General rules
Urolithiasis ( urolithiasis ) is a metabolic disease and is manifested by the formation of stones in any organ of the urinary system: kidneys, ureters or bladder.
The likelihood of developing urolithiasis in people is increased by hormonal imbalance, hereditary metabolic disorders, the patient’s diet, as well as existing anatomical abnormalities. The development of stones is the result of the formation of a nucleus and the accumulation of constantly forming crystals around it. The formation of the nucleus occurs when crystals of various salts settle from urine supersaturated with them. The role of certain nanobacteria in this process has been proven. These atypical gram-negative bacteria produce calcium carbonate on the surface of cells in the urinary system. Substances that maintain salts in a dissolved state and prevent their precipitation include: sodium chloride , magnesium, zinc, manganese ions, hippuric acid , citrates, cobalt. Even in small quantities, these substances inhibit crystallization.
The clinical picture of the disease is quite diverse. In some patients, it manifests itself as a single attack of renal colic, while in others it becomes protracted, an infection occurs and various kidney diseases occur: hydronephrosis , pyelonephritis , pyonephrosis , sclerosis of the renal parenchyma and the development of renal failure . The main symptoms of the disease are pain, blood in the urine, urinary disorders and the passage of stones and salt crystals.
Nutrition for kidney stones will depend on the composition of the stones, and therefore may include mutually exclusive foods. Calcium is the basis of most urinary stones. The greatest prevalence of calcium stones (including calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate), urate, consisting of uric acid salts and magnesium-containing stones is noted. The main role in the formation of calcium oxalate is played by supersaturation of urine with calcium and oxalate.
Initial treatment of any type of KSD is aimed at increasing fluid intake, improving diuresis, changing diet and controlling the acid-base status of urine. Kidney stone disease is a serious problem in urology, since despite the introduction of new, high-tech methods of therapy, there is a high rate of relapse of stone formation.
A rational diet restores normal metabolism and urine reaction, which determines the possibility of stone formation. In an acidic environment, urate stones are formed, oxalate stones in a neutral acidic environment, and phosphate stones in an alkaline environment. A properly selected diet changes the pH of urine and serves as a criterion for the correctness of the diet. If the pH level in the morning is 6.0-6.4, and in the evening 6.4-7.0, then everything is normal in the body, since the optimal level is 6.4-6.5.
Treatment also depends on the composition of the stones and the acid-base state of the urine. “Sand in the kidneys” is expelled by drinking plenty of fluids and medicinal mineral waters, holding watermelon days and dietary recommendations. Herbal decoctions (horsetail, lingonberry leaf, madder, goldenrod) and herbal preparations are widely used.
Thus, the drug Cyston promotes the removal of small oxalate, phosphate and urate stones. It is important that the litholytic effect of the drug does not depend on urine pH. It regulates the crystal-colloid balance, reduces the concentration of oxalic acid and calcium in the urine. At the same time, it increases the level of elements that suppress stone formation (magnesium, sodium, potassium). As a result, it causes demineralization of stones.
An effective method for urate stones is descending litholysis (taking drugs orally). To dissolve them, it is necessary to create a urine pH of 6.2-6.8. be achieved by taking citrate mixtures: Blemaren and Uralit U. Treatment with citrate mixtures leads to complete dissolution within 2-3 months. Stones that are no more than one year old are more amenable to dissolution. Methods of contact dissolution of urate stones using the drug Trometamol . It is inserted through an established nephrostomy drain.
Dissolution of stones of other composition is problematic and often ineffective, so they resort to various methods of their prompt removal. Open operations are now performed quite rarely, since minimally invasive methods have appeared.
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is used ; indications for it include almost all types of stones in patients of any age. Thanks to the use of extracorporeal lithotripsy, it became possible to remove stones on an outpatient basis. The stone comes out in the form of destroyed fragments on its own, which can be complicated by blockage of the ureter and renal colic. Methods of “moderate trauma” include transurethral endoscopic stone extraction .
It must be remembered that even surgical treatment is not a method of completely getting rid of urolithiasis, and after crushing kidney stones, prevention of relapse of the disease is mandatory. The complex of measures that correct metabolic disorders includes: antibacterial therapy, diet therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures and spa treatment.
