Home » Products » Healthy products
Category: Healthy Products
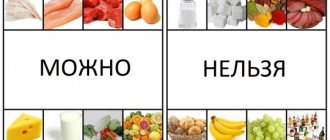
If you think healthy food is boring and bland, you haven't discovered the incredible, palate-pleasing wonders of eating whole foods. But what are whole foods? Clean and unprocessed whole foods include juicy fruits, nutritious and vibrantly colored vegetables, filling and healthy legumes, edible seeds and more.
"Whole" doesn't mean you can't cook those vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and grains, or cut them, puree them, or combine them with other foods. Rather, it means that you buy (or grow and harvest) the items whole, without chemical preservatives, dyes or other additives.
In your own home, you can cut, peel, or otherwise handle them during cooking as you wish. But they remain pure, whole and natural - and grown organically when possible. We recommend that you avoid making homemade versions of unhealthy foods such as potato chips if you want to reap the benefits of eating whole foods.
An architect from Moscow, Emma was always one of those people who could eat whatever she wanted and still stay in shape - until she turned 30. After gaining weight and having skin inflammation, a visit to the doctor's office revealed that she had borderline high cholesterol.
She consulted a nutritionist who suggested she start eating whole foods. After just a few months of focusing on fresh, healthy vegetables and fruits, Emma began to feel (and look) like herself again.
Green tea for weight loss?
What is a Plant Based Diet?
Until now, nutritionists have not come up with a clear definition of what constitutes a complete diet based on the consumption of plant foods. It's not even necessarily a diet - it's more of a lifestyle.
This is because plant-based diets can vary greatly depending on the extent to which a person includes animal products in their diet.
However, the basic principles of a diet based on whole and fresh foods are:
- Eating fresh, minimally processed foods.
- Limiting or eliminating animal products.
- The basis of the diet is vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, seeds and nuts.
- Completely eliminating refined foods such as sugar, white flour and refined (processed) oils.
There is a strong focus on nutritional quality, with many plant-based dieters encouraging local, organic food whenever possible. For these reasons, this diet is often confused with veganism or vegetarianism. However, although the diets in both options are very similar, these diets are not the same. People who follow a vegan diet abstain from consuming any animal products, including dairy, meat, poultry, seafood, eggs and honey. Vegetarians exclude all meat and poultry, but some vegetarians eat eggs, seafood or dairy products.
On the other hand, a plant-based diet (despite its “plant-based” name) is more flexible. Her followers eat mainly plants, but animal products are not strictly limited. While one person following this diet consumes no animal products at all, another may eat small amounts of eggs, poultry, seafood, meat or dairy products. A plant-based diet consists of consuming primarily plant foods while minimizing animal products and processed foods.
Which food to choose?
As you can see, vegetarians were not so wrong. Plant foods actually contain all the substances necessary for the normal functioning of the body. But you can find your pros and cons in any diet. Also in this case. Before you categorically deny vegetarianism, you need to know that there are several types of such a diet.
In some cases, along with plant foods, it is allowed to consume, for example, dairy products. Or vegetarians only give up meat and eat fish and eggs. Therefore, for those who would like to try plant-based nutrition, there is an alternative.
The undoubted advantages of vegetarianism include improving the general condition of the body. Nutritionists note a low percentage of patients with hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis among vegetarians. The functioning of their digestive system is normalized, weight loss is observed and their appearance improves.
A plant-based diet helps you lose weight and improve your health
Obesity is a problem of epidemic proportions. More than 69% of Western adults are overweight or obese. Fortunately, diet and lifestyle changes can make weight loss easier and have long-term health benefits. Many studies have shown that a plant-based diet is beneficial for weight loss. The high protein content of this diet along with the elimination of processed foods is a winning combination for shedding those extra pounds.
A review of 12 studies that looked at a total of more than 1,100 people found that those who followed a plant-based diet lost significantly more weight - about 2 kg on average over 18 weeks - than those who did not limit their intake of animal products ().
Following a plant-based diet and a healthy lifestyle can also help you maintain your weight after losing weight in the long term.
