Diet features
The Soviet therapist was the founder of dietetics in the USSR and his work is still widely used throughout the world.
Therapeutic diets according to Pevzner allowed people to fight serious diseases in sanatorium conditions, thereby reducing the harmful effects of medications.

In the table of diets according to Pevzner you can find menus for many different diseases, among which are:
- Gastrointestinal problems;
- Cardiovascular disease;
- Excessive or underweight;
- Diabetes;
- Problems of the musculoskeletal system;
- Hormonal imbalances.
Medical diets No. 1-No. 15

For many diseases, diet is one of the main methods of treatment, and for some, the only one, for example, obesity and mild diabetes. In clinical nutrition, it is important not only to choose the right products, but also to prepare them correctly. The temperature of the food, the time and frequency of its consumption are also important. Dietary disorders can lead to exacerbation of the disease. For example, in diabetes mellitus this can cause increased blood sugar, increased thirst, dry mouth; in hypertensive patients, eating salty foods can lead to increased blood pressure.
In medical and sanatorium institutions, a numbered system of diets is used, many of which exist in several versions. After the exacerbation of the disease has passed, the patient must continue to follow the general principles of the diet. First of all, this applies to foods that should be excluded from the diet, but other cooking methods can be used. Any, including medical diets No. 1-No. 15, completely exclude alcohol. If one person has a combination of two diseases that require special nutrition, he must follow the principles of both diets. Diet No. 1, 1a, 1b – stomach and duodenal ulcers; Diet No. 2 – chronic and acute gastritis, colitis, enteritis, chronic enterocolitis; Diet No. 3 – constipation; Diet No. 4, 4a, 4b, 4c – intestinal diseases with diarrhea; Diet No. 5, 5a – diseases of the biliary tract and liver; Diet No. 6 – urolithiasis, gout; Diet No. 7, 7a, 7b – chronic and acute nephritis; Diet No. 8 – obesity; Diet No. 9 – diabetes mellitus; Diet No. 10 – diseases of the cardiovascular system; Diet No. 11 – tuberculosis; Diet No. 12 – diseases of the nervous system; Diet No. 13 – acute infectious diseases; Diet No. 14 – kidney disease with the passage of oxalate stones; Diet No. 15 – diseases that do not require special diets. Table No. 1 is indicated for gastritis with high acidity and for ulcers of the duodenum and stomach for six months to a year after an exacerbation. Recommended: pureed soups, boiled pureed vegetables, pureed porridge, boiled lean fish and meat, steamed fish and meat cutlets, boiled skinless chicken, milk, vegetable and butter, cream, non-acidic sour cream and curdled milk, soft-boiled eggs, stale white bread , sweet fruits and berries, fruit and vegetable juices. Food should be taken four to five times a day, warm. Table No. 1a is indicated during the period of exacerbation of chronic gastritis with high acidity, with exacerbation of the ulcer. Recommended: slimy soups, milk, liquid porridges, soft-boiled eggs, soufflé from lean fish or meat, olive and butter, berry jelly, cream, fruit juices, tea, rosehip decoction. Salt should be limited, and liquids should be drunk no more than one and a half liters per day. Food should be taken warm every two to three hours. Table No. 1b is indicated for patients when chronic gastritis and peptic ulcers subside. Recommended: in addition to the previously listed products, you can eat steamed fish and meat dishes, pureed milk soups with vegetables, pureed milk porridge, and wheat crackers. You need to eat six times a day and limit your salt intake. Table No. 2 is indicated for chronic colitis and chronic gastritis with low acidity. Recommended: vegetable and cereal soups in fish, mushroom and meat broths, boiled chicken, lean meat, cutlets, lean boiled fish, lean ham, lean lightly salted herring, butter, milk and fermented milk products, mild cheese, porridge, soft-boiled eggs, stale white bread, fruits, vegetables, vegetable and fruit juices, coffee, tea, cocoa, marmalade sugar. You need to eat it five times a day, preferably in puree form. Table No. 3 is indicated for atonic constipation. You can eat foods containing large amounts of plant fiber, figs, prunes, compotes, fruit and vegetable juices, pureed carrots, beets, dried fruits, kefir, cream, milk, curdled milk, black bread, pearl barley and buckwheat porridge, honey, fried meat and fish, sugar, vegetable and butter. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, including sparkling mineral water. You should not consume cocoa, strong tea, jelly, or slimy soups. If constipation is static, you need to limit foods rich in plant fiber. Table No. 4 is indicated for exacerbations of intestinal diseases. You can eat cocoa, strong coffee and tea, stale crackers from white bread, soft-boiled eggs, cottage cheese, semolina and rice porridge with water, boiled meat and fish, three-day kefir, jelly, blueberry and black currant decoction. Salt should be limited. Table No. 4a is indicated for colitis. You need to eat the same as in the fourth diet, but you need to limit carbohydrate-rich foods and increase the protein content. Table No. 4b is indicated for patients with chronic colitis when the disease subsides. Recommended: stale white bread, broth with meatballs, cereal