After removing kidney stones, it is imperative to maintain an adequate water regime (part of the liquid is taken in the form of cranberry or lingonberry fruit drinks and mineral water). Herbal medicine is of no small importance. Herbal preparations are non-toxic and have a complex effect: antimicrobial, diuretic, litholytic, eliminate spasm and inflammation. These include madder extract, Cystenal , Canephron , Prolit , Fitolysin , Nephrolit .
Daily monitoring of urine pH is important. For oxaluria, prevention is aimed at alkalizing it, as well as eliminating oxalic acid from the diet. With uraturia, it is also necessary to alkalize urine and limit protein foods rich in purine bases. With phosphaturia, it is important to acidify the urine and limit calcium-containing foods.
For patients with oxalate urolithiasis, treatment is recommended at the following resorts: Zheleznovodsk, Pyatigorsk, Essentuki (No. 4, 17), Truskavets. For calcium phosphate - Pyatigorsk, Truskavets, Kislovodsk. For therapeutic and prophylactic purposes, you can drink up to 0.5 liters of medicinal water per day, monitoring your urine levels. The same recommendations apply to patients who have undergone removal of a stone from the ureter. Nutritional features will be discussed below.
Diet for kidney stones
The patient’s nutrition does not depend on the location of the stones, but is completely determined by their composition and the reaction of the urine. The position of the stone determines only the clinical picture of the disease. With kidney stones (located in the pelvis), the outflow of urine is most often not impaired and there may be no pain symptom. When a stone is in the ureter and while passing through it, a blockage of the lumen occurs and the outflow of urine is disrupted. This is accompanied by an attack of renal colic. Acute, paroxysmal pain occurs in the lumbar region. It can radiate to the testicle or labia, accompanied by vomiting and nausea. If the stone is located in the lower third of the ureter, there is a frequent urge to urinate.
Bladder stones are most common in older men. These are single round-shaped stones, and their composition is urate. Their formation is promoted by stagnation of urine in prostate adenoma. In other age categories, the causes are dietary habits, bladder inflammation, alcohol consumption, bladder diverticula, or passing of a kidney stone. An effective and least traumatic method of treatment is endoscopic crushing ( cystolitholapaxy ) through the urethra.
What diet will be prescribed depends entirely on the composition of the stones. In a nutshell, with urate you need to limit meat and eggs, soups with meat broths and sweet wines. With phosphates, the consumption of milk, eggs and all types of cabbage is reduced; with oxalates, you cannot eat radishes, onions, sorrel, spinach, legumes and tomatoes. This will be discussed in more detail below.
Diet for urate kidney stones (uraturia)
An indicator of purine metabolism in the body is the concentration of uric acid in the blood. Purines are synthesized in the body and also come from food. The consequence of disturbances in this metabolism is an increase in uric acid . Salts of uric acid found in urine are called urates.
The main reasons for its occurrence are:
- abuse of foods rich in purines;
- an abundance of high-calorie foods and fatty foods in the diet;
- malignant neoplasms;
- starvation;
- tissue destruction.
If increased synthesis of uric acid occurs, its level in the blood increases, and at the same time crystals of its salts appear in the urine. Urate nephrolithiasis develops in young children; symptoms of hyperuricemia are manifested by muscle pain, arthralgia , tics, nocturnal enuresis, excessive sweating , intoxication and asthenic syndrome.
With uraturia, the patient's nutrition should be aimed at reducing the level of uric acid. The diet is characterized by limiting foods containing purines (meat, offal), oxalic acid (sorrel, radishes, spinach, raspberries, cauliflower, asparagus, cranberries) and salt. At the same time, increase the proportion of alkalizing foods (vegetables, milk, fruits) and the amount of liquid in the diet.
If there is urate in the urine, it is necessary to exclude:
- Canned fish.
- Meat and poultry of young animals, offal, due to the high content of purines. It is allowed to eat meat from older animals to a limited extent - these dishes are included in the diet no more than 2 times a week. Meat portions are up to 150 g, and fish - 170 g.
- Meat broths, smoked meat dishes.
- Cereal sprouts.
- Cheeses, strong tea, chocolate, alcohol.
- Eggs, mushrooms, tomatoes, legumes.
