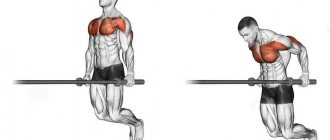
Pull-ups on a horizontal bar are a universal exercise that is recognized as the most common among techniques for working with your own weight. Depending on the grip, technique and variation of the exercise, different muscle groups work when performing pull-ups on the horizontal bar. The good news is that this “simulator” is available to everyone. The exercise involves lifting the weight of your own body by bending your elbows. During pull-ups, the following muscles are primarily pumped:
- biceps;
- large round;
- toothed;
- latissimus dorsi and shoulder muscles;
- trapezoidal;
- diamond-shaped;
- triceps;
- subscapular;
- pectoralis minor muscle.
What muscles are trained during pull-ups?
Pull-ups are considered one of the best exercises for gaining muscle mass. There are many ways to perform this exercise, including wide, narrow, medium, or neutral grip pull-ups. Depending on which technique you choose, different muscle groups will be involved:
- With a straight wide grip, the teres and latissimus dorsi muscles, shoulder muscles and biceps are worked; Beginners will find it easier to perform this technique in the upper block.
- With a medium reverse grip, the biceps (biceps brachii) and back muscles are involved.
- A neutral grip will help engage the teres major and serratus muscles. It is convenient to use special handles for this.
- With a direct grip and a narrow position of the hands, the muscles of the back and shoulder are developed and the serratus muscles are additionally worked out.
- A wide grip allows you to work your back and use the trapezius muscles, but the biceps brachialis will be practically not involved.
Various types of pull-ups help not only in building muscle mass, but also in strengthening the back, shoulders and spine. The grip that is best for doing pull-ups can be chosen based on individual wishes for working specific muscles. It is also worth paying attention to the exercises that you like to do most.
Mass pull-up diagram
When talking about how to gain muscle mass on the horizontal bar, you should clarify that you will need to do different variations of pull-ups and muscle-ups.
To start, focus on pull-ups. This will be a kind of preparation. For example, you can exercise three times a week.
Let's designate training days with numbers:
- Pull-ups with a reverse narrow grip in three approaches for the maximum number of times (but not less than 10 per approach).
- Pull-ups with a wide straight grip on the back, the same amount.
- Pulls with a classic medium grip. We do “unloading”, 3 sets of 10 times.
The last day should be easy so that your muscles do not overwork. Try doing this for a month. In 30 days you will complete approximately 12-13 workouts, then, depending on your results, you can start working on weight.
Yes, you understood correctly, you will need to use weights.
Gradually begin adding additional pounds to your weight. These could be water bottles tied to your waist, a backpack with weight plates, or a classic weight vest. Or maybe you will use leg weights? Your choice.
The training scheme remains the same. On the first and second days, we reduce the number of repetitions in the approach to 6-8. The weight should be such that the last pull-up is difficult for you. The third day is left as a “fasting” day. That is, we work 10 times without weights or with light weights.
We perform all movements slowly, without jerking. If you weigh too many pounds, you won't be able to do all the reps smoothly. You'll have to move in jerks. People with connective tissue defects are at risk of pulling the muscles of the forearm and shoulder. Be aware of these risks and avoid sudden movements.
In parallel with weighted pull-ups, you need to begin to master the power output in different variations. It is better to practice outdoors, since the ceilings prevent you from fully performing exercises indoors.
Exercise on the crossbar regularly, fight laziness - then and only then will you get results. But there is still a nuance on which your progress depends.
There is one problem with exits - if you don't understand the technique, it will be difficult to make them. And it doesn't matter how strong your hands are. Everything will depend on the coordination of the muscles of your body.
Tips and tricks
Parallel bars can be used to achieve a variety of goals. Each technique has its own nuances, but there are basic tips that will help with a specific task.

