Increased formation of gases in the digestive system is a common problem that arises against the background of various factors, including poor nutrition, body characteristics, and intestinal microflora disorders. Treatment after a medical examination and diagnosis is usually carried out with medications and special massage. Diet for flatulence is a mandatory step in addressing the problem; without revising your diet, you will not be able to get rid of excessive gas formation.
When is it prescribed?
Table No. 4 is shown to people:
- Having an intestinal disorder accompanied by diarrhea.
- For stomach diseases (gastritis).
- For intestinal disorders caused by infectious diseases.
- Those with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (colitis, enteritis, duodenitis, etc.).
- With constipation due to previous intestinal diseases, after eliminating the pathology with medication.
- After treatment of intestinal diseases of any etiology.
- During the period of exacerbation of chronic gastrointestinal diseases. A therapeutic diet is also indicated for pain in the intestines due to chronic diseases, even if this is not an exacerbation, such nutrition simply helps to support the body.
- When treating the intestines surgically in the postoperative period.
In adults and children, intestinal diseases are the most common pathology.
Intestinal obstruction, inflammation of the large or small intestine, inflammation of the stomach wall, disruption of the pancreas - for all these pathologies, following a diet is indicated. If you have problems with the intestines and stomach, it is very important to choose the right nutrition option and table number 4 will be optimal. It is used to alleviate the patient’s condition and normalize regular bowel movements with a diseased intestine.
Recommended drinks to reduce gas production
Even following a diet with increased gas formation in the intestines may not be enough, especially if flatulence is caused by serious disorders of the digestive organs. In such cases, nutritionists recommend including drinks in the diet that have a positive effect on the functioning of the organ, reduce flatulence, eliminate fermentation, and stagnation of feces.
In continuation of the chosen diet for gas formation in the intestines in adults, it is useful to regularly consume:
- Peppermint decoction. Grind the dry leaves of the herb, place the resulting gruel (15 g) in an enamel container, steam with boiling water (250 ml). Infuse the liquid for half an hour under the lid; to concentrate the beneficial elements, it is recommended to wrap the container in a warm towel. Strain and once completely cooled, place in the refrigerator. Use three times a day, recommended dosage is 70–80 ml.
- Drink made from chamomile flowers. Place the plant material (20 grams) into a brewing container and steam with boiled water (300 ml). Place in a water bath and simmer for a quarter of an hour under the lid. Remove, leave to cool, strain. Drink 100 ml three times a day. In a diet for flatulence, it is recommended to consume a liquid rich in useful elements before meals - while reducing the release of gas, the product will improve digestive processes.
- Dill decoction. A diet for bloating will be more effective if you regularly drink a drink made with dill seed. The home remedy promotes digestion, reduces flatulence, actively copes with prolonged constipation, and prevents fermentation in the intestines. To prepare the decoction, put the plant seeds (10 grams) in a brewing container, brew with boiling water (200 ml), leave to brew under the lid for half an hour. After straining, start taking it - consume 30–40 ml three times a day.
A rich drink made from rose hips is also recommended for use against flatulence and bloating. The product acts in several directions at once - it prevents the passage of gases, bloating, has a positive effect on digestion, and stabilizes the level of beneficial microflora in the intestines.

To prepare the drink you will need a tablespoon of ripe fruits of the bush. It is not recommended to grind plant materials - the fruits contain small, hard hairs; if strained incorrectly, there is a risk of causing irritation of the mucous membranes of the throat after drinking the drink. Pour water (300 ml) over the rose hips and place on the stove. Boil after boiling for 10 minutes, leave until cooled, strain. There are no restrictions on the consumption of the drink - drinking the tasty aromatic liquid is allowed up to three times a day. It is not prohibited to add sweet ingredients - honey, sugar. If you are worried about excess weight along with flatulence, you will have to give up sweets, otherwise there is a risk of weight gain and accumulation of fat deposits.
Features of dietary table No. 4