- Limit flour and various confectionery products.
The basis of the diet is milk, fermented milk products and vegetables, berries, fruits (seaweed, pumpkin, cabbage, grapes, apples, all citrus fruits, figs, bananas, raisins, currants, gooseberries, lingonberries, strawberries, cherries). Patients should periodically take courses of diuretic herbs: clover, cornflower, burdock and dandelion roots, infusions of dried apricots, blueberries, boneberries, apples, rowan, barberry, carrots, pumpkin, parsley root, beets. Decoctions of grape and black currant leaves help remove stones. During the season, you need to consume these berries as much as possible.
The culinary processing of meat and fish products has its own peculiarities - they must be boiled, and only then used to prepare various dishes. When cooked, 50% of the purines are lost and should never be consumed. Meat, poultry or fish, devoid of some purines, can be stewed, baked, ground for minced meat or fried.
Cereals are an integral part of the diet
The duration of this diet ranges from several months to permanent. The patient should drink 2.5 liters of liquid per day (alkaline mineral water of Essentuki, Borjomi, natural juices) and have fasting days once a week - kefir, curd, fruit, milk.
The main method of treatment and prevention of this type of stones is alkalinization of urine, since urates are poorly soluble in an acidic environment and easily turn into solid form. It is enough to maintain the pH at 6-6.5. Citrate preparations are effective because they prevent crystallization and create conditions for the dissolution of already formed stones.
Phosphates in urine
Phosphates are salts of phosphorus and are normally absent in urine. Their presence may indicate dietary habits or kidney pathology with impaired renal function. Urinary infection is one of the causes of stone formation. It is this that is an important local factor in maintaining the recurrent course of urolithiasis. Thus, the metabolic products of microorganisms contribute to the alkalinization of urine and the formation of calcium phosphate crystals.
An increase in phosphate levels is caused by the consumption of milk, kefir, cottage cheese, fish, seafood, fish caviar, oatmeal, pearl barley and buckwheat porridge. The reason for the precipitation of these salts is the alkaline reaction of urine and the high calcium content in it. The appearance of calcium phosphate stones is found in hyperparathyroidism .
With phosphaturia, foods containing calcium and phosphorus are sharply limited. It is recommended to drink up to 2-2.5 liters of liquid. If hypercalciuria diphosphonates are prescribed . You can increase the acidity of urine by drinking sour juices and mineral waters Narzan, Darasun, Arzni, Smirnovskaya.
During pregnancy , secondary phosphaturia occurs due to changes in diet and alkalinization of urine. If the urine becomes even slightly alkaline (pH > 6.0), phosphate precipitates. This is facilitated by a diet rich in green vegetables and dairy products. It is necessary to repeat urine tests over time, and only if changes are repeatedly detected, an ultrasound scan and a more detailed examination of the kidneys are prescribed. Phosphaturia in pregnant women is usually corrected with diet.
Normal fluid intake (2 liters per day) is necessary unless contraindicated due to the presence of edema and high blood pressure. The following are temporarily excluded from the diet:
- calcium-rich foods: dairy products, eggs, cocoa;
- salty and spicy foods (limit salt to 8 g per day);
- garden greens (lettuce, green onions, dill, parsley, celery leaves and cilantro);
- potato;
- nuts, cocoa;
- sweet confectionery (biscuits, pastries, cakes);
- fruit juices;
- yeast.
Acidification of urine is promoted by:
- meat and fish dishes;
- sour fruit drinks (from cranberries, currants, lingonberries);
- dried fruit compotes;
- Birch juice;
- cereal products;
- bran bread;
- eating pumpkin, asparagus, Brussels sprouts.
Phosphaturia is quite common in children. Up to 5 years, these salts are present in the urine in the form of amorphous crystals, which give it a cloudy tint. Their appearance is associated with high consumption of dairy products at this age. Often crystalluria is transient and appears against the background of acute respiratory viral infections and other diseases, disappearing after the child recovers.
With more serious disorders ( dysmetabolic nephropathies ), damage to the kidney tubules due to metabolic disorders is noted. Dysmetabolic nephropathies are characterized by urine oversaturation and crystalluria.