soups with meat or fish broth, pureed cereals, steamed and boiled vegetables, mild cheese, kefir, sour cream, dry biscuits, soft cookies, jelly and compotes of unsweetened fruits and berries , coffee with milk, tea, butter. You need to eat warm food four to six times a day. Table No. 4c is indicated for chronic and acute intestinal diseases during the recovery period. This diet is prescribed to provide adequate nutrition in case of intestinal dysfunction in order to restore the function of other digestive organs. The diet is physiologically complete with limited salt intake and a slight increase in the amount of protein foods. It excludes foods that enhance the processes of putrefaction and fermentation in the intestines, activates its secretion, as well as the secretion of the pancreas and stomach. You need to prepare dishes by steaming, crushed, or baking or boiling. You need to eat five times a day. Table No. 5 is indicated for people with diseases of the biliary tract, gallbladder and liver outside the acute stage. You should eat milk and fruit soups without meat, cereal soups with vegetable broth, boiled fish, poultry and lean meats, cottage cheese, kefir, milk, flour dishes and cereals, white and black stale bread, sweet berries and fruits, herbs and vegetables. , honey, jam, sugar, fruit and vegetable juices, weak tea with milk. You should limit your intake of fats and salt. You need to eat five times a day. You cannot consume alcoholic beverages, brains, liver, legumes, lard, spinach, mushrooms, onions, sorrel, fatty meat and fish, baked goods, smoked, spicy and fatty foods, vinegar, spices, canned food, cocoa, ice cream, creams, chocolate, drinks with gas. You can read more about this diet here. Table No. 5a is recommended for chronic pancreatitis. The diet is the same as for diet No. 5, but you should eat more protein-containing foods and limit foods containing fats and carbohydrates. All food should be steamed, chopped and pureed. Table No. 6 is indicated for kidney stones and gout. It is recommended to consume black and white bread, milk and dairy products, honey, sugar, milk and vegetable soups, cereal products, sweet fruits, fruit juices, jam, cucumbers, lettuce, carrots, bay leaves, vinegar, lemon, lean fish and meat, eggs. In this case, you need to drink at least two to three liters of liquid. You cannot eat meat soups, kidneys, liver, brains, smoked and fried meat, fish soup, fried fish, herring, lard, sardines, sprats, mushrooms, pates, spinach, sorrel, legumes, cocoa, coffee, alcohol and strong tea. Table No. 7 is indicated for people with chronic kidney disease in the absence of renal failure. You should eat vegetarian soups, lean poultry, meat, fish, gray and white bread with bran, pasta, cereals, flour dishes, milk and dairy products, cottage cheese, vegetables, herbs, fruits, berries, jam, honey, sugar. You should limit your consumption of sour cream and cream. Meals should be six times a day. You cannot drink carbonated drinks, eat creams and cakes, legumes, mushrooms, fish and meat broths, canned food, smoked meats, and pickles. Table No. 7a is indicated for acute and chronic nephritis in the acute stage. You need to eat boiled vegetables, fruits, flour and cereal products, white bread without salt, tea with milk, butter, sugar. Meals should be fractional, salt should be completely eliminated. If uremia develops, you need to reduce your daily protein intake to twenty grams per day, especially vegetable proteins. Table No. 7b is indicated during recovery from acute kidney inflammation. This diet is transitional from No. 7a to No. 7. You can eat white salt-free bread, boiled lean fish and meat, and reduce your salt intake. Table No. 8 is indicated for obesity. This diet is characterized by a decrease in the energy value of the diet due to carbohydrates, partly fats, while the protein content should be normal. In addition, salt, appetite-stimulating foods and free fluids should be consumed in limited quantities. You should consume one hundred grams of protein, eighty grams of fat, one hundred and fifty grams of carbohydrates per day. Recommended products include rye, protein-bran and protein-wheat bread, vegetable soups with cereals, borscht, cabbage soup, beetroot soup, okroshka, lean fish, poultry, stewed, baked or boiled meat, jelly, beef sausages, seafood, milk , cheese, cottage cheese, fermented milk products. Fruits and vegetables can be eaten in any form. Products made from butter dough and high-grade flour, pasta, legumes, cereal and potato soups, fatty fish, poultry and meat, smoked meats, sausages, canned food, sweet berries and fruits, legumes, fatty cheese, cottage cheese, cream, pasta should be excluded from the diet. products, oatmeal and semolina, spicy and fatty snacks, mayonnaise, sauces, spices and herbs. Table No. 9 is indicated for mild to moderate diabetes. The energy value of the diet should be reduced by animal fats and easily digestible carbohydrates, and sweets should be excluded. The daily diet should contain about one hundred grams of protein, eighty grams of fat, and three hundred grams of carbohydrates. You can eat protein-bran, wheat, rye bread, vegetable soups, low-fat fish and meat broths, fish, poultry and lean meats, milk, cheese, low-fat cottage cheese, fermented milk products, cereals, vegetables, potatoes, sweet and sour berries and fruits. You should not eat