A sick intestine is a serious problem and only medications will not help solve it completely. Proper nutrition and medication treatment will only add up to a good result. For intestinal pathologies, a gentle diet is indicated to relieve the intestines and give it the opportunity to begin to work actively on its own.
Dietary table No. 4 has the following features:
- The patient should be fed in small portions of approximately 400 g.
- You need to eat at least five times a day, six meals are allowed. Three meals are always main courses and a couple more are snacks.
- Food should always be slightly warmer than room temperature, and the same goes for all drinks. Too hot or cold food can disrupt the digestion process, which can negatively affect the functioning of the stomach and intestines if a person has a disease of this group of organs.
- For constipation, such a diet may not help very quickly, and therefore you should first eliminate constipation with medication and only then improve intestinal function with proper nutrition.
- All dishes for intestinal diseases should not be prepared by frying. Boiling, steaming and baking are allowed.
- All products must be ground or crushed, and also undergo heat treatment.
- Nutrition at table No. 4 is more balanced, consuming less fat and carbohydrates and more protein. Calorie content will be reduced due to this.
- You need to drink two liters of pure, still water a day to improve and speed up the digestion process.
With intestinal diseases, people have to deny themselves many things, but this does not mean that a person will starve and receive only tasteless food. Let's look at what you can eat on diet number 4.
Basic principles of nutrition
To get rid of flatulence and abdominal discomfort, you need to remember the following principles:
- You should get rid of the habit of eating on the go and snacking. It must be remembered that food is consumed without haste.
- During meals, you should not wash down your meals with water or carbonated drinks. This can cause intestinal problems.
- You need to eat at the same time every day. The daily routine is of considerable importance, so it must be observed.
- Flatulence is often caused by prolonged use of chewing gum. It should be abandoned.
- To heal the intestines and prevent bloating, it is necessary to consume lean foods without spices, food additives and sweeteners. There should be no salty, sour, smoked dishes or flour in the diet.
Dishes are prepared by stewing, boiling, baking or steaming. Frying is strictly prohibited: it negatively affects the functioning of the digestive system and can aggravate the patient’s condition.
Daily calorie content should be 2300-2500 kcal, weight 2.2-2.6 kg.
It is recommended to eat every 2-3 hours. It’s great if you get 5-6 meals a day. At the same time, we must remember: overeating and hunger strikes negatively affect the health of the digestive system.
Small portions that do not lead to a feeling of heaviness in the stomach are the key to health and well-being.
Recommended and prohibited dishes

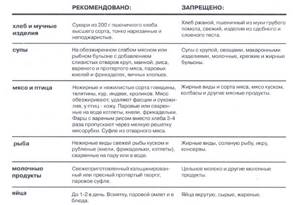
Table No. 4 is characterized by a large list of not recommended dishes, as well as foods that must be consumed according to certain requirements. The table shows which ingredients and how they can be used by a person with a diseased intestine for cooking.
| Allowed | Strictly prohibited | |
| Bread and flour products | Wheat bread in the form of lightly toasted homemade crackers | All other flour products, butter and puff pastry |
| Soups | Only in weak broth, with dietary meat and mucous decoctions of cereals | Fatty broths with the addition of vegetables, frying, fatty fish and meats, pasta |
| Meat and poultry | Chicken, rabbit, turkey, veal, beef, boiled or baked | Fatty meats, sausages |
| Fish | Pieced and chopped lean fish | Salted, fatty fish, caviar, as well as canned food |
| Eggs | 1 soft-boiled egg per day, steamed egg white omelette | Raw or hard-boiled egg, omelette with yolks added |
| Dairy and fermented milk products | Cottage cheese with the lowest percentage of fat content, well pureed | Yoghurt, sour cream, whole milk, full-fat cottage cheese, cheese and cheese curds |
| Cereals | Rice, buckwheat, semolina, oatmeal | Millet, barley, pearl barley |