True phosphaturia occurs in diseases that are accompanied by impaired phosphorus and calcium metabolism during hypercalciuria . The crystals in this case are represented by calcium phosphate. Chronic infection of the urinary system is the cause of secondary phosphaturia. In this case, microorganisms with urease activity are important. By decomposing urea, they alkalinize the urine, which leads to the formation of crystals of amorphous phosphates (magnesium phosphate salts).
For amorphous phosphates in the urine (they do not have a clear structure), it is recommended to take decoctions of lingonberry, bearberry, knotweed, and horsetail leaves. It must be remembered that in an alkaline environment the solubility of phosphates decreases. In this condition Diet No. 14 , which changes the acid-base balance towards acidity.
Oxalates in urine
Calcium oxalate salts occupy a leading place in occurrence. This type of stone appears when eating a diet rich in oxalic acid salts. However, there may also be a congenital disorder of oxalic acid metabolism ( dysmetabolic nephropathy ). Another reason for the formation of these stones in the urine is an increase in intestinal permeability to oxaloacetic acid (it is absorbed from the intestines and enters the urine) and a deficiency of calcium, which normally binds oxalates in the intestines. The increased formation of oxalates is also explained by the consumption of large amounts of ascorbic acid - it is metabolized into oxalic acid. The process of formation of poorly soluble calcium oxalate in the body occurs most actively with a lack of magnesium and vitamin B6 .
Taking into account all these points, adjustments are made to the diet:
- Avoid foods high in oxalic acid: rhubarb, figs, sorrel, spinach, beans, chocolate, parsley, celery. Moderate levels of this acid are found in tea, chicory, carrots, green beans, onions, beets, tomatoes, plums, strawberries, and gooseberries.
- The consumption of vitamin C with foods is limited: grapefruit, strawberries, lemons, sea buckthorn, gooseberries, currants, oranges, tangerines, rose hips, cranberries, rowan berries, strawberries, wild garlic, bell peppers.
- A large amount of plant fiber is introduced.
- A plentiful drinking regimen is observed, which prevents the precipitation of calcium oxalates (3 liters per day). Water is alternated with the consumption of juices (cucumber and other fruits and vegetables), compotes, fruit and vegetable decoctions. Weak solutions of organic acids (malic, citric, benzoic and others) contained in them can dissolve oxalates.
- Alkalinization of urine is carried out by drinking mineral waters: Naftusya, Essentuki No. 4 and No. 20, Truskavetskaya, Luzhanskaya, Morshinskaya, Berezovskaya.
- Oxalates are removed from decoctions of the peels of apples, pears and quinces, birch leaves, elder flowers, and violet roots.
Diet for urolithiasis in women
Severe forms, such as coral nephrolithiasis . With coral stones, the foreign body occupies almost the entire abdominal cavity system of the kidney. For this severe form of ICD, only open surgery is performed. A common cause is hyperparathyroidism (increased function of the parathyroid glands). Thanks to modern diagnostics, such advanced forms have recently become less common.
The growth of urolithiasis is provoked by: the nature of nutrition (abundance of protein in the diet), physical inactivity, which leads to disruption of phosphorus-calcium metabolism. An unbalanced diet makes the situation worse. For example, a bias towards protein foods with frequent adherence to a protein diet provokes the formation of urate stones. With sand in the kidneys, you need to pay attention to nutrition and urine reaction, since this condition is reversible and can be corrected with nutrition and plenty of fluid intake. You can periodically take diuretics. For urolithiasis in women, you should adhere to the general dietary recommendations described above, since they are no different.
It is also important for women:
- fight physical inactivity and lead an active lifestyle;
- avoid weight gain;
- drink enough fluid;
- do not overcool and treat inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary area in a timely manner.
All these factors contribute to stone formation.
For pyelonephritis and urolithiasis
In this case, a more strict approach to both treatment and nutritional therapy is necessary. Pyelonephritis is often a complication of ICD. Antibacterial therapy is mandatory based on the sensitivity of pathogens to antibacterial drugs. At the same time, herbal preparations ( Fitolysin , Canephron , Prolit ) are prescribed. It must be remembered that only removal of the stone creates the conditions for the complete elimination of the infection.