fatty and strong broths, rich flour products, salted fish, sausages, semolina, rice, pasta, pickled and salted vegetables, raisins, grapes, jam, sugar, candy, lemonade, and sweet juices. Table No. 10 is indicated for diseases of the cardiovascular system. You should slightly reduce the energy value due to carbohydrates and fats, limit the consumption of salt and foods that stimulate the cardiovascular system. You should consume ninety grams of protein per day, a little more than half of which is animal, seventy grams of fat, four hundred grams of carbohydrates. You should eat stale bread, biscuits, soft cookies, vegetarian soups, milk, cottage cheese, fermented milk products, poultry, fish and lean meats, cereals and pasta dishes, baked and boiled vegetables, ripe fruits, jam, honey. You need to exclude from your diet products made from butter dough, fresh bread, mushroom, fish and meat broths, legume soups, sausages, smoked meats, kidneys, fatty and salty cheeses, salted fish, legumes, pickled, pickled and salted vegetables, fruits containing coarse fiber, cocoa, strong coffee, tea, chocolate. You can read more about this diet here Table No. 11 is indicated for tuberculosis of the bones, lungs, joints, lymph nodes during the period of mild exacerbation or recovery, in the postoperative period, after injuries, and with exhaustion after infectious diseases. The diet has a high energy value with a high content of proteins, minerals and vitamins. Every day you should consume one hundred twenty grams of protein, one hundred grams of fat, four hundred grams of carbohydrates. You can eat almost all dishes, except for very fatty poultry and meat, culinary, beef and lamb fats, pastries and cakes with a lot of cream. Table No. 12 is indicated for people with functional diseases of the nervous system. You can eat many foods with the exception of strong soups, spicy seasonings, smoked foods, fried and fatty foods, strong coffee, tea, and alcohol. You need to slightly limit salt and meat. It is advisable to consume tongue, liver, legumes, and dairy products more often. Table No. 13 is recommended for people with acute infectious diseases. The energy value of this diet is reduced mainly by carbohydrates and fats, while it is rich in vitamins. You should consume eighty grams of protein, sixty grams of fat, three hundred grams of carbohydrates per day. The diet includes dried wheat bread, lean fish, poultry and meat, low-fat meat and fish broths, mucous cereal decoctions, vegetable soups, cottage cheese, fermented milk drinks, beets, carrots, potatoes, tomatoes, cauliflower, grated buckwheat, semolina and rice. porridge, ripe berries and fruits, marmalade, jam, preserves, honey, sugar, rose hip decoction. Fresh bread, baked flour products, fatty fish, poultry, meat, fatty broths, smoked meats, sausage, canned food, salted fish, cheeses, full-fat sour cream, cream, whole milk, pasta, barley and pearl barley, millet, onions should be excluded from the diet. , garlic, radish, radish, white cabbage, legumes, cucumbers, cocoa, cakes, chocolate, high fiber fruits. Table No. 14 is indicated for urolithiasis. It represents a complete diet with a limit on calcium-rich and alkalizing foods. per day you can consume ninety grams of protein, one hundred grams of fat, four hundred grams of carbohydrates. You can eat bread and flour products, broths and soups, fish and meat, cereals, pumpkin, green peas, sour berries and apples, mushrooms, honey, sugar, and confectionery. Fruit, vegetable and milk soups, salted fish, smoked meats, dairy products, vegetables other than those allowed, potatoes, vegetable and berry juices, cooking and meat fats should be excluded. Table No. 15 is indicated for diseases in which there is no need for therapeutic diets. This diet is physiologically complete, while spicy and difficult to digest foods are excluded. You should consume ninety grams of protein, one hundred grams of fat and four hundred grams of carbohydrates per day. You can eat almost all foods, except fatty poultry and meat, mustard, pepper and refractory fats of animal origin.
Most popular
Depending on the severity of the disease, each person was prescribed an individual diet.

The greatest importance of observing restrictions applies to the group of people who, as a result of an incorrect or riotous lifestyle, have problems with the digestive organs and assimilation of various substances.
One of the first tables according to Pevzner, diet 1, is used if the patient has serious problems with the digestive organs.

In order not to provoke excessive secretion of gastric juice and not to irritate the gastric mucosa, it is necessary to remove too salty foods and fried foods from the menu.

It is allowed to eat cereals, boiled lean meat, various purees and white bread.

After problems with the gastrointestinal tract, liver and gallbladder diseases are common.

In order not to cause the accumulation of toxic substances, it is necessary to reduce the amount of products that provoke the formation of an acidic environment, such as:
- Sour fruits and vegetables;
- Coffee;
- Grilled meat;
- Pickles and smoked meats;
- Bakery products.

Eating porridge with butter, boiled tongue, boiled eggs and root vegetables is allowed. It is also advisable to completely avoid alcohol and carbonated drinks.
Pevzner's Diet 5 is most often used to treat individuals who drink alcohol excessively.
