If your muscles hurt after training, you shouldn’t wait until the discomfort goes away on its own, or constantly put off exercising. Sometimes the pain lasts a couple of days, goes away on its own or drags on for up to a whole week.
Loading …
Consult a doctor!
The site provides reference information . Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor . Any medications have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist and detailed study of the instructions is necessary! Be sure to make an appointment with your doctor .
Is it possible to continue exercising if your muscles hurt after training?
Painful sensations indicate that the load was too serious, excessive, and the body does not have time to recover.
All efforts are aimed at establishing new neural connections, improving immune defense, cell regeneration, eliminating microtrauma in tissues, and distributing energy reserves. It is important to thoughtfully approach your future regimen, take a break, and devote proper time to rest.
Strong pain
If muscle discomfort is clearly felt, there is no need to additionally load the body or test it with heavy strength exercises. This prevents successful recovery and aggravates the problem. Usually the feeling occurs on day 2-3, a burning sensation appears that does not go away for a long time.
Tolerable pain
Minor sore throat may occur from regular activity. If the symptoms do not interfere with daily activities and do not exceed the normal score on the pain scale, you can do a light workout 1-2 days after a grueling workout: perform the usual sets, reduce the number of approaches, repetitions, and working weight.
Whether it's worth it needs to be decided individually. If the condition allows, moderate physical activity will increase blood flow and speed up fiber recovery.
Muscle pain from injury
The last type of post-workout muscle pain to be aware of is muscle pain from an injury. If during training you feel that after a certain exercise you suddenly have aching and severe pain, then do not rush to continue training, as this could be a serious injury, and it is better to take a break and not aggravate the situation.
Signs of an injured muscle:
— pain in the muscle occurred very suddenly;
- pain occurs when performing a certain exercise;
— pain prevents you from doing your usual workout;
- where it hurts, the skin is red and swelling is visible;
— the pain does not go away, but intensifies every day.
If you are familiar with at least one of these signs, then you need to urgently consult a doctor and find out the cause of pain in the muscles. Under no circumstances should you delay this, otherwise it can lead to serious consequences, including surgical intervention.
How to Help Your Muscles Recover After a Workout
Most athletes experience severe soreness from exhausting training; any exercise is serious stress, but there are not always resources for recovery; the body needs help.
The following will help reduce painful symptoms:
- warm-up, cool-down: the right approach to intensity distribution makes the process more comfortable, safer, more effective;
- shower, bath: exposure to high temperatures allows microfibers to become elastic;
- massage: this method helps to cope with the feeling of being “clogged” and significantly reduces pain;
- drink more water.
The cool-down at the end relieves tension and gently relaxes the body. A similar effect is provided by water procedures, visiting a bathhouse, and massage sessions.
What films will help relieve pain after exercise?
For those who decide not to train, it is recommended to stay in bed rather than usual. With any activity, the body will hurt, feel a constant burning sensation, and the discomfort is unpleasant.
A great option is to arrange a movie viewing session.
We offer a small selection for those who want to immerse themselves in the pleasant atmosphere of films in the evening that motivate them to follow a healthy lifestyle:
- "Champions: faster, higher, stronger."
- "Knockdown".
- "Invisible side".
- "The man who changed everything".
- "Coach Carter."
Partial restriction of activity, a break, relaxation spent watching an interesting movie will help you recover faster. It is better to immediately follow this advice; after a few days you can continue to train your body as before.
We told you how to cope with painful sensations, whether you need to resume training, and how to prevent pain. We advise you to look only at how you feel and exercise when you want. The optimal schedule is after 2-3 days, so the body will cope perfectly with recovery and accumulation of strength.
“Muscles hurt...” How to exercise without trouble
I have never been athletic - I could easily be classified as one of the women who prefer manicures to fitness. To all the arguments in favor of sports (it makes you healthier, burns calories, gives positive emotions...) I answered that I feel better not from dumbbells, but from chocolate.
But one day I read a statement by Sophia Loren in a magazine: she claimed that those who play sports walk as if the whole world belongs to them . Something inside me responded to this phrase - and I started thinking.
A simple search of friends, colleagues and acquaintances showed that I was in the minority: almost all of my friends were enrolled in fitness clubs, and among my male friends there were many who liked to play football or volleyball with friends on the weekend.
The regulars at the fitness centers and sports grounds looked perfect, young and fit, their sports uniform definitely suited them - and, in the end, I decided to keep up. I got ready and went for a trial lesson at the nearest fitness club. And the composition of the visitors to this club surprised me!