Patients are shown Table No. 7 , in which correction is carried out taking into account the composition of the stones. In the presence of inflammation, diet therapy is aimed at sparing the kidneys, so it is forbidden to consume: seasonings, pickles, spicy foods, smoked meats, marinades, horseradish, mustard, vinegar, fish roe, onions, garlic, and alcoholic beverages.
Dietary features include significant salt restriction (1.5 g-5 g) depending on the state of kidney function. It is not allowed to take sodium (salty) medicinal waters.
Main course recipes
On a diet you have to eat at home. To avoid boring dishes, you can cook according to new recipes.
Soups
It is recommended to eat liquid meals every day.
Vegetarian cabbage soup is one of the simple, hearty and healthy soup options. For preparation you will need:
- potatoes - 4 pcs.;
- white cabbage - 1 small fork;
- carrots - 1 pc.;
- onions - 0.5 pcs.;
- vegetable oil - 20-30 ml;
- bay leaf - 1 pc.;
- greenery.
Vegetarian cabbage soup is made from sauerkraut.
Finely chop the potatoes and cabbage and place in boiling and salted water. Fry onions and carrots in oil, add to vegetables. Throw a lava leaf into the pan. Before eating, chop the greens into a plate: onion, parsley, dill.
Salads
Salads will diversify the menu and replenish vitamin deficiencies.
In addition, a vegetable salad is an easy and nutritious snack. For preparation you need:
- bell pepper - 1 pc.;
- tomato - 1 pc.;
- cucumber - 1 pc.;
- spinach - 100 g;
- olive oil for dressing;
- salt, pepper to taste.

Vegetable salad is a light, dietary snack.
Grind all ingredients and mix with dressing. Prepare the salad before eating, otherwise the tomatoes will release juice and spoil the taste of the dish.
Porridge
Porridge can be boiled in water - this is a side dish for lunch or dinner.
Dairy products are better absorbed in the morning. Hercules porridge is a nutritious and healthy breakfast. To prepare 4 servings you need:
- 1 tbsp. oatmeal;
- 2.5 tbsp. milk;
- salt, sugar, butter - to taste.

Porridge is cooked in water.
Bring milk to a boil, add cereal. Cook for 10-15 minutes over low heat. Add sugar, salt. Before serving, place a piece of butter in a plate of porridge.
Sweets
You can cook sweets while on a diet.
Cottage cheese casserole with fruits or dried fruits will be a healthy breakfast or snack. To prepare it you will need:
- 250 g cottage cheese;
- 1 egg;
- 4 tbsp. l. flour;
- salt, sugar to taste;
- fruits or dried fruits to taste.

Cottage cheese casserole with fruit is a great dessert.
Cut the fruits into small cubes. Mix all ingredients and beat with a mixer or whisk for a more fluffy consistency. Place in an oven preheated to 150°C for 30-40 minutes. You can serve the dish with condensed milk or homemade jam.
Authorized Products
For uraturia, dairy and plant products are recommended:
- Any vegetables except legumes and those with a high content of oxalic acid. Eggplants, sweet peppers, potatoes, tomatoes, cucumbers. Vegetables, whenever possible, should be eaten raw before meals.
- Enrich your diet with foods rich in vitamin A (broccoli, sour cream, seaweed and other seaweed) and group B (nuts, corn, rose hips, oatmeal, barley, white cabbage, pomegranate, bell peppers, oranges, grapefruits).
- Fruits with a high content of vitamin C: sea buckthorn, rose hips, lemon, currants, kiwi, citrus fruits, strawberries, wild strawberries, grape juice.
- Any cereals.
- Milk, cheese, cottage cheese, eggs, butter.
- Any bread - rye, bran and wheat. It is better to use yeast-free baked goods.
- Dishes made from lean meat and fish can be eaten no more than 3 times a week. When choosing meat, keep in mind that chicken legs have a higher purine content than breasts, just like pork legs. Turkey meat contains 4.5 times less purines than chicken. All meat or fish dishes are pre-cooked to reduce the purine content, and then prepared at your discretion: baked, fried or stewed.
- Vegetarian vegetable and cereal soups.
- Two eggs a day, white omelettes - white does not contain purines.
- Sweets include marmalade, jam, sugar, honey, caramel, marshmallows, marshmallows. Chocolate is excluded.
