What to do when your gluteal muscles hurt after training
How to relieve pain after training.
There are several effective methods! Hello, hello my dears! Your Alena is with you again. After I decided to pump up my beautiful butt, I had to face an unpleasant problem. My gluteal muscles hurt after working out.
Of course, I started collecting information about why this happens and what to do about it, and I hasten to share with you. After all, apparently, many people know such pain after sports exercises.
Why do my buttocks hurt after training?
On the one hand, the fact that muscles hurt after training is good. It means we worked hard, and soon our butt will become what we dreamed of. Sometimes, on the contrary, beginners worry why their buttocks don’t hurt after regular exercise. Let's try to figure it out.
Krepatura, as athletes call muscle pain, occurs for a number of reasons:
- Lactic acid accumulation. This happens if you have just started exercising after a long break or if these are your first steps into the world of sports. Usually such pain goes away after a few days.
- Intensive load. During training, microcracks appear in the muscle fibers and it takes time for the muscles to recover. If you don't give your buttocks rest, the amount of muscle damage increases, and this is all accompanied by pain.
- About the same thing happens if you simply introduce new exercises into the complex or change the pace of execution. The new load damages the muscle fibers and pain appears.
- Sometimes, after training, your legs start to hurt, not your buttocks. This indicates that the technique of performing the exercise is impaired and it is not the butt that is being loaded, but the muscles of the thighs or calves, or the joints are damaged.
Causes of pain in the buttock
The muscles of the thigh and buttocks cannot hurt without a reason. Pain syndrome develops as a result of pathological changes in the spine and lumbosacral region. It is not possible to determine the nature of the pain and the exact location on your own. Often patients complain of pain in a specific place, but often the real reason is completely different.
The causes of pain in the gluteal muscles can be the following pathologies:
- lumbar osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia,
- osteoarthritis of the hip joints,
- osteomyelitis of the ilium or femur,
- phlegmon, abscess,
- injuries of the sacrum, ridge, coccyx,
- sprains, hematomas, fractures,
- pinching of the sciatic nerve in the area of the piriformis muscle,
- lumbago (increased tone of the muscles of the lower back, buttocks and thighs),
- diseases of the pelvic organs (adnexitis),
- pathological processes in the rectum (proctitis, hemorrhoids, paraproctitis),
- myalgia due to infectious lesions and hypothermia,
- myositis - inflammation in the muscles,
- arthritis,
- lumbar stenosis,
- disturbance of blood flow in the arteries or aorta,
- neoplasms in the retroperitoneal region,
- syndrome of chronic compression of the muscles of the gluteal region,
- oncology (lymphosarcoma, myeloma, iliac bone metastases),
- tuberculosis of bone tissue,
- femoral neck fracture,
- inguinal hernia.
- bursitis,
- tendonitis of the tendon connecting to the gluteus medius muscle,
- administration of drugs intramuscularly.
Why do the buttocks hurt during pregnancy?
During the period of bearing a child, women complain that the muscles of the butt hurt. Such conditions are associated with excessive load on the spine. As the fetus grows, the load on the body increases, the center of gravity shifts, and the spine becomes bent.
In the third trimester, the pain only intensifies, because by this time the baby has reached a large size, and the head puts significant pressure on the bottom of the pelvis. The enlarged uterus puts pressure on the nerve roots and blood vessels. The nature of the pain resembles the clinical picture of osteochondrosis. To alleviate the condition, experts advise performing simple exercises, wearing special underwear and a bandage.
How much to exercise so that your muscles don't hurt?
After the first classes, pain always arises and you just have to come to terms with it. As you continue training, you gradually accustom your muscles to the loads, and the pain disappears.
The training schedule should be designed in such a way that there is a break between classes. One or two days of rest are enough for microtraumas to heal and muscles to recover.
You need to increase the load and introduce new exercises gradually, then, perhaps, soreness can be avoided.
Be sure to start your workout with a warm-up. This will allow the muscles to warm up and reduce the likelihood of injury.