By the way people used the exercise machines, how they selected the weight, and the technique of performing the exercises, one could say that the majority were beginners. There were very few of those who practiced confidently, making precise, calibrated movements on each apparatus - and I had a question, why?
It would be logical to expect that all beginners would eventually gain experience and turn into pros - but in reality this was not the case. It turned out that only a few reached the finish line, and the rest were “weeded out” along the way. Something was stopping them - which means it could have stopped me too. Starting training and quitting was an option I didn’t like at all, and after thinking about it, I decided to discuss my concerns with the instructor. And this is what he told me.
It turns out that those who “leave the race” are most often “hurried” - and among those who come to the gym, they are the majority. Those who are “in a hurry” decide to take care of themselves a week or two before the holidays. They want to change radically for these very holidays - they have to lose ten kilograms, build muscles like Schwarzenegger.
They “jump” on the treadmill, pedal the exercise bike as hard as they can, and the next day they can’t sit down, stand up, or hobble to the gym.
The reason is that muscles that are not accustomed to the load are injured . Microscopic tears appear in their fibers, the body responds to these breaks with inflammation and swelling - and the next day or the day after training, the novice athlete feels that the whole body hurts and does not obey, like wood. Often this is where the training ends - the coach doesn’t see such enthusiasts in the gym anymore.
How to avoid the “hasty trap”? It turns out it’s not difficult: you just need to follow three basic rules.
1. WARM UP . Don’t start exercising right off the bat, but first warm up and warm up. Muscles prepared for training are more elastic and less susceptible to injury.
2. REGULARITY . Exercise constantly, not occasionally. Regular exercise is more effective than weekend marches and does not cause pain.
3. GRADUALITY . Increase the load on the muscles smoothly, give them the opportunity to adapt, “gain strength”, get used to it - and not suffer from overload.
“And what, nothing will hurt at all?” — I asked the instructor. It turned out, not really - there is another kind of pain, “positive”. This pain, unlike pain due to microtrauma, occurs immediately after exercise and goes away within a few hours. It is caused by excess lactic acid, which is produced during intense muscle work.
This pain “says” that the muscles have worked well - therefore athletes often consider it a sign of proper training.
In general, the instructor’s words encouraged me - and my first training session took place that day. Behind it there was a second, a third - and, of course, I was unable to avoid either the “right” pain or the “wrong” one. Sometimes it was unbearable to even go down the stairs from my third floor to the first; I could barely get up from my chair at work - and of course I wanted to give up everything. But the advice of experienced people helped “stay in the saddle.”
A hot bath after exercise helped with the “correct” pain - it increased blood circulation, and lactic acid was removed from the body faster. Well, Fastum® gel helped well with “wrong” pain associated with injuries .
This drug was recommended to me by a doctor at a fitness center when I complained that my muscles were hot and aching, even when sitting or lying down. The doctor explained that Fastum® acts in two directions at once - it helps reduce pain and relieve inflammation . And this happens due to the content of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory substance - ketoprofen .
As it turned out, the “merit” of ketoprofen is that it prevents the production of prostaglandins - the main “culprits” of inflammation and pain in injured tissues. By applying Fastum® to the skin, we ensure that its active ingredient, ketoprofen, reaches the site of inflammation. Non-steroidal (and therefore non-hormonal) ketoprofen has the most powerful analgesic effect among similar substances.
From the instructions, I learned that Fastum® is produced in the form of a gel, so it is quickly absorbed and easily penetrates deep into the tissue , straight to the sore spot, and does not leave marks on the surface of the skin. Moreover, the gel does not leave greasy marks, like ointment or cream, it does not stain clothes and the body - that is, it is great, even if you still need to go somewhere after training.
“Somehow I don’t want to use the medicine right away,” I thought at first, but the doctor explained to me that when the drug is applied topically, it only acts on damaged tissue . It does not contain antibiotics or hormones, so it can be treated independently. In addition, it can be used by people with sensitive skin.
I tried Fastum® and the muscle pain quickly went away . Soon I was able to forget about it - and the desire to go to training appeared again. And then it turned out that the “good” pain was felt less after training with Fastum and a tube of this drug was “registered” in my sports medicine cabinet .
Recently, my friends and I from fitness - it’s been three years since I started working out. I like my own reflection in the mirror more and more, my figure has become toned - in general, the result is obvious. But Fastum® is still with me, and I often recommend it to beginners. I really want them to become friends with sports for a long time.