A study of 65 overweight and obese people found that those who followed a plant-based diet lost significantly more weight than the control group and were able to avoid regaining the weight (an average of 4.2 kg) over a one-year follow-up. ().
Additionally, even just eliminating processed foods that are not allowed on a plant-based diet, such as soda, candy, fast food and refined grains, is a powerful tool for weight loss ().
Many studies have shown that a plant-based diet is effective for weight loss. It can also help you maintain your weight loss results in the long term.
Plant-protein diet
This method of losing weight allows you to get rid of most of the fat deposits, because the method is very similar to “drying”. The duration is short - 10 days, but during this period you can safely say goodbye to 5-6 kilograms. A plant-protein diet requires discipline and strict adherence to a given schedule. Eating food should correspond to a built-in system: on certain days you need to eat only the specified foods.
Plant-protein diet menu:
Day No. 1, 2, 7: the menu should consist exclusively of kefir. The total volume per day is 1.5 liters.
Day No. 3, 6, 8: eating protein foods - low-fat dairy products, boiled or steamed meat, fish, meat broths, eggs.
Day No. 4, 5, 9, 10: vegetarian products - fresh vegetables, fruits, steamed food, smoothies, freshly squeezed juices, salads with lemon juice dressing are allowed.

The first days it is difficult to adhere to this scheme, but already on the third day the body will adapt, and a feeling of lightness and satiety will appear. Do not forget about drinking herbal teas, and it is better to refrain from coffee.
It is not recommended to follow any diets during pregnancy, but sometimes it is simply necessary. For pregnant women, the regimen should be prescribed by a nutritionist so as not to harm the unborn child and the mother herself, because the immune system during this period is already weakened.
Pregnant women exclude from the diet all sweets, flour, fried, smoked, salty, as well as grapes, melon, bananas, and sweet varieties of apples. Portions should be small, high in protein and fiber to provide a basic calorie intake. While losing weight, the expectant mother should be under the supervision of doctors. The course of the program is 8 days.
Sample menu:
Day No. 1, 2: low-fat steamed fish and meat, clean water, green tea.
Day No. 3, 4: stewed, boiled and fresh vegetables, unsweetened fruits.
Days No. 5, 6: days number one and two are repeated.
Days 7 and 8: Days three and four are repeated.
A plant-based diet improves health outcomes
Eating whole, fresh foods will not only help you lose weight, but it will also greatly improve your health by reducing your risk and symptoms of some chronic diseases.
Heart disease
One of the most well-known benefits of a plant-based diet is that it is very good for the heart. However, the quality and types of foods included in the diet matter.
A large study of more than 200,000 people found that those who followed a healthy plant-based diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes and nuts had a significantly lower risk of developing heart disease than those who did not consume food plant products.
However, unhealthy plant-based diets that included sugary drinks, fruit juices, and refined grains were associated with a slightly increased risk of heart disease ().
Eating the right types of food is critical to preventing heart disease when following a plant-based diet, which is why following a plant-based diet is the best choice for people at increased risk of developing heart disease.
Cancer
Research shows that a plant-based diet may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer.
A study of more than 69,000 people found that vegetarian diets were associated with a significantly lower risk of developing gastrointestinal cancer, especially for those who followed a vegetarian lacto-diet (vegetarians who eat eggs and dairy products). .
Another large study of 77,000 people found that those who followed a vegetarian diet had a 22% lower risk of developing colorectal cancer than non-vegetarians. Vegetarians (vegetarians who eat fish) had the greatest protection against colorectal cancer, with a 43% reduction in risk compared to non-vegetarians ().
Decreased cognitive abilities
Some research suggests that diets rich in fruits and vegetables may help slow or prevent cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease in older adults. Plant-based diets include higher amounts of plant compounds and antioxidants, which have been shown to slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease and reverse cognitive deficits.
Many studies have shown that high consumption of fruits and vegetables has a great impact on reducing cognitive decline. A review of nine studies, totaling more than 31,000 people, found that eating more fruits and vegetables led to a 20% lower risk of developing cognitive impairment or dementia ().
