Many people want to have a strong physical shape and look beautiful and athletic. But not everyone has the opportunity to visit a gym or organize a sports corner at home. In this case, an excellent exercise will help - push-ups. It can be performed without any additional equipment or sports equipment. To keep yourself in shape, all you need is desire and a well-designed training program. This exercise is universal: men, women, children, and the elderly can perform it. In this article you will learn which muscles are pumped up thanks to push-ups.
- What are the benefits of push-ups?
- What muscles are involved and pumped when doing push-ups?
- Pectoral muscles
- Triceps
- Deltoid muscles of the shoulder
- Serratus anterior muscle
- Abdominal muscles
- Neck
- Basic types of push-ups. Execution technique
- Classic push-ups
- Wide grip
- Wide grip with maximum development of the pectoral muscles
- Medium grip
- Narrow grip
- One-arm push-ups
- Video: 19 types of push-ups for beginners
- Lightweight push-ups
- Knee push-ups
- Do wall push-ups develop muscles?
- What are the effects of complicated push-ups?
- Push-ups with cotton
- Weighted push-ups
- Video: Basic types of push-ups
- Push-up training program for beginners
- Recommendations for performing push-ups. What muscles work
- Video: 3 most serious mistakes when doing push-ups
What are the benefits of push-ups?
Push-ups work different muscle groups. Exercise affects the development of strength indicators and an increase in muscle mass. There are several dozen varieties of push-ups, each of which is aimed at working a specific muscle group. For example, if you do push-ups with your arms spread wide apart (wide grip), the main load will fall on the pectoral muscles. If you do push-ups with a fairly narrow grip, the triceps will be worked the most. More details about the varieties and their execution techniques will be written below.
The essence of the exercise is that you take a strictly horizontal position parallel to the floor, face down. Next, you need to lower and raise your body using flexion and extension movements of your arms. In the classic version, this exercise is performed without the use of additional weights. Only experienced athletes practice push-ups with weights.
The main benefit of the exercise is an increase in muscle mass of certain muscle groups, as well as giving them a sculpted shape. Exercise helps increase strength and endurance. When regularly performing push-ups, the body's metabolism is normalized, which has a positive effect on a person's general condition and well-being.
It is also worth noting that after the age of 30, the human body begins to lose muscle mass: per year, about 2% of muscle mass is replaced by fat. Performing the exercise will stop the loss of muscle mass, develop muscles, improve heart function and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. In addition, push-ups help improve your posture.
Types of push-ups
There are a huge number of types of push-ups. Each type of technique has its own individual characteristics and develops specific areas of the body.
Wide
They are considered one of the easiest types of exercises, since the amplitude up and down is noticeably reduced due to the wide stance of the arms. Allows you to move your elbows further to the side and practically does not use the triceps muscles. The main load falls on the outer part of the pectoral muscles, giving them fullness and volume.
The technique is as follows:
- Take an emphasis lying on straight arms. Place your palms wider than your shoulders and spread your hands to the sides.
- Keep the body absolutely straight, do not allow the lower back to bend, the neck is an extension of the spine, you need to lower your gaze, tighten your abdominal muscles.
- As you inhale, begin lowering down, while spreading your elbows to the sides. The chest should touch the floor.
- As you exhale, rise up and return to the original position.
The main thing is that each repetition is done with the correct technique and in full amplitude. If this option is difficult to perform, then it is recommended to train from your knees or do push-ups from a vertical surface.
Narrow
When performing push-ups with a narrow position of the arms, the elbows should be pressed against the body, shifting the emphasis to the triceps brachii muscle. Compared to the previous version, the chest is practically not involved.
Technique:
- Take a lying position, arms should be straight. Place your palms narrower than shoulder width or form something like a triangle.
- Tighten your abdominal muscles, keep your body straight, and avoid bending.
- Inhale and begin to slowly lower down. While lowering, you need to press your elbows to your sides and make sure that they do not move apart.