As an advertisement
What is indicated by dull, pulling, aching or sharp pain?
Muscle soreness can manifest itself in a variety of symptoms, be concentrated in different parts of the body, or affect the entire person. It may bother you constantly or appear when you move. It all depends on the main reason for its occurrence.
Most often, disturbing muscle pain (myalgia) appears in the following cases:
- Injury.
- Stretching.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Intense sports training.
- Virus, flu.
- Hypothermia.
- Neurosis.
- Stress.
- Rheumatism.
- Inactivity.
Myalgia, accompanied by decreased performance, fatigue, cramps and numbness of the limbs, impaired motor function - the consequences of changing weather.
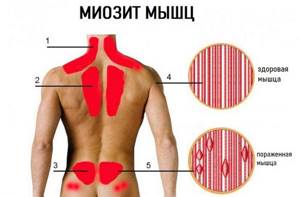
Myositis is an inflammation of muscle tissue, manifested by swelling and redness of the skin in the affected area. The pain is concentrated in one muscle and does not spread further.
The strength of its manifestation increases with movement, tension, and exposure to cold. The nature of pain also responds to changes in weather conditions.
Leg myalgia is caused by:
- Injury.
- Disease of the joints and spine.
- Sedentary or standing work. Unpleasant sensations in the legs are dull, aching, stabbing in nature.
- Prolonged immobility of the lower extremities. Painful negative sensations occur due to the formation of blood stagnation.
- Thrombophlebitis. The pain is of a burning nature, concentrated in the calves.
- Arterial diseases: atherosclerosis, endarteritis. The sensation intensifies when walking, and subsides at rest.
The back feels unwell in the following cases:
- Pathologies of the spine.
- Overvoltage. Often associated with the performance of work duties.
- Stagnation of blood as a result of being in the same position for a long time.
- Mechanical injury.
- Inflammation.
- Wrong massage. Impact on pain points.
The cause of myalgia in the back area can also be the anatomical features of a person. These are flat feet, asymmetry of the pelvic bones, and a shortened leg.
Soreness in the collar area is caused by excessive strain, injury or disease:
- Osteochondrosis.
- Oncology.
- Infectious lesion.
Malaise that occurs after overexertion or unusual stress for a person lasts several days.
The muscles in the hands are susceptible to infection and inflammation.
Often the pain is concentrated in the upper extremities due to:
- Tendon sprain.
- Rheumatism.
Malaise spreading throughout the body indicates in most cases that a viral infection has entered the body. This condition is typical for influenza.
When should you not exercise?
Severe muscle pain after an overly diligent, intense workout the day before may indicate traumatic injuries, fiber breaks, or sprains.
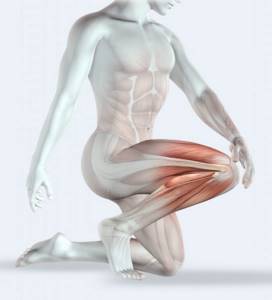
The following symptoms indicate serious problems:
- sharp, unbearable painful sensations;
- swelling;
- formation of subcutaneous hematoma;
- redness, hyperemia of the skin;
- increase in local body temperature.
In such situations, you should not only refrain from training, but also visit a doctor to identify the exact causes of pain and prescribe adequate therapy. It will be possible to return to sports activities only after complete restoration of damaged muscles and ligaments. This usually takes about a month.
When you need to see a doctor urgently, which specialist will help?
Pain can be relieved by taking painkillers, folk remedies, and using massage. But there are certain moments when contacting a medical facility is mandatory. Ignoring the body's signals about pathologies can lead to severe irreversible consequences.
Alarming manifestations:
- Unbearable pain that occurs when receiving physical injury. A doctor's examination is required. Only he, through examinations, can accurately determine the nature of the damage and establish a course of treatment. It is possible to take a painkiller first.
- Advanced age. Failure to consult a doctor for muscle ailments or lack of treatment will create a risk for older citizens of developing a chronic form of the disease.
- Soreness lasting more than five days. It is necessary to exclude serious injuries and determine the cause of the pain.
- Inflammation. Myositis in its progressive form can lead to muscle atrophy.
Only a doctor can diagnose the cause of pain, identify concomitant diseases, and prescribe a course of treatment. To do this, he gets acquainted with the patient’s medical history, determines symptomatic manifestations, localization and intensity of pain, and the presence of changes in the skin. During the initial examination, he conducts tests to make a conclusion about neurological abnormalities.
