Patients suffering from renal failure are prescribed hemodialysis. It helps cleanse the blood when the kidneys are unable to cope with their function on their own. When undergoing such a major procedure, the patient must take into account many associated factors, including a special diet, to support the body and ensure maximum effectiveness of the therapy.
Diet for hemodialysis or the so-called treatment table No. 7 is a special “renal” nutrition program, quite well known and popular in medical practice. It has a number of variations depending on the stages of the disease. Thus, diet No. 7 G is indicated for patients with end-stage chronic renal failure (CRF) when hemodialysis is required.
General rules
Hemodialysis is a method of treating patients with end-stage chronic renal failure , the essence of which is the use of hardware methods to cleanse the patient's body of toxic substances and normalize the water-salt balance (programmed hemodialysis / peritoneal dialysis ). Unfortunately, regular hemodialysis does not fully replace renal function, which contributes to the persistence of a number of metabolic characteristic of patients with chronic renal failure.
In addition, dialysis has side effects that lead to the loss of a number of food nutrients and the development of protein-energy malnutrition. Therefore, the condition of patients who are on hemodialysis is largely determined by proper diet therapy. The diet of such patients depends on a number of factors: the frequency/duration of procedures, the degree and nature of metabolic changes, the characteristics of dialysis solutions and the presence/severity of complications. Thus, nutrition during hemodialysis is a dynamic concept that requires individual selection of diet.
In addition to maintaining the necessary nutritional status of the patient, therapeutic nutrition is aimed at slowing the development of cardiovascular diseases and cerebrovascular changes, preventing mineral-bone disorders and correcting metabolic disorders resulting from uremic intoxication, and often inadequate kidney dialysis. At the same time, despite the need for an individual approach to the nutrition of patients undergoing regular hemodialysis, there are general principles of nutrition, which are presented below.
The diet for kidney hemodialysis is based on treatment table No. 7 G according to Pevzner, which in a number of ways differs from therapeutic nutrition in the pre-hemodialysis period. The diet is aimed at a balanced supply of food macro/micronutrients, taking into account individual metabolic characteristics and relieving the side effects of hemodialysis.
The diet provides for an increase in protein consumption to a level of 1.0-1.2 g/kg body weight/day (60-75 g), which is caused by protein losses during the hemodialysis procedure, a deterioration in its digestion and an increase in the rate of its breakdown. It is with this amount of protein consumption that the level of albumin and a positive/neutral nitrogen balance is maintained. However, protein consumption at this level does not induce uremic intoxication.
Insufficient protein content in the diet contributes to the development of protein-energy malnutrition (decrease in body weight index, levels of prealbumin , albumin , cholesterol ) and increases the risk of death. Excessive protein content in the diet contributes to an increase in nitrogenous waste in the blood and the development of uremia. Protein should be predominantly of animal origin, the source of which can be dietary red meat, rabbit, poultry, moderately fatty fish, chicken eggs, cottage cheese, milk and fermented milk drinks.
The energy value of the daily diet is calculated from the ratio of 35-40 kcal/kg/day (2800-2900 kcal/day). At the same time, a neutral energy balance is achieved with a consumption of 35 kcal/kg/day. Elderly people or those on bed rest are allowed to reduce the energy value of the diet to 2400-2500 Kcal/day.
The content of fats and carbohydrates in the diet must correspond to the physiological nutritional standards of a particular patient and provide the necessary energy value of the diet. On average, 100-110 g of fat and 400-450 g of carbohydrates per day. However, given the frequent disorders of lipid metabolism, the diet of such patients should not be overloaded with fats rich in cholesterol and saturated fatty acids.
It is advisable to include in the diet various vegetable oils and fish oils, which are sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids. In case of poor appetite and signs of hypoglycemia , it is permissible to increase the content of easily digestible carbohydrates in the diet (confectionery, honey, jam, jelly, mousses). However, if you have diabetes , carbohydrates in the diet are limited.
The content of table salt and free liquid has a special place in the diet of hemodialysis patients. Their quantity is determined individually depending on the level of blood pressure and the degree of water retention in the body. During hemodialysis, as a rule, the amount of urine excreted continuously decreases, which leads to sodium retention in the body, and even a slight increase in its consumption increases thirst and increases the consumption of free fluid, which contributes to the development of arterial hypertension and edema .