Characteristics of treatment tables
Characteristics of treatment tables
Table No. 1 is mechanically and chemically gentle, with a reduction in mechanical and chemical irritants. Prescribed for peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, as well as for gastritis. Tables No. 1a and 16 are intended for more stringent regimes, when it is necessary to give the greatest rest to the inflamed gastric mucosa.
Table No. 1a. Food is given frequently (6 times a day) and in small portions in liquid or semi-liquid form. Prescribe milk, cream, butter, mucous soups (made from rice, pearl barley, etc.), liquid (raw) and semi-liquid (soft-boiled) eggs, jelly (non-sour), milk jelly or from sweet berries and fruits. Raw vegetable or fruit juices are added to soups and jellies. Liquid milk porridges made from ground rice and semolina are allowed once a day. You can also give a soufflé of boiled meat. Food is prepared without salt, as salt increases the secretion of gastric juice.
Table No. 16. It differs from table No. 1a in that it is less strict. To this table it is allowed to add 50-70 g of white crackers, mashed porridge with butter, mashed potatoes, meat or fish dumplings and meatballs. The patient should also receive food in fractional portions 5-6 times a day.
Table No. 1. Prescribed for chronic gastritis with high acidity. On table No. 1, in addition to the dishes assigned to tables No. 1a and 16, they give stale white bread, dry cookies, biscuits, fresh cottage cheese, sour milk, porridge with butter or milk, noodles, pasta, steamed cutlets, boiled soft chicken, boiled lean meat and fish. Low-fat varieties of fish include: pike perch, pike, perch. Greens and vegetables are given in pureed or finely chopped form; Sweet berries (strawberries, raspberries), sweet fruits, boiled or pureed, are allowed. Drinks can only be consumed that do not irritate the gastric mucosa, namely: whole milk, cream, weak tea with milk. Food is prepared with a significant limitation of table salt.
For gastric and duodenal ulcers at the onset of the disease during an acute attack, table No. 1a is given for 1 week, the patient is kept on table No. 16 for the next week, and then transferred to table No. 1.
Table No. 2. Prescribed for gastritis with reduced secretion of gastric juice. Mechanical irritants should be excluded from this table, while chemical irritants that increase the secretion of gastric juice should be preserved, but to such an extent that they do not increase the inflammatory process of the mucous membrane. The table should be mixed: all dishes are prepared pureed or chopped. Food is given 4-5 times a day so that the patient does not consume large quantities of it at one time. Table salt is allowed to taste, in unlimited quantities. You can give tea, cocoa, coffee with milk and cream. All kinds of soups are allowed - meat, fish, vegetables, but only pureed; give white stale bread and white crackers; low-fat varieties of fish and minced meat; pureed vegetables, compotes of pureed fruits and berries, and for appetizers - low-fat ham, black caviar, mild cheeses. The patient receives eggs and egg dishes in limited quantities.
Table No. 3. Used for constipation. Rough food is prescribed, rich in plant fiber, which provides a large amount of food residues that are not digestible by the body, which stimulate intestinal peristalsis and thereby restore normal intestinal activity. Large quantities of raw fruits and vegetables are added to the general rational table; Prescribe compotes, black bread, buckwheat porridge, sour milk. You should refrain from drinking hot drinks, as heat reduces intestinal motility. Therefore, it is recommended to give cold vegetable and fruit soups or cold compotes. If intestinal tone is increased, for example with spastic constipation, then these same foods are prescribed in pureed form.
Table No. 4. Prescribed for diarrhea, acute enteritis and colitis, when significant irritation of the intestinal mucosa is observed. Food should be mechanically gentle, milk and eggs are excluded. In the first days of illness, liquid and semi-liquid food is prescribed: weak tea, meat broth, mucous soups, jelly, blueberry jelly or red wine. Then add white crackers, butter, fresh cottage cheese, boiled meat in the form of steam cutlets, dumplings, meatballs, boiled lean fish, pureed porridge, steam pudding. Of the vitamins, orange or lemon juice is preferable. For acute colitis (colon catarrh), apple days are prescribed (see “Regimes of incomplete and partial fasting”). For chronic colitis, mechanically gentle pureed food is prescribed: vegetable and meat soups, boiled pureed vegetables and fruits, lean meat in the form of cutlets, pureed cereals, pasta, noodles, stale white bread, butter, fresh cottage cheese, sour cream, milk, eggs are allowed only in food. The patient should be fed 4-5 times a day to avoid taking large amounts of food at one time. Cold foods and drinks should be avoided, as they increase intestinal motility. In case of chronic colitis without pronounced clinical phenomena, they gradually switch to a general rational diet with the exception of raw vegetables and fruits, as well as pure milk.