To increase strength you need:
- adhere to a slow rise of the body and a fast descent;
- gradually increase the number of approaches;
- strain your muscles as much as possible while lifting;
- take a break between sets for no more than 3 minutes.
If you are interested in building muscle mass, you should listen to these recommendations:
- lift your body at a fast pace and lower it at a slow pace;
- try to stick to the same number of approaches;
- Tighten your muscles as much as possible during the descent;
- take breaks between sets of more than 3 minutes;
- To speed up the results, you should eat an energy-rich diet after training.
Pull-up rules
The first thing you should do before doing pull-ups on the horizontal bar is to warm up. This can range from jumping rope to jogging or basic warm-up exercises for the neck, arms and shoulders. The main task is to warm up the muscles. Warming up is essential to prevent muscle strains and other health problems.

Regardless of the type of pull-up, there is a list of recommendations on how to do this exercise correctly:
- The first position for each type of pull-up is hanging with an arched back, crossed at the knees and bent legs. The only exception is the use of a wide head grip.
- It is necessary to lift the body smoothly and without jerking.
- The body is in the most static position, positioned vertically, and lifting occurs only due to muscle strength, and not swaying.
- Proper breathing is equally important: exhale on the way up, and inhale on the way down.
- Don't forget about a strong grip.
- At the top point of the pull-up, the chin is above the bar.
- The descent is smooth and lasts no less than the ascent.
These rules are general in nature, because each type of pull-up on a horizontal bar has its own characteristics. These recommendations will help pump up your muscles, bringing only health benefits.
Pull-up patterns

In order to pump up muscle mass, special “schemes” of pull-ups were invented. They are developed by professional athletes based on their experience and knowledge. These methods allow you to achieve impressive success in the shortest possible time (of course, provided that the correct execution technique is followed):
Direct progression method. The scheme involves increasing the number of pull-ups every day. Thus, your body gets used to the loads and quickly adapts to new ones.
| Day of the week | Number of approaches | Number of pull-ups | Scheme |
| Monday | 3 | 5 | 1-5, 2-5, 3-5 |
| Tuesday | 3 | 6 | 1-6, 2-6, 3-6 |
| Wednesday | 3 | 6 | 1-6, 2-6, 3-6 |
| Thursday | 3 | 7 | 1-7, 2-7, 3-7 |
| Friday | 3 | 7 | 1-7, 2-7, 3-7 |
| Saturday | 3 | 8 | 1-8, 2-8, 3-8 |

The last day of the week is a day off, which is needed to restore strength and relax the muscles.
It is recommended to increase the load every new week, for example, by adding 1 approach or a pair of pull-ups. However, it is important to observe the limit - the total number of daily pull-ups should not exceed 100.
Reverse progression method. The essence of the scheme is to arrange the number of pull-ups in descending order. For example, when you start training, you perform the maximum number of repetitions per approach, and closer to the last approach the number of repetitions is reduced.
| Day of the week | Number of approaches | Scheme |
| Monday | 6 | 1-5, 2-4, 3-3, 4-2, 5-1, 6-1 |
| Tuesday | 6 | 1-6, 2-5, 3-4,4-3, 5-2, 6-1 |
| Wednesday | 6 | 1-7, 2-6, 3-5/, 4-4, 5-3, 6-2 |
| Thursday | 6 | 1-7, 2-6, 3-5, 4-4, 5-3, 6-3 |
| Friday | 6 | 1-8, 2-7, 3-6, 4-5, 5-4, 6-4 |
| Saturday | 6 | 1-8, 2-7, 3-6, 4-5, 5-5, 6-5 |
Proper breathing when performing the exercise