People with a diseased intestine who adhere to diet No. 4 are contraindicated to consume:
- Spices.
- All types of sweets (honey, jam, candies, packaged jelly, etc.).
- Products with added preservatives and dyes.
- Carbonated water, coffee, strong tea, undiluted juices, alcoholic drinks.
- Marinades and pickles.
- Fruits and berries.
- Vegetables.
- Hard and processed cheese.
At table No. 4, it will be useful for patients to include the following foods in their diet:
- Vegetable decoctions.
- Kissels, diluted juices, clean water.
- Rice water.
- Slimy porridge.
- Teas and herbal infusions.
- Applesauce made from sour apples.
Products should be well combined with each other and constantly replace each other so that the patient’s diet is balanced and not monotonous.
Let's take into account the features of the disease
Select other products depending on the characteristics of the disease. After all, for example, diarrhea and constipation require completely different diets. Products that stimulate bowel movements and have a strong laxative effect
: black bread, raw vegetables and fruits, dried fruits, legumes, oatmeal and buckwheat, stringy meat, fresh kefir, koumiss.
Foods rich in tannin (tea, blueberries), slimy soups and pureed porridges, warm and hot dishes weaken the functioning of the intestines
Recipes for the table No. 4

Many people believe that it is very difficult for people with a diseased intestine to prepare a dish according to the specified diet, but this is not so.
There are several simple recipes that will be useful for diet No. 4:
- Barley soup. 40 g of pearl barley, previously well washed, should be thrown into 600 ml of low-fat meat broth. On the stove, simmer the soup over low heat, stirring all the time, until the pearl barley is well boiled. The soup is cooled to just above room temperature and given to the patient.
- Meatballs made from meat and fish. The meat is thoroughly ground in a meat grinder and mixed with boiled rice cereal. To prepare meatballs, you need to take minced meat, which consists of five parts meat and 1 part rice. Meatballs are molded and steamed.
- Semolina. For 50 grams of semolina take 5 grams of sugar and cow butter. Add semolina to boiling water (one glass) with salt and sugar and stir it. The fire is turned on and the porridge cooks for 25 minutes. Then add a piece of butter.
- Blueberry compote. Only dried berries are suitable. 20 grams of blueberries are poured with boiling water (1 cup) and sugar is added as desired. Place on the fire for 25 minutes and boil all this time. Remove the compote from the stove and let it brew for three hours.
These dishes are prepared very quickly, and you don't need a lot of ingredients. But such dishes are very useful for people with sick intestines; they help not only make food easier to eat, but also nourish the body, allowing the intestines to independently establish the digestion process.
Video
Diet cooking
The method of cooking is dictated by the permitted products. But, as mentioned earlier, all irritants are prohibited. The food is prepared as much as possible without spices; you can only add a little salt and season with a small amount of herbs.
There are also strict requirements for the consistency of dishes. No hard pieces! Therefore, any dish or product requires chopping. Since the diet will be followed for a long time, sometimes it is needed for life, you should take care of purchasing a powerful blender. It is difficult to knead or wipe food manually; not all products lend themselves to this.
How to prepare meals for a diet:
- just cook. These can be individual products or soups, stews. For cooking, a liquid is used, which, if necessary, will be broth. Since fatty foods are prohibited, skin, fat, and any layers must be removed from meat and fish immediately;
- steam. This option is especially good if you want to prepare something like a salad or get an appetizing side dish. When steamed, products retain their aroma and taste as much as possible;
- simmer with water, broth, sauce. Unlike cooking in water, such products have a more pronounced taste and aroma. Dishes are prepared over very low heat in a saucepan or frying pan. You can use multicookers;
- baking in the oven, microwave. You can allow baked dishes, but do not overuse them. They are mainly prepared in the oven. The mode and temperature are dictated by the selected products and recipes. It is important not to achieve a crust. To do this, cover the mold with foil and a lid.
The diet for intestinal diseases in adults is excellent for feeding children of any age. It can also be used for weight loss. Often in the presence of stomach problems. They often complement intestinal diseases.

Weekly menu for intestinal diseases

The weekly meal plan for a patient should be varied, since the same type of nutrition will not provide the body with all the necessary vitamins and minerals that the intestines so need after an illness.
Sample menu for table No. 4:
Monday:
- For Breakfast: rice porridge, crackers or biscuits, jelly.
- Second breakfast: pureed cottage cheese, weak tea.
- At lunchtime: pearl barley soup, minced meat, diluted apple juice.
- Afternoon snack: a glass of jelly or compote, homemade crackers.
- Dinner: steamed omelette, rice porridge, tea.
Tuesday:
- In the morning: oatmeal, a little grated cottage cheese, jelly.
- Second breakfast: soft-boiled egg.
- Lunch: buckwheat porridge with fish, tea or herbal decoction.
- Snack: crackers with jelly.
- Dinner: fish or meat quenelles, compote.

