What is caffeine?
Before we figure out the pros and cons of this substance, as well as the benefits of caffeine for a bodybuilder, let's figure out what it is in general.
At the end of the article, as always, I will describe to you my experience of taking caffeine (regular coffee and caffeine capsules), and also tell you where to buy it cheaper.
Caffeine is an alkaloid and a powerful CNS (central nervous system) stimulant. It can also be classified as a narcotic drug (it is addictive and requires an increase in dosage).
Caffeine is found in plants such as:
- Coffee.
- Tea.
- Mate (drink of the Guarani Indians).
- Guarane (evergreen creeping shrub from the Sapindaceae family).
- Kole.
- And many others.
Also, caffeine can be found in energy drinks, sports nutrition, almost all fat burners, and many pre-workout complexes.
Reviews from real customers
- Alena: I consumed caffeine while dieting. A minimum of calories put my body into energy-saving mode. With this drug it is easier for me to play sports, study and lead an active lifestyle.
- Svetlana: There is an effect, I take caffeine benzoate in tablets as recommended in the instructions. Initially, a simple method was not enough, I had to take up sports and master the culture of nutrition. The kilograms are falling off, but I feel cheerful.
By consuming caffeine wisely, you will get good spirits and rapid weight loss.
Caffeine for weight loss. Effects for a bodybuilder
You and I, as people involved in sports, are interested in three main questions:
- How does caffeine help you lose weight?
- Is there any point in taking caffeine?
- And if it makes sense, then how much and how to take?
I think I'm right)
So, let's talk about the main effects of caffeine directly for a bodybuilder.
Most of the studies that have been conducted with caffeine have been aimed specifically at those sports that require a significant increase in endurance.
From this point of view, caffeine really helps to achieve more serious results.
First theory: fat-burning effect of caffeine
The very first and MOST BELIEVABLE theory is that caffeine promotes the production of ADRENALINE (the fear hormone), which accelerates the release of free fatty acids into the blood and is a stimulant of the central nervous system.
In an article about how to overcome fear, we looked at a very interesting ability of adrenaline, which was used by our ancestors tens of thousands of years ago.
I'm talking about the ability of adrenaline at the reflex level to force the human body (and not only) to mobilize all its energy reserves for instant decision making.
This is a reaction called "Fight or Flight!" This is what adrenaline can trigger.
Caffeine promotes the production of this same adrenaline.
Due to this, at the very beginning of our training, the muscles begin to “eat” or “burn” available fatty acids, while maintaining reserves of muscle glycogen (fast fuel, stored carbohydrates in the muscles and liver).
Scientific research has confirmed this theory.
Do you understand?
Those. THE MAIN FUEL for muscles (glycogen) is not yet consumed, but FATs are already burning. I think it's perfect. Due to this, endurance increases.
But, in fact, it is obvious that this effect is very beneficial for any athlete training with iron, and not just for a person seeking to increase his endurance.
You feel an energy boost at the very beginning of training, your performance is at a high level, and your glycogen “tanks” are still full, despite the fact that fats have already begun to burn.
- Those. we are not sluggish (the central nervous system is stimulated by caffeine) - this is the case.
- We burn fat reserves - that's two.
- And we have unspent glycogen for longer workouts.
How cool is that? Still would.
Very often they talk about the ability of coffee to suppress appetite. Research doesn't support this.
Fat burning is associated precisely with the processes of starting the production of adrenaline and starting the burning of fatty acids in the blood as a priority.
Second theory: caffeine directly affects muscles
This theory is that caffeine can directly affect skeletal muscles (the ones we pump), changing key systems that regulate the breakdown of carbohydrates inside cells.
That is, roughly speaking, scientists wanted to draw the conclusion that caffeine directly causes muscles to reduce glycogen consumption.
Many studies have been conducted, none of which have been completed, so no clear results have been obtained.
Third Theory: Caffeine Makes You Work Harder
The third, MOST COMMON and MOST PROVEN by scientific experiments theory of all.
Caffeine can make a person feel like they have done less work than they actually have.
This is explained by the fact that caffeine, due to its effect on the nervous system, can provide a psychological effect to athletes that they are not working as hard. Also, caffeine can enhance the strength of muscle contractions.
Oddly enough, caffeine is VERY SIMILAR to adenosine! Why strange?
Yes, because adenosine is an inhibitory type nucleoside neurotransmitter that plays a role in stimulating sleep and suppressing alertness, because its concentration increases during prolonged wakefulness of the body and decreases during subsequent sleep.
Those. Caffeine is a stimulant, but similar to adenosine, which promotes sleepiness. How so?
The fact is that caffeine does NOT have the same effect as adenosine, although it can interact with adenosine receptors on brain cells.
Instead, caffeine STIMULATES the production of adrenaline, a hormone that makes you feel better during exercise.
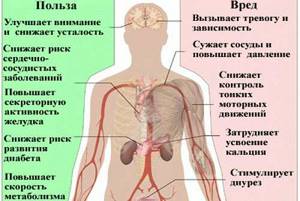
Other effects of caffeine
Here are other, no less interesting, effects of caffeine:
- Prevents Alzheimer's disease and dementia when consumed 3 to 5 cups per day (by preventing the formation of beta-amyloid plaques in the brain).
- Coffee lovers live longer (coffee helps slow down the process of brain destruction).
- Reduces the risk of developing breast cancer in women (Nutrigenet and Nutrigenomics Study 2015).
- Helps avoid systemic inflammation, heart and vascular diseases.
- Helps increase testosterone levels after training (by an average of 21%).
Negative effects of caffeine
Since caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant, one should not forget about the negative effects of caffeine on the body, especially if used improperly or in excess.
- May aggravate the ulcer.
- Worsening of the course of cardiovascular diseases.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Anemia (hypertension).
With these contraindications, it is better to stop drinking caffeine and try to improve athletic performance through training programs and nutrition.
Beneficial features
The invigorating substance has a number of useful properties:
- Helps improve mood. Inspiration and creativity appear. A person wants new achievements, new ideas arise. This is why coffee is popular among creative people.
- Helps cope with headaches by dilating blood vessels. It will be enough to brew yourself a cup of aromatic drink.

