Many diets for weight loss have many contraindications, the main one being diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. However, despite their health problems, these people may also be overweight. A gentle diet for weight loss was developed especially for these patients; it can be followed for gastritis, ulcers, pancreatitis, liver and kidney diseases.
A gentle diet is a balanced diet, the observance of which allows you to quickly lose weight with health benefits. Nutritionists consider this method one of the best for the prevention of many diseases and deep cleansing of the body from toxins. Following such a special diet will strengthen the immune system, because the diet consists of many useful substances.
Rules for a gentle diet
The term “gentle diet” was introduced into the lexicon of nutritionists by the Soviet scientist-therapist M.I. Pevzner. The doctor was preparing a nutrition plan for people with gastrointestinal diseases and diabetes. Gentle diets according to Pevzner are called “tables”, each of which has its own number. Each of the “tables” consists of a specific set of products allowed for a specific disease.
The menu of a gentle diet for weight loss consists of simple and light dishes that do not put a strain on the digestive system and provide the body with all the necessary elements. The essence of this version of the dietary method comes down to the fact that a specially formulated diet allows a person suffering from a gastrointestinal tract disease not to limit himself in the energy necessary for the full functioning of the body.
A gentle diet is based on the following rules:
- Meals should be five times a day.
- Food should be at room temperature.
- Dishes should be as light as possible.
- Preference is given to those methods of cooking in which the least loss of vitamins and microelements occurs. While you are losing weight or improving your health, you should completely stop using a frying pan for cooking. Food should be cooked in a steamer or oven.
- The average daily calorie intake should be at least 2250 kcal.
- The human body should receive 85 grams of protein, 90 grams of fat and 250 grams of carbohydrates daily. These indicators may vary slightly depending on the type of disease.
- 20 minutes before meals, you can drink a glass of warm still water with lemon juice. This way you will feel fuller more quickly during the meal.
A gentle diet is prescribed for diseases of the intestines, gall bladder, pancreas, stomach, kidneys and liver.
Popular diets: harm or benefit?
On the Internet and in printed literature you can find dozens of different diets that promise amazing results. Moreover, when communicating with friends or on an online forum, you will probably find a lot of personal evidence of how wonderfully this or that diet works. And this is actually true. The whole secret is that any diet works at all, since each of them, regardless of the composition of the products, is based on calorie restriction, often very strict. Of course, if you follow this diet, you will quickly lose weight. However, in the vast majority of cases, after some time, the weight will return again, and even in greater quantities. But you physically cannot stick to a strict diet all the time.
In this sense, very strict diets are very dangerous - Japanese, mono-diet, buckwheat. All of them are built on unhealthy combinations and strict exclusion of certain products. The effect of them is very short-term and is achieved mainly through the removal of excess fluid and loss of muscle mass. After switching to a normal diet, you will not only weigh much more, but you will also look worse due to muscle loss.

Not all diets are good for the body
Low-carbohydrate diets that are based on an almost complete restriction of carbohydrates - the Kremlin diet, the Dukan diet - have an excellent effect. Due to a sufficient amount of protein, weight loss is very effective, and muscle mass is also preserved. At the same time, due to the presence of the right fats, the condition of the skin, hair, and nails improves. The main danger is only one: if you move away from this type of diet, you will begin to gain weight literally from a spoonful of rice. Low-carbohydrate diets are often used by professional athletes to prepare for competitions, but are not suitable for ordinary people as a permanent eating style.
In order for your weight loss to be as effective as possible, you need to start gradually, choosing a gentle diet, which will ultimately give the best results.
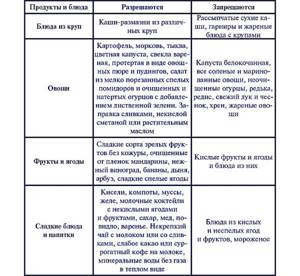
Allowed and prohibited foods on a gentle diet

