An increased level of insulin in the blood can cause problems with the pancreas, since it is responsible for the production of this hormone.
Insulin itself is associated with blood sugar levels, so a sharp increase in its level can lead to hypoglycemia, obesity, and diabetes.
That is why it is important not only to consult a doctor in a timely manner, but also to strictly follow a certain diet. Diet is the safest (compared to medications) way to regulate insulin in the blood.
A properly composed menu will reduce sudden hormone surges, which have a negative effect on protein-fat and carbohydrate metabolism in the body.
IMPORTANT : Excess insulin in the blood can lead to serious consequences, including hypoglycemic coma. The worst case scenario could be death, so it is strongly recommended that at the first sign of a hormone imbalance, you consult a specialist and formulate a course of treatment, including diet, exercise, and taking medications prescribed by a specialist!
The need for a diet with high insulin
When specialists prescribe a diet for patients with high insulin levels, they are trying to stabilize hormone levels. It is necessary to prevent sudden changes in the amount of sugar in the blood. Regular foods affect this indicator and stimulate the production of insulin in large quantities.
If a diabetic eats foods with a high glycemic index, serious changes occur in the body. The patient's health is at risk. Therefore, foods with high GI should be excluded from the diet forever.
It is undesirable to go to extremes; doctors do not advise limiting your diet as much as possible. Too little blood sugar leads to hypoglycemia. To prevent health problems, you need to consume foods regularly in small quantities. If you keep a short interval between meals, the patient will not feel hungry.
The number of calories contained in foods is also taken into account. Diabetes is more difficult in overweight patients.
There are no symptoms of diabetes in the early stages of the disease. Complications develop slowly, the patient does not experience discomfort. If you do not follow a diet with high insulin levels, you need to be prepared for negative consequences. An insulin-dependent form of the disorder develops.
The pancreas cannot always work intensively. The gland cells are depleted, the level of secreted enzymes decreases. You have to inject yourself with insulin all your life to regulate the amount of carbohydrates.

If a diabetic does not want to adjust his diet, he will have to take medications. The drugs compensate for carbohydrate metabolism and accelerate the transition of diabetes to the insulin-dependent form.
If you don't follow the diet, complications arise:
- the retina of the eyes is destroyed,
- diabetic foot often causes amputation,
- kidneys are failing
- life expectancy decreases,
- heart attacks and strokes occur frequently.
A diet with high insulin levels does not help manage diabetes fully. This is an integral part of complex therapy. A properly formulated diet helps reduce glucose and insulin levels.
Nutrition
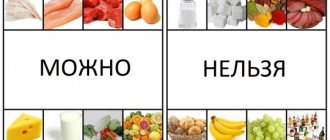
What products should I include?
If you follow all the rules of the diet, then keep in mind that you will have to create a menu every week. This is necessary in order to maintain a balance of nutrients in the body. Keep in mind that the daily calorie intake is 2300 kcal .
The diet itself should be balanced and varied, since diet is not a one-day phenomenon. You will have to carefully plan your menu, because in no case should it include foods that can stimulate insulin production. Eliminate fatty, fried and spicy foods forever. The daily salt intake should be no more than 10 grams. You can use the following products as a basis:
- Boiled lean meat without skin (turkey, chicken, rabbit, veal);
- Boiled or baked fish (hake, pollock, pike perch);
IMPORTANT: Fish is digested by the body much easier than meat products. Therefore, if you feel uncomfortable eating meat frequently, you can reduce the amount of meat in your diet and increase the amount of fish dishes.
- Boiled and raw vegetables (except for starchy types);
- Berries and fruits with low sugar content (apples, pears, cherries, blueberries, raspberries, etc.);
- Fruit drinks (natural juices, unsweetened compotes);
- Chicken eggs;
- Porridge (oatmeal, millet);
- Products containing soy;
- Low-fat dairy products.
What should you not eat?
- Sweets in any form, including confectionery;
- Sugar;
- Juices in packages and carbonated sweet water;
- Alcohol;
- Butter pastries;
- Wheat bread;
- Fatty meats;
- Fried foods;
- Spicy dishes;
- Pickled products;
- Smoked products.
Basic diet rules
Proper preparation and adherence to an approved diet helps improve the condition of high insulin levels. Signs of hypoglycemia can be stopped if specific foods are consumed in a timely manner. The approved diet is followed until the patient recovers.