- As you exhale, rise up.
You can make the workout more difficult by placing your hands as close to each other as possible. It will be much more difficult to rise from such a position, but the result will not be long in coming. Your triceps muscles will burn.

On one hand
A very difficult exercise that is only suitable for advanced athletes. The work involves not only the triceps and chest, but also the entire abdominal press, stabilizing the body during the execution of the approach.
Execution technique:
- The starting position is to take an emphasis lying on one hand. The second one needs to be removed behind the back, the brush should be placed on the buttock or slightly lower. Keep your feet on your toes and keep your body straight. The distance between the feet should be shoulder width.
- As you inhale, bend your working arm at the elbow and lower your chest almost to the floor. Do not bend your lower back under any circumstances.
- As you exhale, perform a push-up and return to the starting point.
The wider your legs are, the easier it is to maintain balance.

Sloping down
This type of push-up is suitable for experienced athletes who want to engage the upper pectoral muscles. The work also includes the oblique and abdominal muscles.
How to do it:
- Place your feet on an elevated platform. It could be a sofa, bench, fitball. The body must be kept straight, the lower back should not bend. The abs and back are in a static position.
- As you inhale, lower to the lowest point. The chest should touch the floor, without bending the lower back.
- As you exhale, push yourself up using the efforts of the target muscle group.
The higher the legs are on the hill, the more difficult it is to perform the exercise.

Tilt up
Incline push-ups are recommended for beginner athletes or those who find it difficult to do classic push-ups. Here the load on the elbow joints is greatly reduced. Allows you to work in energy-saving mode and is considered the safest type of push-ups.
How to do it correctly:
- Approach any horizontal surface (table, bench, cabinet), rest your hands on it, place your palms shoulder-width apart. Take a plank position at an angle in relation to the bench, tense your abdominal muscles, and direct your gaze forward.
- Take a breath, begin to slowly bend your arms at the elbow joints, touch your chest to the edge of the table or bench.
- As you exhale, push up and return to the starting point. Repeat several times.
In addition to the above methods, there are many more types of push-ups that make them more difficult to perform and stimulate muscle growth in a new way.

What muscles are involved and pumped when doing push-ups?
This exercise has a comprehensive effect on the body. What muscles are pumped? The following muscle groups are simultaneously involved:
- the upper and lower parts of the pectoral muscles are well worked out;
- triceps of both arms are involved;
- anterior and middle bundle of deltoid muscles of the shoulder girdle;
- the serratus anterior muscle of the body is worked out;
- upper, lower and lateral abdominal muscles;
- neck.
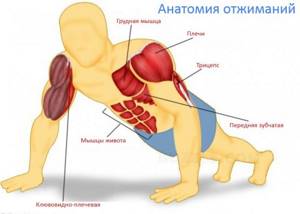
Push-ups have a complex effect on different muscle groups
Let's look at each muscle group in more detail.
Pectoral muscles
When performing various types of push-ups, the pectoral muscles are the most frequently used. When lifting and lowering the body, it is the pectoralis major muscle that takes the main load. In the everyday life of the average person, the pectoral muscles receive practically no load, so they atrophy very quickly. Push-ups will help activate your pectoral muscles and increase their size.
Triceps
The triceps is responsible for extending the arms. It is the second most important muscle that is used when performing push-ups. Depending on the grip width, the load on the triceps will change when performing the exercise. The narrower the grip, the greater the load.
Deltoid muscles of the shoulder
The deltoid muscles consist of three bundles (posterior, anterior and middle). When performing push-ups, part of the load goes to the anterior and middle bundle of the deltoid muscles of the shoulder. The deltoids help the pectoral muscles lift the body during push-ups.
Serratus anterior muscle
When performing push-ups, this subtle but very important muscle of the human body, which is located in the back of the sternum, works and strengthens.
Abdominal muscles
The abs consists of several muscles that are involved when performing the exercise. It is the abs that help keep the body in an even position when doing push-ups, so it can give the abs a certain definition.