- Before going to bed, drink 1 glass of liquid (bran decoction, juices, water with lemon or other citrus fruits, herbal tea, kefir).
For oxalaturia :
- A dairy-vegetable (“alkaline”) diet is followed. It is recommended to regularly consume foods rich in calcium - dairy products (sour cream, fermented milk products, cottage cheese).
- To reduce the level you need to eat foods rich in vitamins B1 and B6 . These are eggs, meat, liver. Fish, meat and poultry should be low-fat varieties (boiled or baked).
- Wheat and rye bread.
- All cereals.
- Vegetable oil and butter.
- The diet is enriched with foods rich in magnesium: oatmeal, buckwheat, pearl barley, wheat bran, seafood, seaweed, wholemeal bread, dried apricots, oatmeal, peas, soybeans, radish. Magnesium ions bind up to 40% of oxalic acid in urine to form magnesium oxalates , which are highly soluble. Magnesium deficiency is manifested by the formation of calcium oxalate .
- Cauliflower and white cabbage, potatoes in any form, eggplants (in moderation), carrots, pumpkin, cucumbers, cilantro.
- Apricots, bananas, pears, prunes, grapes, apricots, apples, watermelons, melon, peaches, quince, dogwood. Apples, pears, quince, decoctions of currant leaves, pears and grapes, as well as decoctions of fruit peels contribute to the removal of oxalates. To alkalize urine, you need to eat dried fruits.
For phosphaturia, a diet with a predominance of meat and flour dishes is indicated:
- Any fish, mild fish snacks, soaked herring, and also in small quantities and infrequently - canned fish.
- Meat and poultry in any preparation.
- Pasta and unleavened dough dishes.
- Any bread and flour products.
- Soups on a weak broth with cereals, pasta, egg dressing.
- Fats, except refractory ones.
- Enrichment of the diet with vitamin A : liver of animals, birds, cod and halibut liver, fish caviar, butter.
- Introduction of additional vitamin D : tuna, salmon, pink salmon, fish caviar.
- Dairy products include only small amounts of sour cream for dressing.
- A variety of porridges cooked in water.
- One egg a day.
- Vegetables are excluded, but pumpkin, green peas, Brussels sprouts and mushrooms are allowed; vegetable juices are excluded.
- Sour varieties of apples, compotes, jelly from them, cranberries, lingonberries, red currants.
- You can drink weak tea and coffee, but without milk, fruit drinks from cranberries and lingonberries, rosehip decoction, bread kvass.
- Confectionery, sugar, jam and honey.
Dietary table for phosphates
If a lot of phosphates are detected in the kidneys, it’s time to give up dairy products. Phosphates provoke infectious diseases, kidney shrinkage and colic, acute and chronic deficiency. You will have to give up dishes containing:
- sour cream and eggs;
- nuts and pickles, smoked meats;
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- alcoholic beverages, seasonings and hot sauces;
- cheese and milk.

A patient with phosphates in the kidneys can have breakfast in the morning with carrot salad and millet porridge, washed down with fruit nectar. For second breakfast, berry jelly and unsweetened apple pie are allowed. For lunch they prepare boiled chicken and weak tea.
Lazy dumplings with sour cream will be served for an afternoon snack, and fish cooked in the oven with jacket potatoes and cabbage salad will be served for dinner.
Fully or partially limited products
Nutrition for urolithiasis of the kidneys caused by urate should not contain:
- Offal.
- Meat products and canned meat. Animal protein is limited. Red meat from young animals is excluded because it contains the highest amount of purines.
- Dishes from carp, halibut, sardines, tuna, sea bass, mussels and herring; the use of canned fish is excluded.
- Any broths - in rare cases, secondary broth can be used.
- Beef and pork fat.
- Vegetables rich in oxalic acid (radish, spinach, cauliflower, sorrel, asparagus, cranberries, raspberries) and pickled vegetables.
- Soups made from spinach, sorrel and legumes.
- Legumes and mushrooms (porcini and champignons).
- Oatmeal and white rice.
- Cheeses, chocolate, cocoa, red wine, tea and coffee are also rich in purines.
- Confectionery products, brewer's yeast.
