How does protein affect weight loss?
To lose weight, you need to include foods containing large amounts of protein in your diet.
Their benefits are that they:
- prevents the feeling of hunger from arising, prolonging the period of satiety, since digestion and assimilation require a long time;
- accelerate metabolic processes, which helps burn calories;
- help maintain weight and muscle volume at the same time;
- maintain the balance of blood biochemical parameters, including sugar levels.
Protein foods are absorbed by the digestive system in about 9 hours. To process it, the body spends a lot of calories.
If the intake of carbohydrates from food is limited, then the processing of proteins helps to reduce the amount of adipose tissue, since it is the source of energy.
Plant foods containing protein
The table provides a list of plant-based protein products for weight loss. Indicators mean the approximate content of the substance in 100 g of product.
| Product | Amount of protein per 100 g (g) |
| Peas | 23 |
| Beans | 22,5 |
| Soybeans | 35 |
| Mushrooms | 3-4 |
| Sunflower seeds | 48 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 28 |
| Flax seeds | 18 |
| NUTS: | |
| Gretsky | 13 |
| Almond | 21 |
| Pistachios | 20 |
| Hazelnut | 15 |
| Cashew | 18 |
| Cabbage | 2 |
| Potato | 2 |
| Eggplant | 1 |
| Dried apricots | 5 |
| CEREALS: | |
| Wheat | 14 |
| Oats | 12 |
| Barley | 13 |
| Corn | 19,5 |
| Rice | 7 |
| Millet | 11,50 |
| Chickpeas | 20,10 |
| Hercules cereal | 11,00 |
| Potato | 2,50 |
| Dark rice | 2,58 |
| Spinach | 2,90 |
| Tofu | 17,19 |
| Buckwheat | 12,6 |
| Rice groats | 7 |
| Spinach | 4 |
| Avocado | 4 |
| Broccoli | 3 |
| Green pea | 5 |
| Soy milk | 3 |
| Banana | 1,5 |
High carbohydrate foods
The purpose of carbohydrates is to serve as the human body’s main source of energy and to help our muscles work. They are needed for the normal process of metabolism of fats and proteins. Carbohydrates in combination with proteins contribute to the formation of certain hormones, enzymes, secretions of salivary and mucus-forming glands, and other important compounds. In the daily diet of an adult, the average carbohydrate intake is 400-500 g.
Carbohydrates are divided into two groups - simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates differ in chemical structure from complex carbohydrates. They include monosaccharides (fructose, glucose, galactose) and disaccharides (lactose, sucrose, and maltose). Simple carbohydrates are found in sweet-tasting foods. This is sugar, honey, maple syrup, etc.
Polysaccharides are the name given to complex carbohydrates. Their source is plant foods - cereals, legumes, vegetables. The group of complex carbohydrates includes pectins, starch, glycogen, fiber, hemicellulose, etc. The basis of dietary fiber is polysaccharides, which is why their role in nutrition is so important.
For the body, the main suppliers of sucrose are sugar, candied fruits, jam, confectionery, candies, sweet drinks, cotton candy, ice cream, and some types of vegetables and fruits: beets, apricots, carrots, peaches, sweet plums, dates, etc.
When sucrose enters the intestines, it is broken down into fructose and glucose. Sugar was called the "white death" in the 70s. last century. In her book "Sweet Blues", W. Daphnia wrote: "It is more harmful than opium and more dangerous than nuclear bombing." After this, the persecution of sugar began. Nowadays, the dangers of sugar are being questioned. WHO experts in their 2002 report said that dietary sugars are only among the factors that increase the risk of developing dental caries, but they do not affect cardiovascular, cancer and other mass diseases. Sugar itself is not dangerous to humans, but its excess consumption (instead of healthy foods) leads to a decrease in the nutritional value of any diet.
Glucose (dextrose) is called the main supplier of energy for the brain, muscle cells and red blood cells. It is found in berries and fruits. In people with a body weight of 70 kg, the brain consumes about 100 g of glucose, striated muscles - 35 g, red blood cells - 30 g. For the formation of the glycogen we need in the liver, glucose is also necessary. Interestingly, it is involved in regulating appetite. The glucose level in the blood decreases, which signals the body's need for food.