If you maintain regular exercise, do not neglect warm-up and stretching, and gradually increase the load, then the training will be effective, but without the appearance of muscle pain.
Types of muscle pain
Experts identify several types of pain that occurs after sports training. These include:
- Moderate post-workout pain. It appears due to excessive physical activity. A person feels mild soreness, muscle fatigue, a feeling of fullness and swelling of the muscles. The soreness becomes worse when the tissue contracts or stretches completely. The pain continues for several days, but is not dangerous.
- Delayed muscle pain. It does not appear immediately, but after 2-3 days after training. It appears clearly. The cause of pain is considered to be changes in load, long-term lack of physical activity. The symptom is also not dangerous and goes away on its own as the muscles get used to the load.
- Pain from injuries. It is acute and hinders movement. Muscles are usually damaged due to insufficient warm-up before the main set of exercises.
Also, many athletes experience burning pain that occurs when repeating the same action multiple times.
Myths about the gluteal muscles
It turns out that among newcomers to the sport, like me, several erroneous judgments, so-called myths about how to properly train the butt, are common:
- If your buttocks don’t hurt after exercise, then the workout was wasted. Actually this is not true. Muscles may ache after a long break from exercise or after increasing the load or using a new set of exercises. With regular training, muscle fibers are not injured and therefore do not hurt.
- After squats, your butt will be pumped up well. In general, everything is correct and this exercise works the gluteal muscles well, but other movements must be included in the complex.
- You should give preference to exercises with heavy weights. During training, you need to target both fast and slow muscle fibers. Therefore, it is optimal to alternate a large number of repetitions with a small weight and several repetitions with a large one.
- The load on the butt muscles needs to be constantly increased. In principle this is true. The muscles get used to the usual load, and the training does not bring results. But first of all, you need to focus on sensations. If you feel like your butt is on fire during training, then you can take your time with increasing the load.
- Once a week is enough to work the buttocks. If the main goal is to pump up your butt, then you can and should exercise at least 4 times a week. The buttock muscles are large and durable, so they do not require long-term recovery.
- A couple of exercises are enough to pump up your butt. Not true. There are many muscles in the buttocks and each one needs attention, so the complex should include exercises for different groups of gluteal muscles.
Prevention
Prevention of pain in the gluteal muscle is aimed at preventing the development of unpleasant sensations. It is practically no different from actions to prevent diseases of the musculoskeletal system and soft tissues surrounding the spine.
General recommendations for health improvement:
- Regular exercise will help strengthen muscles and skeleton,
- warming up every 20-40 minutes during sedentary work restores tissue nutrition, reduces the risk of venous blood stagnation,
- an integrated approach to the treatment of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system,
- hypothermia warning,
- timely seeking medical help.
Reference. Self-medication leads to increased pain, the disease develops into a chronic form.
How to relieve pain from muscles after exercise?
How to relieve pain after training. There are several effective methods:
- a hot bath followed by rubbing the buttocks with a washcloth or hard towel will warm up and stretch the muscles, improve blood circulation and speed up the elimination of lactic acid;
- bath or sauna. The principle of operation is the same, but in the bathhouse an additional assistant is a broom;
- a contrast shower after a workout is also quite capable of relieving muscle pain;
- massage. This is probably the best remedy for recovery after exercise;
- rubs, creams and ointments that have a warming, analgesic or cooling effect will be very useful for treating areas where soreness is felt.
You can, of course, resort to the help of analgesics, but it is still better not to poison the body with medications once again, but to choose a safer and simpler way to relieve pain. In addition, do not forget that ordinary clean water helps the rapid restoration of muscle fibers. Make it a rule to drink 6-8 glasses of cool water daily. This will not only reduce the recovery period, but also speed up metabolic processes and fat burning.
Diagnostics
Persistent pain requires consultation with a specialist. The main goal of diagnosis is to exclude conditions that pose a threat to human life. The doctor’s task is to collect data for anamnesis. For this purpose, a number of procedures are prescribed:
- Visual inspection. Determining the characteristics of pain, muscle tone, sensitivity, and biomechanical tests help determine the diagnosis halfway.