- Spicy snacks and spices.
- Dried fruits (prunes are possible).
- Alcohol.
With oxalaturia are excluded or limited:
- Products with oxalic acid.
- Jelly and gelatin-containing dishes.
- Sprouted grains.
- Fatty meats and fish. Low-fat meat and fish dishes can be up to 150 g per day.
- Soups made with strong broths and containing legumes.
- Cocoa, bread kvass, coffee, chocolate.
- Limit the consumption of potatoes, beets, tomatoes, onions, carrots, eggplants, zucchini, Brussels sprouts, legumes, tomatoes and tomato juice, celery, parsley, rhubarb.
- Salty cheeses, canned food, smoked meats.
- The consumption of milk and fermented milk products is limited.
- Products made from butter dough.
- Products with vitamin C are reduced: lemon, grapefruit, currants, rose hips, oranges, rowan berries, strawberries, gooseberries, Antonov apples, cranberries, tangerines, dill, wild garlic, sweet peppers.
- Limit salt to 3-4 g.
For phosphaturia it is not recommended:
- Calcium-containing products (milk, cottage cheese, cheese), sesame seeds.
- Greens and vegetables (you can use Brussels sprouts and peas).
- Spicy dishes, smoked meats, sauces.
- Nuts, cocoa.
- Alcohol.
- Sweet yeast baked goods.
Sample menu for the week
Most patients with urolithiasis have urate or phosphate stones. The diet for urolithiasis in women is aimed at restoring potassium-phosphorus metabolism. It is almost impossible to create a universal nutrition system for all sick people. Many foods that are useful for uraturia cannot be used for cystinuria, calcifications and other types of stones.
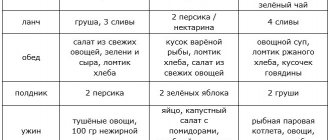
Sample menu for ICD for 7 days
| Days of the week | 1 breakfast | 2 breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Monday | muesli with milk, apple jelly, oatmeal cookies | boiled eggs (without yolk), apple juice | okroshka with chicken fillet, puree with vegetables, compote | pasta with vegetable cutlets, cottage cheese casserole, bearberry decoction |
| Tuesday | milk oatmeal, toast with jam, weak coffee | cottage cheese with raisins, vegetable juice | barley and potato soup, carrot cutlets, baked hake, tea | rice porridge, cottage cheese with dried fruits, fruit juice |
| Wednesday | buckwheat with water, bran bread toast, weak tea | 100 g dried fruits | cream soup with cauliflower, baked potatoes, vegetable salad, compote | cream soup with broccoli, pancakes with sour cream, tea |
| Thursday | rice pudding, wheat toast with jam, mineral water | homemade yogurt with prunes | meatless noodle soup, fish cutlets, vinaigrette, tea | stuffed peppers, vegetable stew, jelly |
| Friday | oatmeal with dates, toast with jam, milk | baked pear with honey, weak coffee | vegetarian cabbage soup, fish meatballs, vegetable salad, herbal decoction | dumplings with strawberries, cottage cheese with sour cream, juice |
| Saturday | semolina with dried fruits, tea with lemon | fruit pudding, homemade yogurt | rice soup, steamed cutlets, stew, compote | baked pollock, cheesecakes with cottage cheese, apricot jelly |
| Sunday | fruit salad, boiled egg, tea | baked pear with honey | vegetarian borscht, boiled veal, vegetable salad, tea | noodle and broccoli soup, pudding, boiled eggs, bearberry decoction |
From this set of dishes, you need to exclude foods that are prohibited for a certain type of stone and replace them with permitted ones.

The last meal is recommended 1.5 hours before bedtime.
If urolithiasis is complicated by pyelonephritis, more fermented milk products are introduced into the diet.
Diet menu for kidney stones (Diet)
As can be seen from the list of permitted products, it is difficult to create a universal menu for different types of nephrolithiasis , since products allowed in one case are contraindicated in another. So, with oxalate nephrolithiasis, the diet is vegetable-meat, with urate nephrolithiasis , it is vegetable-milk, and with phosphaturia , on the contrary, meat food should predominate. The issue of preparing a diet in each specific case is decided individually, and the doctor gives nutritional recommendations.