Glycogen is classified as animal carbohydrates. This is a glucose polymer, a polysaccharide, similar to starch. The body should contain about 500 g of glycogen. Food sources of glycogen are meat and liver of animals and birds, fish, seafood.
Fructose (levulose) is the sweetest of all natural sugars. Its absorption requires almost no hormone insulin; this quality allows it to be used by patients with diabetes, but also in very limited quantities.
Lactose (milk sugar) is contained in dairy products. This carbohydrate normalizes the activity of microflora that is beneficial to us, and suppresses the processes of decay in the intestines. Lactose helps calcium absorption. In the case of a congenital or acquired deficiency of the lactose enzyme in the intestines, the process of its breakdown into galactose and glucose is disrupted. This leads to dairy intolerance. Fermented milk products contain less lactose than whole fresh milk, because... During ripening, lactose is converted to lactic acid.
Maltose is called malt sugar. It is an intermediate product formed when starch is broken down by sprouted grain enzymes and digestive enzymes. Maltose is formed, then it breaks down to glucose. Free maltose is contained in honey, malt extract, and beer.
About 85% of all carbohydrates in the human diet are starch. Its sources are bread, flour, cereals, legumes, potatoes and pasta. Starch tends to be digested rather slowly, breaking down into glucose. You need to know that starch from semolina and rice can be digested faster and easier than that obtained from pearl barley and barley, millet and buckwheat, from bread and potatoes. Starch from jelly is absorbed faster, i.e. in its natural form, subjected to heat treatment.
Dietary fiber consists of a complex of carbohydrates (fiber, hemicellulose, pectins, mucus, gum) and lignin, which is not a carbohydrate. A lot of dietary fiber is contained in bran; it contains wholemeal flour and bread made from it, cereals with shells, nuts and legumes.
Fiber is a complex carbohydrate that the human body cannot digest. It enhances intestinal motility, and for this reason is necessary for proper digestion. Cholesterol is removed from the body with the help of fiber. Insoluble fiber is able to remove toxins, cleansing the body of harmful substances. Fiber is present in wheat bran and in many types of vegetables and fruits.
Pectins are designed to stimulate digestion and also remove harmful toxins from the body. A large amount of pectin is contained in plums, apples, peaches, gooseberries, cranberries, apricots, as well as some vegetables - potatoes, cabbage, cucumbers, onions, eggplants. Pectins are also beneficial because their presence in the intestines reduces putrefactive processes, and they are also needed for the healing of the intestinal mucosa.
The polysaccharide inulin is a polymer of fructose. Jerusalem artichoke, artichokes and chicory contain a lot of inulin.
Hemicellulose is a cell wall polysaccharide. It is capable of holding water. Cereal products contain the most hemicellulose.
Food products with a high carbohydrate content (per 100 g of product)
| Product | Amount of carbohydrates, g |
| Sugar, candy, honey, marmalade, butter cookies, cereals, pasta, jam, dates, raisins | 65 |
| Bread, beans, peas, oatmeal, chocolate, halva, cakes, prunes, apricots | from 40 to 60 |
| Sweet curd cheese, green peas, ice cream, potatoes, beets, grapes, cherries, sweet cherries, figs, bananas | from 11 to 20 |
| Carrots, watermelon, melon, apricots, peaches, pears, apples, plums, oranges, tangerines, currants, strawberries, gooseberries, blueberries, lemon | from 5 to 10 |
When calculating the amount of carbohydrates in your diet, try to avoid consuming them in excess, as this can lead to obesity. And if you consume sugar (or foods high in sugar) every day and in excess, you can provoke the manifestation of latent diabetes mellitus.
You need to know that it is not sugar that causes this disease. Sweet dishes act as a kind of catalysts (accelerators) for an already existing disease. After all, they overload the pancreas, depleting the cells that produce insulin. And you can’t do without it when absorbing glucose.