Each exercise has its own technique. If you do not adhere to it, a person risks, at a minimum, not achieving the desired effect, and at maximum, causing harm to health or injury. Proper breathing is one of the most important things to consider when doing a pull-up. In order to breathe correctly during exercise, you must:
- Before doing a pull-up, take as much air into your lungs as possible and hold your breath. This will help relax your back muscles, making it easier to lift your body up.
- Start to pull yourself up gradually, while at the same time exhaling the air slowly and calmly.
Pull-up mistakes and how to avoid them
Errors in breathing are far from the only nuance that can ruin the results of a workout. The table below shows the most common mistakes made by beginners, as well as the correct technique:
| Incorrect technique | Risks | Proper execution |
| Instinctively throwing your head back with a jerk while inhaling, while bringing your shoulders together. |
| Inhalation must be done before pulling up. When bending your elbows, your body and head should remain motionless. |
| Writhing the whole body during the pull-up process, striving to do more repetitions at any cost. |
| When performing the exercise, the body should be strictly vertical to the floor. Pull-ups are performed only by lowering the elbows. |
| A sharp descent from the top point. |
| You should lower yourself with full control of the weight, distributing it evenly on both hands. The arms must be tense to the lowest point; they cannot be “thrown.” |
It is obvious that incorrect execution of an exercise can significantly affect the quality, result, and, most importantly, the health of a novice athlete.
What are the benefits of exercise
Pull-ups are a unique exercise in their effectiveness. It is part of many sports complexes aimed at developing the muscle groups of the arms, back, shoulders and chest. Exercise allows you to form correct posture, work muscle groups, and increase muscle mass.
When doing pull-ups on the horizontal bar, a huge number of muscles are involved:
| Muscle involved | Location | Muscle work in exercise |
| Latissimus muscle (so-called “wings”) | Lower back and upper side back |
|
| Teres major muscle | Upper side back (muscle located directly under the armpit) |
|
| Rhomboid muscle | Middle upper back |
|
| Pectoralis major muscle | Upper chest |
|
| Pectoralis minor muscle | Upper chest, covered by the pectoralis major muscle |
|
| Biceps | Upper chest, front |
|
| Triceps | Upper arm, back |
|
| Coracobrachialis muscle | Upper arm, inner area at the shoulder joint |
|
| Subscapularis muscle | Subscapularis fossa (obscured by muscles) |
|
What else is good about pull-ups?
Few people know the benefits of pull-ups on a horizontal bar.
You work with your body weight. The body is genetically optimized to work with its own weight. If you can do different strength exercises on the horizontal bar, then your muscles are in excellent condition. If not, it’s worth thinking about.
When you hang from the bar, your spine does not experience compression. On the contrary, it is stretched. This is useful from the point of view of preventing pinching and pinching. The muscles hold the vertebrae, pulling them towards each other, but if you relax, you can achieve a healing effect. If you work out in the gym and perform a vertical load with heavy weights, you must hang on the horizontal bar for at least 60 seconds a day, trying to completely relax your back and abs.
Of course, when you actively pull yourself up, you won’t be able to relax. But there is another feature here - firstly, you disperse blood throughout the body, and secondly, in fact, you remind the muscles why they are needed.
These are the benefits of pull-ups even without weights.
Choosing the optimal type of pull-up

Everyone who starts doing pull-ups on horizontal bars is concerned about the specific method of performing the exercise. Athletes recommend starting pull-ups with a regular grip technique. This is a kind of classic or base, from which it will then be easy to move on to varieties of pull-ups.
Types of pull-ups are designed in such a way that each of them is “responsible” for pumping different muscle groups. Therefore, ideally, you need to take your technique to a level where each workout you perform a series of exercises with a full set of grips.
Wide-grip pull-ups are considered the most difficult - unlike classic pull-ups, they involve more muscles. In turn, a direct grip works the trapezius muscles, and pull-ups with different grips help develop the shoulder muscle. Each type of pull-up on a horizontal bar deserves attention, so you shouldn’t limit yourself to just one type of exercise. It will be much more effective to combine techniques and types of grips in order to achieve an even load on the entire upper body.
Medium overhand grip
Correct technique:
- The width of the arms is slightly wider than the width of the shoulders;
- outer direction of the palms (overhand grip);
- arms bend at the elbows at the peak point;
- the chin is above the bar;
- at the lowest point the arms are straight.