- Increased performance and mental activity. This is useful in work, sports, and study. They can be consumed in the form of dietary supplements and pre-workout complexes.
- Promotes the production of gastric juice, which improves the digestion process.
- Diuretic. For kidney problems, it can have a positive effect.
- Increased blood pressure. Recommended for people with low blood pressure.
- Promotes weight loss.
Caffeine with creatine: can I take it?
I have already talked about the interaction of these substances in an article about creatine monohydrate.
People very often hear the misconception that caffeine inhibits the action of creatine by destroying the latter's molecules.
But the interaction between creatine and caffeine is still debated. Many studies contradict each other.
If we analyze the collected scientific data, we can conclude that caffeine is indeed an antagonist of creatine, but their TOTAL EFFECT will be more positive than individually.
If it is very exaggerated, then you can take the effect of creatine = 2, the effect of caffeine = 2. Accordingly, caffeine + creatine = 3 (effect of caffeine = 2, effect of creatine = 1).
Conclusion: We will not get the same effect as we would like to expect by reducing the effectiveness of creatine, but the total effect will be greater.
How coffee helps you lose weight

Is it possible to drink coffee while losing weight? Caffeine actually has a positive effect on lipolysis (the breakdown of fat tissue). In this regard, caffeine can partially replace the hormone adrenaline. Adrenaline causes lipolysis - by compressing fat cells, it releases fats into the blood.
About an hour after a person drinks coffee, the concentration of fatty acids in his blood increases.
By the way, this feature applies not only to coffee, but also to many types of tea (green, black, oolong tea) - in short, all caffeine-containing drinks. This also includes green coffee, which has caused so much noise. Believe me, it is no better at promoting the destruction of adipose tissue and the release of fats into the blood than the usual black version of the drink.
Where is there more caffeine: tea or coffee?
Let me list below the main caffeine-containing drinks and show the caffeine content in each:
- Black tea – 40 – 60 mg;
- Green tea – 75 mg;
- Freeze-dried coffee – 60 mg;
- Coffee brewed in a coffee maker – 60 – 120 mg;
- Red Bull, Burn – 100 mg;
- Coca-Cola – 40 mg;
- Dark chocolate (~50g) – 40 mg;
- Milk chocolate (~50g) – 12 mg.
Those. we need to understand what kind of tea and what kind of coffee we mean.
If you compare black tea and freeze-dried coffee, you may end up with roughly the same caffeine content per cup.
But if you compare the same black tea and coffee from a coffee maker, the caffeine content may differ in favor of coffee by almost two times.
Does coffee burn fat or not?

