Hello my dear readers. Today we will talk about whether bcaa amino acids are harmful to the body? I think it was the fear of side effects that stopped many people from buying sports nutrition. Unfortunately, there is a lot of conflicting information on the Internet. Let's look for answers together. First, let's figure out what btsaa is and why it is needed.
BCAA are amino acids with a branched side chain in their structure. Our body cannot synthesize these substances. They are irreplaceable. There are only three of them in this complex: valine + leucine + isoleucine
- Leucine regulates protein synthesis in the body, as well as nitrogen balance. It is this amino acid that makes up the bulk of all proteins;
- Valine is a source of energy in muscles, as well as one of the important components of tissue synthesis;
- Isoleucine is needed for hemoglobin synthesis and blood sugar regulation. This amino acid is also necessary for the metabolism of leucine.
All these substances are involved in the construction of new muscle fibers. And also, they play an important role in restoration processes. They enter our bodies exclusively through food or supplements. BSAA amino acids are most often found in sports nutrition.
What functions does BCAA perform?
Acting together, three amino acids increase muscle endurance, restore muscles and bones, and replenish energy reserves.
They are extremely important during high physical activity, during rehabilitation after operations and injuries. The capabilities of essential amino acids BCAA allow them to be used for mass gain, reducing fat mass, and working out the relief. BCAA are relevant during aerobic or strength training. Even with moderately intense training, almost 80% of the amino acids that are in a free state in the body are consumed. BCAAs need to be taken additionally to:
- Provide energy flow. When the amino acid pool is full, the body receives additional energy.
- Accelerate protein synthesis in muscles. BCAA stimulates the production of the anabolic hormone insulin and activates mTOR, which responds to muscle growth.
- Suppress catabolism. Amino acid support protects muscle fibers from destruction after training, during drying, and during weight loss diets.
- Increase lean mass and burn fat. The fat burning effect is achieved by activating mTOR.
- Increase the nutritional value of sports nutrition. The effectiveness of other supplements (especially with incomplete protein) increases in alliance with BCAA.
The leucine-isoleucine-valine trio is a precursor for the production of other amino acids, including alanine and glutamine.
In 1990, Bulgarian athletes conducted a study to find out whether free amino acids really accelerate muscle growth. The experiment went brilliantly and completely confirmed the theory.
BCAA composition
As is already known, BCA contains three amino acids. Let's look at their action in more detail.
Isoleucine
It is a valuable source of energy for muscles and is necessarily involved in cellular processes. There are also disadvantages to the effects of this amino acid if taken incorrectly, such as:
- reduction in muscle mass in the human body;
- decrease in blood sugar levels;
- the occurrence of a state of drowsiness, lethargy.
Leucine
It has a major influence on proper muscle growth. Leucine ensures the formation of protein in muscle and liver fibers, and also helps organize the protection of its molecules from destruction processes. In addition, this amino acid balances the amount of serotonin at the highest level, making a person less tired. Leucine also delivers additional energy to muscle fibers.
Valin
It is also a source of additional energy for muscle fiber cells, similar to leucine. It keeps serotonin levels at the highest levels, resulting in the body becoming much less tired.
Important! BCAA, which has a generally positive effect on the body, can lead to a negative effect if used incorrectly. For example, negative consequences of use may be as follows: gastrointestinal upset, drowsiness.
Now, based on the effects of the BCA amino acid complex, let's take a closer look at the benefits and harms of them.
About
Brief description of BCAA:
1) Leucine
A source of energy for muscles and nutrition for the brain. Resists catabolic breakdown. Accelerates wound regeneration and bone healing.
Leucine was discovered by accident when it was found in moldy cheese. In medicine, it is used in the treatment of liver diseases and anemia. The beneficial properties of L-leucine include the ability to normalize serotonin levels, accelerate the synthesis of protein and somatotropin - growth hormone.
2) Isoleucine
First class energy supplier. Helps overcome muscle fatigue and avoid fatigue. Needed for the production of hemoglobin. Slows down catabolism.
The amino acid L-isoleucine not only participates in energy metabolism, but also improves the production of hormones and also strengthens the immune system. There is a lot of it in meat products and nuts, but in order to get the required 1.5-2 g of isoleucine, you will have to eat several kilograms of these products, which is difficult for the gastrointestinal tract. On the other hand, if the dosage is exceeded, isoleucine can lead to loss of muscle mass, drowsiness and lethargy. Sports nutrition with BCAA allows you to accurately calculate how much isoleucine enters the body.
3) Valin
Along with leucine and isoleucine, it is involved in energy supply to muscles. It is not metabolized in the liver and is actively used by muscle cells.