The most important thing is to perform the exercise without swaying the body, evenly raising and lowering the body. It is necessary to bring your shoulder blades together in the process and try to touch the bar with your upper chest, pulling yourself up to the peak point. In order to better stretch the muscles, at the lowest point you need to fully straighten your arms.
Athletes also recommend lowering the body twice as slow as raising it, since elbow extension is the most difficult phase to perform.
If a person cannot yet lower himself smoothly, he needs the help of a partner who will support the body and help him rise and fall.
Load:
- biceps;
- trapezius muscles;
- latissimus dorsi muscles.
Medium underhand grip
Correct technique:
- The grip width should correspond to the width of the shoulders;
- palms facing yourself (lower grip);
- when pulling up, it is necessary to direct your shoulders back and down from the very beginning of the movement;
- at the highest point the chin is above the crossbar;
- at the lowest point the arms are straightened.

This option is simpler than the previous one, since when performing pull-ups with a medium grip from below, the biceps work more than the brachialis muscle. For beginners, as a rule, it is the biceps that are stronger, so it is recommended to take a closer look at this option if you belong to this category.
Load emphasis:
- biceps;
- latissimus dorsi muscles.
Wide grip to chest
Correct technique:
- a wide grip is approximately similar to that used in the barbell press;
- the projectile should be grasped from above with the thumbs, which will help to more effectively develop the back muscles;
- you need to smoothly bring your shoulder blades together and try to touch the horizontal bar with your upper chest;
- you should look straight up and bend your back;
- At the top point you need to linger a little.
Wide-grip chest pull-ups are the most difficult, but also the most effective exercise option. Even athletes sometimes make mistakes in their technique, which can lead to a decrease in efficiency. If you perform wide-grip pull-ups correctly, you can see results after a short period of time.
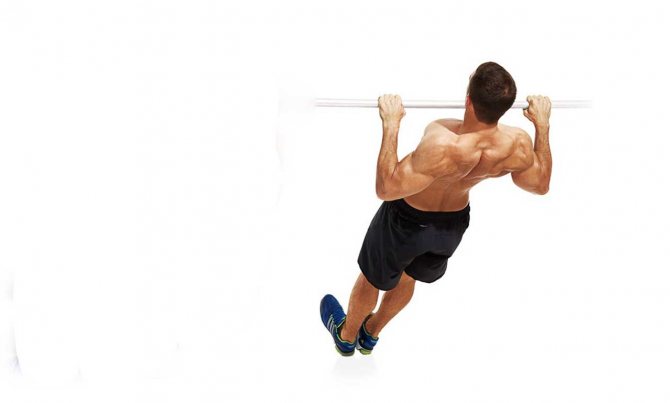

Load:
- trapezius muscles;
- top of lats;
- paired round.
Wide head grip
Correct technique:
- tightening should be gradual;
- grip width, as in the previous technique;
- When doing a pull-up, you need to bend your back and make your legs straight;
- It is important to point your elbows down, not back, throughout the entire execution.
Pull-ups with a wide grip behind the head are also popular, but also quite dangerous. If your joints have poor mobility, it is not worth doing. You should be especially careful with the wide-grip pull-up technique, since if you do it carelessly or ignore the correct method of doing it, you can get seriously injured.
The load is distributed among the following types of muscles:
- paired teres muscles;
- trapezoidal;
- the upper and middle part of the latissimus muscles.
Narrow overhand grip
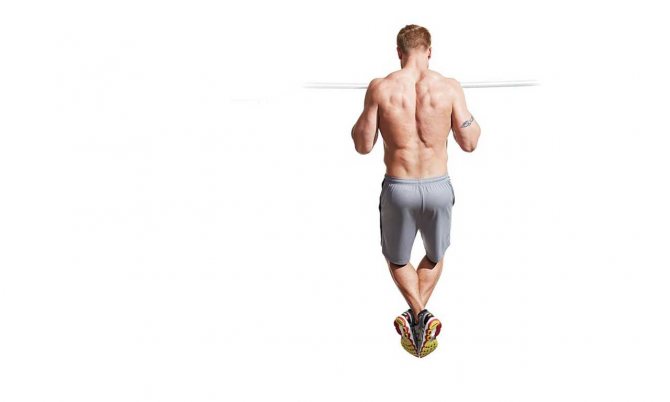