Neck
When performing push-ups from the floor, your head should be level, your gaze directed strictly at the floor. Thanks to this, the neck muscles are also involved in the work.
The remaining muscle groups (biceps and back muscles) are involved to a minimal extent during push-ups.
Anatomy
So, what muscles work during push-ups? It works the muscle tissue of the shoulder girdle and upper limbs. When performed systematically, areas of the biceps, deltoid muscles, as well as the forearms and triceps of both upper extremities are pumped. The wrists, elbow joints and hands are also strengthened.
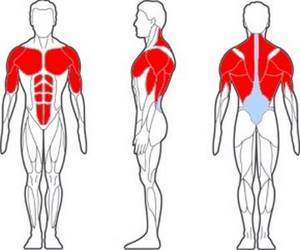
Muscle group involved in push-ups
When doing push-ups, the pectoral muscles are also worked out. With constant training, you can strengthen and enlarge the large chest muscle. Girls who constantly do push-ups have a tightening of their décolleté area and it looks perfect.
By training, you will be able to feel how the back muscles, or more precisely, the upper and lower ones, work. The muscular apparatus of the upper section is pumped together with the muscle tissues of the upper limbs and shoulder girdle while lowering and lifting the body, and the muscles of the lower section are pumped while holding the body in a straight position.
By extending your arms, the tension passes from the back muscles to the entire torso, and the muscles of the arms, shoulders and back relax a little. The abdominal muscles also actively work, which is aimed at raising and lowering the body. The abs are also worked because they help keep the body in a straight position during exercise. To feel the work of these muscles, during push-ups you need to listen to the sensations in the abdomen. As the abs tense and muscle areas stretch, a slight burning sensation is felt. If it is not there, then you are doing the exercise incorrectly. The gluteal muscles and quadriceps are less involved in push-ups. They are worked out if you exercise with one leg raised in the air.
Drawing a conclusion from the above, we can say that push-ups engage most muscles, improve coordination, work the muscular system along the spine and strengthen the skeletal corset that holds it.
Basic types of push-ups. Execution technique
There are many varieties of push-ups, each of which is aimed at working a specific muscle group. Let's look at the most basic options.
Classic push-ups

The most common type of push-up
The classic version of push-ups is taught at school during physical education classes. The technique is quite simple:
- First, a lying position with support on your palms and toes is adopted.
- Legs and back are one straight line.
- The palms are located slightly wider than the shoulders. The fingers are not widely spaced and point forward.
- Feet together or hip-width apart.
- As you inhale, slowly bring your chest toward the floor, bending your elbows. Don't spread them too far apart.
- Exhale and return to the starting position.
Wide grip
This exercise works the pectoral muscles
The technique is similar to the previous one with some exceptions:
- Hands should be placed at a distance equal to approximately two shoulder widths.
- Elbows should be directed to the sides.
- You can gather your palms into a fist or do push-ups with open palms, as in the classic version.
- The legs are shoulder-width apart or slightly narrower.
- When lowering your body, you need to watch your elbows: they should always look to the sides.
- Your back, neck and head should form one straight line.
If you bend or stick out your buttocks, the effectiveness of the exercise will be significantly reduced. A wide grip allows you to maximally pump the pectoral and deltoid muscles.
Wide grip with maximum development of the pectoral muscles

Wide grip with maximum development of the pectoral muscles
This type of push-up is aimed at maximizing the development of the pectoralis major muscle. The technique is the same as in the case of a wide grip, only the legs must be placed on a hill. For beginners, a stand of 30–35 centimeters will be sufficient. Professionals can do push-ups with a stand of 60 centimeters. The higher the stand, the greater the load on the pectoral muscles. You can experiment with the width of your grip. The wider the grip, the greater the load.