- X-ray. The study is aimed at identifying spinal column injuries, disc displacement, congenital malformations, tumors, osteochondrosis and osteoporosis.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging. Visualization of a section of the spine, identification of pathologies in soft tissues and joints.
- Isotope contrast scintigraphy. Determines possible metastases, osteomyelitis, abscesses, defects of the vertebral arches.
- Electroneuromyography. The method is used to determine muscle tone.
- Puncture, ultrasound of the hip joints. Prescribed for the detection of malignant and benign tumors.
- General analysis of urine and blood. Allows you to determine the presence or absence of inflammatory processes in the body.
Myths about butt training for girls.
Rate this article
“Training should be with weights, since this is required by fast-twitch fibers in the muscles...”
Many studies have proven that the gluteal muscles
consist of slow and fast fibers approximately 50/50. As scientists say, fast fibers make up only 48% of the gluteal muscle, and slow fibers make up 32%. This means that butt training for girls should be done with a minimum number of repetitions and heavy weights, and with multiple repetitions but at the same time light weight.
As we know from the experience of athletes, high-repetition butt training for girls is as effective for hypertrophy as training with heavy weights but a minimum number of repetitions.
To achieve hypertrophy of the gluteal muscle, you need to include both fast and slow fibers of the muscle in the work. This means that butt training for girls should combine several heavy repetitions and several light ones with appropriate weights.
“Squat and your butt will be like a nut...”
In 2006, scientists conducted an experiment in which, by studying the bioelectrical activity in the muscles that occur when muscle fibers work, they found that a squat in no way activates the work of muscle fibers to the fullest extent; in addition, other exercises can launch them into work more effective. The same deadlift or reverse hyperextension. Training for the buttocks and thighs should be divided into several exercises for all parts of the legs.
“The gluteal muscles need to be trained once every seven days for them to develop well...”
Most bodybuilders think that each individual muscle group needs to be trained once a week. Some of them end up so confused that they begin to contradict themselves and resort to an extra time training a muscle group that is a little behind, for example, if the calf muscle is weak. The gluteal muscle is one of the largest in the human body and is quite capable of withstanding heavy loads and high frequency training for the buttocks and thighs, about four per week.
“You don’t need a wide variety of exercises to train your buttocks, three or four are enough...”
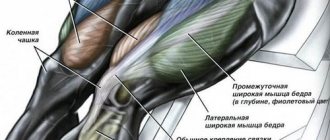
Structure of the gluteal muscles
It is built from three parts and each of them has its own operating mechanism. For example, squats and lunges put more stress on the lower muscles. For the gluteal muscle, it is vital to perform both general and isolation exercises, using basic exercises aimed at developing the strength of the gluteal muscle to work in tandem with the rest of the muscles of the whole body. Training in the buttocks gym for girls usually starts with easy exercises and gradually becomes more difficult.
There are three basic mechanisms for muscle hypertrophy; they are mechanical loading, metabolic stress and microdamage to muscle fibers - and each condition requires specific activation methods. For this reason, it is important to do exercises for three groups of gluteal muscles, and four exercises cannot be done here. It is best to do a workout in the buttocks gym for girls with a trainer who will suggest the best exercises.
“Soreness the next day, which means the training was a success...”

Most people think that since the muscles do not hurt after training their buttocks in the gym for girls, it means that the muscles were poorly loaded and the training was wasted. This only happens if butt training occurs rarely, and if during the training process you perform exercises aimed at stretching the gluteal muscles, such as lunges, and also after exercises that are new to you.
In other cases, muscle pain after working out in the gym is not an indicator of active growth or maximum load on the body. In addition, the gluteal muscles tend not to respond with pain to stress after several workouts.
“Increasing the load and using more weight in training helps develop the buttocks...”
The key to muscle growth
– development of strength. It follows that if the strength of your body remains the same as it was a year ago, the muscles do not grow. The gluteal muscle does not develop if, during a squat, the knees move together when working with heavy weights, and the back is strongly arched or rounded. Home training for the buttocks is dangerous because it is difficult to see your technique, because... there are no mirrors around.