A diet with high blood insulin is followed according to the following rules:
- The patient's diet must be balanced,
- You should not consume sugar in any form,
- It is recommended to give preference to foods with low GI,
- A diabetic should never go hungry
- the amount of calories in foods should be minimal,
- consume 25% of calories in the morning, 30% in the afternoon, 10% for each additional snack,
- it is necessary to reduce the amount of carbohydrates,
- you should not drink sweet drinks,
- There should not be a lot of fatty foods,
- you need to eat more fruits and vegetables, plant foods,
- dairy products should not contain fat,
- diabetics require split meals 4-5 times a day in small portions,
- you need to drink more water.
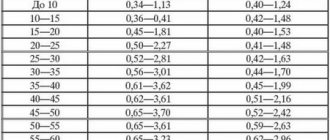
If insulin levels are high, you will have to limit your consumption of foods with a high glycemic index.
With increased physical activity, the level of carbohydrate metabolism stabilizes. The body's sensitivity to insulin increases. Enzyme concentrations are normalized with moderate physical activity.
If you have high blood pressure, you should not subject the body to forceful loads; a hypertensive crisis may develop. Increase the load during training gradually.
Causes and consequences of increased hormones in the body
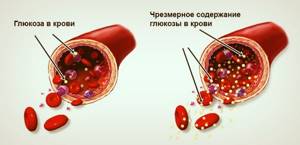
Excess insulin produced in the body disrupts all types of metabolism - carbohydrate, protein and fat. An elevated hormone leads to non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, when the receptors stop responding to the presence of insulin, and the transport of sugar to the organs does not occur, and the functioning of the organs depends on this, since glucose provides energy for the functioning of the human body's systems.
In addition, this situation can increase the volume of the hormone in the blood. The mechanism of action of its increase is as follows - due to the lack of sensitivity of receptors to insulin, the food taken acts by increasing the volume of glucose in the blood vessels, the increased glucose causes additional formation of insulin, and its level increases above normal.
The next reason for an increase in the hormone is a tumor disease, in which tumor cells begin to produce the hormone, and its amount increases. The growth of the substance can also be caused by severe stress, heavy physical work or participation in strength sports. An increase in the hormone is possible with multiple ovarian cysts in women.
High insulin can also cause type 1 diabetes. This happens because when there is an excess of the hormone, the pancreas reduces the rate of its generation, receiving a signal that the production of the hormone is not required.
Since the insulin produced has a vasoconstrictor effect, its excess leads to surges in blood pressure. Elevated hormones can cause kidney failure. It negatively affects the functioning of the nervous system. An excess of the hormone sometimes causes gangrene of the extremities, which begins with poor circulation. Excess hormone has a detrimental effect on the reproductive sphere, causing difficulties in conceiving a baby and causing infertility.
The consequence of excess hormone can be hypoglycemic coma. In severe cases, it is fatal. Therefore, insulin levels need to be monitored, especially in patients with type 2 diabetes.

Recommended Products
A balanced diet for adjusting insulin levels includes vegetable and fat components. Seafood is very good for diabetics. Fruits and nuts contain a lot of chromium.
Fish oil contains omega-3 acids. Flax or pumpkin seeds have a beneficial effect on the digestive system and help normalize sugar and insulin levels.

List of recommended products:
- chicken without fat, beef, lamb,
- dietary fish,
- rye bread without refined flour,
- oatmeal or buckwheat porridge,
- legumes,
- vegetables, fruits with a small amount of carbohydrates,
- green vegetables, celery, spinach, lettuce,
- kiwi, apples, pears,
- garlic helps normalize cholesterol levels,
- potatoes in small quantities,
- seaweed,
- fermented milk products,
- berries, jellies, mousses,
- avocados, oranges, lemons,
- vegetable oils,
- honey in small quantities,
- eggs,
- almonds, other nuts,
- coffee with milk in small quantities,
- freshly squeezed juices, fruit drinks without sugar.
Using this list, diabetics can create their own diet for the week.
To prevent your sugar level from jumping sharply, you need to use the glycemic index table of foods.
Diagnostics
If you suspect insulin resistance, you should check:
- is there protein in the urine;
- triglyceride level;
- glucose concentration;
- ratio of good and bad cholesterol.
Tissue resistance to insulin can be confirmed using specially calculated indices:
- HOMAIR indicator should be less than 2.7;
- CARO indicator is less than 0.33.
If their values are higher, then the tissues do not absorb insulin well. In this case, all efforts should be aimed at reducing the patient’s weight. But keep in mind that you should properly prepare for the tests. Only in this case will they be informative.
Before taking blood for testing, you must:
- Do not eat food for 8-12 hours;
- stop smoking half an hour before sampling;
- Avoid physical activity and stress on the eve of the analysis.
You should tell your doctor if you are taking any medications; they may affect the results of the examination.
Patients should know that if insulin resistance is diagnosed, there is no need to despair. This is a fairly serious pathology, and you can cope with it with the help of a proper low-carbohydrate diet and physical activity.
You need to pay attention to foods that have a low glycemic index. The diet focuses on them. When the state is normalized, the menu expands. You can eat foods with an average glycemic index. Losing weight by 10% significantly improves the condition of the body and the prognosis for the patient.
Restrictions
As with any diet, not all foods are allowed to be consumed.