Medium grip
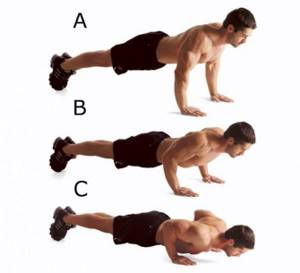
This type of push-up is aimed at working the triceps.
The effectiveness of the exercise will depend on the correct placement of the hands.
- Hands should be placed strictly at shoulder level.
- The elbow joints should be directed back.
- Feet together.
- When lowering the body, the elbows move not to the sides, but back along the body.
- The body must be positioned strictly parallel to the floor.
- You can do push-ups on both your palms and your fists.
Narrow grip

Works the triceps and shoulder girdle well
A narrow grip promotes good development of the triceps and anterior deltoid muscles.
- The palms are located next to each other and directed slightly inward.
- Feet are shoulder-width apart or together.
- When lowering the body, the arms bend along the body, and do not diverge to the sides.
One-arm push-ups

This exercise works well on the pectoral and abdominal muscles.
Doing push-ups on one arm is quite difficult; you should switch to this version of the exercise only if classic push-ups do not provide enough load.
- To maintain balance, you need to spread your legs wide apart.
- The supporting arm is located at the shoulder line, and the other arm is slightly bent and placed behind the back.
- When the descent phase occurs, the elbow bends to the side.
- You can do push-ups, alternating your hand after each push-up, or do a few reps on one hand and then change your supporting hand.
How to Know You're Doing the Right Push-Ups
To make sure you're getting the most out of the push-up and hitting the right muscle groups, you need to check your form. To start, make sure your elbows are pointing back to your body at 45 degrees in an A-shape rather than a T-shape at the bottom.
“The direction of the elbow determines what happens at the joint, and if your elbows are shaped like a T, you are tearing down your rotator cuff (the muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint) due to extreme internal rotation.”
Additionally, if you pull your elbows to your sides in an I-shape, you are doing a triceps push-up. This isn't necessarily wrong, but you're not challenging your chest and back muscles as much as you would at a 45-degree angle, Atkins explains.
Next, focus on your muscle core, which is located in the abdominal area. If your hips drop or you lift your butt up, it means your midsection is not engaged enough to support a straight plank. “Tuck your tailbone (a little forward) so your pelvis is tilted back to help protect your lower back.”
To maintain this straight line, you must also ensure that your neck remains in a neutral position. Don't let your head flop or your chin tuck into your chest, which can create tension in your neck and shoulders, Atkins says. Direct your gaze to the front of the mat or to your hands.
For your arms, make sure your shoulders stay directly above your wrists to keep your body stable and maximize those pushing mechanics. Atkins says to move your weight forward a little as you lower down to maintain that position. Your hands should also be slightly wider than shoulder-width apart—your thumbs should touch your armpits at the bottom of the movement.
Finally, remember that the closer your feet are together, the more difficult it is to do push-ups. The farther they are from each other, the more stable your body is. Atkins suggests keeping them hip distance apart when you work out.
Lightweight push-ups
For beginners with poorly developed muscles, especially women and the elderly, it can be difficult to perform classic push-ups, not to mention more complicated options. Lightweight push-up options have been developed for them.
Knee push-ups

Suitable for girls with weakly developed muscles
The technique is similar to the classic version, only the legs rest on the knees rather than on the toes. The feet should be crossed and raised above the floor. The workload on the main muscle groups in this position is significantly reduced.
Do wall push-ups develop muscles?
This exercise will strengthen your muscles and prepare them for classic push-ups.
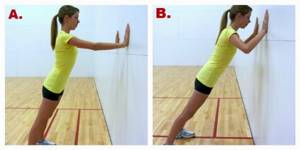
If push-ups from the floor are not easy for you, then you can start with push-ups from the wall.
Technique:
- You need to stand straight in front of the wall at a distance of about one step from it.
- We take the emphasis from the wall.
- The distance between the crayfish should be slightly wider than shoulder level.
- Lift your heels off the floor and perform push-ups.