L-valine is needed for muscle growth and muscle synthesis. The amino acid's ability to increase the body's adaptive capabilities, increase serotonin, and shorten the recovery period after exercise has been experimentally proven.
BCAA - benefits and harm, 10 functions
BCAA photo
1. BCAAs increase muscle protein synthesis. There is an increase in muscle mass and its maintenance during the non-training period (recovery after injury). This occurs when consuming alanine, aspartic and glutamic acids.
2. The increased content of leucine in the BCAA mixture enhances the building of muscle mass in older athletes who strive for body relief. Its proportions will be 4:1 in relation to valine and isoleucine.
3. BCAAs increase fat burning (leucine) and glucose tolerance (isoleucine). During training periods for fat loss, the athlete reduces calorie intake and takes nutritional supplements high in BCAA.
Leucine increases energy expenditure, therefore, fat “disappears” faster and at the same time reduces the feeling of hunger. As a result, a person eats less, uses more energy and ultimately leads to loss of fat mass. Isoleucine, in turn, increases fat burning and prevents its accumulation.
4. BCAAs improve hormonal balance for strength and endurance by increasing testosterone and decreasing cortisol levels in addition to reducing inflammation.
5. BCAA develops strength when receiving more than 4 grams of leucine per day. Improves neuromuscular coordination.
6. Increases endurance and reduces fatigue. BCAAs are used as a source of energy in the human body, preventing premature fatigue and fatigue by inhibiting tryptophan in the brain.
During exercise, signals are sent to the brain that the body is tired. This leads to a decrease in muscle strength and endurance. The amino acid tryptophan is responsible for signal transmission, valine can reduce activity and its quantity, so the feeling of fatigue is “extinguished.”
7. BCAA maintains the integrity of muscle fibers. Reduces muscle soreness and allows you to train more often to effectively and maximize your athletic potential.
8. Reduces muscle catabolism (degradation), protects muscle tissue. Prevents a decrease in muscle mass if the BCAA content in the blood plasma drops sharply.
9. Normalizes insulin production and metabolic rate, reduces the risk of developing diabetes.
10. BCAAs protect the body from aging and are used in the treatment of oncology and liver. They increase the formation of new mitochondria, thereby reducing age-related muscle loss.
Daily requirement for BCAA in women and men
There is a persistent stereotype that sports nutrition is only for men. If a girl is interested in starting training, she is concerned about how much and in what dosage to take sports nutrition drugs. The dose is calculated based on body weight, not gender.
Where are BCAAs found?
Essential branched-chain amino acids BCAA must come from outside - with food or sports nutrition.
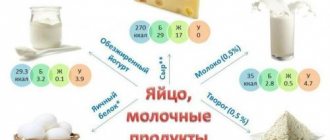
Food sources of BCAA:
- Lean meat, poultry.
- Fish.
- Dairy products.
- Eggs.
- Cereals.
- Legumes.
- Nuts.
Some types of meat contain up to 15-20 g of BCAA per 100 g of protein. However, most professional athletes prefer special protein and amino acid mixtures to natural proteins, since BCAA has greater bioavailability. In other words, nutrients are better and more fully absorbed from sports nutrition rather than food. For comparison, amino acids from a steak will enter the bloodstream in 1.5 hours, and from amino acid supplements in 15 minutes.
Within 45-50 minutes after physical activity, the “protein corridor” is open. Amino acids from a piece of meat eaten after a workout will be connected to the metabolism after the “corridor” closes. After training, you need to take free amino acids, supplementing them with carbohydrates - to restore glycogen reserves.
Which form to choose
BSAA is most often taken in powder. Amino acids reach their destination faster and immediately begin to work. Moreover, the dispersed mass easily mixes into a protein shake.
- the capsules
with water.
Gelatin shells take longer to dissolve than powder. It is recommended to take 2 pieces 1-3 times
. - Manufacturers offer BCAA drinks
- complexes in the form of tablets with a liquid substance inside.
They are inferior to the previous ones in terms of results. Consume 3-5 pieces during training and 4-6 after, as well as 3 pieces in pauses between meals
. - The bcaa liquid complex
is absorbed faster than the powder.
The norm
is
45 ml before and after work in the gym
.
The daily norm
is
3-4 times
.
Supplements can be combined with all types of sports nutrition. To gain weight, take it together with citrulline and anabolic steroids. To find out why BCAA is needed in sports, you can include it in your daily menu and compare the results before and after taking it a month later.
They are not produced naturally, but enter the body with protein foods.