What is possible with a gentle diet is important to know for everyone who has decided to lose weight using this technique. The diet menu is not limited to a strict set of certain products, but nutritionists recommend building your diet on the healthiest foods. For example, calcium is needed for proper intestinal function, so it is advisable to include cheese or low-fat cottage cheese in your breakfast.
There are other requirements when compiling a dietary diet:
- Your daily diet must contain protein, as it maintains metabolic processes at the desired level, resulting in accelerated fat burning.
- To burn fat deposits, you need to eat foods rich in iron - meat, eggs, liver. Nutritionists recommend eating meat products as protein in the first half of the day, and it is better to prefer fish for dinner.
- The diet should contain complex carbohydrates, it should include wholemeal bread and brown rice.
- Even when losing weight, the body needs a small amount of vegetable oils. Their regular use will make your skin smooth and elastic, and your hair and nails strong and healthy. Vegetable oils also cleanse the body of toxins; you can eat olive, sesame, flaxseed, and grape seed oil.
- It is recommended to start lunch and dinner with a vegetable salad. Fresh vegetables will help satisfy intense hunger and make you feel full faster.
A gentle version of the diet is based on the consumption of permitted foods and the exclusion of forbidden ones.
They are presented in the table below:
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
| Lean beef | Fatty food |
| Yesterday's wheat bread | Semi-finished products |
| Lean beef | Pork, goose, duck |
| Chicken without skin | Sausages, smoked meats |
| Turkey | Carbonated drinks |
| Rabbit | Alcohol |
| Omelette | Canned food |
| Lean fish | Vermicelli |
| Low-fat milk and sour cream | Legumes |
| Non-acidic low fat cottage cheese | Coarse porridges – pearl barley, barley, millet |
| Mild cheese | Butter pastries |
| Dairy products | Radish, radish, cabbage |
| Refined butter and vegetable oil | Coffee, strong tea, cocoa |
| Soft porridge on water with added milk | Spicy cheese |
| Boiled or steamed vegetables | Full fat milk and cottage cheese |
| Fresh vegetables in the form of soufflé and puree | Sorrel, spinach |
| Vegetable Lenten Soups | Onion garlic |
| Mushrooms | |
| Pickled vegetables | |
| Chocolate | |
| Ice cream | |
| Hard and sour fruits | |
| Berries with large grains | |
| Fatty and smoked fish, caviar | |
| Fresh and whole grain bread |
Forecasts for recovery from gastritis
Prognosis for gastritis largely depends on the patient himself. The lion's share of success is diet. Therefore, it all depends on how conscientiously the patient adhered to the therapeutic diet.
Whether a person can get rid of gastritis forever depends on the root cause of the disease. For example, infectious gastritis can be completely cured. This requires only competent antibacterial therapy. But gastritis of an autoimmune nature is still incurable. In this case, the patient needs to monitor his health throughout his life, control both the immune system and adhere to a special diet.
Prognosis for recovery from gastritis depends on the nature of the course and type of disease. As mentioned above, acute gastritis is much easier to treat. As for chronic forms, much depends on the type of gastritis. For example, atrophic gastritis is considered one of the most complex and dangerous, since with this type of gastritis part of the glandular tissue of the stomach atrophies.
Quick gentle diet: menu for 3 days
A gentle diet menu for 3 days may have the following option:
1st day:
- Breakfast: a cup of coffee and a slice of black bread with jam or honey.
- For lunch: 3 radishes, a boiled egg, a piece of black bread and a glass of 1% kefir.
- You can have lunch with a celery salad, a cutlet made from lean meat, a serving of mushroom soup and one cup of green tea.
- For an afternoon snack - any fruit, but not more than 200 g, and one cracker.
- For dinner you can eat 200 g of low-fat cottage cheese, a stale bun, a glass of milk or kefir.
Day 2:
- For breakfast, nutritionists suggest drinking a glass of milk with honey and crackers.
- For lunch - two tomatoes, 2 sandwiches with low-fat sausage, a cup of green tea.
- Have lunch with 200 g of stewed vegetables, baked apples, and one medium portion of meat broth.
- For an afternoon snack - any fruit, but not more than 200 grams.
- You can have dinner with two slices of black bread with boiled fish, drink a glass of 1% kefir and eat one green apple.
3rd day:
- Breakfast – a cup of green tea and one cracker with honey.
- For lunch – 2 slices of black bread with butter and celery leaves, two slices of cheese.
- Have lunch with meat broth, boiled fish - no more than 150 g, drink a glass of jelly or kefir.
- For an afternoon snack - a biscuit and a glass of freshly squeezed carrot juice.
- You can have dinner with a vegetable salad of celery, boiled liver, and one glass of low-fat kefir.
Diseases as causes of stomach pain
Pain in the stomach area can be the result of pathological processes, if they occur, it is necessary to urgently seek advice from a specialist:
| Diseases | Image | Description |
| Pancreatitis | Inflammatory pathology of the pancreas occurs with severe symptoms. The patient complains of pain in the stomach area, to the left of it, radiating to the back. Nausea, vomiting, weakness, and tachycardia develop. There are food residues in the stool | |
| Cholecystitis | Inflammatory process in the gallbladder due to blockage of the ducts. It occurs with a sharp, severe pain syndrome in the stomach and below the ribs. As the pathology develops, the patient's body temperature rises, vomiting and nausea occur. The process of bile entering the intestines is disrupted, which causes a change in the color of the skin and eye sclera, which acquire a yellowish tint | |
| Stomach polyps | Benign neoplasms formed from organ tissue. With small sizes they do not cause discomfort. In the process of growth, they can cause severe pain in the stomach, bleeding in the organ, and changes in stool | |
| Stomach cancer | Malignant neoplasms that in the initial stages of development do not lead to the development of a clinical picture. Later, the patient may complain of a constant feeling of fatigue, fatigue, and rapid weight loss. As tumors grow, the patient suffers from stomach pain that occurs after eating, flatulence, a feeling of heaviness, discomfort, loss of appetite, heartburn, pain when swallowing, vomiting, diarrhea mixed with blood or dark color, which indicates the opening of internal bleeding | |
| Stomach ulcer | A chronic pathology in which erosions form on the walls of the organ. It is the most commonly diagnosed pathology. The disease can be recognized by pain and discomfort in the stomach, which worsen after eating. The patient may complain of decreased appetite, body weight, flatulence, constipation, and the appearance of a specific coating on the tongue | |
| Gastritis | Inflammatory pathology of the organ with damage to the mucous membrane. The disease can occur without symptoms or have a pronounced clinical picture, which is characterized by: pain in the stomach after eating certain foods, burning sensation, vomiting, belching, flatulence, bad breath, diarrhea, constipation, nausea after waking up | |
| Stomach infections | A disease that develops as a result of penetration and proliferation of pathogenic microflora in the stomach. Symptoms of pathology are clearly expressed. The patient refuses food, complains of pain, heaviness, discomfort in the solar plexus, and headache. As the disease progresses, these symptoms may include vomiting, diarrhea, chills, excessive sweating, and increased body temperature. | |
| Ulcer perforation | The formation of a hole in the wall of the organ and the penetration of its contents into the abdominal space. The process of perforation is characterized by acute pain in the stomach area, radiating to the entire abdomen; a rapid change in the color of the skin occurs, which turns pale. Increased sweating, decreased blood pressure and slower heart rate |
Unlike many other pathological processes in the body, diet for diseases of the digestive tract is an important element of treatment, which determines its effectiveness, the speed of restoration of normal stomach function and elimination of the symptomatic picture.
For stomach pain of various etiologies, complex treatment is prescribed by the attending physician. It is aimed at:
- elimination of factors that led to the development of pathological processes;
- protecting the organ from the aggressive effects of pathogenic microflora, poor nutrition, and other predisposing factors;
- destruction of Helicobacter pylori;
- restoration of normal stomach function;
- elimination of psycho-emotional signs of pathologies that arose against the background of gastric diseases and do not go away after therapy and recovery.