In addition to the general examination, he prescribes special diagnostic methods:
- ultrasonography;
- radiography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT.
If you suspect the presence of specific pathologies, you can make an appointment directly with a doctor specializing in this field. Myalgia is provoked by various diseases.
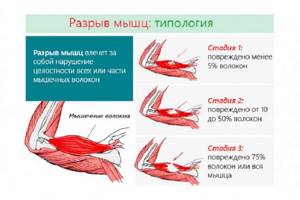
Doctors who diagnose and treat it include:
- Traumatologist - orthopedist. If myositis, osteoarthritis or osteoporosis is suspected.
- Traumatologist. After being injured.
- Surgeon. In case of complicated injury associated with a violation of the integrity of muscles, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
- Neurologist. For osteochondrosis, periodic convulsions.
- Rheumatologist. For gout, rheumatic polyarthralgia.
- Therapist. For secondary pain arising from an acute respiratory disease.
- Endocrinologist. For diabetes mellitus, the consequences of obesity.
- Infectious disease specialist. For meningitis, encephalitis, and other diseases associated with infection.
- Phlebologist. For varicose veins, thrombophlebitis.
- Angiologist. For atherosclerosis, Raynaud's syndrome.
- Gynecologist. For diseases of the reproductive system.
- Gastroenterologist. When symptoms of ulceration or failure of the normal functioning of the digestive system occur.
For advice, you can initially contact a therapist, who will identify health problems and refer you to a specialist.
Painkillers
Analgesics are designed to combat the painful condition.
The most common and frequently used of them:
- Metamizole. Preparations based on it: Analgin, Sulperin. Has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic effect. Relieves mild, mild discomfort. Available in different forms: tablets, suppositories, capsules, injection solutions. Valid for up to six hours. Contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation. Obstacles to choosing Metamizole include liver disease and individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
- Ketorolac. Derivative drugs: Ketanov, Ketolong, Ketalgin, Ketoprofen. A potent drug that has powerful analgesic properties and relieves fever. Produced in tablets and in the form of solutions for injection. Pain relief for up to eight hours. It has side effects that include migraines, nausea, increased blood pressure, swelling, and allergies. Not recommended for children, nursing and pregnant women. Not suitable for ulcer sufferers during exacerbation of the disease, or asthmatics.
- Dexalgin (Dexketoprofen). Relieves myalgia, prevents the progression of myositis, reduces high fever. Effective for eight hours. Available in tablets and injections. When side effects occur, it causes hypertension, allergies, heartburn, migraines, and loss of sleep. The list of contraindications for the use of the drug includes ulcers, bleeding, kidney, liver pathologies, pregnancy, breastfeeding, sensitivity to components.
- Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid). Eliminates fever, malaise, myositis. Available in plain and effervescent tablets, soluble in water. The therapeutic effect lasts three hours. Contraindications to taking the medicine include categories of people suffering from a lack of vitamin K in the body, changes in blood composition, and a tendency to bleed. For women carrying a child, the drug is dangerous.
- Lornoxicam. Preparations that contain it: Xefocam, Zornica. Treats rheumatism, inflammatory processes. Available in tablet form and powder for diluting a solution for injections. Effective for eight hours. Contraindicated for expectant and young nursing mothers. Not recommended for patients with pathologies of the heart, kidneys, liver, or ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Riabal. Available in the form of tablets, solution for injection, syrup. Contraindicated in glaucoma.
- No-shpa. Antispasmodic. Allowed for use even during pregnancy.
- Papaverine. Reduces tense smooth muscle tone. Has an antispasmodic effect.
NSAIDs are also used as painkillers. They not only have an analgesic effect, but also treat and eliminate the very cause of pain.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed for treatment in cases where discomfort is the result of inflammation in the body.
The main painkillers of this group:
- Paracetamol. Derivatives: Dolomin, Efferalgan, Panadol. Used for arthritis, neuralgia, migraine, myalgia.
- Indomethacin. Antirheumatic medicine. Eliminates swelling, heat, inflammation.
- Ibuprofen. Analogs: Nurofen, Ibufen. Effective in the initial stages of disease development.
- Nimesulide. Derivatives: Nimesil, Nise, Nimid. Fights inflammation, pain, protects cartilage tissue from destruction.
