Beneficial properties of tyrosine and its effect on the body
Repeated clinical experiments have proven that the best natural antidepressant is tyrosine. Scientists have noted a certain pattern according to which the higher the level of tyrosine in the blood, the higher its ability to withstand stress.
It is important to note that the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine components is related to the amount of tyrosine in the body.
This amino acid, without the need for additional use of chemicals, controls the amount of tyrosine in the human body and, therefore, reduces the likelihood of depressive disorders, stress, anxiety and irritability.
It is generally accepted that it has a significant effect on the functioning of the peripheral and central nervous systems. Tyrosine components have a significant impact on improving the quality and intensity of training in athletes, reduce the time factor of periods of rest and work, reduce fatigue, and are responsible for the prevention of overtraining.
It was noted that tyrosine molecules are included in the process of production of the thyroid hormonal component, which provides an opportunity to increase the hormonal action of the thyroid gland.
The effects of tyrosine components have been observed to reduce the painful effects of the premenstrual period.
When the required level of tyrosine is found in human cells, an improvement in the functioning of the blood-brain barrier is observed.
It is a barrier between blood flow areas and brain cells. They form membranes, allowing only molecules of certain types of substances to pass through and creating a barrier for other types (bacteria, viruses, proteins, low-molecular toxins). The ability of unwanted elements to penetrate the brain is determined by the strength of the protective barrier of the EBC. Protection of the amino group by chemical elements allows the beneficial amino acid to pass through the barrier protection and protects it from unnecessary substances.
The enormous beneficial effects of tyrosine have been identified in the fight against addiction to caffeine and narcotic drugs, and in the fight against uncontrolled drug use.
Tyrosine is the starting material for the production of certain hormones, such as dopamine, thyroxine, epinephrine and some others.
In addition, as a result of the transformation of tyrosine, the production of melanin pigment is noted.
Signs of tyrosine deficiency in the body
- obesity;
- fast fatiguability;
- state of depression;
- poor resistance to stress;
- sudden mood swings;
- premenstrual pain;
- decreased appetite;
- decreased brain activity;
- manifestations of Parkinson's disease;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- hyperactivity;
- disruptions in the functioning of the adrenal glands.
Signs of excess tyrosine in the body
- loss of muscle mass;
- manifestation of hypertension;
- decreased body temperature;
- increased heart rate.
What is tyrosine needed for?
The tyrosine formula is converted into hormonal components, which have a certain effect on the human condition:
- improve mood and create a feeling of reliability and well-being;
- increase the perception of information;
- help to recover from stressful situations and anxiety;
- improve attention and increase activity;
- participate in building the body (protein synthesis);
- L-tyrosine is needed in hypothyroidism for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland;
- restores strength and increases physical endurance;
- increases metabolism, causing the body to lose weight;
- improves adrenal function;
- partially relieves detoxification of the body (poisoning, slagging);
- relieves the effects of PMS.
What is tyrosine needed for? Photo: xtendhealthasia.com
Interesting fact: Proteins containing tyrosine perform important functions: creating antibodies for immune defense, building muscle fibers, transmitting hereditary information.
The amino acid works in tandem with the thyroid gland, which increases or slows down metabolic processes, controlling body weight. This is a powerful antidepressant that regulates hormonal levels.
Functions and actions of l-tyrosine
Tyrosine is formed and formed in the body through phenylalanine, which is absorbed as dopamine, norepinephrine, and adrenaline. Connections regulate neurophysiological function: • memory parameters; • attentiveness; • emotional state and mood; • mobility; • observation; • vigilance.
Note. Tyrosine produces and synthesizes auxiliary chemical compounds and hormones. Helps the performance of organs that produce and control the level of hormones throughout the body - the adrenal glands, the thyroid gland and the pituitary gland.
What are the benefits of tyrosine for the body?
The main function of tyrosine is to participate in the production of neurotransmitters responsible for good sleep and general well-being of a person, as well as a number of other biological processes. The body absorbs tyrosine in the form of dopamine, norepinephrine and adrenaline - catecholamines (physiologically active substances that act as chemical intermediaries. The listed substances affect neurophysiological processes:
- mood,
- memory,
- energy,
- attention,
- vigilance.

Tyrosine is responsible for the synthesis of several other substances in the body. For example, melanin is the pigment that determines the color of hair and skin. Tyrosine is also important for the functioning of organs that produce hormones. These are the thyroid gland, pituitary gland and adrenal glands.
Taking this into account, the beneficial actions of tyrosine include:
- protection from anxiety and nervous shock;
- improved mood;
- creating a sense of subjective well-being;
- giving vigor;
- increased vigilance, especially in those who do not get enough sleep;
- stimulation of the production of dopamine (“pleasure hormone”);
- improved cognitive function, especially during times of stress.