Conclusion one
– the technique of performing each exercise must be brought to automaticity, which will contribute to the development of the necessary muscles that are involved in this. Training the buttock muscles is a complex process that takes a lot of energy and requires maximum concentration.
How to prevent post-workout pain?
What can you do to prevent your legs from hurting after training? This is a question that beginner athletes ask. At first, pain will accompany the person until the muscles get used to the physical activity. Then pain can arise due to various reasons, but it is quite possible to prevent it.
The first rule that all athletes, without exception, must follow is warming up the muscles before training. Preparation for the main load is carried out with the help of a warm-up.
If you don't stretch your muscle tissue, you increase the risk of injury.

Warming up the muscles does not take much time, just 10-15 minutes is enough.
After training, you need to do some stretching. It helps prevent tissue damage, makes them more elastic, and promotes the removal of metabolic products.
It is important for athletes to follow a diet to achieve maximum results from training. Muscle tissue must receive sufficient nutrients to grow and recover quickly after sports activities.
Trainers advise eating more protein foods. It allows muscles to grow properly, be strong and respond adequately to physical activity. You can use special sports nutrition, enriched with the necessary beneficial components.
Lack of water in the body can cause muscle spasms during exercise, as well as inflammatory processes in tissues. To prevent this, doctors advise maintaining a drinking regime. He suggests that a person should drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day.
It is not recommended to use boiled water, as it loses its beneficial properties and is not able to take part in the life of the body.
Trainers advise people who play sports to take vitamins. After all, they are exposed to physical activity more often and spend a lot of energy. Muscles cannot fully function if the body suffers from a deficiency of vitamins and minerals.
It is allowed to take medications after consulting a doctor and strictly in accordance with the prescribed dosage: an excess of nutrients is extremely undesirable.

It is strictly forbidden to spend a lot of time in gyms. The result depends on the regularity of exercise, but not on the time of exercise. Athletes should maintain a balance of work and rest. There must be a pause between approaches.
Fitness myths: muscle pain in the morning is a sign of a good workout
Muscle pain is almost always considered a sign of a well-executed workout - both immediately during and the next day. No pain no gain is the motto of a real rocking chair. And there is some truth in this: to get what you don’t have, you need to leave your comfort zone, and leaving your comfort zone is always stressful and unpleasant.
But beginners don’t always understand what needs to be tolerated and what not. Pain comes in different forms, some are beneficial, others are harmful, so it is better to learn to distinguish one from the other.

Treatment
How to treat pain from the buttock to the knee and below? Therapy for pain in the gluteal area is aimed at eliminating the root causes. Blocking the source of pain impulses leads to a decrease in pain and discomfort. If muscle pain is an independent symptom and a source of discomfort, therapy is carried out using general local effects:
- ensuring peace, immobilizing the ridge,
- Crick,
- massage,
- warming compress and physiotherapy,
- manual therapy,
- use of local non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (“Voltaren”),
- taking oral muscle relaxants (“Mydocalm”),
- post-isometric relaxation,
- weight loss,
- Exercise therapy.
What should you do if you hit a nerve during an injection in the buttock? In this case, anti-inflammatory painkillers and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed for treatment. If serious pathologies of the spinal column or radicular syndrome are detected, novocaine blockades are prescribed.
Treatment tactics depend on the nature of the pain and the rate of development of inflammation. Specialists focus their efforts on relieving pain and preventing the recurrence of pathology. For treatment, not only analgesics from the non-steroidal group (Meloxicam), but also glucocorticoids (Dexamethasone) and antioxidants (Emicidin) are prescribed.
Massage, manual therapy to stretch muscles, and physical therapy provide positive results. It is thanks to an integrated approach that it is possible to correct the patient’s condition. Surgical treatment methods are practically not used. Only in cases of unsuccessful therapy and acute conditions do surgeons get down to business.