Diabetes
A plant-based diet can be an effective tool in managing and reducing the risk of diabetes. A study of 200,000 people found that those who ate a healthy, plant-based diet had a 34% lower risk of developing diabetes than those who ate few plant-based foods ().
Another study found that plant-based diets (vegetarian and lacto-vegetarian) reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 50% ()! Additionally, plant-based diets have been shown to improve blood sugar control in people with diabetes ().
Eating a plant-based diet may reduce your risk of heart disease, some types of cancer, cognitive decline and diabetes.
List of foods for a plant-based diet
Eggs and bacon for breakfast and steak for dinner are the traditional diet for many people today.
When switching to a plant-based diet, your nutrition should be centered around plant foods.
If you continue to consume animal products, they should be in a large minority and only of good quality (farm meat, not supermarket salami).
Dairy products, eggs, poultry, meat and seafood should be used as a complement to basic plant foods, not as a main meal.
Full list of recommended products
Fruits : berries, citrus fruits, pears, peaches, pineapple, bananas, etc.
Vegetables : cabbage, spinach, tomatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, asparagus, bell peppers, etc.
Starchy vegetables : potatoes, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, etc.
Whole grains : brown rice, oats, bulgur, quinoa, amaranth, brown rice paste, barley, etc.
Healthy fats : avocado, olive oil, coconut oil, etc.
Legumes : peas, chickpeas, lentils, peanuts, black beans, etc.
Seeds, nuts and nut butters : almonds, cashews, macadamia nuts, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, natural peanut butter, tahini, etc.
Unsweetened plant milk : coconut milk, almond milk, cashew milk, etc.
Spices, herbs and seasonings: basil, rosemary, turmeric, curry, black pepper, sea salt, etc.
Condiments : salsa, mustard, soy sauce, vinegar, lemon juice, etc.
Plant Protein : Tofu, plant protein sources or powders with no added sugar or artificial ingredients.
Drinks : coffee, tea, water, etc.
If you add animal products to your plant-based diet, choose quality products from grocery stores or, better yet, buy them from local farmers.
Eggs : Farm eggs if possible.
Poultry : Free-range, organic if possible.
Beef and Pork : Grass-fed if possible.
Seafood : Wild caught, not farmed.
Dairy: Organic, pasture-raised dairy if possible.
A healthy plant-based diet should focus on eating plant foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. If you eat animal products, they should be consumed in smaller quantities compared to plant foods.
Foods to avoid or minimize on this diet
A plant-based diet is a diet that focuses on consuming foods in their most natural form. This means highly processed foods are eliminated.
When shopping for cereals and breads, focus on fresh produce and when shopping for labeled foods, aim for items with the fewest ingredients possible.
Fast food: French fries, cheeseburgers, hot dogs, chicken nuggets, etc.
Added sugars and sweets: sugar, soda, juice, baked goods, cookies, candy, sweet tea, sweet cereals, etc.
Refined grains : white rice, white pasta, white bread, bagels, etc.
Convenience foods : chips, crackers, cereals, frozen meals, etc.
Processed "vegetarian" foods: specialty meats, artificial cheeses, vegetarian oils, etc.
Artificial sweeteners: synthetic sweeteners, etc.
Processed animal products : bacon, breakfast meats, sausage, beef chops, salami, etc.
Products whose consumption should be limited
While healthy animal foods can be included in a plant-based diet, they should be consumed in minimal quantities:
- Govdina
- Pork
- Sheep
- Domestic bird
- Eggs
- Dairy
- Seafood
When following a plant-based diet, highly processed foods should be avoided and animal products should be minimized.
What is processed food
And what makes processed foods processed? Again, the definition depends on who you're talking to about it and what type of "processing" we're talking about.
Types of Food Processing
There are four different types of foods that are classified as processed.
First type
- minimally processed foods.2 This group includes “naturally occurring edible parts of plants” that are “slightly modified for an essential preservation purpose, but these modifications do not substantially alter the nutritional value of the product.” These include “fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts.”
Next comes a group of processed culinary ingredients belonging to the second type.
. This group includes “food ingredients obtained from foods by minimal processing by pressing, refining, crushing or grinding.” These include "oils from plants, seeds and nuts or whole grain flours and pastas."