Harmful foods that should not be eaten on an empty stomach
For stomach pain, the choice of treatment table is made by the attending physician, based on the type of pathological process, the degree of damage to the stomach and the degree of disruption of its functioning, the stage of the disease, the general condition of the patient, as well as his nutritional status.
As a rule, depending on the level of stomach acidity, diets are prescribed in accordance with the recommendations of the treatment table:
- No. 1 and its modifications 1a and 1b at normal and elevated pH levels;
- No. 2 for low acidity;
- No. 16 is at the stage of recovery from the disease.
These treatment tables contain basic nutritional recommendations, according to which the patient needs to exclude from the diet and add some food products that will help cope with pathological processes and restore normal functioning of the stomach.
Diet for ulcerative lesions of the gastric mucosa
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, diet recommendations No. 1a and No. 1b are considered the most gentle, which help reduce the influence of chemical, physical and mechanical factors on the stomach, which have a negative effect on the secretory function of the organ. However, tables No. 1a and 1b are not full-fledged, and therefore are assigned for a period of no more than 10-14 days.
Diet No. 1 is complete, regardless of its modification - pureed or not pureed, and therefore can be used for up to six months. This treatment table is recommended for patients with chronic stomach pathologies. It is also recommended for the recovery period after treatment table 1a and 1b, which allows you to prepare the stomach for the transition to the previous way of eating.
Treatment table No. 2 is recommended for diseases accompanied by low acidity, which entails many dangerous complications. Recommendations of diet No. 2 allow you to enhance the secretory function of the organ and reduce the fermentation process. It is complete and can be prescribed for a long time.
Video - Nutrition for stomach ulcers
You can use the following gentle diet recipes for weight loss and treatment:
Recipe 1. Dietary buckwheat porridge