For children
Most often at this age, calcium oxalates and phosphates are detected, less often urate stones and extremely rarely cystine stones. Salts of oxalates, urates and phosphates can appear periodically and depend on fluctuations in diet, and the presence of cystine is a sign of pathology.
Nutrition with salts in the urine in children of different ages does not differ from that in adults.
For oxalate crystalluria, a potato-cabbage diet is prescribed. It is necessary to exclude extractive meat dishes, as well as oxalate-rich cranberries, beets, carrots, sorrel, spinach, cocoa, and chocolate. Prunes, dried apricots and pears have an “alkalizing” effect. Of the mineral waters, Slavyanovskaya and Smirnovskaya are used in monthly courses 2-3 times a year. In addition to diet therapy for oxalate stones, Vitamin B6 , magnesium preparations and Phytin .
Treatment of phosphate crystalluria is aimed at acidifying the urine. For this purpose, mineral waters are used: Dzau-suar, Narzan, Arzni and drugs: methionine , cystenal , ascorbic acid . A diet is prescribed with a limit on foods with phosphorus (legumes, chocolate, cheese, dairy products, liver, fish roe, chicken). If there is a large amount of calcium phosphate in the urine, it is necessary to reduce the absorption of phosphorus and calcium in the intestine by prescribing Almagel . If tripelphosphates , antibacterial therapy and uroantiseptics to sanitize the urinary system.
When treating urate crystalluria, the child’s diet includes the exclusion of purine bases. These are the following products: meat broths, liver, kidneys, nuts, peas, beans, cocoa. Preference is given to products of dairy and vegetable origin. It is important to drink 1-2 liters of liquid. These should be slightly alkaline mineral waters, oat decoction and herbal decoctions (dill, horsetail, lingonberry leaf, birch leaf, clover, knotweed). To maintain urine pH, citrate mixtures ( magurlit , uralit-U , blemaren , solimok ) are used.
Stone formation in a child is provoked by conditions that lead to permanent obstruction of the urinary tract: anomalies of development and position, endocrinopathies ( hyperparathyroidism , hyperthyroidism , infantile hypercalcemia ), acquired tubulopathy and chronic urinary infection. Of course, it is important to eliminate the main cause of stone formation.
Reviews and results
Diet for urolithiasis is a mandatory component of treatment. There is a need for its constant observance in cases of hereditary or recurrent forms of the disease. This is confirmed by the reviews of many patients who had to undergo more than one operation for nephrolithiasis . If you do not follow dietary and medication recommendations and do not receive spa treatment, there is a high risk of relapse of the disease.
- “... With an attack of colic, I was admitted to the hospital, they used drops, injections, relieved the pain and spasm, but the stone came out at home after discharge. Drank up to 2 liters of water. It was a terrible pain that radiated into the scapula and into the ureter. During the attack there was nausea. On the one hand, it’s scary, but on the other hand, I’m glad that there was no surgery. I hope this doesn't happen again. I went to a urologist, he prescribed a diuretic, Phytolysin, and told me about the diet. The composition of the stone has not been determined, but now I will take urine and observe. The doctor said that urates and oxalates are more common and the diet is almost the same - vegetable and dairy”;
- “... The salts in my kidneys are very fine, like sand. I don’t feel them, and when they come out after a steam room, a lot of liquid or spicy foods, there are attacks of cystitis. Twice a year I take urological preparations and Canephron. It is plant-based and helps normalize kidney function. The doctor said that it reduces the likelihood of new salts appearing. Now I try to stick to a diet, drink a lot of purified water and feel fine. I follow a general diet - no fatty foods, no fried foods, no broths, less meat and milk, more vegetables. There are different salts in urine: sometimes urates, sometimes oxalates.”
The need to follow a diet
Compliance with the principles of therapeutic nutrition for kidney stones is extremely important because:
- helps prevent the formation of new stones;
- dissolves existing stones;
- removes stones in the form of salt deposits and small formations from the kidneys.
In addition, a diet for urolithiasis is useful for weight loss and normalizes the functioning of the digestive tract and cardiovascular system. If a patient with kidney stones adheres to a therapeutic diet, the risk of inflammatory diseases of the urinary system is reduced.