Table No. 5a. Prescribed for acute liver diseases, hepatic colic, inflammation of the gallbladder and bile ducts. All products are given pureed. Table No. 5a is mainly dairy-vegetable; meat and fish (low-fat varieties) are allowed no more than once a day and only in boiled and ground form. They serve milk and vegetarian soups, milk porridges, non-sour jelly and compotes with pureed fruit. Butter is allowed in limited quantities: you can give cottage cheese, sour cream and yogurt, white stale bread. Extractive substances, spices and spicy foods are prohibited: pickled and smoked foods, sausage and other snacks, sharp cheeses, meat, fish and mushroom soups, coffee and cocoa, as well as eggs; and from vegetables - spinach, sorrel and tomatoes.
During attacks of hepatic colic, meat and fish are completely excluded from the diet. Drinking for patients is prescribed in large quantities.
Table No. 5. Recommended for chronic liver diseases, and therefore is basically the same as table No. 5a, but not as strict. Table No. 5 is also mainly dairy-vegetable, but the products included in it can be given to the patient not in pureed form. Allowed are black bread, egg whites in the form of omelettes and soufflés, lean meats and boiled fish. You can occasionally give caviar as a snack. All kinds of salads, berries, sweet fruits and compotes are recommended. Of animal fats, only butter is allowed, and of vegetable fats - olive oil as a choleretic oil, as well as sunflower and corn oil.
Table No. 6. Prescribed for protein metabolism disorders and gout. Table No. 6 excludes foods rich in animal proteins. This is a dairy-vegetable table. Patients are allowed dairy, egg, flour and sweet dishes, all kinds of berries, fruits, herbs and vegetables, with the exception of legumes, sorrel, spinach and tomatoes. Dairy and vegetarian soups are allowed; meat and fish are not given every day and only in boiled form. Just like at table No. 5, all kinds of extractive and spicy substances are prohibited: snacks, smoked meats, marinades, canned food, sausages, sharp cheeses. Such patients are prescribed to drink plenty of fluids.
Table No. 6 is also used for pyelitis (inflammation of the renal pelvis).
Table No. 7. The seventh tables are intended for kidney patients. Of these, table No. 7a is intended for the most strict regime; it is prescribed for acute nephritis and nephrosis, as well as in advanced cases of chronic nephritis. Animal and some plant proteins, such as legumes and mushrooms, are excluded from food; milk is sharply limited. The renal diet is achloride, i.e., salt-free; All food is prepared without salt, special salt-free bread is baked, since 1 kg of black bread contains 8-16 g of salt. All kinds of extractive liquids are prohibited. In addition to the liquid contained in food, you are allowed to drink no more than 200-400 ml. Patients are given all kinds of flour and sweet dishes, butter, berries, fruits, compotes, jelly, vegetarian and fruit soups, and for drinks - weak tea with cream or milk and fruit juices. You can give all kinds of vegetables, except horseradish and spinach. If the achloride diet is prescribed for a long time, then on some days patients receive 1-4 g of salt per day.
Table No. 76. Prescribed when there is some improvement in the patient’s condition, when acute symptoms decrease. Drinking is allowed in larger quantities; give milk, allow the intake of proteins, first plant, and then, occasionally, animals in the form of meat and fish.
Table No. 7. They move to table No. 7 after table No. 76; it is also used for chronic nephritis. It is allowed to lightly add salt to food (1-4 g), which is prepared without salt, and a certain amount of salt is given to patients. In addition to what is allowed on diets No. 7a and 76, patients receiving table No. 7 increase the amount of drink and protein foods. Sometimes patients are given eggs, mainly from egg yolks. Of course, the listed tables cannot be provided to all patients with various impaired renal function and various manifestations of diseases of this organ. With azotemia, with the accumulation of waste in the blood, with a decrease in the concentration function of the kidneys, patients should not limit drinking and should sharply reduce, and sometimes exclude, proteins from the diet. In such cases, they are given plenty of fluids - up to 2 liters or more of liquid per day and fasting days are prescribed 1-2 times a week or 2 days in a row: sugar, milk, apple and vegetable. For nephrosis, when patients lose a lot of protein and hypoproteinemia develops, you need to “load” it with protein. The protein load approximately consists of 300 g of cottage cheese and 150 g of meat per day.
Table No. 8. Prescribed for lipid metabolism disorders and obesity. The principle of therapeutic nutrition for obesity is to reduce total caloric intake. To do this, prescribe food with a large amount of plant fiber, with a limit on fats, sweets and starchy foods. Drinking is limited and therefore food should be lightly salted. Dairy products, brown bread, vegetables, fruits, berries, lean meat and fish are allowed. For obesity, it is recommended to establish semi-fasting days in the form of milk or berry days. On milk day, the patient is given 8 glasses of milk in small portions throughout the day, approximately one glass of milk every 2 hours. During the apple day, as already mentioned, give 1.5-2 kg of apples per day (see “Regimes of incomplete fasting,” p. 373).
Table No. 9. Prescribed for patients with diabetes mellitus. The diabetic table is an individual one, which means that for each patient a specific diet is prepared for each day.
Table No. 10a. Prescribed for diseases of the cardiovascular system in a state of decompensation (with the appearance of significant shortness of breath, edema, etc.).