Correct technique:
- The grip width should be narrower than shoulder width;
- at the highest point, the hands should be on both sides of the chin;
- it is necessary to pull yourself up, bending your back;
- at the highest point you should touch the horizontal bar with your chest.
Close-grip pull-ups are suitable for those with poor wrist mobility. It is noteworthy that the narrower the grip, the more load is placed on the biceps. Therefore, if you are interested in pumping up these particular muscles, this version of the technique will suit you much better than pull-ups with a wide or medium grip.
Muscles that are pumped in this technique:
- lower latissimus muscles;
- toothed;
- brachial muscle.
Narrow underhand grip
Correct technique:
- you should grab the horizontal bar with a reverse grip, if possible, put your palms together;
- hanging on straight arms, arch your back and look at your hands;
- during the pull-up process, focus on moving your shoulders back as much as possible and bringing your shoulder blades together;
- at the top point, try to bend your back even further to touch the projectile with your lower chest.

Close-grip pull-ups are good for pulling the lats downward. This technique is worth including in your routine if you are focused on varied approaches and pumping as many muscles as possible.
The horizontal bar grip exercise is considered one of the best for pumping up the biceps, as it works its peak. It is due to pumping the peak of the biceps that the arm appears more muscular and voluminous.
Emphasis on the following muscle groups:
- lower latissimus muscles;
- biceps.
Neutral grip along the bar
Correct technique:
- you need to grab the crossbar so that one fist is in front of the other crosswise;
- when pulling up, you should actively bend your back;
- on the way out, try to touch the horizontal bar with your lower chest;
- at the top point, you should take turns turning your head in different directions from the horizontal bar;
- Between approaches you need to change the position of your hands in order to provide different loads.

The technology is notable for the fact that the grip width can be either regular or narrow. Depending on the choice of grip, different muscles are pumped. This is why the grip along the bar is popular - each athlete can choose individual parameters for pumping the muscles he needs.
Responsible for this type of technology:
- lower latissimus muscles;
- toothed;
- brachial muscle.
Partial pull-ups with underhand grip
Correct technique:
- grab the bar with a medium reverse grip;
- pull yourself up exactly halfway;
- At the highest point, fix the body at an angle of 90 degrees to the floor, then bend your arms, trying to bring your collarbones as close as possible to the crossbar.
Partial pull-ups are aimed at high-quality development of the biceps due to the principle of load concentration. Maximum tension is achieved if you use a small range of motion and do not connect the stretching and resting points of the biceps. The correct technique for performing pull-ups with an underhand grip involves keeping the body in constant tension. This can be done due to incomplete bending of the elbows.
The load goes on the following muscles:
- biceps brachii muscles;
- biceps.
Problems when pulling up

Pull-ups on horizontal bars, like any other exercise, are fraught with the appearance of nuances and various problems at different stages of training. There are four categories of problems that you may encounter when performing the exercise:
| Category | Description | Recommendations |
| First | Can perform 1-2 pull-ups in one approach | The result is normal for a beginner. It indicates that it is too early to exercise with your own weight. To improve your skills, you need to start with the passive part of the pull-up:
It is recommended to do 3 sets of 5 repetitions at first; the process of lowering the body lasts 5-6 seconds. After a couple of weeks, you can reduce the number to two and lower the body more slowly. In addition, to make pull-ups easier, you can perform the exercise by resting your feet on the floor and gradually increasing the load on your arms. If you can’t reach the bar with your chin, you can do the lift halfway, just bend your elbows as far as the load allows. |
| Second | 2-4 reps per set | The second group should stretch the number of approaches and reduce the number of repetitions. At the same time, do not forget about the maximum intensity of pull-ups. Thanks to this, a large number of muscle fibers will be under load, and neuromuscular connections will be strengthened. The first two weeks you need:
After two weeks, it is recommended to perform 8 approaches as many times as possible, with the same break. An exercise called the “static hang” also helps. You must initially take a lifting position with your arms bent, and then try to hold your body at the top point for as long as possible and perform the descent. |
| Third | Best attempt – 5-7 times | The problem for people in the third category is that they have sufficient strength but insufficient endurance. The recommendations are as follows:
|
| Fourth | 8-12 reps per set | If you are in this category, then your body weight is too low for you. Therefore, it is necessary to use weights in training. These can be either special weights or any acceptable option. The main rule that must be followed is that the weight of the equipment should not be higher than 10% of its own weight. This load will help reduce the number of repetitions by 3-4. |
Benefits of Pull-Ups