Wednesday:
- For breakfast: rice porridge, mashed apple, tea.
- Snack: jelly.
- Lunch: soup with semolina, meat cutlets, compote.
- Second snack: blueberry compote and biscuits.
- Dinner: buckwheat porridge with pieces of meat.
Thursday:
- Breakfast: rice porridge, cocoa, biscuits.
- Second breakfast: currant jelly.
- Food for lunch: buckwheat soup, meatballs, tea.
- For afternoon snack: jelly with crackers.
- Dinner: vegetable broth, fish dumplings, jelly.
Friday:
- Breakfast: steam omelette, steamed chicken cutlets, tea.
- Snack: crackers, jelly.
- At lunchtime: pearl barley soup, chopped chicken pieces, tea.
- Afternoon snack: mashed cottage cheese, jelly.
- For dinner: semolina porridge, biscuits, tea.

Saturday:
- In the morning for breakfast: curd pudding, compote.
- Second breakfast: applesauce.
- Lunch: chicken meatballs, buckwheat soup.
- Snack before dinner: soft-boiled egg, tea.
- Dinner: oatmeal, grated apple, jelly.
Sunday:
- Breakfast: buckwheat porridge, jelly with crackers.
- For second breakfast: savory cookies, tea.
- Lunch: meat broth, buckwheat porridge, compote.
- Afternoon snack: baked apple.
- For dinner: potato salad with pieces of chicken, jelly.
This diet is approximate and a person with intestinal diseases can independently select dishes from permitted products.
The diet should be balanced; it is important for the patient to eat no more than 3 kg of ready-made meals per day.
Results and reviews
Following a diet can reduce the manifestations of flatulence, as evidenced by patient reviews. However, as practice shows, in the presence of any gastrointestinal diseases, diet alone is not enough.
- “... The problem with flatulence arose a long time ago, which is why I often had to avoid public events. I went to a gastroenterologist, I was examined and diagnosed with colitis. After 3 months of treatment and following a diet, I got rid of my problem”;
- “... Flatulence against the background of constant constipation is a common occurrence for me. Therefore, I am constantly on a diet both for constipation and flatulence. But while I’m on a diet, after 1-2 weeks everything returns to normal, as soon as I stop it, everything appears again. It’s probably necessary to see a doctor and switch to medications in addition to the diet.”
What drink is good for intestinal pathology?
People with a diseased intestine need not only to eat the right food, but also to drink herbal infusions and mixtures.
It helps very well to relieve inflammation from the intestines and improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Chamomile tea made from natural herbs.
- St. John's wort infusion for those who have normal rather than high blood pressure.
- Melissa decoction.
- Blueberry decoction.
- Fennel decoction.

These herbs are excellent in combating intestinal diseases. It is worth drinking different decoctions every day and then the disease will quickly recede, and the rehabilitation period will pass unnoticed and easily.
Advantages and disadvantages
This diet is recommended by many nutritionists due to its many benefits:
- High efficiency.
- There is no need to go hungry.
- You can not only get rid of flatulence, but also lose some weight by eliminating junk food from your diet.
- The menu is varied.
The main disadvantage of this diet is the need to give up your usual food. It won't be easy at first: self-control is required. No other disadvantages have been identified with this diet.
Chronic human diseases may be contraindications, so before starting the diet you should consult a doctor. Perhaps he will change the menu a little, or add certain products to it.
Why is it necessary to follow a diet?
Diet for intestinal diseases is an important part of treatment.
Without it, medications will cope with the disease itself (eliminate bacteria, viruses, improve the condition of the intestinal microflora), but the intestines themselves will take a long time and painfully to accept food, since the walls of the mucous membrane are damaged, and peristalsis may also be impaired. The diet is needed so that the patient’s intestines can gradually start working, and not experience a heavy load every time they eat.
Diet No. 4 helps the patient do this easily and without much effort; all products are quickly absorbed by the body and are easily excreted by the intestines, since they do not form dense feces. Over time, the intestines will be fully operational and you will be able to switch to a normal diet.
What are the dangers of lack of diet for flatulence?
Nutritionists warn that if the diet for flatulence and bloating is not followed, there is a risk of a significant deterioration in health and the appearance of additional problems. Among the complications dangerous to the body, doctors note:
- lack of certain vitamins that take an active part in digestive processes;
- decrease in the level of beneficial intestinal microflora;
- proliferation of bacteria responsible for the fermentation of food particles;
- increased release of toxins (these harmful compounds are the result of bacterial activity);
- dehydration, intoxication of the body.
It is not recommended to give up proper nutrition - diet is no less effective in reducing gas formation than powerful medications. Eating the “correct” dishes and complying with the requirements for heat treatment of products will simultaneously remove all manifestations, reducing the risk of a repeated increase in the passage of gases.
Following a special diet for problems with gas discharge is one of the stages in effectively and quickly eliminating an unpleasant manifestation that can result in unwanted complications. There won’t be any particular difficulties if you arm yourself with a piece of paper and a pen in advance, create a healthy menu and follow the rules of cooking - the body will sensitively respond to a healthy diet by stabilizing digestive processes and reducing flatulence. If even proper nutrition is not enough, gas formation does not decrease, immediately go to a doctor who will find out the reason for the lack of results and prescribe treatment that increases the effectiveness of the diet.

Important! Informational article! Before use, consult a specialist!
How to switch to a normal diet?
Diet No. 4 should be maintained by the patient for 5-7 days.
It is not recommended to follow it for longer, since the monotony of products will not allow the body to receive all the necessary vitamins and minerals. You need to introduce new food gradually every day, adding a couple of new foods in small quantities. If the intestines do not work well after some food, then you should temporarily exclude it from the diet and check how the body reacts.
If everything works out and the intestines are working, then you just need to give up this product. A complete transition to a normal diet can be completely accomplished in two weeks, but it can also be extended for a month if the intestines are still weak.
Table No. 4 is often prescribed by doctors for diseases of the intestines and other gastrointestinal organs. The diet is also recommended for people after intestinal surgery. If you do not comply with this requirement, the rehabilitation process will be long, and complications may also arise. Therefore, it is better to eat as the doctor tells you for several days, so that later there will be no problems with the intestines.
Video: expert advice
Effect on the body
This diet is necessary in order to reduce the load on the intestines and restore its healthy microflora.
Thanks to this diet, the condition of not only the intestines, but also all digestive organs improves. It is possible to prevent the fermentation process . Metabolism will be restored.
In the first days, a person will feel an improvement in health: pain and discomfort in the abdomen will disappear. Eating healthy foods will ensure that the body receives the necessary vitamins, which will also improve the condition.
Necessary foods in the diet
Nutrition for flatulence includes foods that have a “carminative effect” and do not contribute to the formation of gases.
Healthy foods that do not cause flatulence are:

- broth (from lean fish, beef and chicken);
- vegetable soups;
- buckwheat porridge;
- boiled rice;
- semolina;
- oatmeal;
- wheat crackers;
- lean meat (turkey, chicken, rabbit, beef) and fish;
- seafood;
- cottage cheese;
- scrambled eggs;
- low-fat yogurt;
- kefir;
- low-fat sour cream;
- greens (dill and parsley);
- dried bread;
- homemade low-fat pate;
- cocoa prepared with water;
- rosehip and blueberry decoction;
- green tea;
- diluted juice;
- compote;
- egg white omelet.
Allowed foods for bloating
For flatulence, doctors advise including in the diet those foods that do not cause increased formation, as well as those that have carminative properties and, therefore, alleviate the patient’s condition.
It is better to give preference to food that normalizes stool due to soft and slow passage through the intestines. However, special attention should be paid to those products that can affect its microflora, stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Important! The diet for flatulence should be maximally enriched with vitamins and microelements, including potassium, iron, calcium, as well as lipotropic substances, as they have a beneficial effect on bile and blood vessels.
Allowed use:
- crackers made from wheat flour and dried bread;
- lean fish - it can be boiled in pieces or used as part of cutlets and other minced meat dishes;
- lean types of meat without skin - you can use it to make steamed cutlets, meatballs, meatballs or soufflé;
- low-fat and non-acidic dairy products, cottage cheese, sour cream, yogurt, curd soufflé or biokefir, provided that the person does not have lactose intolerance;
- boiled eggs (not hard-boiled), omelettes;
- drinks: green tea, rose hip, bird cherry or blueberry decoction, cocoa prepared with water, fennel tea, compote;
- vegetables: pumpkin, potatoes, carrots, zucchini;
- soups cooked in weak meat or fish broths;
- porridge: buckwheat, oatmeal, semolina, rice, cooked in water and ground;
- greens: dill and parsley;
- bay leaf, cumin.
Prevention measures
For preventive purposes, experts advise doing a fasting day once a week. During this period, it is recommended to consume only buckwheat porridge or kefir.
To prevent flatulence, separate meals are ideal, which eliminates the intake of incompatible foods.
It is important to include healthy and permitted foods in your diet, and to minimize foods that cause flatulence.
Proper nutrition is a method of treating and preventing increased gas formation and bloating, and also helps eliminate other unpleasant symptoms. A diet for flatulence excludes the consumption of prohibited foods and is aimed at observing the rules of food intake and diet.
A feeling of heaviness, increased gas formation, bloating and distension of the abdomen, pain - these are the most common and unpleasant symptoms of flatulence. The disease can be annoying at any age and arise due to various factors. Meanwhile, she is successfully retreating while following simple nutritional recommendations. A special diet for flatulence concerns not only permitted and prohibited foods, but also the frequency of food intake and its temperature.
What not to eat if you have bloating
In the vast majority of patients, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, belching and flatulence are caused by:
- peas, beans, lentils, beans, soybeans (if you use them constantly, then over time they begin to be absorbed better);
- cabbage – kohlrabi, red, white, cauliflower, broccoli;
- milk;
- raw onions, turnips, radishes, potatoes;
- carbonated drinks, kvass, beer;
- grape;
- fresh baked goods, especially with yeast;
- smoking, products with flavor enhancers, preservatives;
- pearl barley, millet;
- hard boiled eggs;
- fatty meat, fish, cream, cottage cheese;
- grain, rye bread;
- nuts, seeds;
- confectionery, sweets.
Potentially dangerous ones (not everyone gets bloated) include pears, apples, mushrooms, bananas, apricots, plums, and celery. Everyone's reaction to foods is purely individual, so in order to identify harmful ingredients, a food diary is needed. All eaten dishes, their composition are entered into it and their tolerance is noted.
Prohibited Products
Products that cause flatulence include:

- yeast baked goods;
- sweets;
- pasta;
- fermented milk foods;
- rye and wheat bread;
- carbonated drinks;
- ice cream;
- whole milk;
- semi-finished products;
- caviar;
- corn;
- meat and fish of fatty varieties;
- sausage;
- salted fish;
- marinades;
- mushrooms;
- smoked meats;
- pickles;
- seasonings and spices;
- canned food;
- sauces;
- nuts;
- salo;
- cream;
- fried or hard-boiled eggs;
- millet, pearl barley and barley cereals;
- sugar substitute;
- jam;
- beer;
- kvass.
It is not allowed to eat foods that contain large amounts of proteins and carbohydrates. It is not recommended to eat a lot of salty and sweet foods.
Bloating and increased gas production are caused by vegetables such as:
- radish;
- cabbage;
- turnip;
- radish;
- spinach;
- soy;
- swede;
- garlic;
- legumes (peas, chickpeas, beans, beans);
- bell pepper;
- onion.
Fruits that are not recommended to eat if you are sick include:
Dried fruits such as prunes or raisins can also cause flatulence. If you have intestinal flatulence, you should not eat fatty foods. Exotic foods and foods containing a lot of spices and seasonings are prohibited.
It is forbidden to eat food containing poorly indigestible fiber and simple carbohydrates, which provoke putrefactive processes. If a person has an individual intolerance to a certain product, then such food should not be consumed either.