- Meloxicam. A powerful analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent. Analogues: Movalis, Revmaxikam.
Among the painkillers, ointments and gels are used to relieve pain symptoms:
- Diclofenac;
- Voltaren;
- Indomethacin;
- Ketoprofen;
- Bystrumgel;
- Ketonal gel;
- Fastumgel;
- Nise gel.
Gel-form preparations are easy to use and effective in treatment. They can be used independently, without a doctor's prescription.
Prevention as an effective method to prevent pain
Basic preventive methods to prevent muscle abnormalities include:
- limiting heavy physical activity;
- maintaining emotional calm;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- timely treatment of diseases, including those of infectious origin.
Maintaining constant muscle tone will help prevent increased pain associated with sports activities during training. This requires regular exercises for different muscle groups and physical therapy exercises.
After suffering from infectious, rheumatoid, neurological pathologies, the prevention of their relapse is following the doctor’s recommendations and eating in accordance with the established diet.
In order to ease the stress on muscles during training, it is recommended to take a hot bath with sea salt. To achieve a similar effect, athletes use ointments specially created based on turpentine, apple cider vinegar or badger fat.
Honey compresses, which are applied to the disturbing area at night, wrapped in a blanket, also have a beneficial effect on muscle relaxation.
It is recommended to leave spasmed muscles alone for several days, protect them from possible stress, and allow them to relax.
Muscle pain: is it good or bad?
In the minds of a huge number of athletes, soreness is strongly associated with the idea of high training efficiency. Well, I trained heartily - accordingly, severe pain in the muscles, and, as a result, progress in building strength and muscle mass. This opinion is only partly true. Everything is much more complicated: pain also depends on genetic characteristics, length of time and frequency of training, the exercises used, and even the specific muscle. It is known that the deltoids very rarely hurt very much (at least as much as, for example, the buttocks and quadriceps after heavy squats), but is this really necessary for competent intensive training? Of course not.
Muscle pain is actually neither good nor bad: it is simply a sign that certain biochemical processes are running in the body. There is no need to focus on muscle pain. The main indicator characterizing the effectiveness of training is progress in terms of the goals that the athlete sets for himself (in most cases, this is muscle mass and strength). Whether the muscles hurt or not is a secondary question.
How to train so that muscle pain does not appear?
Let's now try to figure out how to get rid of muscle pain by preventing it at the planning stage of the training process. This possibility actually exists. However, we emphasize once again: you should not be afraid of post-workout muscle pain, this is a completely normal natural process during training.
Below are a few tips that can significantly reduce muscle soreness:
- You should warm up more thoroughly before a serious workout. Never forget about warming up, it should last 5-10 minutes, no less.
- You should not change the set of exercises performed too often: new, unmastered movements cause much more severe muscle pain. However, you also can’t focus on one set of exercises forever; the muscles will get used to it and stop reacting to training stress. From time to time they need to be shocked by unusual loads, so there are periods when the soreness will have to be endured in any case.
- No need to force the load. For example, immediately lifting a large weight of weights after a long break from training or sharply increasing the weight lifted. If you do interval or cardio training, the loads also need to be increased gradually (training time, number of repetitions, execution speed, etc.).
- It is necessary to train regularly; long breaks cause the muscles to become unaccustomed to the training, therefore, the soreness increases. A small lyrical digression: Mike Mentzer’s “Supertraining” and other similar HIT methods are based on such a rare training that does not cause muscles to become accustomed to loads. During such training, muscles are severely injured and, accordingly, react more strongly to training stress. It’s an interesting technique, but you can’t progress indefinitely this way.
- You can conduct separate workouts using single repetitions - singles, instead of the usual multi-repetition ones. Of course, singles cannot be performed in several workouts in a row. And one more thing: strength can be increased this way, but mass cannot.
- You can use incomplete, partial amplitude in some exercises (example: lockouts, partial presses).
- It is better to avoid very harsh training methods - you need to know moderation in everything. But you don’t need to feel too sorry for yourself if you want to achieve good results.
What to do if your muscles don’t hurt after strength training?
The answer to this question is partially already contained in the previous paragraph: progress in mass and strength is the main and only, by and large, measure of success in strength training. Strength also grows in different ways: for powerlifters, this is primarily the result in one maximum repetition in competitive movements; for bodybuilders, an increase in strength in relation to working weights of 6-12 repetitions is interesting.