Pain during exercise
Pain from stretching a muscle under load
This occurs when a muscle is stretched by weight. For example, stretched glutes and hamstrings in the Romanian deadlift. This is a dispersed pain throughout the muscle, as if it is “tearing off” from the bone (figuratively speaking). Moderate sensations are normal. Moreover, it is assumed that controlled stretching of the muscle under load is one of the additional stimuli for muscle growth. Therefore, there is even a separate type of training based on “negatives”, when the phase of stretching the muscle under weight is deliberately long.
Pain-burning during exercise
A strong burning sensation in the muscle appears when it is under load for a long time, that is, 12 repetitions or more. Somewhere in the middle of the exercise, a burning sensation appears, and then from repetition to repetition it grows until it becomes so unbearable that it is impossible to continue.
Oxygen stops flowing to muscle cells; they are acidified by the breakdown products of the main muscle fuel during training - glucose. This chemical poisoning is also one of the stimuli for muscle growth, so training until the burning sensation is effective (although there is little pleasure in it).
Joint pain
Another type of pain during exercise is a sharp, needle-like pain in the joint that quickly increases from repetition to repetition. Many people train through pain, using bandages, orthoses, bandages, warming and pain-relieving ointments. But pain is a signal that it is dangerous to continue moving.
Pain in the joint (and probable injury in the future, as a consequence) can be caused by non-compliance with the technique, potentially dangerous and simply unnatural exercises for the joints, incomplete recovery of not only muscles, but also connective tissue between workouts, poor warming up before training, and poor posture. and incorrect joint position.
Features of pain in the buttock
Pain in the gluteal muscles differs in each individual patient. Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis based on the description of the sensation and localization of unpleasant sensations.
Types of pain syndrome:
- spontaneous pain radiating to the back, lower limbs, intensifies when walking,
- severe pain, up to numbness of the leg,
- painful sensations in the middle of the buttock, spreading down the limb and accompanied by a lumbago in the lumbar region,
- constant, unremitting pain, intensifies with physical activity,
- nagging pain, followed by spasms, intensifies when the body overheats.
Unpleasant sensations in the gluteal region directly depend on the causes, time of occurrence and the presence of concomitant diseases. Using the example of common pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, let’s consider the types of pain:
- With osteochondrosis, pain manifests itself on the surface of the buttocks and spreads along the back of the thigh. Signs intensify with clumsy movements and physical activity and subside at rest, after massage and warming up.
- With stenosis, blockage of the aorta or arteries, patients complain of intense pain that does not go away for a long time. Discomfort decreases on its own, but often increases at night. In addition, the disease is accompanied by lethargy, pain in the lower extremities, numbness, lameness and “running goosebumps”.
- Piriformis syndrome develops as a result of damage to the muscles of the same name. The nature of the pain in the buttocks, tailbone and hip area is pulling, burning. Symptoms of inflammation of the gluteal muscles disappear when lying down and increase when walking. Often pain in the gluteal muscle radiates to the leg, knees, and fingers.
- Lumbodynia is characterized by throbbing and severe pain radiating to the legs. Patients feel lumbago in the back, thighs, and buttocks.
- Osteomyelitis develops as a result of inflammatory processes in the tissues of the thigh and the accumulation of purulent exudate. The nature of the pain syndrome is sharp, acute, constant. The person loses the ability to move. The discomfort does not go away even at rest. The disease is accompanied by fever, dizziness, and nausea.
- With phlegmon and abscess, the patient experiences unbearable pain, which intensifies when sitting on a hard surface. Such conditions are accompanied by fever and swelling in the area of inflammation.
- Intervertebral hernia is accompanied by acute pain in the buttocks, which is preceded by discomfort in the lumbar region. Patients complain of pain on the left and right sides.
On topic: Bridge exercise with weights for the buttocks
Pain at the injection site is completely normal and goes away on its own. Increased discomfort indicates that the needle has entered a small vessel, nerve, or fatty tissue. The gluteal muscles often hurt after training, especially for beginners. When the body gets used to the stress, these sensations will no longer bother you.
Important! The acute hematogenous form of osteomyelitis leads to coma.