In addition, excessive salt consumption in hemodialysis patients leads to an increase in body weight in the period between hemodialysis sessions, myocardial hypertrophy, and the development of heart failure . Therefore, the sodium content in the diet is limited to 2.0-2.8 g/day (4-5 g of table salt). The food is not salted. In the absence of edema and high blood pressure, 2-3 g of salt are acceptable in the diet for adding salt to prepared foods, and if they are present, salt is completely excluded from the diet, and salty foods are also excluded - semi-finished products, canned food, smoked meats and pickles.
The amount of free fluid consumed is calculated from the ratio: 600 ml + daily diuresis volume + extrarenal causes of dehydration. On average - 800-1000 ml of liquid. To monitor fluid intake, it is necessary to weigh the patient daily and determine urine output for the previous day. The increase in body weight between dialysis sessions should not be more than 1.5-2 kg. Excessive consumption of free fluid promotes overhydration hyponatremia develops , and edema appears.
To compensate for the loss of vitamins during regular hemodialysis, it is recommended to supplement the diet with multivitamin preparations (group B, C, E), 1-2 tablets per day and taking vitamin D , since such patients develop D-hypovitaminosis . Additional intake of beta-carotene and vitamin A is undesirable.
The intake rates for phosphorus, potassium and calcium are determined primarily by laboratory and clinical indicators. In hemodialysis patients, hyperkalemia is associated with a high risk of death. Therefore, the amount of potassium intake in dialysis patients should not exceed 3 g potassium/day. Potassium is found mainly in fruits/dried fruits (raisins, dates, apricots, figs), bananas, nuts (peanuts, walnuts, pistachios, hazelnuts), legumes, mushrooms, garden greens (spinach, parsley, dill), rice, baked goods from wholemeal flour, vegetable broths, chocolate, fruit juices, ketchup, instant coffee, cocoa. The patient can eat no more than 1 vegetable and 1 fruit (in any form) per day. At the same time, raw vegetables and fruits must be peeled, washed with water and left in water for 2-3 hours, since potassium dissolves well in water.
The requirement for magnesium in patients on hemodialysis is 200–300 mg/day. Hypermagnesemia due to the relatively low content of magnesium in food and its low absorption in the intestine (40-50%) is less common than hyperkalemia, however, it is important to control the prescription of drugs containing magnesium ( magnesium sulfate , antacids), since it can cause severe hypermagnesemia with respiratory depression, neurological disorders.
The calcium requirement of patients on hemodialysis is at least 1.5 g/day. Excessive calcium intake is caused by the prescription of calcium-containing agents designed to bind phosphates ( calcium acetate , calcium carbonate , calcium gluconate ). Excessive calcium intake leads to hypercalcemia as well as vascular/tissue calcification. If there is no need to control phosphorus with calcium-containing products, it is recommended to reduce calcium intake to 900-1000 mg/day.
The need for phosphorus in the diet of a healthy person is 1600-1700 mg/day. During one hemodialysis procedure, an average of 250 mg of phosphorus is removed. That is, hemodialysis does not ensure the removal of phosphorus from the body in the required amount and cannot of hyperphosphatemia Since increased phosphorus content significantly increases the risk of myocardial infarction and the development of cardiovascular diseases, phosphorus intake during dialysis should be strictly limited. Since organic phosphorus is the most bioavailable, it is necessary to limit the content of animal products first of all to animal products containing it in large quantities and to a lesser extent to plant products.
Considering that protein is the main source of phosphorus, it seems advisable to include in the diet foods with a minimum phosphorus content in relation to protein - egg whites, sea fish, chicken drumstick, beef, turkey fillet, pork, cod and limit foods such as cheese, milk, muesli, bran, whole grain bread, legumes, cocoa, cereals, cottage cheese, nuts. If it is impossible to normalize phosphorus levels, calcium-containing/calcium-free drugs that bind phosphates are prescribed.
The diet for kidney hemodialysis involves the exclusion of a number of foods from the diet. List of products prohibited for consumption during dialysis: concentrated broths with meat/fish/mushrooms, fatty meat of animals and waterfowl, legumes (except soy protein), sausages, smoked meats, liver, brains, kidneys, canned snack foods, hard/processed cheeses, salted/fermented foods and vegetables rich in oxalic acid, hard-boiled eggs, refractory animal fats, margarine, chocolate, peaches, apricots, grapes, cherries, figs, black currants, bananas, dried fruits, peppers, cinnamon, horseradish, mustard, cocoa .
To diversify the diet and improve the taste of salt-free dishes, various methods of culinary processing of foods are used, including frying and stewing, adding spices, natural vinegar, citric acid, and using homemade sauces.