Products not recommended for consumption:
- jam,
- cakes,
- cakes,
- pastries with cream,
- lemonade,
- semolina,
- fatty meat, smoked food,
- canned food,
- spicy foods,
- pickled vegetables,
- boiled carrots,
- beet,
- horseradish,
- melon,
- mango,
- dried fruits,
- vermicelli,
- baked goods made from wheat flour,
- chocolate,
- sugar,
- mayonnaise,
- cream,
- salo,
- duck,
- animal fat,
- grape juice.
This is not a complete list, since the diet for diabetics is determined individually; a nutritionist will tell you what you can eat and what you cannot eat.
Hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus: symptoms and treatment
The main method of combating this pathological condition is to reduce fat deposits in the body. This is done either radically (surgically) or conservatively (diet and exercise).
A properly selected diet allows you to reduce the consumption of harmful carbohydrates; regular sports activities strengthen muscles and burn excess fat. By changing your lifestyle to a healthy one, your metabolism (metabolism in the body) returns to normal and the development of diabetes is prevented.
Menu for the day
Doctors advise establishing a diet and sticking to it every day. Consume foods at the same time regularly 5-6 times a day in small portions. Dietary fiber, bran, fruits, and vegetables are of considerable importance to the body. A nutritionist compiles a list of foods according to certain rules.
Preference should be given to foods with a low glycemic index. Fruits can be used as a snack after the main meal. If you eat them immediately after breakfast or lunch, the fermentation process will begin in the stomach.
Sweets are excluded from the diet; fruits and berries will help satisfy this need. You can’t eat on the go; it’s not advisable to eat anything before going to bed.