- When performing the exercise, you must ensure that your body is even.
The Best Way to Increase Push-Up Intensity
You've probably seen people who can't get all the way down to the floor in a push-up. Or have trouble holding the plank while lowering your knees to the ground to change the movement.
But Atkins says that in this case we should replace this method of push-ups. Instead, place your hands on a sofa, chair, table or bench and perform incline push-ups. “When you kneel, you're taking half your body weight off the load and training poor body mechanics,” Atkins says. “A very important part of being able to do push-ups is having strong abdominal muscles.
The purpose of a push-up is to be able to push the equivalent of your body weight away from you. By taking it on an incline instead, you still maintain that straight line and get used to the movement of your entire body. As you get stronger, simply lower this incline lower until you can maintain a straight plank shape while doing a pushup on the ground.
To do this, it is important to know how to do the plank exercise correctly.
“At the end of the day, how you train the body is how it will respond. If you started doing push-ups from your knees, someday you will move on to classic push-ups.
But the memory of the mechanics of the exercise will sense that you are doing something wrong. Therefore, it is best to start doing push-ups with your body in a straight line. This is exactly what you were supposed to do in a proper push-up,” says Atkins. “Bending reduces the amount of body weight or stress on the arms and shoulders. But as you gradually lower yourself, you add stress to your upper body by controlling the process."
For those who regularly do push-ups on the ground, Atkins suggests making the challenge more challenging by changing the incline and placing your feet on yoga blocks, a sofa, chair or bench.
This increases the load on your upper body. You can also change the pace to make the push-up more difficult.
Try pausing for a count of three to five at the bottom or at the top. And then go down four or six to the lowest or highest position. “The goal is to increase time under tension. This is another way to change up your push-ups,” says Atkins.
What are the effects of complicated push-ups?
Push-ups with cotton

Quite a difficult exercise to work the pectoral muscles
This type of exercise helps not only to work out muscles, but also to increase agility and overall strength.
- The legs are slightly narrower than shoulder width, and the arms are approximately 2 times wider.
- We lower the body and push it up with a powerful push.
- We lift our palms off the floor and clap.
- The landing back should be soft.
- Hands should work rhythmically and energetically.
Weighted push-ups

Weighted push-ups are aimed at increasing muscle mass
Weighted push-ups are aimed at increasing muscle mass and strength in the pectoral muscles and triceps. The additional weight allows you to work the muscle groups quite deeply. As weights for exercise, you can use special sports vests with weights or regular backpacks with weights. The technique is exactly the same as for classic push-ups. You need to start training with small weights (2–3 kilograms), gradually increasing the load. Below you will find an explanatory video.
Features of muscle function
When performing push-ups , you use almost all the muscles of the body, which means that not only the muscles of your arms or chest, but also the muscles of your back, legs, shoulders, and abs are developed and pumped up. Push-ups are often compared to the bench press, only they are performed in reverse. Push-ups are a more accessible and convenient option for loading the body, since the regular floor acts as a support, and you can do them even at home.
To complicate the process in order to obtain greater results, you can do push-ups by placing your feet on a platform or weighting your back with objects such as a bottle of water or a weight. There are a large number of different variations of push-ups and they provide different loads on different groups of muscle tissue.
Push-up training program for beginners
If you are a beginner, it is recommended to exercise every other day (3-4 times a week) to give your muscles time to rest and recover. At the initial stage, you should not overexert your muscles; you can get seriously injured.
A training program for a beginner may look like this:
First training week:
- do a warm-up;
- first training approach - no more than 8 push-ups;
- second training approach - no more than 6 push-ups;
- third training approach - 5 push-ups;
- fourth approach - 5 push-ups;
- if you still have strength, then you can perform 2-3 sets of 5 repetitions;
- Rest between each approach should be 1-2 minutes.
Second training week:
- do a warm-up;
- four sets of 8 push-ups with breaks of 1-2 minutes between sets.