It is necessary to limit drinking in order to relieve the cardiovascular system from excessive amounts of fluid. To reduce the feeling of thirst, food is prepared without salt. To do this, exclude spicy dishes and snacks. Due to the fact that when the stomach is full, the patient's shortness of breath increases, meals should be divided (6 times a day) and given in small portions; food should be easily digestible and well digestible. Vegetables with coarse fiber are excluded from the diet; vegetables and fruits are given pureed; meat and fish are also pureed and only boiled, and no more than once a day. White stale bread is allowed; Butter dough and soft bread are prohibited. Soups are only dairy and vegetarian. It is necessary to introduce vitamins into the body in the form of raw berry and vegetable juices or rosehip infusion, as well as more sugar in porridges, compotes, and jelly.
Table No. 10. Prescribed for cardiovascular diseases, but in a state of compensation. A small amount of salt and all kinds of dairy and flour products are allowed. The food may not be pureed. It is recommended to give meat and fish only in boiled form; meat and fish soups, as well as all kinds of snacks and spicy seasonings are excluded. Drinking should also be limited. Eggs can be given in all forms, but in case of atherosclerosis and hypertension, their intake should be limited, especially the intake of egg yolks.
Table No. 11 is a reinforced nutrition table. Prescribed for patients with tuberculosis, anemia and those recovering from serious illnesses. The table should be mixed, varied, contain a sufficient amount of complete protein, salts (primarily calcium) and vitamins to improve nutrition and strengthen the patient’s strength. Therefore, the patient should be given large quantities of greens, fruits, and berries, since the latter, in addition to vitamins, contain a large amount of calcium. There is a lot of calcium in dairy products - milk, cottage cheese, cheese. More meat, fish and egg dishes are also given.
There is no need to get carried away with the increased supply of fats, especially to the detriment of other nutrients. In case of low nutrition, fish oil containing vitamins A and D is recommended. However, the patient should not be overfed, as this often leads to loss of appetite and sometimes gastrointestinal upset. Rapid weight gain, as already mentioned, is usually unsustainable.
Table No. 12. Prescribed for diseases of the nervous system. This is a mixed, varied table, limiting meat and excluding spicy foods and seasonings, as well as stimulants, such as strong tea and coffee.
Table No. 13. Designed for patients with acute infectious diseases accompanied by high body temperature. First of all, such patients need to be administered large amounts of fluid, including fruit, berry and vegetable juices. Small amounts of wine sometimes have a good nutritional and medicinal effect. The patient should receive food often, but in small portions. Food is given high-calorie, in liquid, semi-liquid, pureed and chopped form. The diet includes milk, coffee with milk or cream, meat broth with eggs or meatballs, soups from pureed cereals or vegetables with butter or sour cream, milk porridge with butter, sugar, meat or fish dumplings, chopped cutlets with mashed potatoes and butter , pureed vegetables with butter, soft-boiled eggs or egg omelet, white crackers or white bread with butter, sweet compotes from pureed fruits, fruit and berry jelly, jelly.
If during acute infectious diseases damage to any organs is observed, the diet must be modified accordingly. Thus, in case of heart failure, heavy drinking is prohibited, in case of intestinal infections (typhoid fever, dysentery) they do not give bread, and in case of jaundice, fats are limited and eggs are not given; In case of acute nephritis, meat soups, meat, and eggs are prohibited.
Tables No. 14a and 14. Prescribed for relatively rare metabolic diseases, when it is necessary to increase blood acidity (table No. 14a) or alkalinity (table No. 14). At table No. 14a, it is necessary to exclude foods rich in calcium and spicy foods. The diet should be predominantly meat.
With so-called oxaluria, when salts of oxalic acid are excreted from the body in large quantities, table No. 14 is prescribed. Food is given mainly dairy-vegetable with the exception of vegetables containing large quantities of oxalic acid: sorrel, spinach, beans, potatoes, etc. In these cases modes, you need to introduce a lot of fluid into the body.
Table number 15 is the so-called general rational table. Prescribed to patients who do not require any special treatment regimen. The diet must be sufficient in calorie content and quality. The diet should include all the nutrients necessary for proper nutrition, with a normal quantitative ratio of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, salts and a sufficient content of vitamins.
Table number 0 is not high in calories. Prescribed if it is necessary to limit nutrition, in a semi-conscious state, after operations on the stomach or intestines, after fasting days. It includes milk, slimy soups, broth, jelly, jelly, fruit and berry juices.
How to end the diet
The use of tables cannot occur on a permanent basis. Firstly, it will have a bad effect on the nervous system, and secondly, a deficiency of certain elements may begin.

New standard diets for health care institutions
(1) The main version of the standard diet (instead of the previous diets of the number system No. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15).
Proteins (including animal): 85 - 90 (40 - 45) g. Total fats (including vegetable): 70 - 80 (25 - 30) g. Total carbohydrates (including mono - and disaccharides): 300 - 330 (30 - 40) g. Refined carbohydrates are excluded from the diet of diabetics.