Recently, experts are increasingly talking about the low effectiveness of individual amino acid intake. They support their point of view by the fact that eating a healthy piece of steak is much cheaper and healthier, and there is even more protein. The only difference is that in this case the amino acids will enter the body a few minutes later than when taking BCAA.
Who are BCAA's suitable for?
Amino acid support, and especially taking BCAA, is always useful:
- While building muscle mass.
- On drying, during relief work.
- During aerobic exercise
It is especially important for weightlifters and bodybuilders to take BCAAs. Additional amino acids have a positive effect on protein synthesis, increase energy potential and prevent muscle breakdown. Incorporating essential BCAA amino acids into your diet can significantly increase your overall body weight and protect your muscles.
BCAA contraindications
You can often hear the question: can I take BCAA amino acids, what is the harm to the body and is it safe? Often we lack basic knowledge of the structure and functioning of the human body. Bcaa amino acids are not dangerous, beneficial and necessary for the normal functioning and functioning of the body.
Only for an ordinary person who does not regularly and seriously engage in any kind of sport, additional intake of amino acids is unlikely to be necessary, provided that they have a complete diet rich in protein foods. In the case when sports activities take place on a regular basis, rapid recovery after exercise, increased endurance and progress in muscle building are necessary; it is impossible to do without BCAAs. Otherwise, energy losses and the rate of destruction of protein fibers will negate all efforts during training.
It depends on you how the amino acids will manifest themselves. Choose high-quality drugs, take into account the dosage, then you can get a lot of benefits from the use of BCAA amino acids.
Release forms
BCAA are available on the market in liquid, powder, capsule, and tablet forms. All of them are equally effective, regardless of what the athlete takes - a cocktail of dissolved powder, tablets or liquid amino acids.
Powdered BCAA amino acids are bitter and poorly soluble in liquid. The quality of a product can be determined by its characteristic taste and the film that forms when stirred in water.
There are BCAA amino acids available for intravenous injection, but they do not provide any benefits and increase the risk of side effects.
Real Side Effects
Adverse reactions occur due to improper use of the sports supplement. BCAA can cause belching, heartburn, and problems with bowel movements. This occurs when the drug is taken on an empty stomach.
Amino acids activate the digestive system, gastric juice begins to be produced in larger quantities (in other words, the gastrointestinal tract functions in full mode). Because of this, undesirable consequences arise.
Conventionally, side effects include sprains and tears of muscles, wear and damage to joints. BCAA increases endurance and helps muscle growth. Because of this, people involved in bodybuilding and other sports significantly exceed permissible physical activity. This is where injuries happen. For a supplement to be beneficial, you need to take it wisely.
Production
Manufacturers use 4 main technologies:
- Extraction of whey hydrolyzate.
- Biofermentation.
- Chemical synthesis.
- Enzymatic synthesis (using enzymes).
The last two methods are used extremely rarely. Nowadays, BCAA amino acids are produced mainly by biofermentation, when strains of bacteria E. coli and C. Glutamicum, aspartic and pyruvic acids are used to isolate leucine, isoleucine and valine. This technique is 3-4 times more expensive than chemical hydrolysis.
Leucine, isoleucine and valine are produced together not so much because they enhance each other's effects, but because such a fraction is easier to isolate. Separating BCAA into individual amino acids is much more difficult and expensive.
BCAA composition
These 3 essential acids differ in their molecular lattice and aliphatic (side) chain structure. Amino make up 1/3, are responsible for the formation of muscle tissue, and participate in many processes. Each of them performs specific functions
- Isoleucine
is a source of energy. Deficiency leads to chronic fatigue, apathy, and decreased muscle mass. Promotes the healing of microtraumas of fibers received after strength training, increases the body's endurance. - Valine
supports nitrogen metabolism, accelerates regeneration, and prevents protein denaturation (destruction). - Leucine
stabilizes glucose levels, stimulates the synthesis of growth hormone, cell and tissue renewal. Bcaa leucine gives energy and enhances the effects of the others.
Ratio of amino acids in BCAA
On the sports nutrition market there are formulations with different ratios of essential amino acids leucine, isoleucine and valine - 2:1:1, 4:1:1, 8:1:1, 10:1:1 (2-10 g of leucine per 1 g of isoleucine and 1 g valine). There are other options, such as BCAA 3:1:2. The proportion 2:1:1 is considered classic. Moreover, it is the most effective.
The proportion of L-leucine is always higher, since it serves as the key that opens muscle protein synthesis and accelerates muscle growth. Isoleucine increases the energy-burning abilities of BCAA, and valine completes the energetic and stimulating effect of amino acids.