But if there is no progress and no muscle pain, then the athlete should ask himself the question: why don’t the muscles hurt after training? Is it because the intensity of training to trigger the mechanisms of muscle growth is simply not enough? Most likely, this is exactly the case.
In this case, you need to seriously reconsider your entire training methodology: place the main emphasis on basic multi-joint exercises, work with free weights, spending less time on those machines that only make doing exercises comfortable and convenient. If you are working on muscle mass, then training should be regular and moderately intense. Then progress will not be long in coming. Of course, this will be growth through muscle pain. But let us emphasize once again that it is impossible to judge the results of training only by the presence or absence of soreness.
How to distinguish sore throat from injury?
For an experienced athlete, determining the difference between pleasant post-workout muscle pain and sharp pain from an injury is not difficult. Well, for those who do not yet have much experience in sports, the list of main differences is as follows:
- No matter how strong the soreness is, it will almost never make it impossible to perform an exercise on the target muscle. Sharp “shooting” or “cutting” pain in an injured joint or tendon, which severely limits movement, is not characteristic of sore throat.
- The two types of pain also differ in areas of localization: it is clear that if discomfort is felt inside the joint, where there is no muscle tissue, then this is definitely an injury; but a mild “sipping” pain in the muscle is soreness, there is nothing to worry about.
- Injured areas may swell, and it happens that they become hotter to the touch than neighboring areas of the skin - this does not happen with sore throat.
What not to do if you have a sore throat?
If an athlete experiences significant muscle pain after exercise, there are three things they should NOT do:
- Perform a new high-intensity workout on a muscle in which the pain has not yet completely gone away. A light one, on the contrary, is possible, it will reduce pain.
- You should not overload your body with various medications: painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc. This symptomatic treatment will still not speed up muscle recovery, but there is a risk of side effects from the systematic use of the same medications. In addition, medications cost money - it is better to spend money on good sports nutrition.
- And most importantly, you should not give up playing sports. Hard work in the gym, in which the trainee overcomes certain discomfort during and after training, can turn a weak, thin guy into a muscular athlete, only in one way and in no other way. And soreness is just a concomitant effect.
What does sudden pain mean?
Occurring suddenly, without any special external reasons, it may indicate the development of diseases:
- Myositis. The location of the lesion is the part of the limbs located below the knee. A dull, growing wave appears as a result of a complication that has arisen after suffering a viral infection or physical exercises that are unusual for the patient.
- Intervertebral hernia. The attack covers the lumbar area and spreads to the hips. The leg becomes completely or partially numb.
- Neuralgia. A shooting, pronounced wave. Localized in the thigh, the cause is pinched nerve endings. It subsides at rest, but intensifies with careless or sudden movement of the leg.
- Osteomyelitis. The pain is unbearable in its intensity. They occur after the formation of purulent foci against the background of bone tissue infection.
- Convulsive syndrome. It manifests itself as stiffness, an aching sensation that increases over time. Occurs due to dehydration, lack of calcium and magnesium in the body.
- Fibromyalgia. The lesion covers the calves. The wave is dull, wandering.
The main symptom of such diseases is myalgia. A specific deviation can be determined by additionally exhibiting other characteristics characteristic of it. Correct and timely diagnosis of the condition can only be carried out by a doctor.
Why does pain occur during training, and what is it like?

Pain during training is known to both beginners and experienced athletes. It can be of different nature and intensity - from barely perceptible to acute, preventing movement. Essentially, pain occurs due to damage and destruction of muscle fibers. They are destroyed or damaged for the following reasons:
- the athlete has not trained for a long time;
- he changed his training program;
- the athlete trains for too long, through “I can’t.” The result is a symptom called overtraining, where all the muscles hurt;
- poor technique of performing the exercise;
- excessive weight of the projectile;
- untreated injury;
- a training device not adjusted to the athlete’s body type;
- the athlete was injured during training.

By its nature, pain is divided into:
- traumatic – that is, received as a result of an injury that occurred during training;
- burning sensation when performing the exercise. This is natural pain. It occurs when muscles contract due to their pressure on the lactic acid accumulated there. After a short rest it usually goes away;
- delayed muscle soreness (so-called soreness). Most of the time it is felt the next day after exercise. Its cause is muscle microtrauma. With each subsequent workout, with proper muscle load, this pain becomes less and less, and eventually disappears completely;
- lagging It usually occurs a few days after training and happens if an athlete has changed his training program and has not had time to adapt to it, or has not trained for a long time, or is not prepared for intense physical activity.