How does coffee burn fat? Of course, this is not a magic drink that can rid you of extra pounds in a couple of weeks. The caffeine it contains increases performance and artificially invigorates the body. In addition, coffee increases metabolic rate by 20%. An interesting fact is that coffee reduces addiction to sweets by blocking the corresponding receptors in the brain. Therefore, if you really want something sweet, trick your body with a cup of coffee.
Why does coffee make me sleepy?
There is a scientific explanation for this.
- The most unpleasant thing that can happen is a problem with the adrenal glands. If such a symptom occurs regularly after drinking coffee, then you should consult a doctor.
- This can happen if you drink several cups of coffee one after another, after a short period of time. There may be spasms or constriction of blood vessels in the brain, which will make you want to sleep. It is worth thinking about the amount of coffee you drink.
- One of the latest studies confirms that if you feel sleepy after drinking coffee, this may indicate the presence of the Einstein-Barr virus in the body. This virus adversely affects the nervous system and promotes the formation of cancer cells. Maybe the name of the virus makes you smile, but it has been established that 50% of people on Earth carry this virus in their blood.
- Drowsiness after coffee may indicate problems with the pancreas. In this case, enzymes poorly digest substances entering the body, caffeine is not completely filtered out, and the lion's share of it ends up in the brain.
- The last and most common reason is that caffeine affects the central nervous system differently among people. Nerve cells in the brain can not only be stimulated by caffeine, but also inhibited. In most cases, this is a sign of caffeine overdose and overstimulation, and, as a result, triggers a defense mechanism that causes drowsiness.
Green coffee, Green coffee with ginger, Tropicana Slim green coffee
We should also talk about the now popular dietary supplement “Green Coffee”. Some scammers even use the names of popular bloggers (such as Tatyana Rybakova) to promote their product.
This wonderful unroasted coffee is designed to help with weight loss due to the content of Chlorogenic acid (which is also found in regular roasted coffee, but in smaller quantities). This acid has received little research to date, but dietary supplement manufacturers have seized on the fact that, according to some experiments, it can create conditions under which fats in the body are used as energy during exercise.
Thus, it will be much more effective to purchase a proven sports fat burner than to rely on Green Coffee. Without a well-thought-out training program and calorie counting, you should not hope to lose weight.
If you liked the article, share with your friends!
My experience with caffeine
To be honest, I’m still a coffee lover.
I fucking love coffee, in all its forms. And the very smell of coffee gives me a feeling of such homely warmth and comfort.
This is probably due to the fact that when I visit my parents in my hometown, my mother, who always gets up early in the morning, makes coffee in a Turk.
The aroma spreads throughout the house! After that I wake up. Such a warm feeling, even now. I want coffee made by my mother)
And after a trip with my Ksyushka to Thailand, I also fell in love with iced coffee - Frappuccino! If you haven't tried it, I highly recommend it! You're lucky if there's a Starbucks in your city) I'm jealous)

So here it is.
Usually, I drink 1-2 cups a day. I don’t allow myself more, despite the fact that I bought a coffee machine for home - my very old dream) Another confirmation that dreams come true!
So, I try not to drink more than 1-2 cups of coffee a day.
During cutting, when the low-carb diet is completely annoying, I buy a jar of caffeine to feel good:

I literally take one tablet (200 mg) 30-60 minutes before training once a day and feel better during training.
I think it’s stupid to describe the sensations of taking caffeine, but let’s stick to tradition and tell you exactly my experience:
- Mental focus is MUCH BETTER. Even after work, concentration on training is higher.
- Endurance improves. It takes much longer to do cardio, and the intensity of the exercise increases.
- The head becomes light. I don’t know how to describe it, but you start thinking from scratch. It helps a lot after work.
- Separately, I would like to highlight strength in training. It becomes 5-15% higher on average. Depending on the condition and recovery the day before. If you go to the gym on a day off, having slept, rested, eaten, then your strength will increase on average to 5%, if after work, then by 10-15% of the possible (since initially you are more tired).
I bought this caffeine at the cheapest price using this link.
1 cup of coffee (237 ml) contains approximately 100 mg of caffeine. The recommended dose to achieve an effect during training is 3-6 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
Let me explain, for example, if you weigh an average of 70 kg, then 200-210 mg of caffeine before training will give you the desired effect.
What about dehydration during training from caffeine?
A 1977 study in the United States in Ohio confirmed that caffeine does not contribute to dehydration during training.
They took six cyclists and forced them to pedal for 3 hours each. There were no differences in performance or urine output during exercise.
Instructions and recipes for use
For weight loss, the use of caffeine-sodium benzoate is effective. There are the following forms:
- Diet pills. They are recommended to take one or two tablets per day, 100 mg each.
- Caffeine injections for weight loss. Application is possible both for performing wraps and for subcutaneous injection into problem areas (1-2 ml of a 10% solution is injected). Caffeine injections for weight loss should be performed only after consultation with a specialist.
- Powder for performing body wraps.
Basic wrap recipes:
- With papaverine. Caffeine powder is mixed with papaverine solution. The resulting product is used to lubricate the problem areas, cover everything on top with cling film and leave for about 40 minutes. Then everything is washed off with water.
- With Capsicam. 4 ampoules of caffeine are mixed with Capsicam ointment and baby cream. The product is applied to areas of the skin that are more prone to fatty deposits, especially the thighs and sides of the legs, and everything is covered with cling film on top. The composition is kept for about 3 hours, after which it is washed off.
Various caffeine-containing drinks can be prepared for oral administration. Quite effective with ginger and guarana.