To improve suppressed appetite, the list of products can be expanded by including alcoholic beverages in the diet (in the absence of contraindications) - dry/semi-dry grape wine, vermouth, sherry or spirits, the volume of consumption of which (in terms of ethyl alcohol) should not be consumed by women exceed 20 g/day and 40 g/day for men. It is advisable to eat meals in small portions 5-6 times a day.
Nutrition for hemodialysis
Chronic renal failure (CRF) is the final stage of all renal diseases.
Program hemodialysis is one of the methods of its treatment. If a person’s diet in the pre-dialysis period depended on what kind of kidney disease he suffered from, then during program hemodialysis the recommendations may be completely different.
But specific recommendations on the patient’s nutrition should be given by the attending physician. After all, they depend on the duration of the patient’s hemodialysis experience, residual renal function, the presence of complications and many other reasons.
We can only give general recommendations.
Authorized Products
The diet of hemodialysis patients includes the consumption of salt-free bread and vegetarian soups with the addition of vegetables and cereals, as well as cabbage soup, beetroot soup, and borscht. For main courses, we recommend lean types of red meat (veal, beef), chicken, turkey, rabbit, which are served boiled. Pre-boiling the meat is mandatory, since the process of cooking in large quantities of water removes nitrogenous substances from the food.
After boiling, the meat can be further cooked. For fish, low-fat sea fish or river fish (pollock, pike, hake, pike perch, cod), which are prepared in a similar way, are recommended.
Vegetables and garden herbs (tomatoes, carrots, dill, lettuce, cucumbers, beets, parsley, cauliflower, tomatoes, green onions, potatoes) that are boiled or stewed are allowed as side dishes. Chicken eggs are allowed to be consumed in the amount of 2-4 pieces per week in the form of a steamed protein omelet or soft-boiled. In the absence of restrictions, it is allowed to include milk and fermented milk products in the diet in the amount of 200-300 g per day.
Homemade white sauces with sour cream/milk, unsalted vegetable vinaigrette, and vegetable/fruit salads are allowed. Unsalted butter and various vegetable oils are recommended as fats. Fruit/berries can be consumed in various forms, taking into account the potassium content, if its limitation is prescribed to the patient. Drinks you can drink include rosehip infusion, weak tea and coffee, and freshly prepared fruit juices.
Table of permitted products
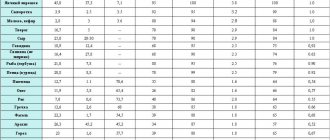
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
| sago | 1,0 | 0,7 | 85,0 | 350 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| milk candies | 2,7 | 4,3 | 82,3 | 364 |
| fondant candies | 2,2 | 4,6 | 83,6 | 369 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| cinnamon | 3,9 | 3,2 | 79,8 | 261 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| dried parsley | 22,4 | 4,4 | 21,2 | 276 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
| sour cream sauce | 1,9 | 5,7 | 5,2 | 78 |
| caraway | 19,8 | 14,6 | 11,9 | 333 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
| yogurt | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled beef tongue | 23,9 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 231 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| peasant unsalted butter | 1,0 | 72,5 | 1,4 | 662 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| ghee | 0,2 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 892 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| coffee with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 1,0 | 11,2 | 58 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Cooking recommendations
All food must be prepared from fresh ingredients. Dishes are consumed boiled, stewed, steamed or fried.
In the latter case, you need to remember that you should not fry food until golden brown and do not use a large amount of oil.
It is allowed to add spices, vinegar or lemon juice to improve the taste of finished dishes.
Portions should be small, their weight is calculated by the doctor individually for each patient. It is imperative to exclude from the diet foods that contain large amounts of potassium.
In chronic renal failure, patients' kidney functions are inhibited; they are responsible for its excretion, so in most cases hyperkalemia develops.
In some cases, as an exception, small amounts of products containing potassium are allowed. But this should be done only with the knowledge of a specialist; in no case should you make such decisions on your own.
Approximate menu
Consider an approximate menu from diet No. 7:
- in the morning it is recommended to eat 1 soft-boiled egg and a vegetable salad dressed with olive oil; drink compote or weak tea;
- For a snack, use a baked apple with cottage cheese and honey or fruit salad;
- for lunch - vegetable soup, boiled meat (chicken or rabbit), steamed vegetables and jelly;
- fruit mousse for afternoon snack;
- dinner - mashed potatoes with stewed meat, fresh vegetables, juice;
- Before going to bed, it is recommended to drink a glass of warm milk with honey or herbal tea.