The most important ability of tyrosine is considered to be the weakening of stressful conditions, which is due to the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine. The amino acid helps relieve fatigue, especially after heavy exercise.
The amino acid is necessary for the production of dopamine, without which a person cannot experience a feeling of pleasure, and norepinephrine, which is responsible for memory. Tyrosine is also used for weight loss, as it helps reduce fat accumulation and suppress excessive appetite. Such actions are due to the fact that the amino acid increases the levels of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine, which act as neurotransmitters in the body.
Why is tyrosine needed in sports?
Tyrosine is used in bodybuilding to avoid fatigue, eliminate drowsiness and increase endurance. As a precursor to dopamine (a substance involved in synthesis), the amino acid helps improve well-being, improve exercise technique and improve mood.
Sports nutrition uses L-tyrosine, a form of tyrosine that protects muscles from catabolic (destructive) processes. Thus, the supplement is used to preserve muscle mass, and additionally to burn fat deposits.
L-tyrosine for the thyroid gland
L-tyrosine supports the functioning of the thyroid gland, is able to increase the concentration of thyroxine and triiodothyronine, and is important for: • the level of energy balance; • body weight control; • emotional state; • skin health. The component is able to fight depression, diabetes, stroke, obesity and others. L-tyrosine is prescribed to improve brain function and motivation, strengthen sexual function and strength of libido.

Note. Available in pharmacies without a doctor's prescription, tyrosine can be taken in small doses by adults (over 18 years of age).
Functions of tyrosine

Tyrosine protects the body from stress by being a precursor to the neurotransmitter dopamine and catecholamine hormones. It helps maintain high performance during night work, working in noise and cold conditions, helps maintain high concentration under stress, and make the right decisions in conditions of multitasking and distractions. Preparing and passing exams, intellectual work in offices, work as a dispatcher, especially around the clock - tyrosine will help you maintain a clear mind and quickly make the right choice. Studies on volunteers have shown that tyrosine helps solve complex problems, but it has no effect on solving simple, routine operations.
Tyrosine is a precursor of melanin, a substance that colors the skin, hair, and iris of the eyes. Biological supplements with L-tyrosine are of medical importance in the treatment of vitiligo, a disease accompanied by the appearance of white spots on the skin due to insufficient melanin production.
Tyrosine contributes to the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, being a precursor to the hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). The main function of thyroid hormones is to stimulate metabolism
, i.e. they trigger the biochemical conveyor belt, promote the processes of burning glucose and fat, which helps in weight loss programs.
It increases endurance and aids recovery during physical activity, which is used by professional athletes. Tyrosine helps maintain muscle mass, maintain high motivation, and fight lethargy and apathy.
Consequences of l-tyrosine deficiency
Due to a lack of tyrosine, a pathological disease such as tyrosinemia can occur. This is due to insufficient activity of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase. Mutation processes entail impaired tyrosine exchange with the liver, kidneys, and peripheral nerves. Some side effects occur due to low energy balance: • uncontrolled weight gain; • sharp decrease in muscle tissue; • swollen neck condition; • dementia; • disrupted functioning of the menstrual cycle in women; • constipation; • long incurable migraines; • pain in the spinal region; • dry and brittle hair; • circulatory disorders; • lowering blood pressure; • sluggish and apathetic state. Tyrosine for the thyroid gland is prescribed to maintain the function of the thyroid gland in a dosage of 500 mg to 1000 mg daily 2-3 times. It is not recommended to take with food to ensure proper absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Some side effects are known: • nausea; • vomit; • diarrhea; • headache. Be sure to consult an endocrinologist before use.

There are other options for maintaining hormone levels that are used in conjunction with the use of L-tyrosine. These methods include: • constant healthy eating, a stable diet; • performing breathing exercises and yoga; • periodic meditations; • support for an active lifestyle; • consumption of sufficient levels of clean water, drinking balance; • participation in therapeutic practices such as acupuncture, massages. It is l-tyrosine that has an effect on the pituitary gland, the glands responsible for transmitting signals for sufficient reproduction of thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Daily norm
A person over 18 years of age requires 25 mg of the substance per 1 kilogram of body weight per 24 hours. At least half of the daily requirement in standard situations enters the body with food, and therefore, to resist stress or improve brain functionality, approximately 12 mg per 1 kilogram of body weight will be required.
Attention. For depressive conditions, a dose of 0.5-1 g of tyrosine 3 times a day is advisable; for normalizing sleep - 1500 mg.
Signs of deficiency in the body
Contraindications and side effects of tyrosine
If the recommended dosage is exceeded, side effects of tyrosine may occur:
- increased anxiety;
- digestive disorders;
- migraine;
- cardiopalmus;
- nervousness.
People with an overactive thyroid gland should be especially careful when taking tyrosine. It is not recommended to take the amino acid if you have digestive disorders, use antidepressants, or Felling's disease.