Take a glass of washed cereal for 1 liter of water. Boil water and add buckwheat, cook over low heat for 15 minutes without adding salt.
Recipe 2. Chicken broth

Boil the chicken in water, place the carrots and onion in the pan. Bring to a boil, reduce heat and cook for another 15 minutes, remove the vegetables. After an hour and a half, remove the meat. Add a little salt to the broth.
Recipe 3. Fruit smoothie

Mix 200 g of low-fat yoghurt with 10 small pieces of pineapple, the juice of one orange and chopped banana. Beat everything in a blender.
Recommendations of the treatment table No. 1
Prescribed for acute and chronic gastritis with normal or high acidity, peptic ulcer. The duration of the therapeutic course using healthy nutrition is from 3 to 5 months.
During this period, you should avoid foods that cause fermentation, irritate the walls of the stomach, and stimulate excessive production of gastric secretions. These include heavy foods: canned, smoked, pickled, fried and salted.
Fatty meat and fish, mushrooms and broths based on them have an aggressive effect on the functioning of the stomach. Yeast products should be excluded from the diet: fresh bread, rich sweet bakery products.
To reduce fermentation in the organs of the digestive tract, which will entail a reduction in the feeling of discomfort and pain, the complete exclusion of raw vegetables and fruits will help, especially the consumption of cabbage, sorrel, cucumbers, and onions, which contribute to the formation of gases, should be strictly limited.
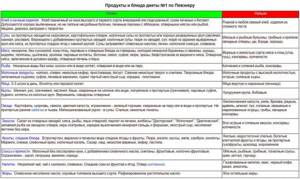
Products and nutrition of treatment table No. 1
During the treatment period, the patient should avoid cocoa-containing products, caffeine, kvass, carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
You can replace excluded products with stale bread and crackers. Instead of pork, steam or boil lean meats and fish. As a side dish, eat boiled pasta, various cereals, excluding pearl barley, steamed and pureed vegetables.
For the first course, you can prepare light vegetable, cereal or milk soups. During cooking, add a small amount of butter or clarified vegetable oil.
As a dessert, it is allowed to eat marshmallows, marshmallows, curd mass, sweet fruits, berries, on the basis of which you can prepare mousse, jelly, and jelly.
When it comes to drinking, preference should be given to natural drinks and decoctions of medicinal herbs. You can prepare juices and compotes based on sweet fruits and berries. Drink only weak tea, adding a small amount of cream and milk is allowed.
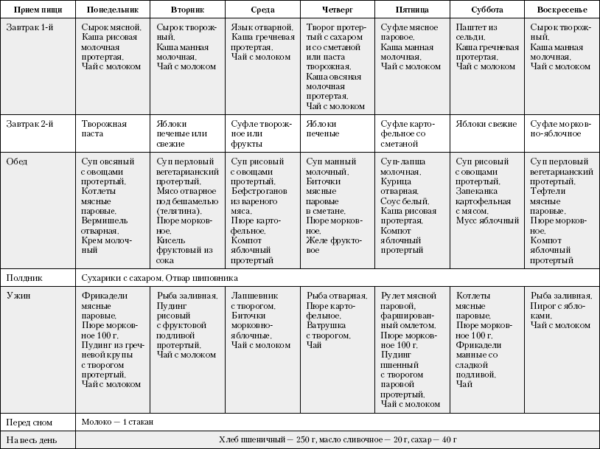
Sample menu
Important! The acute period of gastritis and ulcers, as a rule, lasts from 5 to 8 days, during which time foods should be completely excluded from the list of prohibited foods. Further nutritional adjustments are carried out by the treating specialist.
A gentle diet for liver diseases, gastritis and stomach ulcers
A gentle diet for patients is developed taking into account the disease. For example, in case of diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to introduce restrictions on animal fats, carbohydrates, liver, and chicken yolk into the main nutrition system intended for weight loss.
In case of heart failure, it is necessary to reduce carbohydrate intake to a minimum. Patients with cardiovascular diseases should also eat fats and fruits with caution. Tea should be completely removed from the diet during treatment. For patients with kidney disease, nutritionists prescribe a diet with a minimum amount of protein, tea and water. All food should be desalted.