Third training week:
- do a warm-up;
- four sets of maximum repetitions; rest between approaches no more than 1 minute.
You can create subsequent training weeks on your own, gradually increasing the number of push-ups in each approach.
Recommendations for performing push-ups. What muscles work
- When performing push-ups, there should be no discomfort in the elbow and shoulder joints. The joints should not twist; to do this, choose the palm placement that suits you best.
- Push-ups require a certain flexibility, so it is recommended to develop this in parallel with classes.
- To avoid injuring your wrists, do a good warm-up before each activity. In addition, you can use special bandages or sports wristbands.
- If you are planning to gain muscle mass and increase muscle size, then you should pay special attention to nutrition. Food should contain sufficient amounts of protein and vitamins.
Push-ups are a simple exercise that will help you get rid of belly fat.
Push-ups will help you strengthen not only your upper body, but also get a toned stomach. They allow you to pump up the stabilizing abdominal muscles by performing vigorous pushing movements of the upper body from a support. This is, in fact, one of the best and most basic exercises for your abs.
According to the online magazine The Post Game:
“Push-ups are a core exercise that not only develops your abdominal muscles by holding them while gravity pushes your hips towards the floor, but also strengthens your upper body muscles by toning your chest, shoulders and triceps.”
Watch the video on how to do push-ups correctly.
Indeed, push-ups don't just strengthen your upper body; they also train your abdominal muscles, as long as you do it right. Usually the accompanying videos for an article are helpful for general introduction, but this video is a must watch as it actually demonstrates the technique and techniques described below.
"Better to see once than hear a hundred times"
In the video, renowned fitness trainer Deryn Steen demonstrates the perfect push-up and shows three basic strategies for improving your abdominal muscles:
- correct position;
- alternating techniques designed for different muscle groups;
- progressively more complex exercises to strengthen muscles.
Correct positioning is essential to help you avoid injury and achieve the results you want.
Common mistakes that most people make when doing push-ups:
- too fast pace of movements;
- performing movements not completely.
Perform push-ups slowly and use the 3-second rule. Try to really get a feel for the muscle groups you want to train. Perform exercises with maximum amplitude, that is, completely lower your body to the floor and, pushing off, rise until you fully straighten your arms.
Pay special attention to the position of your elbows. The ideal angle with your body is approximately 45 degrees. This will allow you to effectively develop your pectoral muscles.
I recommend watching the demo video carefully, but here I would like to draw your attention to a few key points to remember:
- When performing exercises, keep your body straight and stretched out like a board at all times.
- Keep your elbows at a 45-degree angle to your body line.
- Inhale as you lower down.
- Lower your body as far as possible, allowing your chest to lightly touch the floor.
- As you rise, exhale.
Exercise technique for different muscle groups
Push-ups are traditionally performed to train the chest muscles, but by changing the technique you can work different muscle groups, including the abdominal muscles.
But first, let's understand the structure of the abdominal muscles.
The transverse abdominal muscles, like the inner lining, support the digestive tract. In addition, there are the internal and external obliques, and above them the rectus abdominis muscle with a six-pack. Below, at the base of the abdominal wall, are the pelvic muscles responsible for genitourinary functions. At the top there is a diaphragm.
The technique Darin demonstrates allows you to focus and really feel those abdominal muscles in action when you do push-ups.
Here are two key points:
- In the upper position, make sure that your body is perfectly straight and draw in your navel. Your belly button is attached to the transverse abdominal muscles, so that the inner lining, which supports the digestive tract from the inside, holds your back and spine up like a well-tightened belt. Thus, by retracting it, you begin to contract the deep internal transverse abdominal muscle.
- Then do the skittle exercise. Women are probably more familiar with this term than men. When performing the pin exercise, you need to strain and squeeze tightly the lowest muscles of the pelvis. For men who are not familiar with this term, it is similar to trying to stop urinating in the middle of the process. This contraction will allow you to feel and focus on your abdominal muscles.
