashes and skin irritations, and establishes a “supply” of blood enriched with useful substances to problem areas. Raw vegetables, fruits, bran and other foods rich in cellulose should be consumed especially by pregnant women: the daily dose is 28-29 g for every 1000 kcal. With this approach, the expectant mother will get rid of constipation, normalize blood glucose levels, and obesity will not develop after childbirth.

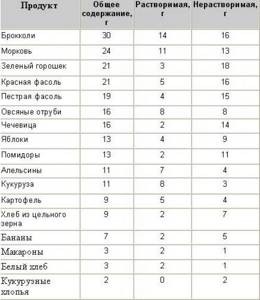
Content of dietary fiber in food products
Research shows that there is an increasing trend towards lower fiber intake in developed countries4. It is also noted that women consume less fiber than men. The optimal average daily dosage of dietary fiber is 30-45 grams; on average, a modern person satisfies the body’s fiber needs by only a third5.
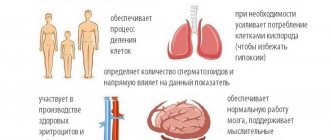
Protein and fiber menu. Why does the body need protein and fiber?
A high-fiber diet, like most protein diets, is noted for its ability to reduce hunger and prolong feelings of fullness. The fiber and protein in food slows stomach emptying, so you feel full sooner and hunger much later. This may help you eat less at your next meal. When choosing a high-fiber, high-protein menu, focus on a few sets of foods and turn to them at every meal or snack. Eat low-calorie foods or choose foods that are low in saturated fat and high in vitamins and minerals.
Most people need about 0.8g of protein per day for every kilogram of weight. Athletes or people who lead an active lifestyle will need approximately 1.5 g of protein per 1 kg of weight.
There are two types of proteins: complete and incomplete. Complete proteins contain all the essential amino acids - substances critically necessary for the functioning of the body. Incomplete proteins lack at least one of the nine essential amino acids. There are also two types of fibers: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber helps maintain healthy cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Insoluble fiber aids digestion.
At every meal, protein and fiber work to create a feeling of fullness in the body, increase the thermic effect and reduce the effect of the body's "glycemic response". The glycemic response refers to two things: firstly, the rate at which carbohydrates entering the body are converted into sugar, and secondly, the level of the insulin surge. The slower this process, the less sugar is sent for storage in adipose tissue. Additionally, by choosing the right fats and limiting your intake of saturated fats from dairy and meat, you can prevent heart disease, obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Recipes with fiber for effective weight loss
Fiber can be called a unique product for effective weight loss, containing a lot of plant fiber. It promotes weight loss by removing extra pounds. Diets containing fiber are quite effective. It is necessary to accustom the stomach to plant fibers gradually, since nutritionists note negative consequences of a sudden transition to a diet with a high fiber content.
If you are using dry fiber powder, your diet should look like this:

The daily norm of products is given, it is divided into 4 doses and with each of them they consume 2 tsp of fiber powder. You should not sit on such a minimal diet for a long time; starting for up to 5 days on such a diet is quite enough.
If you use fiber in tablets when losing weight, your diet changes significantly and looks like this:
With this diet, fiber tablets are washed down with plenty of water.
If you are a supporter of natural fiber, then you need to create a diet so that 70% of it is occupied by foods rich in fiber. You will find a table for creating a diet below.
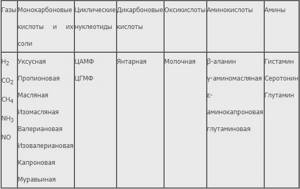
Main metabolic effects of dietary fiber
Short-chain fatty acids, which are formed from dietary fiber, participate in aerobic tissue metabolism and are used by the body as energy sources. At the same time, acids formed from non-starch polysaccharides provide up to 70% of the total energy received by the body from the carbohydrate component of the diet10.
The formation of gases (mainly hydrogen and methane) is a limiting factor in fiber intake. However, not only dietary fiber leads to gas formation, the same metabolic effect is provided by oligosaccharides, for example, verbascose, raffinose and stachyose, which are found in large quantities in legumes.
The third metabolic effect of fermentable dietary fiber is the production of energy, which is absorbed by the intestinal microflora for the purpose of development and performance of direct functions. An increase in dietary fiber, which is susceptible to intestinal fermentation, leads to a proportional increase in microflora. At the same time, when non-starch polysaccharides are included in the diet, nitrogen excretion, bile acid metabolism, vitamin production and other processes may change.
Also, low-molecular microflora metabolites formed during interaction with fiber support ion exchange, have an antibacterial effect, suppress the development of pathogens, activate local immunity, participate in the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate compounds, and in the conversion of acetyl-CoA into fatty acids.
Authorized Products
A fiber diet includes soups based on vegetable broth with the addition of cereals, whole grain porridges cooked in water (buckwheat, pearl barley, barley, millet porridge).
Only brown, unpolished rice is allowed. Aromatic herbs (dill, parsley, basil, rosemary) and mild seasonings - paprika, allspice - are added to dishes.
The diet includes small quantities of chicken, rabbit, turkey, low-fat white fish, low-fat fermented milk products, low-fat cottage cheese, and chicken egg whites.
Both raw and cooked vegetables (cabbage, carrots, zucchini, eggplant, celery, beets, onions, garlic, radishes, asparagus, cucumbers, peppers, tomatoes) and various fruits (with the exception of grapes) should occupy a large share in the diet , bananas), which are recommended to be consumed with the skin.
It is necessary to include in the diet legumes, whole grain bread, bran, nuts, seeds, vegetable oils - flaxseed, olive, sesame, walnut oil. For drinks, it is recommended to use herbal and green teas, still mineral water, rosehip decoction, freshly prepared vegetable and fruit juices.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| green peas | 5,0 | 0,2 | 13,8 | 73 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| boiled broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 4,0 | 27 |
| kohlrabi cabbage | 2,8 | 0,0 | 10,7 | 42 |
| red cabbage | 0,8 | 0,0 | 7,6 | 24 |
| watercress | 2,3 | 0,1 | 1,3 | 11 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| olives | 0,8 | 10,7 | 6,3 | 115 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| arugula | 2,6 | 0,7 | 2,1 | 25 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| green beans | 2,0 | 0,2 | 3,6 | 24 |
| zucchini | 1,5 | 0,2 | 3,0 | 16 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Fruits | ||||
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| seeds | 22,6 | 49,4 | 4,1 | 567 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat | 4,5 | 2,3 | 25,0 | 132 |
| oatmeal with water | 3,0 | 1,7 | 15,0 | 88 |
| pearl barley porridge on water | 3,1 | 0,4 | 22,2 | 109 |
| boiled brown rice | 2,6 | 0,9 | 22,8 | 110 |
| barley porridge on water | 2,3 | 0,3 | 15,7 | 76 |
Dairy | ||||
| dairy products | 3,2 | 6,5 | 4,1 | 117 |
| kefir 1% | 2,8 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
| fruit yogurt 1.5% | 3,7 | 1,5 | 8,9 | 63 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| steamed chicken breast | 23,6 | 1,9 | 0,0 | 113 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| boiled fish | 17,3 | 5,0 | 0,0 | 116 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | – |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | – |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot compote | 0,5 | 0,0 | 21,0 | 85 |
| Pineapple juice | 0,3 | 0,1 | 11,4 | 48 |
| cucumber juice | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,5 | 14 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||