What are BCAA amino acids?

Muscle tissue is made of protein, and protein is made of amino acids, which are strung like pearls in a necklace. For muscles to grow, new beads (amino acids) are needed. Protein biosynthesis is impossible without important components in the strings of the necklace - BCAA amino acids.
The composition of bcaa amino acids is leucine, isoleucine and valine. These are three powerful weapons with which the body quickly reacts under stress and strain. When training takes place and the muscles are loaded, it is these three amino acids that first come to the rescue and restore muscle fibers.
Bcaa amino acid complex is essential for the human body. The chemical structure of each BCAAs resembles a branch, hence their name. They are known for their powerful effects, reducing the feeling of fatigue during exercise and nourishing muscles during exercise, as they are located directly in them, and not in the liver.
During training, BCAA amino acids act as a source of fuel, when the workout is completed they are involved in building muscle mass. The effect of taking it is to enhance protein synthesis, the production of insulin and glucagon. The amino acid leucine is the most powerful stimulator of insulin secretion, which plays an important role in post-workout recovery. To get results, you need to take BCAA amino acids immediately after finishing your workout.
Valin
A branched chain amino acid, it has industrial applications in the fermentation of alcoholic beverages and serves as a central building block of many important enzymes. Valine is necessary for creating energy reserves in the human body and increases the physical strength of muscle mass. Foods containing high amounts of valine are popular among athletes and bodybuilders who want to accelerate muscle growth.
Leucine
Occupies a central place in the metabolism of muscle tissue, promotes growth and maintenance. An important building block for many proteins, supports tissue healing processes. Adults need to consume between 10 and 50 mg of leucine per kilogram of body weight. A deficiency in the body can be caused by a lack of vitamin B6.
Isoleucine
Amino acids play a key role in energy supply to muscle tissue. This is important during periods of extensive exercise or acute hunger. If isoleucine is present in sufficient quantities in the blood, the body does not have access to storage reserves, which would inevitably lead to a decrease in leucine and a decrease in muscle mass.
This effect should be avoided by athletes trying to build muscle mass.
How they work
BCAA amino acids are a structural component of proteins, a supplier of building materials and nutrition for muscles. Each serving of a protein shake or protein meal first goes through the process of protein oxidation, is broken down into amino acids, and only then is transported to the muscle fibers. Literally: amino acids, coming from food, on the way to the muscles are processed in the liver before getting to where they are needed, that is, into the muscles.
The value of BCAA amino acids is that the body does not need to waste time on their absorption. Free amino acids are quickly absorbed in the stomach and enter the blood, and then transported to the muscles.
Which is better, regular amino acids or BCAA?
What is better to take regular amino acids or bcaa? The answer to this question depends on your aspirations. To achieve results, build muscle, maintain volume and not feel exhausted after exercise, choose bcaa. They act purposefully and quickly reach where they are needed.
Branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) are important for the human body. Critical for muscle hypertrophy (growth) and maintenance during periods of non-training. They have a positive effect on tissue regeneration, healing and metabolic processes through protein synthesis in the liver.
Plant sources of protein, meat, milk and eggs are most suitable for meeting the recommended daily protein intake. Professional athletes should compensate for protein deficiency by consuming dietary supplements, which are useful for the prevention and treatment of certain diseases (diabetes).
Supplementation with BCAAs is recommended during periods of high intensity exercise, which will promote muscle growth.
Are BCAA's harmful?
The idea that BCAA amino acids can be harmful makes no sense. If we consider them dangerous, then we will also have to talk about fish, meat, milk and other protein products.
Possible adverse reactions always have clear prerequisites:
- Poor quality raw materials, violation of production technology.
- The use of biofermentation technology, in which the final product may contain D-isomers with potentially unsafe effects.
A possible risk of using BCAAs is that leucine is too strong an mTOR stimulator. This is why it is not advisable to constantly take BCAA in high dosages for the purpose of gaining mass.
Conventionally, side effects include sprains, muscle damage, and wear and tear of joints. BCAA amino acids, as an energy substrate, provide an increase in strength and endurance, so bodybuilders sharply increase loads, which leads to injuries. With a reasonable approach, such troubles are excluded.
Myths about harm
There are many myths surrounding these beneficial substances. At the same time, there are no clinical trials confirming their harm. I would like to go over the main “horror stories” in a few words. I hope this will finally dispel your doubts.
In sports nutrition, you simply get a concentrated set of BCAAs. Those. The daily intake of such amino acids in the diet corresponds to several scoops. Just because the product is concentrated, it does not become chemical. These are still natural ingredients.