Energy value 2170 - 2400 kilocalories. Indications for use: chronic gastritis in remission (remission is a stage in the course of the disease, characterized by a temporary weakening or disappearance of its manifestations); peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in remission; chronic intestinal diseases with a predominance of IBS with predominant constipation (as written); acute cholecystitis and acute hepatitis in the recovery stage; chronic hepatitis with mild signs of functional liver failure; chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. And also: gout, uric acid diathesis, nephrolithiasis (urolithiasis), hyperuricemia (increased uric acid levels in the blood), phosphaturia (increased excretion of phosphates in the urine); type II diabetes mellitus without concomitant overweight or obesity; diseases of the cardiovascular system with mild circulatory disorders, hypertension, coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis of cerebral and peripheral vessels; acute infectious diseases and febrile conditions. General characteristics, culinary processing. A diet with a physiological content of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, enriched with vitamins, minerals, plant fiber (vegetables, fruits). Limit nitrogenous extractive substances, salt (6 - 8 g/day), foods rich in essential oils, exclude hot seasonings, spinach, sorrel, and smoked meats. Dishes are prepared boiled or steamed, baked. The temperature of hot dishes is no more than 60-65 degrees, cold dishes is not lower than 15 degrees. Free liquid 1.5 - 2 l. Eating 4 - 6 times a day. (2) Diet option with mechanical and chemical sparing (previously - number system diets No. 1b, 4b, 4c, 5p option I). Proteins (including animal): 85 - 90 (40 - 45) g. Total fats (including vegetable): 70 - 80 (25 - 30) g. Total carbohydrates (including mono - and disaccharides): 300 - 350 (50 - 60) g. Energy value 2170 - 2480 kcal. Indications for use:
peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute stage and unstable remission;
acute gastritis; chronic gastritis with preserved and high acidity in the stage of mild exacerbation; gastroesophageal reflux disease; dysfunction of the masticatory apparatus; acute pancreatitis, stage of fading exacerbation; severe exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis; recovery period after acute infections; after operations (not on internal organs). General characteristics, culinary processing. A diet with a physiological content of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, enriched with vitamins, minerals, with moderate limitation of chemical and mechanical irritants of the mucous membrane and the receptor apparatus of the digestive tract. Avoid spicy snacks, seasonings, spices; limit salt (6 - 8 g/day). Dishes are prepared boiled or steamed, pureed or not pureed. Food temperature - from 15 to 60-65 degrees. Free liquid 1.5 - 2 l. Eating 5 - 6 times a day. (3) Option of a diet with an increased amount of protein - high-protein diet (previously - diets of the number system No. 4e, 4ag, 5p option II, 7c, 7d, 9b, 10b, 11, RI, R-II) Proteins (incl. animals): 110 - 120 (40 - 45) g. Total fats (including vegetable): 80 - 90 (30) g. Total carbohydrates (including mono- and disaccharides): 250 - 350 (30 - 40) g. Refined carbohydrates (sugar) are excluded from the diet of diabetic patients and patients after gastric resection with dumping syndrome. Energy value 2080 - 2690 kcal. General characteristics, culinary processing. A diet with a high protein content, a normal amount of fat, complex carbohydrates and a limitation of easily digestible carbohydrates (sugar, sweets). When prescribing a diet for patients with diabetes and after gastric resection with dumping syndrome, refined carbohydrates (sugar) are excluded. Limit salt (6-8 g/day), chemical and mechanical irritants of the stomach and bile ducts. Dishes are prepared boiled, stewed, baked, pureed or not pureed, steamed. Food temperature - from 15 to 60-65 degrees. Free liquid 1.5 - 2 l. Eating 4 - 6 times a day. (4) A diet option with a reduced amount of protein is a low-protein diet (formerly number system diets No. 7b, 7a). Proteins (including animal): 20 - 60 (15 - 30) g. Total fats (including vegetable): 80 - 90 (20 - 30) g. Total carbohydrates (including mono - and disaccharides): 350 - 400 (50 - 100) g. Energy value 2120 - 2650 kcal. Indications for use: chronic glomerulonephritis with severe and moderate impairment of nitrogen excretory function of the kidneys and severe and moderate azotemia (renal failure). General characteristics, culinary processing.
Diet with protein restriction to 0.8 g or 0.6 g or 0.3 g/kg of ideal body weight (up to 60, 40 or 20 g/day), with a sharp restriction of salt (1.5-3 g/day) and liquids (0.8 - 1 l).