To prepare vegetable soup, use only vegetables, for example, potatoes, carrots, celery, onions, and parsley root. It is allowed to add a little salt and spices, as well as a tablespoon of olive oil.
Meat and fish need to be alternated; they can be baked in the oven or cooked in a slow cooker. It is very important to eat freshly prepared meals every day.
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for patients undergoing hemodialysis involves the exclusion from the diet of concentrated meat/fish/mushroom broths, various refractory animal fats, fatty meats, foods high in salt (canned food, hard/processed cheeses, chips, bouillon cubes, salted nuts, sausages, sauces, marinades, ketchups, salted butter, margarine, canned vegetables), legumes, liver, brains, kidneys, smoked meats, hard-boiled eggs, cereals and pasta, dairy products.
Limit the consumption of foods containing a lot of potassium - curry, mushrooms, coffee, milk powder, fruit juices, sorrel, bananas, sea fish, seeds, sesame, nuts, soy products, chocolate, milk formula, dried apples, peanut butter, dried fruits, rhubarb , ketchup, spinach, beets, beer, avocado, fruit juices, tomato sauce, apricots, molasses, grapes, cherries, figs, lentils.
Products containing phosphorus are subject to restrictions: bran, nuts, whole grain bread, cereals, cocoa milk, cheese, eggs, legumes, muesli, cottage cheese. Strong tea/coffee, cocoa, and sodium mineral waters are excluded from drinks.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| pickles | 0,8 | 0,1 | 1,7 | 11 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ginger | 1,8 | 0,8 | 15,8 | 80 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| tomato sauce | 1,7 | 7,8 | 4,5 | 80 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Prevention of kidney diseases
In order to prevent the body from causing serious “failures”, you should not neglect a preventive medical examination. Your kidneys will enjoy excellent health if you follow these simple rules:
- Diet. Protein and fatty foods should be kept to a minimum.
- Refusal of salt and alcohol.
- Drinking regimen: 30-40 ml/kg body weight. (The norm is for a healthy adult; for a child the numbers are slightly different).
- Gut health (avoid constipation).
- Temperature balance and strengthening the immune system. (Protect yourself from hypothermia).
Yoga and oriental dancing are very useful. But heavy physical activity can only bring harm.
Reviews and results
A strict diet for patients on hemodialysis is a vital necessity, especially for patients with high blood pressure, edema and disorders of phosphorus-calcium metabolism. According to patient reviews, it is difficult to get used to unsalted or low-salt food; the dishes are tasteless, but there is no choice.
- “... After toxic damage to the kidneys and the development of chronic kidney disease, I was prescribed hemodialysis. There were bad tests, constantly elevated blood pressure, and swelling. A therapeutic salt-free diet was prescribed. It was very difficult to get used to unsalted food right away. Garden herbs (parsley, dill, garlic, onions, parsnips) helped out, and I also made sauces based on milk and cream. I had to strictly control my diet. I cook everything in vegetable oil. So far I’m sticking to the diet normally, and there’s nowhere to go, you need to adapt if you want to live.”
Limiting medications containing aluminum
Another very important recommendation is to limit medications containing aluminum. It is extremely toxic for a patient with renal failure and causes a number of serious complications: aluminum dementia (severe damage to the nervous system), bone damage, anemia. It is no coincidence that hemodialysis departments use special water purification systems aimed, among other things, at getting rid of aluminum. But often aluminum-containing drugs are prescribed to treat concomitant diseases. For example, Almagel, phosphalugel - for gastritis, peptic ulcers. This causes serious harm to kidney patients.
Patients should also not cook food in aluminum containers and take multivitamin complexes containing vitamin A and mineral supplements without consulting a nephrologist.
In conclusion, we emphasize once again: the diet for hemodialysis should be balanced, complete and, in the absence of complications, not significantly different from the diet of a healthy person.
Drinking regime
Healthy kidneys maintain fluid and electrolyte balance on their own. In sick people, it is impaired. Excess fluid is not completely removed from the body and accumulates. Therefore, it is very important to strictly observe the drinking regime and not exceed the norm specified by the doctor.
If the patient does not follow the recommendations given to him, then this is fraught with the development of hypertension, cerebral or pulmonary edema. Even during hardware removal of excess fluid, the patient feels surges in blood pressure. This greatly increases the load on the heart.
If the volume of urine remains normal, then after a short period of time the amount of liquid drunk can be increased to a liter (sometimes up to 1200 - 1500 ml). However, when selecting the volume needed for the patient, physical activity, its intensity, and how the intestines work must be taken into account.