Myth No. 2:
BCAA amino acids cause ulcers and gastrointestinal upset
. Studies show that even if you exceed the daily norm, you will not get poisoned. If you systematically abuse these substances, you can only harm your kidneys. In this case, for a long time it is necessary to exceed the daily intake by 10-15 times.
Myth #3:
Proteins and BCAAs lead to impotence
. It was always strange for me to read about this. Millions of men around the world use sports nutrition. However, none of them spoke about its harmful effects. Moreover, there are no clinical trials to confirm this.
When purchasing a dietary supplement, just pay attention to the ingredients. Various dyes, sweeteners, and preservatives found there cause gastrointestinal upset. They can also provoke allergies and negatively affect liver function. It is better to buy amino acids from well-known companies and with a minimum of additives.
Contraindications
BCAA amino acids are not beneficial for everyone. Reasons to give them up include:
- Pathologies of the pancreas.
- Diabetes.
- Gastritis, ulcers, other problems with gastrointestinal tract functions.
- Diseases of the heart, kidneys, liver, gall bladder.
It is not recommended to consume amino acids without examination by a doctor and consultation with a specialist.
In addition to the presence of direct contraindications, a risk factor when using BCAA is exceeding dosages.
Why is it so important to get enough BCAA's?
BCAA are the only amino acids that are not broken down in the liver. All other amino acids are regulated in the intestines before entering the body. But the drugs go straight into the bloodstream. This means that their consumption directly affects its levels in the blood and muscle tissue. What's also interesting is that BCAAs can be oxidized to provide energy during exercise, so they can also be considered an important fuel for exercise.
Consuming bcaa before exercise can increase the amount of the substance that ends up in muscle tissue. This has many benefits, such as reducing the amount of lactic acid produced during strenuous exercise. This will improve the rate of oxidation in the muscles.
They can also improve the circulation of growth hormone in the body. Growth hormone is an anabolic hormone that causes muscle growth.
BCAAs play their most important role in muscles. Their concentration is higher in muscle cells. That's where she does her work. Bcaa is continuously released from the liver and other organs and redirected to the skeletal muscles to help normalize blood sugar levels. In addition, they may be responsible for producing 40% of the sugar released into the blood during exercise.
Due to the importance of amino acids for muscle tissue and blood sugar production, it is important to get enough of them for an effective workout. Consuming a shake that is high in carbohydrates, protein, and amino acids will trigger an insulin response that will help transport BCAAs into muscle cells. However, leucine is more important than insulin. There is one regulatory receptor in muscle cells that, when stimulated by insulin, triggers protein synthesis. But it also depends on leucine. In other words, protein synthesis (and therefore the rate of muscle regeneration) depends on how much free leucine is available. BCAA levels decrease during exercise, making supplementation with them very important during exercise.

In order for the body to synthesize new proteins, you need to consume 1 to 4 grams of leucine per day every day. This has been confirmed by the World Health Organization. This minimum amount must be consumed for leucine to begin interacting with insulin receptors. But this is just the minimum. In fact, if you are an athlete or bodybuilder doing heavy lifting, you should take about 12 grams per day.
BCAA content in different protein sources (per 100 g of product):
Admission standards
Drinking BCAA amino acids with every meal is not profitable, because they are expensive. That's why:
- To gain weight, it is more beneficial to drink BCAAs before and after training, when the body needs a quick supply of amino acids. On non-training days, it is better to take protein shakes.
- To lose weight, you need more BCAA - before and after training, in the morning and between meals. This regimen will reduce catabolism, protect muscles and suppress hunger. It is possible to take BCAA during training.
Bodybuilders consume amino acids in various dosages. It is optimal that 1 dose contains at least 5 g of BCAA (15 g per day). The maximum result is achieved with a single dose of 10-20 g of BCAA. Smaller doses do not compensate for the amino acids used by the body.
You can take BCAA-based sports supplements constantly, without breaks or cycling.
When choosing a product, it is important to consider the ratio and number of components in the complex. Unscrupulous manufacturers underestimate doses in order to inflate the cost of products.
Instructions for use of BCAA for women and men
Every person who is seriously involved in sports knows that after training, protein intake is mandatory for muscle growth, increased strength and faster recovery.
The metabolic window occurs immediately after exercise and has a huge impact on the success of the workout. Regardless of whether the load is for endurance or building muscle volume. It is unacceptable to miss the “golden hour” and deprive yourself of results by not correctly using changes in the metabolic process.