Avoid nitrogenous extractives, alcohol, cocoa, chocolate, coffee, and salty snacks. The diet includes sago dishes, protein-free bread, purees, and mousses made from swelling starch. The diet is enriched with vitamins and minerals. Dishes are prepared without salt, boiled, steamed, not pureed. Free liquid 0.8 - 1.0 l. Eating 4 - 6 times a day. (5) A variant of a diet with a reduced calorie content is a low-calorie diet (formerly number system diets No. 8, 8a, 8o, 9a, 10c). Proteins (including animals): 70 - 80 (40) g. Total fats (including vegetable): 60 - 70 (25) g. Total carbohydrates (including mono- and disaccharides) : 130 - 150 (0) g. Energy value 1340 - 1550 kcal. Indications for use: Various degrees of nutritional (from overeating) obesity in the absence of pronounced complications from the digestive system, circulatory system and other diseases requiring special diets. Diabetes mellitus type II with obesity. Cardiovascular diseases in the presence of excess weight. General characteristics, culinary processing. A diet with a moderate restriction of energy value (up to 1300-1600 kcal/day), mainly from fats and carbohydrates. Avoid simple sugars, limit animal fats and salt (3-5 g/day). Includes vegetable fats, dietary fiber (raw vegetables, fruits, dietary bran). Liquid is limited to 0.8 - 1.5 liters. Food is prepared boiled or steamed, without salt. Eating 4 - 6 times a day. Additional information Along with the basic standard diet and its variants, special surgical diets, fasting diets and special diets are used in medical institutions in accordance with their profile. I personally cannot explain the recommendation to limit nitrogenous extractive substances (NES) in the main version of the standard diet. A possible reason is that the diet is recommended for the duration of your stay in a medical institution. AEVs are a significant number of important organic compounds, in particular, soluble proteins, a set of amino acids, and creatine. AEs are transferred and extracted into water when cooking meat with or without bones. In fact, this is a rich broth without fat (of course, not from “cubes”, but a cold dish, jelly, a hot dish, khash, etc.). All meat AEVs, in addition to having a certain nutritional value, increase appetite, stimulate gastric secretion during meals, and, therefore, only promote digestion. It is known, for example, that broth from veal legs leaves the stomach faster than boiled beef, and lean types of meat are digested worse than others. Ph.D. Vladimir Vasilenko
Rules for diet therapy.
As a rule, especially in patients over 40-50 years of age, the underlying disease is accompanied by concomitant ones. Therefore, a nutritionist must create a therapeutic diet that takes into account all factors. For example, if chronic cholecystitis is accompanied by excess weight, the amount of fats, fried foods and rich soups, simple carbohydrates, smoked foods, spicy and salty foods is excluded or limited. And the total calorie content of the daily diet decreases.
It is recommended to include in your food unrefined vegetable oils containing polyunsaturated fatty acids, which stimulate the body's defenses and strengthen the immune system, and vitamin E: vegetable, flaxseed, corn and olive. These oils also have a choleretic effect and are a preventative against cholecystitis.
For intestinal diseases, chronic constipation, in combination with traditional medicine recipes, rye and wheat bran, containing fiber and B vitamins, as well as vegetables: cabbage, carrots and beets, are useful.
It is also necessary to take into account the time that the body needs to absorb various foods. Dairy and lactic acid products, soft-boiled eggs, berries and fruits are quickly absorbed. Slowly – legume dishes, fried meats, fresh bread.
Increased secretion of gastric juice is caused by extractive substances contained in meat and fish, mushrooms and mushroom broths, fruit and vegetable juices, cheese and spices, cucumbers and cabbage. Weak - steamed or boiled vegetables, bran bread, carrots and green peas, boiled meat.
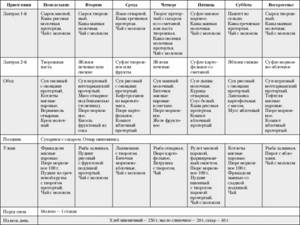
The basic rule of therapeutic diets is the regularity and fractionation of meals at a certain time. During an exacerbation, strict diets are prescribed, and subsequently the “step system” rule is applied, which allows a smooth transition to a normal and balanced diet due to the gradual expansion of the diet, and the “zigzag” rule.
In dietetics, the “zigzag” rule is a short-term, over the course of several days, significant change in the diet menu. Contrasting days can be load days – “plus zigzags” and unloading days – “minus zigzags”.
The main significance of the days when the menu includes foods that are limited or excluded from the diet is to provide the body with those nutrients that are supplied in insufficient quantities, stimulate metabolic processes, and test the body’s reaction to certain foods.
They also have a positive psychological effect, eliminating the discomfort and stress that usually accompany strict diets. The closer the patient is to recovery, the more varied his menu becomes, the fewer dietary restrictions. Initially, it is recommended to carry out such days once every 7-10 days, then every 4-5 days.
Therapeutic fasting days are prescribed for 1-2 days, once a week; they can be vegetable or fruit, dairy, meat or fish, based on whole grain porridges: buckwheat, rice or oatmeal.
They are recommended for diseases of the cardiovascular system: insufficient blood circulation, atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease, which is accompanied by excess weight, and hypertension.
It is necessary to spend low-calorie days with a diagnosis of obesity, diabetes mellitus, acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially during exacerbations, with diseases of the kidneys and liver, biliary tract, with chronic cholecystitis, with cholelithiasis and urolithiasis, with gout.
If you plan to spend 2 fasting days in a row, then one of them can be vegetable or fruit, and the other can be dairy, meat or fish.