Pull-ups on the horizontal bar have a positive effect not only on the condition of the muscles. They have a number of other positive aspects:
- When performing a pull-up, the body is in good shape, all muscles are tense and involved with a high load.
- The horizontal bar or crossbar on which the exercise is performed can be found not only in the gym, but also in any yard, which makes pull-ups incredibly accessible.
- Thanks to tightening, you can prevent the appearance and development of diseases such as scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis.
- During the exercise, your posture improves significantly.
- The body quickly acquires relief.
- Pull-ups can be performed either as independent exercises or combined with other sports elements - in any case they will be effective.
- Depending on the execution technique and grip width, different muscle groups are pumped. Therefore, it is possible to select an individual technique and method of implementation to meet specific requests.
What muscles work when pulling up[edit | edit code]
This complex exercise requires the joint work of several muscle groups and includes movements in two joints (shoulder and elbow). When doing a pull-up, you first use multiple muscles in your hands and forearms to grab the bar. Strengthening them is of great importance for performing various everyday tasks - both for working at the computer and for doing physical labor. Then you engage the large paired muscles of the shoulders, shoulder girdle, and back.
LATISM DORSI
. They play an important role in performing pull-ups. They are responsible for rotating the arms in the shoulder joints inward, towards the center of the body, for moving the arms towards the center of the body and back, behind the back. In addition, they play a synergistic role in stretching and flexing the lumbar spine in any direction. In sports jargon, this pair of muscles is often called wings.
TRAPEZIUS MUSCLES
. They also play an important role in performing pull-ups. This is a pair of large superficial muscles that stretch from top to bottom from the base of the skull to the middle of the back and laterally from the thoracic vertebrae to the shoulder joints. Their main function is to move the shoulder blades and support the arms.
FOREARM FLEXORS AND EXTENSORS
. The muscle structures between the elbows and wrists include a large number of muscles, including the finger flexors and extensors, brachioradialis (flex the elbows), pronators (turn the palms down), and supinators (turn the palms up). These are the muscles that allow you to grip the bar.
BICEPS
. One of the auxiliary muscles involved in pulling up. Responsible for rotating the forearms and bending the arms at the elbows. They are located on the front side of the shoulders. The biceps are best worked with reverse grip pull-ups.
MUSCLES OF THE MIDDLE BODY
. This group of muscles consists of the rectus abdominis (the six quadrants called the abdominals), the obliques, the transverse abdominis, and the erector spinae. This area is the source of functional movement throughout the body and provides stability during exercise, including pull-ups, and maintains correct posture while standing and sitting. Strong midsection muscles are absolutely essential to maintaining good physical fitness, as body strength must be built on a strong and reliable foundation.
DELTOID MUSCLES
. They are responsible for the attractive sloping contour of the shoulders and consist of three beams: front, side (middle) and back. Pull-ups, although not the main exercise for developing the deltoid muscles (with the exception of their posterior bundles), still significantly strengthen them
PULL-UP RECORD IN 3 MINUTES (MEN): 100 Ngo Xuan Chuyen (Vietnam) 1988, “The Strongest Soldier in Vietnam” competition
3 MINUTE PULL-UP RECORD (WOMEN): 67 Elicia Weber (USA) July 28, 2009, Claremont, Florida
In the USA, the President's Council on Physical Culture and Sports has established the following standards for performing pull-ups on the bar: Men: norm = 8; excellent = 13; Women: norm = 1; excellent = 8.