From the 15th minute to the 45th minute after training is the best time to increase protein synthesis and restore glycogen. Within an hour, this potential completely disappears, and after 2 hours, insulin receptors become resistant to insulin and from that moment on, a 100% negative protein balance occurs.
For this reason, without supplementation in the post-workout period, you will lose muscle mass. All the hard work in the gym is completely lost because post-workout nutrition is not received, glycogen and protein synthesis are not restored.
After training, you need to quickly stop the process of tissue breakdown, so take BCAAs. Before starting classes, they will “take care” of muscle nutrition, this is especially important for those who:
- has solid muscle mass and needs high doses of protein;
- starts training;
- classes were interrupted.

Instructions for use of BCAA
The goal is to gain muscle mass
BCAAs are taken immediately at the beginning of training, during and after physical activity. The liquid form is convenient to take. Amino acids and a little sugar are dissolved in water.
Drink little by little throughout the workout to ensure a constant supply of amino acids, carbohydrates and fluids. Amino acid capsules are taken in the morning to prevent muscle catabolism. The more intense and longer the workout, the more BCAAs will be used as fuel. This will allow, after taking a dose of amino acids, to retain energy during exercise and train with greater intensity from start to finish.
The goal is to lose weight
In addition to the rules described above, amino acids are added throughout the day in between meals. This will prevent the destruction of protein fibers during the period of “hunger”.
How to take BCAA amino acids?
Each time you take it you need 5-10 grams. When building muscle mass, make sure to get amino acids in the morning, immediately after waking up, to stop the muscle breakdown that occurs while you sleep. An additional dose at any time during the day (5-10 g) will provide increased mental energy, reduce hunger and promote muscle growth. Be sure to take a dose of BCAAs before and after exercise.
The same principle is used to calculate the bcaa amino acid intake for girls or bodybuilders who are cutting or want to reduce body fat. It is important to consider that the calorie content of the diet is reduced, the muscles maintain their size and condition due to the supply of important BCAAs.
The benefit from smaller doses is unlikely to be noticeable; it will not be enough for the body's needs. Please note that not all manufacturers act honestly; they often deliberately underestimate the dosage of amino acids per serving, but the cost remains high. Before purchasing, compare several medications to estimate the number of servings and dosage.
Interaction of BCAA with other drugs
BCAA's can be combined with almost any sports nutrition. However, amino acids cannot always be mixed with other products.
You cannot take amino acids and gainers, protein, meal replacements at the same time, or drink them during meals - this slows down the absorption of BCAA amino acids and, therefore, makes taking them impractical.
BCAA's are not combined with L-carnitine as they interfere with its absorption.
If the formula does not contain vitamin B6, take it separately. Pyridoxine (B6) is involved in protein synthesis.
BCAA for weight loss. Taking BCAA for weight loss

BCAA amino acids are used during periods of low-calorie diets and weight loss as the main means of preserving muscle mass. Contrary to popular misconceptions, BCAA's themselves do not burn fat, but they can contribute to this process by increasing protein synthesis. In this article we will look at the correct method of using BCAA amino acids for weight loss.
BCAA and weight loss
You must immediately understand that BCAA amino acids by themselves do not build muscle and do not contribute to weight loss. This is just a building material that is actively used by the body after a certain physical activity. And nothing more.
In terms of weight loss, BCAAs can perform 2 main functions:
- Preservation of muscle mass
- Increased calorie expenditure (by increasing the rate of protein synthesis)
To maintain muscle mass during periods of low-calorie diets and extensive, long-term physical activity, the body needs amino acids. If there is a shortage of them, your own muscle tissue is consumed. Taking BCAA during this period allows you to saturate the body with amino acids, thereby suppressing catabolic processes and preserving muscle mass.
BCAAs may also indirectly stimulate fat loss by increasing calorie expenditure. How does this happen? The fact is that the process of protein synthesis (muscle growth) is very energy-intensive and requires a large amount of calories. Thus, heavy intense exercise and high levels of amino acids in the blood will not only create conditions for muscle growth, but will also significantly increase calorie consumption, and with it the consumption of subcutaneous fat. Taking BCAA during this period will promote weight loss.
How to take BCAA for weight loss?
First, wisely create a plan and diet that will ensure a calorie deficit. In simple terms, create a nutrition program in such a way that you consume fewer calories than you expend.
Secondly, start using high-intensity strength loads - maximum working weight, 6-8 repetitions. There is a misconception that high repetitions are the best for burning fat, but this is not true - intense strength loads and the use of basic multi-joint exercises give much greater results.
Thirdly, consume enough protein - each meal should contain 30-35 grams. quality protein. Yes, BCAAs contribute to a significant increase in the concentration of amino acids in the blood, but this is not enough - the main amount of amino acids must come from food.