Third type
are common processed foods that fall into “any of the previous two groups that have added salt, sugar, or fat” and include “certain canned fruits and vegetables, freshly prepared bread.” These are products from 2-3 ingredients, and most often they are ready to eat.
Finally, we are faced with truly harmful, ultra-processed or highly processed foods, which are included in the fourth type
. These are foods “from the previous group that contain excess salt, sweeteners or fat and include artificial colors and flavors, as well as preservatives to promote shelf stability, maintain texture and enhance palatability.” These foods are typically foods that are low in nutritional value and high in sugar, such as "sweetened beverages, cookies, some crackers, chips and breakfast cereals, some frozen dinners, and various processed foods."
Definition of processed foods
For example, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) defines processed foods as
“products that have undergone any change in their natural state, that is, any raw agricultural commodity that has been washed, peeled, crushed, cut, heated, pasteurized, blanched, boiled, canned, frozen, dried, dehydrated, mixed, packaged or other procedures that change food, depriving it of its natural state.”
So, this means that a bag of raw, pre-floreted cauliflower is actually "processed," according to the USDA.
However, the definition is not limited to this.
The USDA further defines “processed” as any food that “may include the addition of other ingredients, such as preservatives, flavors, nutrients and other food additives or substances approved for use in foods, such as salt, sugar and fats.” "
We're almost done!
The Institute of Food Technologists has decided to include terms such as "storage, filtration, fermentation, extraction, concentration, microwave and packaging" in its list of processed food identifiers.
So, at the end of the day, processed food can mean anything other than completely raw real fruits and vegetables. But that then means you need to eliminate grains, nuts and seeds that have been processed in some way.

Don't complicate your life
It would be almost impossible to give up processed foods. This would entail a huge effort in shipping your food, particularly to local farmers, who would then have to deliver the produce from the garden directly into your hands. Not completely impossible, but difficult.
So let's go ahead and say that unprocessed and minimally processed foods are already great!
The only things you need to worry about are processed and ultra-processed foods. This means avoiding anything that's been pre-cooked, frozen, or packaged. When you're at the grocery store and you see that an item has more than five ingredients, especially ones that you don't understand, then it's been processed or ultra-processed.
Sample menu for the week
When switching to whole foods, your diet doesn't have to be complicated.
The following one-week menu will help you get your bearings. It does include small amounts of animal products, but the extent to which you include animal products in your diet depends on your preferences and goals.
Monday
Breakfast : Oatmeal with coconut milk, berries and walnuts.
Lunch : Large salad of fresh vegetables, chickpeas, avocado, pumpkin seeds and goat cheese.
Dinner : pumpkin curry.
Tuesday
Breakfast : Plain (non-fat) yogurt with sliced strawberries, unsweetened coconut and pumpkin seeds.
Lunch : chili without meat.
Dinner : Boiled sweet potatoes and black beans.
Wednesday
Breakfast : coconut milk smoothie with berries, peanut butter.
Lunch : hummus and fresh or boiled vegetables.
Dinner : Zucchini noodles with pesto and chicken meatballs.
Thursday
Breakfast : Oatmeal with avocado, salsa and black beans.
Lunch : quinoa with feta cheese.
Dinner : Grilled fish with roasted sweet potatoes and broccoli.
Friday
Breakfast : Tofu and frittata with vegetables.
Lunch : large vegetable salad with grilled shrimp.
Dinner : Roasted bell peppers with brown rice.
Saturday
Breakfast : Coconut milk smoothie with blackberries and cashews.
Lunch : Avocado and brown rice sushi with seaweed salad.
Dinner : Eggplant lasagna with cheese and a large green salad.
Sunday
Breakfast : vegetable omelet with eggs.
Lunch : stewed vegetables with bulgur.
Dinner : large salad of vegetables and avocado.
As you can see, a plant-based diet is all about consuming animal products in moderation.
However, many people following this diet consume more or less animal products depending on their specific dietary needs and preferences.
You can enjoy a variety of delicious foods while following a plant-based diet. Our suggested menu for the week will help you get started.