If you want to pump up your abs and also develop your thigh muscles, do the following exercise - stretch your legs back and rest your toes on the floor, bend your elbows and, leaning on them, pull your chin towards your chest to see your toes, while simultaneously drawing in your navel.
These techniques are very effective and will help you build the deep inner core muscles that lay the foundation for your six-pack abs. However, keep in mind that to truly get six-pack abs, you first need to lose weight. Men and women need to reduce body fat to achieve those classic six-pack abs.
How to become stronger and build muscle?
Once you can do two or three sets of 12, 15, or 18 reps, it's time to move on to the next level and start learning a different technique.
If you're just starting to do push-ups, you may want to do the exercises with your knees on the floor. Pull your heels toward your buttocks and keep your body straight. In this position, you can still retract your belly button and perform the pin exercise to develop the deep abdominal muscles. Remember: take your time and perform all movements completely, allowing your chest to gently touch the floor. By changing the position of your elbows relative to your sides, you can pay more attention to your pectoral muscles.
Once you can easily perform about a dozen push-ups on your knees, move on to regular push-ups while keeping your legs straight and resting on your toes.
A more advanced technique that will improve the strength and grip of your hands is to perform push-ups with just your fingertips on the floor.
Another advanced exercise is performing push-ups on an unstable surface. Two leather medicine balls work well for this exercise. Place your palms on the balls and perform push-ups.
The next exercise could be this: place your legs above your arms. This will place additional weight on your chest and abdominal muscles. Find a bench, stool or other surface approximately 30-40 cm high, place your feet on this surface and perform push-ups.
If at any point during the exercise you feel pain in your wrists, use a pair of light dumbbells or special push-up supports. You will not rest your hands on the floor, but will squeeze the dumbbells. The wrist will take a more comfortable position and the painful sensation will go away.
And finally, the most advanced exercise is the dumbbell row. This exercise develops the abdominal muscles very well!
Deryn uses 20-pound dumbbells for this exercise, but you can start with a weight that's more appropriate for your current level, fitness, and fitness level. Position the dumbbells at a 45-degree angle to your body, pull your belly button in, tighten your lowest pelvic muscles (pin exercises), and take a deep breath as you lower your upper body to the floor. Exhale as you move up and once your arms are fully straightened, slowly begin to lift the dumbbell in your right hand towards your chest, using only your left hand as support.
The next time you do a push-up, do the same with your left hand.
This technique will help you develop your transverse abdominal muscles, and also targets the deep internal muscles.
Plyometric push-ups (mini-sprints) and other exercises
To further stimulate your core muscles, try plyometric push-ups. Plyometric exercises use fast, explosive movements to develop muscle strength and quickness.
To perform plyometric push-ups, you need to get into a low position with your chest lightly touching the floor, breathe for about three seconds, then push up powerfully and quickly. You should kind of “bounce” on your hands, your hands should come off the floor a little. An even more difficult option is to do push-ups so quickly and sharply that you have time to clap your hands at the top of the push-up.
Another technique called three-minute push-ups is extremely difficult but produces fantastic results.
This is a fairly simple technique. How many push-ups can you do in three minutes?
You must have good technique, correct body position and strategy. If you get exhausted and lose all your energy, you probably won't last even three minutes. Therefore, start slowly, using 80% of your potential, and when you feel that you can no longer perform the exercise, give yourself a rest for 20-30 seconds in straight arms and then resume the exercise.
The final technique, the handstand push-up, is the most advanced and works the shoulder muscles, triceps, and core muscles.
Place your palms on the floor a short distance from the wall (about 1-2 palm lengths), cross your legs over the wall and stand on your hands upside down, using the wall as support. Standing on your hands, perform push-ups, inhaling as you go down and exhaling as you go up.
Again, I recommend that you watch the video to clearly see the correct technique for performing the exercises before you begin training on your own. This will help you avoid wasting time and effort on ineffective technology.