Fourth, take BCAA before (30 minutes) and after (immediately) training - 6-8 grams. at a time. On rest days, you can take BCAA in the morning in the amount of 4-6 grams. - this will help suppress catabolic processes and further increase the rate of protein synthesis. By following the above recommendations, you will not only lose excess fat mass, but also gain lean muscle mass. And remember one simple truth: BCAA is just a supplement that helps improve the results of your training and diet. However, it will not do the main work for you. Improve your workouts, create a competent nutrition plan and constantly monitor your body's reaction to changes. Only in this case, sports supplements, including BCAA, will bring the desired result.
What types of food contain the most BCAA?

BCAAs have been a necessary part of the human diet long before they were taken with supplements. Branched chain amino acid supplements are very popular for their ability to increase protein synthesis during and after exercise. In addition, they allow you to conveniently increase the leucine content in your muscles, without the need to eat anything. However, with the advent of supplement popularity, the importance of dietary sources of these amino acids has faded into the background.
Chewing and swallowing food that contains essential amino acids is much more difficult than mixing powder with water and drinking. But on the other hand, you can’t always get by with supplements alone. Products, real food, always contain many other beneficial substances besides BCAA, which is why it is so important to include them in the diet.
If you're trying to get the most out of your diet to build stronger muscles and recover faster from workouts, check out these statistics on the amino acid content of some popular protein sources.
This table shows interesting information about the amino acid composition of food. For example, turkey breast provides more protein than any other source (not counting eggs, which are measured differently altogether). But turkey contains the least amount of BCAA. For comparison, dry roasted peanuts contain much more leucine, and other bcaas, than any other source, even meat. But peanuts have much less protein.
Table of BCAA content in products
| Products | A portion | Protein | BCAAs | Leucine | Isoleucine | Valin | BCAA per 1 gram | Leucine per 1 gram |
| Chicken breast | 180 g | 36 g | 6.6 g | 2.6 g | 1.8 G | 1.9 g | 0,18 | 0,8 |
| Lean beef | 180 g | 36 g | 6.2 g | 2.8 g | 1.6 G | 1.8 g | 0,17 | 0,8 |
| Tuna | 180 g | 33 g | 5.6 g | 2.5 g | 1.5 G | 1.6 g | 0,17 | 0,8 |
| Salmon | 180 g | 34 g | 5.9 g | 2.7 g | 1.5 G | 1.7 g | 0,17 | 0,8 |
| Beef steak | 180 g | 36 g | 6.2 g | 2.8 g | 1.6 G | 1.8 g | 0,17 | 0,8 |
| Telapia | 180 g | 34 g | 5.9 g | 2.7 g | 1.6 G | 1.6 g | 0,17 | 0,8 |
| Turkey breast | 1 | 40 g | 5.2 g | 2.8 g | 1.1 G | 1.3 g | 0,13 | 0,7 |
| Egg | 1 | 6.3 g | 1.3 g | 0.54 g | 0.3 G | 0.4 g | 0,21 | 0,9 |
| Egg white | 1 | 3.6 g | 0.8 g | 0.3 g | 0.2 G | 0.3 g | 0,23 | 0,9 |
| Roasted peanuts | 180 g | 12 g | 6.8 g | 3.1 g | 1.7 G | 2 g | 0,14 | 0,7 |
To avoid confusion and make things clearer, two right-hand columns have been inserted into the table to make it easier to compare one protein source to another. Note that per gram of protein, eggs, both white and yolk, contain the most BCAAs. Eggs are also very high in leucine. This should be of interest to many, because leucine is the most important in terms of muscle protein synthesis. But, nevertheless, the leucine content in eggs is only slightly higher than its content in other protein foods.
What food is the best source of BCAA?
Any of the foods listed above are a good source of BCAA as well as protein. The approximate amount of leucine that should be present in each meal is 3 grams, so 200 grams of any meat is enough for one meal.
If you can eat them, six whole eggs or the whites of nine eggs will give you 3 grams of leucine. On the other hand, 200 grams of peanuts may not seem like a lot, but when you consider that you have to take six handfuls of peanuts to get 200 grams, then the amount is actually impressive.
The next step is to study your diet (meal schedule, number of calories and BJU). Are you getting enough leucine in each meal? If not, try changing your diet. If your diet doesn't change, then it's time for you to increase your BCAA intake through supplementation.