We advise you to learn about all the main amino acids and their role in the body: “Amino acids for athletes: an overview of types and forms in a comparative table.”
Don't miss interesting news and events in the telegram channel: https://tlgg.ru/fitbarnews
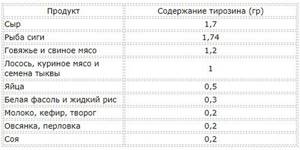
Tyrosine-rich foods
The highest concentration of tyrosine is found in the following products. Tyrosine in food, table:
What other food products contain tyrosine: • cereals: peas and lentils, semolina, buckwheat, millet, miso and hummus, fresh and canned green peas; • fruits and vegetables: bananas, avocado, pear, persimmon, orange, papaya, feijoa, kiwi, figs, mango, apple, tangerine, pineapple, white cabbage, potatoes, zucchini; • berries: plum, cherry, apricot, watermelon, grapes, blueberries, strawberries, peach, strawberry, cranberry; • greens, mushrooms: dill, parsley, basil, champignons, shiitake; • nuts and seeds: peanuts, pistachios, cashews, walnuts, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, pine nuts, hazelnuts, almonds; • flour products: pasta, bread made from wheat and rye flour, wheat flour. The tyrosine content in products can cover the need by 50% or more. The diet should be enriched with the above-listed foods containing tyrosine. This is required for the normal functioning of the entire human body. If necessary, you need to start taking tyrosine medications, which will start the fight against brain disorders, fatigue, bad mood and other manifestations, as well as in the complex treatment of drug addiction and alcoholism.
Excess tyrosine
Excess tyrosine cannot be obtained from regular foods. This is a problem with taking high doses of the drug L-tyrosine. The usual dosage for taking this drug is 1.5 - 3 g per day, the highest single dose is 12 g per day. However, such large doses can cause negative reactions.
- From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, increased acidity of gastric juice, heartburn; up to stomach ulcers,
- From the nervous system: migraines, increased excitability, anxiety, insomnia, dizziness, or, conversely, increased fatigue, drowsiness.
- From the cardiovascular system: increase (decrease) in blood pressure, increased heart rate, chest pain, feeling of shortness of breath
- Allergic reactions: rash, joint pain
- Thyroid dysfunction, weight loss
If these symptoms occur, depending on their severity, you should either stop taking the drug or reduce the dosage to the recommended or minimum
The influence of nutrition on tyrosine content in the body
It is known that the substance belongs to the non-essential amino acids. If it is insufficiently supplied to the body, the deficiency is compensated by phenylalanine, which undergoes synthesis.
Daily requirement
Experts do not recommend exceeding the dosage of the substance. To obtain the daily requirement, you need to include a variety of foods in your diet.
The maximum daily intake does not exceed 12 g. The average is 1-5 g of the substance. This amount is sufficient to adequately perform functions in the human body.
An increase in tyrosine dosage is required in the following cases:
- excess weight;
- poor memory;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- hyperactivity;
- tendency to depression;
- Parkinson's disease;
- PMS symptoms;
- intense physical activity.
You should not overuse foods containing tyrosine if you have digestive disorders, Felling's disease, or are taking antidepressants.
Digestibility
The body absorbs the amino acid in the form of adrenaline, norepinephrine and dopamine (catecholamines). These neurotransmitters correct the following processes:
Insufficient intake of catecholamines into the body leads to cognitive dysfunction. To normalize their level, you need to consume foods with significant concentrations of the substance. These include turkey, fish, chicken. In some cases, it is advisable to take medications and dietary supplements.
Tyrosine is introduced into the nervous system (central) by quickly crossing the blood-brain barrier. At the same time, the level of dopamine, norepinephrine, and adrenaline increases. Thus, the organic compound affects a whole range of processes occurring in the body.
Daily norm
The body should receive from 1 to 5 g of tyrosine per day. In the form of a dietary supplement, the permissible norm is 12 g. The exact dosage is determined by gender, age, diet and is prescribed by a doctor. With a deficiency or excess of amino acids, various pathological conditions are observed. Increasing the dosage is recommended for people who are overweight, have poor memory, have problems with the functioning of the thyroid gland, are prone to depression, or are overly active.
Interesting fact: The amino acid is better absorbed when taken on an empty stomach with B vitamins and (for example, tyrosine with orange juice). The combination with St. John's wort, lemon balm, chamomile, and valerian has a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous system.
What foods contain tyrosine?
The amino acid is present mainly in protein products:
- meat (chicken, turkey);
- fish (cod, tuna, mackerel, halibut);
- dairy products (yogurt, cottage cheese);
- nuts (almonds, peanuts, pistachios);
- fruits (bananas, avocados);
- legumes (chickpeas, beans, lentils);
- seeds (sesame, sunflower);
- soy;
- seafood (shrimp, crabs).
The leader in the presence of organic compounds is cheese.