Products for creating a menu for the day:
- tea, omelet with mushrooms, rye bread,
- juice, bran sandwich,
- vegetable soup, chicken, salad, compote,
- cottage cheese casserole,
- boiled fish, cabbage, carrots, tea,
- low-fat kefir,
- oatmeal, low-fat cheese, tea,
- vegetable salad, juice, bread,
- borscht, boiled beef, salad, berry juice,
- orange,
- fish cutlet, vegetable salad, tea.
- yogurt,
- seaweed, boiled egg, tea,
- mushroom broth, chicken, stewed vegetables, uzvar,
- fruit mousse,
- cottage cheese casserole, tea,
- yogurt.
Diabetics have a varied diet, the products are affordable, so the diet will not be expensive.
Not everyone can normally tolerate a reduction in the amount of simple carbohydrates in food. Such measures are needed to regulate sugar levels in the body.
Hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus: symptoms and treatment
Before you figure out how to eat to increase tissue sensitivity to insulin, you need to make sure that you have insulin resistance. Symptoms of the pathology include:
- drowsiness after eating;
- increased incidence of flatulence;
- absent-minded attention;
- accumulation of fat in the waist and abdomen;
- increased feeling of hunger;
- depressive disorders.
If these signs occur, you should undergo a full examination.
Hypoglycemia is when blood sugar drops below normal. Mild hypoglycemia causes unpleasant symptoms, which are described below in the article.
If severe hypoglycemia occurs, the person becomes unconscious and this can lead to death or disability due to permanent brain damage. The official definition of hypoglycemia is a decrease in blood glucose to less than 2.8 mmol/L, which is accompanied by adverse symptoms and may cause impairment of consciousness.
Hypoglycemia is also a decrease in blood sugar to less than 2.2 mmol/L, even if a person does not feel symptoms.
Our definition of hypoglycemia is when a person with diabetes's blood sugar drops so much that it is 0.6 mmol/L below their individual goal level or less. Mild hypoglycemia is blood sugar 0.6-1.1 mmol/L below the target level.
If sugar continues to fall, then hypoglycemia becomes severe when there is not enough glucose to feed the brain. The nuance is that the target blood sugar level is different for each patient.
As a general rule, you should try to maintain your blood sugar levels as in healthy people without diabetes. But in severe cases of diabetes, patients have to specifically maintain elevated sugar levels for the first time.
Read more in the article “Goals of diabetes treatment. What blood sugar needs to be maintained.”
- Symptoms of hypoglycemia
- Nocturnal hypoglycemia during sleep
- If symptoms of hypoglycemia are dulled
- Causes of hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus
- How to figure out what caused hypoglycemia
- Treatment (relief) of hypoglycemia
- How to cure hypoglycemia without raising blood sugar above normal
- Glucose tablets
- What to do if your blood sugar is low just before a meal
- How to cope with a binge eating disorder due to hypoglycemia
- Sugar increased to normal, but symptoms of hypoglycemia do not go away
- Aggressive behavior of diabetics in a state of hypoglycemia
- What to do if a diabetic is already on the verge of losing consciousness
- Emergency assistance if a diabetic patient loses consciousness
- Stock up on hypoglycemia medications in advance
- Diabetes identification bracelets
- Hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus: conclusions
Hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus can be caused by two main reasons:
- insulin injections;
- taking pills that force the pancreas to produce more of its own insulin.
Insulin injections for the treatment of type 1 and 2 diabetes are extremely important, and the benefits of them far outweigh the possible risk of hypoglycemia. Moreover, when you master the method of small loads and can manage with small doses of insulin, the risk of hypoglycemia will be very low.
We strongly recommend that you avoid taking pills that cause the pancreas to produce more insulin. These include all diabetes medications from the sulfonylurea and meglitinide classes.
Not only can these pills cause hypoglycemia, but they also cause harm in other ways. Read “Which diabetes medications do more harm than good.”

Doctors who are behind the times still continue to prescribe them to patients with type 2 diabetes. Alternative methods, such as those described in the Type 2 Diabetes Treatment Program, can control your blood sugar without the risk of hypoglycemia.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia
The symptoms of hypoglycemia become more pronounced the faster the blood glucose level decreases.
Early symptoms of hypoglycemia (you urgently need to eat “fast” carbohydrates, specifically glucose tablets):
- pale skin;
- sweating;
- trembling, palpitations;
- severe hunger;
- inability to concentrate;
- nausea;
- anxiety, aggressiveness.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia, when blood sugar is critically low and a hypoglycemic coma is already very close:
- weakness;
- dizziness, headache;
- feeling of fear;
- speech and visual behavioral disorders;
- confusion;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- loss of orientation in space;
- trembling of limbs, convulsions.
Not all symptoms of glycemia appear at the same time. For the same diabetic, the signs of hypoglycemia may change each time. For many patients, the symptoms of hypoglycemia are “dulled.” Such diabetics suddenly lose consciousness each time due to the development of hypoglycemic coma. They are at high risk of disability or death due to severe hypoglycemia. Why this happens:
- Constantly very low blood sugar levels;
- the person has been suffering from diabetes for a long time;
- elderly age;
- if hypoglycemia occurs frequently, the symptoms are not felt so clearly.
Such people are obliged not to pose a danger to others at the time of sudden severe hypoglycemia. This means that they are contraindicated from performing work on which the lives of other people depend. In particular, such diabetics should not drive a car or use public transport.
Prevention and recommendations
To prevent the formation of large amounts of insulin in the blood, it is necessary to stabilize the presence of hormones. At the initial symptoms of insulin, it is necessary to get tested.

- continuous course of treatment by an endocrinologist,
- special diet,
- take time to rest,
- exercise.
It is important to exclude everything that increases insulin in the blood:
- overvoltage,
- bad habits.
A proper lifestyle serves as a preventive measure against increased hormone levels, as well as other diseases.
The manifestation of increased insulin should not be left to chance, as this is a signal from the body about the development of type 2 diabetes. If necessary, it is important to undergo tests and treatment in a timely manner.
Source of the article: https://diabetsahar.ru/insulin/vysokiy-insulin-pri-normalnom-pokazatele-sahara.html