Roles of BCAA
BCAA have many functions in the body:
Protein synthesis
BCAAs can speed up protein synthesis in muscles. This makes them both an anabolic (muscle-building) and anti-catabolic (protecting muscles from damage) supplement. But how exactly does this happen?
Muscle protein synthesis occurs when amino acids combine to create muscle tissue.
This constant movement of protein in the body and the accelerated oxidation of leucine for energy means that leucine is in demand during exercise. Therefore, if there is not enough of it, it may not help you gain weight.
As you probably already know, muscle tissue is made of protein. And protein is made of amino acids, which are connected like beads on a string. Thus, you can see that muscle is built from amino acids, which are combined into proteins. This is called muscle protein synthesis. Although leucine, valine and isoleucine are important elements in building muscle, their role is much more important than the simple “blocks” from which proteins are built.
Research has shown that beta, and leucine in particular, stimulates muscle growth by directly stimulating the muscle protein synthesis machinery. Leucine works as a key to start the synthesis process, during which amino acids combine and build muscle protein. In addition, leucine increases the amount of insulin in the blood. Insulin can also be considered an anabolic hormone because it speeds up the protein building process. Protein synthesis stimulates the release of insulin, which allows muscle cells to take sugar from the blood and use it as energy. Insulin also causes muscle cells to take amino acids from the blood.

Another hormone affected by BCAAs is cortisol. Research has shown that athletes who took amino acid supplements had lower blood levels of the hormone cortisol during exercise. Reducing the release of cortisol allows you to further speed up protein synthesis because cortisol stimulates muscle breakdown and interferes with the hormone testosterone. Athletes taking this supplement lose almost no muscle mass after exercise and recover faster after training. This anti-catabolic effect reduces post-workout pain.
Energy production
Amino acids are marketed as glucogenic, ketogenic, or a combination of the two. Glucogenic amino acid can be used to produce glucose using gluconeogenesis. And the ketogenic amino acid creates acetyl, which is a precursor to many fatty acids.
Leucine is fully ketogenic, valine is fully glucogenic, and isoleucine has both qualities. Valine and isoleucine can be used to produce glucose.
Leucine is especially powerful in terms of energy production. It can provide high amounts of ATP to skeletal muscles. ATP is a molecule that transfers energy to cells that contract in muscles (and ATP also performs many other functions).
To meet the increased energy demands that occur during exercise, the body begins to break down muscle tissue to produce BCAAs. But if you took a bca supplement before the exercise, you can cover these requirements without breaking down muscle to do so. This will allow you to do an intense workout without losing weight.
Creation of Alanine and Glutamine
The human body also needs alanine and glutamine during exercise. Again, muscle fibers are destroyed to produce them. And the destruction of muscle fibers leads to mass loss, which no athlete can afford. By adding BCAA supplements to your food, you can provide the body with the material to produce alanine and glutamine from the outside.
Intense weight training produces a severe catabolic response. Glycogen reserves are depleted quickly, and the liver has to compensate by synthesizing glucose and L-alanine for energy. Supplements can help you maintain the right amount of alanine.
Also, drinks enriched with these supplements can help the body create the amino acid glutamine directly inside skeletal muscles. Glutamine levels within muscles control protein synthesis and nitrogen balance. This is what drives muscle mass gain.
Glutamine adds volume well, expanding cells. An increase in cell volume stimulates anabolism and stops catabolism. In addition, glutamine transports nitrogen between organs and provides energy to cells of the immune and digestive systems.
Leptin regulation
Consuming leucine supplements stimulates the release of the hormone leptin. Leptin is associated with the regulation of metabolism, weight and appetite.
The release of leptin in the body is related to the body's fat content. The more leptin is released, the more fat the body stores. If you follow a low-calorie diet, the amount of leptin drops, which causes obsessive thoughts about food - because the body is trying to regain the amount of fat. He now has a certain level.
And leucine has the same effects as leptin, tricking your body into thinking you just ate and are getting enough calories. This will relieve you of hunger and speed up your metabolism.
BCAA in proteins
One question many people ask is should you take bza while on a balanced diet that already contains a lot of protein? Although BCAAs are found in many protein foods, supplementing with them still has specific benefits.
Even such an easily digestible protein as whey cannot quickly deliver amino acids to the muscles. The addition of pure amino acids is much more effective in this case. Once purified, they almost instantly enter the bloodstream. Although whey protein is rapidly absorbed, the metabolic response will be different.
When whey protein reaches the intestines, it will take 4 minutes to digest before the amino acids are available to the body. If you were relying on protein, you most likely won't notice its effects in time.
In other words, although you get BCAA from protein, you get it much faster from a supplement than from food, making it much more effective for your workout.