Muscle pain after exercise

Everyone is waiting for her in the morning to evaluate how well the training was done. It seems to many: the more difficult it is to walk after “leg day,” the better for muscle growth. There is a direct connection between both. And when pain = growth, strength becomes the ultimate goal of training. But there is no direct connection, and pain is not a necessary condition for muscle growth, and in some cases it even interferes.
Why do my muscles hurt the next day?
Typically, soreness appears 6-24 hours after training and goes away within a few days. It can be very strong or barely noticeable. Most often, soreness appears if you have strained your muscles more than usual: increased working weights or returned to training after a break.
Most often, pain appears after exercises with a greater emphasis on the eccentric phase (stretching the muscle under load).
For example, during a biceps curl, the muscle contracts and becomes shorter. When you lower the barbell down, the muscle is stretched by the gravity of the barbell. In this phase, called the eccentric phase, microdamage to fibers occurs in the muscles.
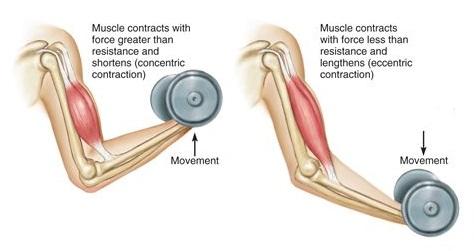
Today it is generally accepted that delayed pain is the result of inflammation after microdamage to the muscle and the body’s immune response.
Sometimes you can still hear that “in the morning” muscles hurt because of lactic acid, but it is eliminated from the body within an hour after training.
Is it harmful?
There is the concept of an inverted U-curve, which shows the dependence of the effect on the dose. Too little is bad and ineffective, too much is also bad, and something in between is best.
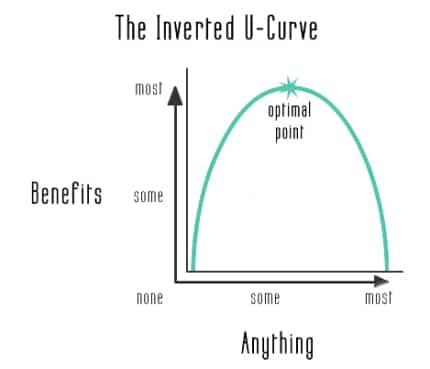
Severe damage over and over again can increase the growth of connective tissue in the muscles, this will make them inelastic and rigid. The proportion of collagen fibers, which are responsible for strength, increases (this is a mechanism of adaptation to frequent damage). Because of this, the range of motion may decrease, joints become less mobile, and strength is lost.

Taking more than a week to recover from a workout does more harm than good. If it hurts to sit, walk up the stairs, raise your arms, if the pain interferes with everyday life, you have exceeded your body’s ability to recover. Well, in the most extreme cases, rhabdomyolysis can develop. Fortunately, this happens very rarely.
What should you not do if you have muscle pain?
If the pain in the leg muscles after sports activities is severe, then it is not recommended to continue training. It is worth giving the body more rest for full recovery. It is advisable to consult with a trainer: he can change the set of exercises, duration and intensity of their implementation.
If pain bothers you due to injury, then you can no longer train and you should visit a doctor. Further exercises after damage to muscle fibers are allowed to begin after complete recovery of the lower limb.
Buttocks after workout
Hello. After training my buttocks, it feels like one hurts more than the other. Are these normal sensations or was the load different for each of them?
Woman.ru experts
Find out the opinion of an expert on your topic
Sokol Larisa Ivanovna
Psychologist, Gestalt therapist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Pustovoitova Elena Yurievna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Muratova Anna Eduardovna
Psychologist, Online consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Ekaterina Gomez Suarez
Psychologist, Psychologist-consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Slobodyanik Marina Valerievna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Dyachenko Elena Vladimirovna
Psychologist, Gestalt therapist in training. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Natalya Maratovna Rozhnova
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Alexander Trofimov
Psychologist, Online consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Svetlana Chernyshova
Psychologist, Consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru