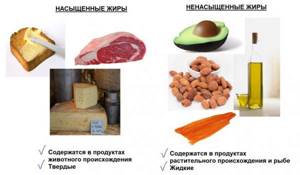
Types of fats by type of fatty acids
Fatty acids are organic compounds that belong to the class of lipids. They can be found in the body not only as separate components, but also play the role of building material for other organic compounds. The human body does not produce these acids on its own, which is why they are called essential.
There are several types:
- Plant origin - found in seeds and fruits of oily plants.
- Animal origin - found in meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, milk.
They differ in appearance:
- Saturated – palmitic, stearic, myristic, lauric acids.
- Unsaturated:
- Polyunsaturated – linoleic, alpha-linolenic, eicosapentaenoic, docosahexaenoic, arachidonic acids.
- Monounsaturated – oleic acid.
Trans fats are also released, which are formed as a result of industrial processing of foods and turn into unsaturated solid fats (convenience foods, fried foods, confectionery and bakery products).
They do more harm than good, so such foods should be excluded from the diet or their consumption reduced.
Saturated fats

They are of the solid type and can be obtained mainly from animal products. They are formed from saturated fatty acids, assembled from at least 8 carbon atoms.
This is the main source of energy that helps the internal organs work. Thanks to them, vitamin D3 is produced, which affects the synthesis of immune cells and the formation of bone tissue, and vitamin A is also absorbed in greater quantities (affecting the functioning of the entire body as a whole).
Be sure to read: Lecithin for weight loss: forms, how to take, daily requirement, what products you need
Solid fats affect the accumulation of fatty deposits, which leads to obesity and increased cholesterol levels in the blood.
Unsaturated fats

Unsaturated ones are more useful for consumption; they can help replenish the body’s reserves of nutrients and elements that are necessary for good health.
And their participation in the processes of lipid metabolism and accumulation in the blood plasma helps to avoid disturbances in the functioning of the liver and intestines and reduces the likelihood of diabetes.
There are two types:
- Monounsaturated (Omega-9) . Thanks to their consumption, the protective function is increased, antibodies are produced that fight cancer cells, viruses, and allergens. They regulate the functioning of hormones, metabolism, and the amount of cholesterol.
- Polyunsaturated (Omega-3 and Omega-6). They regulate cell metabolism, increase immunity, accumulate vitamins, and help fight inflammatory processes.
Why are fats healthy?
Of course, in order to meet the required caloric intake, it is much easier to exclude high-calorie fats from the diet, giving preference to carbohydrates or proteins, which you can eat much more of. But by doing this, you risk getting a whole bunch of health problems caused by a deficiency of healthy fats in the body.
The value of fats for our body should not be underestimated. Firstly, they play a significant role in the construction of skin cells, blood vessels and nerve endings. By consuming fats correctly, you will provide yourself with healthy and elastic skin, a strong heart and a strong nervous system.
Secondly, healthy fats are the building blocks of many hormones in our body, including hormones responsible for reproductive function, as well as corticosteroid hormones. Men who are keen on rocking and sports should pay attention to this, because it is from cholesterol that steroid hormones are formed.
Fat deficiency causes a decrease in the body's immune forces. This is manifested by frequent colds, weakness and increased fatigue
Thirdly, no matter how many healthy vitamins you eat along with salads, without fat they will not be absorbed by the intestinal walls. Thus, along with fats, the entire group of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) is absorbed. It is logical that in the absence of fats in the diet, their deficiency develops.
Therefore, if you decide to go on a diet again, allow yourself to consume at least 25 g of fat for every thousand kilocalories (1 tablespoon of vegetable oil). This amount will fully cover the proportion of fats in the daily diet recommended by nutritionists (20–30%).
Daily fat intake
The rate of fat consumption depends on the age, sex, type of activity, and gender of the person. Consumption of EFAs should not exceed 10%, MUFAs – 13-15%, PUFAs – 6-10% of daily calories.
For people with cardiovascular diseases, consumption is reduced to an average of 7%. For athletes and those who perform heavy physical work, the level rises to 12-14%.
List of healthy fatty foods
It cannot be said unequivocally that foods rich in saturated fatty acids are harmful. Everything is good in moderation. To ensure that food is not harmful to health, you must follow a few simple rules:
- the optimal amount of fat is 1 gram per 1 kg of weight;
- fats should comprise 1/3 of the daily diet;
- It is necessary to increase fat consumption during intense physical activity, as well as in case of stay in a cold climate zone.
Include saturated fats in your diet in limited quantities; the list of products presented in the table below will help in creating a menu for every day. Only a balanced diet will allow you to maintain youth, beauty, health and slimness for many years.
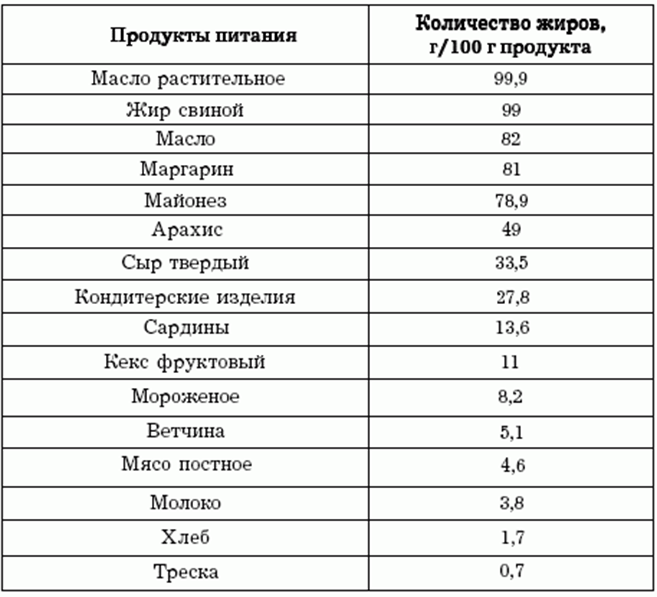
+1
How do saturated fats differ from unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats have a more complex structure of organic compounds; they are converted into solid fats and deposited in the form of cholesterol plaques in subcutaneous reserves.
Unsaturated ones, passing through cell membranes, do not form solid compounds. Therefore, they normalize blood cholesterol levels. They have a double carbon formula, which allows them to be constantly in an active state.
List of products containing them:
- lard;
- rapeseed, olive, ghee, butter, margarine;
- cod;
- duck;
- pistachios;
- walnuts and pine nuts;
- boiled pork;
- avocado;
- eggs.
Trans isomers in food consumed
During the preparation of margarine, modification of unsaturated vegetable fats occurs under the influence of high temperatures, causing trans-isomerization of molecules. All organic substances have a specific geometric structure. When margarine hardens, cis isomers turn into trans isomers, which affect the metabolism of linolenic acid and provoke an increase in the level of bad cholesterol, causing heart and vascular diseases. Oncologists claim that trans isomers of unsaturated fatty acids provoke cancer.
Products containing fats table. Contraindications
The diet has general restrictions associated with chronic diseases:
- cardiovascular pathology;
- chronic hepatitis, pancreatitis, other pathology of the gastrointestinal tract;
- oncology;
- endocrine diseases;
- kidney problems;
- elderly age;
- pregnancy;
- mental illness.
The diet is absolutely contraindicated for children and adolescents due to the possibility of metabolic disorders. Many nutritionists do not accept this system due to the complete lack of fruits and vegetables and the risk of high cholesterol levels. Their patients note the monotony of their diet.

We described the Kwasniewski diet as a controversial method, which, however, has proven to be effective. You don't have to resort to such drastic measures by including some foods in your diet that make it easier to lose pounds.
- Fish fat
Obtained from cod liver. Today it is used in capsules as a regular medicine. The weight loss effect is based on the ability to regulate insulin levels and create a long-lasting feeling of fullness. Take 30 mg (2 capsules) three times a day for three weeks. Then they take a break for three months, after which the course is repeated.
- Meat
Nutritionists consider the meat of young animals (lamb, goat, calf) as a source of monounsaturated fatty acids, which trigger the process of breakdown of lipid reserves.
- Vegetable oils
Traditional source of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The leader is olive - a tablespoon contains 9 g. It is no less useful, but has a specific taste. Regular consumption of vegetable oils has a beneficial effect on digestion and metabolism, which accelerates weight loss.
- bitter chocolate
- Nuts
A very high-calorie product, but a recognized “champion” in terms of the content of valuable lipids.
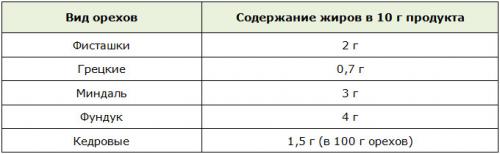
Given these numbers, you can safely include a small amount of treats in the diet of a person losing weight.
- Hard cheese
If the fat content is less than 40%, the product is considered dietary. There are products that help you quickly lose a few kilograms. Unlike margarine, they are composed of healthy fatty acids.
- Avocado
This exotic fruit has long been known as an effective fat burner. But 10 g of its pulp contains 1 g of fat. It is important to eat fresh fruits that have not been heat-treated. This rule applies to all products, since at high temperatures fatty acids are converted into difficult-to-digest toxic substances.
- A diet enriched with fatty foods reduces the incidence of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
- You can distinguish the structure of fats by their appearance: unsaturated - liquid, saturated - solid.
- A decrease in substances below the physiological norm leads to weight gain. The body turns on the stress response, and carbohydrates begin to be deposited in fat depots. For weight loss, it is important not to reduce the total amount in food, but to redistribute it towards useful fractions.
- Olive oil should not be used for frying. It completely loses its properties.
- Vegetables are better digested with vegetable fats, so seasoned salads are much healthier.
Fats are no longer the enemy of your figure. They are included in many weight loss systems and, when used correctly, bring benefits and beauty to the body.
Fats are an integral part of a healthy diet, as are proteins and carbohydrates. The assumption that fatty products do not bring anything good to the body, but only exceptional harm, is devoid of common sense, since the role of fats for the coordinated functioning of the organs and systems of the human body is very great. You just need to differentiate between the concepts of lipids and know which of them are useful, and which ones should be completely avoided.
In the human body, lipids are concentrated mostly in subcutaneous fat. They are found in small concentrations in the brain, liver and muscle tissue. These substances are vital for the body, in the correct concentration, of course. A lack of compounds, as well as an excess, can lead to unpleasant consequences. Today we’ll talk about the benefits and possible harm of lipids, as well as their role and functions.
List of foods containing high amounts of fat:
- Butter, spread, vegetable oil, margarine, lard, lard - 80%.
- Nuts (walnuts, peanuts, almonds, hazelnuts) - 40%-80%.
- Sunflower seeds - 40%.
- Cheese, full-fat sour cream (more than 20%), pork, duck, goose, eel, smoked sausage, rolls with condensed milk or cream, chocolate, halva - 20%.
- Fat cottage cheese (from 10%), cream, ice cream - from 10% to 19%.
- Lamb, beef, chicken (drumstick, ham), eggs, low-fat sausage - from 10% to 19%.
- Salmon, herring, mackerel, caviar - from 10% to 19%.
- Avocado (fruit) - from 10%.
Which foods contain the most trans isomers?
Of course, there are a lot of them in fast food, cooked in a lot of fat. For example, chips contain about 30%, and French fries contain more than 40%.
In confectionery products, trans isomers of unsaturated fatty acids range from 30 to 50%. In margarines their amount reaches 25-30%. In mixed fats, 33% of mutation molecules are formed during the frying process, since overheating causes transformation of molecules, which accelerates the formation of trans isomers. If margarine contains about 24% trans isomers, then during frying their level increases significantly. Raw vegetable oils contain up to 1% trans isomers, while butter contains about 4-8%. In animal fats, trans isomers range from 2% to 10%. Remember that trans fats are junk and should be avoided entirely.

The effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids on the human body has not yet been fully studied, but it is now obvious that for healthy active life, a person must introduce foods that contain unsaturated fatty acids into his diet.