But it is also not recommended to limit the amount of carbohydrates consumed to a minimum. Even people on a diet need to consume at least 100 g of carbohydrates in their daily diet. If there is a lack of carbohydrates in the body, the metabolism of fats and proteins is disrupted. Harmful products of incomplete oxidation of certain amino acids and fatty acids begin to accumulate in the blood. Carbohydrate deficiency develops. Its symptoms: lethargy and drowsiness, headaches, weakness, hunger, dizziness, trembling hands, nausea, sweating. To return to good health, you need to quickly give the person a cup of sweet tea or a piece of sugar or candy.
Protein products of animal origin
Animal proteins are absorbed 1.5 times better than plant proteins. Products that contain large amounts of protein are more preferable when creating a menu for weight loss.
Approximate protein content per 100 g of product:
| Product | Amount of protein per 100 g (g) |
| Red caviar | 31 |
| Other sea fish | 13-19 |
| red fish | 21-22 |
| Freshwater fish | 16-17 |
| Sea fish caviar | 28-31 |
| Crabs, shrimp, squid | 18 |
| Tuna | 23 |
| crucian carp | 18 |
| Pollock | 16 |
| Veal | 19,7 |
| Chicken breast | 23,6 |
| Chicken's meat | 18-20 |
| Turkey | 19 |
| Rabbit | 21 |
| Beef | 18-20 |
| Beef by-products (liver, kidneys, lungs) | 14-17 |
| Pork | 11-14 |
| Pork by-products | 14-19 |
| Fresh cow's milk | 3 |
| Powdered milk | 25-26 |
| Kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt | 3 |
| Cottage cheese | 14-18 |
| Eggs | 13 |
| Cheese | 23,4 |
| Sour cream | 3 |
| Yogurt | 5 |
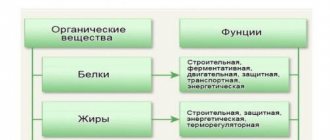
The role of proteins in our life
An essential part of our food is proteins. They are used to build new cells, and cells that replace worn-out ones take an active part in the metabolism that occurs continuously in our body. It is not for nothing that scientists called them “proteins” - on behalf of the Greek god Proteus, who constantly changed his shape. The protein molecule is also prone to metamorphosis. Proteins in the body can only be formed from food proteins.
The main sources of animal proteins are meat, cottage cheese, fish, eggs. Plant foods also contain proteins. Legumes and nuts are especially rich in them.
By consuming plant and animal foods, a person receives protein. It must be said that food proteins differ significantly from the proteins from which the human body is built.
Proteins can be broken down into amino acids during digestion. They are absorbed and the body uses them to produce its own protein. There are 22 types of the most important amino acids. Eight of them are called irreplaceable. They are called that because the body cannot synthesize them on its own, and we only get them from food. The remaining 14 amino acids are considered replaceable.
Different proteins contain different complexes of amino acids, and it is very important for us that the body constantly receives the full set of proteins it needs. In the surrounding world there are no such unique products that, in terms of their amino acid composition, would coincide with the proteins of the Homo sapiens body. To build them, the diet must include both animal protein products and plant products. Please note that the menu must contain at least 1/3 animal proteins. In the daily diet of a healthy adult, the average protein norm should be 100-120 g, and when people perform heavy physical work, the norm increases to 150-160 g.
The term “rational nutrition” means a combination of plant-based and animal products. This combination will ensure a balanced set of amino acids, promoting better metabolism.
Proteins obtained from dairy products are digested the fastest. Meat and fish are digested a little slower (beef is much faster than pork and lamb). Next come cereals and bread. The stomach digests proteins from wheat baked goods made from white flour (higher grades) well, and dishes prepared from semolina.
How to calculate your daily protein intake
The amount of protein consumed per day a person needs depends on several factors:
- body conditions (overweight, pregnancy);
- age;
- gender;
- daily physical activity;
- medical contraindications.
Approximate daily protein intake in grams per 1 kg of human weight:
- Children:
- up to one year - 3 g;
- older than a year - 1.5 g.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women – 2 g.
- Athletes experiencing intense physical activity – 2-3 g.
- Men – 1.5 g.
- Women - 0.75 g.
- Elderly people – 0.8 g.