Between procedures, the patient must control his own weight. There should not be an increase of more than 3-5 percent of body weight in 24 hours (this is with three times hemodialysis in 7 days). Sometimes patients skip regular tea parties, eat few soups, but swelling still appears.
This means that the diet contains more than the normal amount of carbohydrates and fats, which release liquid when broken down. Then you should at the same time limit all foods containing water (fruits, watermelons, etc.).
Please note: if the daily weight gain of a patient on an “artificial kidney” is more than 5% per day, this indicates stagnation of fluid in the body. If the increase is 10-15% or higher, the patient’s condition is threatening and he needs hospitalization.
What can you eat?
Patients undergoing kidney hemodialysis can eat:
- chicken protein prepared in any way;
- steamed or boiled fish with vegetables;
- first courses with vegetables;
- up to 300 g of unsalted black or bran bread;
- lean meats prepared by any method other than frying;
- watermelons, pumpkin, dried apples, pears;
- vegetable or butter;
- low-fat milk;
- juices from fruits or vegetables diluted with water, tea;
- vermicelli, stewed vegetables.
Sample menu for the week
For patients undergoing hemodialysis, a strict diet is a vital necessity. Therefore, it is so important that it does not cause disgust, and that the food is well and completely absorbed. A variety of dishes and the use of aromatic herbs, permitted sauces and gravies will help you get used to a salt-free diet.
Below is an approximate menu layout for a week, which can be used as a basis when creating a diet.
Monday:
| Breakfast | Omelette, vegetable salad, oatmeal jelly |
| Snack | Apple baked in egg whites |
| Dinner | Vegetarian cabbage soup, boiled chicken, potatoes stewed in sour cream, fruit juice |
| Afternoon snack | Biscuits, rosehip infusion |
| Dinner | Cabbage zrazy with minced meat and onions, tea with milk |
| Before bedtime | A glass of kefir |
| All day | Salt-free bread - 200 g, sugar - 50 g, jam or honey - 40 g, cow butter - 20 g. |
Tuesday:
| Breakfast | Carrot casserole with apples, pancakes, juice |
| Snack | Fruit and berry salad |
| Dinner | Rice soup with vegetables, boiled fish, mashed potatoes, jelly |
| Afternoon snack | Butter bun, rosehip infusion |
| Dinner | Fruit pilaf, 100 ml sour cream, tea with milk |
| Before bedtime | Glass of yogurt |
| All day | Like Monday |
Wednesday:
| Breakfast | Grated carrot salad with sugar, pancakes, juice |
| Snack | Fruits |
| Dinner | Vegetarian borscht with sour cream, stewed meat, buckwheat, jelly |
| Afternoon snack | Cupcake, rosehip decoction |
| Dinner | Cabbage cutlets, noodle soup with cottage cheese, tea |
| Before bedtime | A glass of curdled milk |
| All day | Like Monday |
Thursday:
| Breakfast | Rice soufflé, cabbage salad, oatmeal jelly |
| Snack | Fruits |
| Dinner | Puree soup from mixed vegetables, meat stew with potatoes, compote |
| Afternoon snack | Cabbage pie, rosehip decoction |
| Dinner | Peppers stewed in sour cream, unleavened cheese |
| Before bedtime | A glass of kefir |
| All day | Like Monday |
Friday:
| Breakfast | Omelette, vinaigrette, oatmeal jelly |
| Snack | Fruit salad |
| Dinner | Noodle soup with milk, stewed chicken, rice, compote |
| Afternoon snack | Carrot cutlets, rosehip infusion |
| Dinner | Potato casserole with meat, sour cream, tea |
| Before bedtime | Glass of yogurt |
| All day | Like Monday |
Saturday:
| Breakfast | Fruit pilaf, pancakes, juice |
| Snack | Oatmeal jelly |
| Dinner | Buckwheat soup with vegetable broth, baked fish, mashed potatoes, compote |
| Afternoon snack | Steam pudding from cottage cheese |
| Dinner | Vegetable stew with chicken, tea with milk |
| Before bedtime | Glass of fermented baked milk |
| All day | Like Monday |
Sunday:
| Breakfast | Fruit salad with sour cream, Dutch cheese, oatmeal jelly |
| Snack | Cabbage salad |
| Dinner | Soup with dumplings, pilaf with chicken, compote |
| Afternoon snack | Potato zrazy, rosehip infusion |
| Dinner | Stuffed zucchini, apple pie, tea |
| Before bedtime | A glass of kefir |
| All day | Like Monday |