A liver-friendly diet mainly consists of water-based cereals, vegetables and fruits. Homemade fermented milk products made from starter cultures will also be beneficial for the liver. You need to eat 5-6 times a day, with the first meal being before 8 am.
A gentle diet for gastritis with high acidity is based on a diet with a minimum amount of raw vegetables and fruits. With increased acidity, the amount of these products in the daily diet of a sick person should be maximum. For gastritis, fish and meat must be thoroughly ground.

The gentle diet menu for stomach ulcers and gastritis is designed for a long period of time and is based on eating light foods. The calorie content of the daily diet for these stomach diseases cannot be reduced by more than 10%. For any form of gastritis, the diet should include liquid and semi-liquid dishes - soups, purees, jelly. During an exacerbation of these stomach diseases, animal fats should be excluded from the diet, replacing them with vegetable ones. It is necessary to completely abandon dried fruits and all products that contain a large amount of fiber - turnips, beets, peeled apples, currants, broccoli. Food must be chewed well, since large pieces of food can injure the inflamed gastric mucosa.

It is better to stew or boil vegetables; after such processing, this food will be much easier for the stomach to digest. If you have gastritis and ulcers, you should not drink water at the same time as food; you must wait a half-hour interval. A gentle diet for gastritis and ulcers does not recommend that patients consume proteins and carbohydrates at the same time; it is advisable to adhere to separate meals.

You need to remove salt, pepper and all irritating spices from your diet. If you have stomach diseases, drinking strong coffee and tea is prohibited. These drinks are drinkable, but weak.
Approximately the daily menu looks like this:
- Breakfast - oatmeal, weak tea with milk.
- 2nd breakfast – baked apple.
- Lunch – steam cutlet, broth with meatballs and compote.
- Afternoon snack – kefir with crackers.
- Dinner – cottage cheese with vegetable puree.
Rules for losing weight for people with stomach problems
There are general patterns of behavior in which losing weight during gastritis will give a positive result.
- You cannot begin weight correction if chronic gastritis, duodenal ulcer, or other gastrointestinal diseases are in the process of exacerbation. Only after treatment and the onset of stable remission can you begin to fight extra pounds.
- First of all, it is necessary to remove all the factors that provoked both gastritis and obesity:
- solve the problem of chronic stress;
- eliminate the negative effects of medications on the mucous membrane;
- reduce alcohol intake and smoking to a minimum.
- It is necessary to lead an active lifestyle: physical exercise not only burns calories, but also stimulates digestion and speeds up metabolism. For gastritis, it is useful to do aerobics, swimming, gymnastics, and yoga. Strength sports are contraindicated - excessive muscle tension will injure the walls of the stomach.
- The most important thing is to strictly adhere to the rules of safe weight loss when eating:
- do not starve or overeat: eat small portions 5-6 times a day. The amount of food at one time should fit into a 250-gram glass;
- don’t overeat at night, but don’t go hungry in the evening; before going to bed, be sure to fortify yourself with a glass of kefir;
- refuse hot and cold dishes, eat only warm food, boiled, stewed or baked in the oven, chew it thoroughly;
- drink up to 1.5-2 liters of water daily to dilute aggressive gastric juice between meals;
- Only allowed foods should be included in the diet; forbidden foods and spicy dishes should be resolutely abandoned;
- You should not eat liquid and solid foods at the same time. Eat protein foods with carbohydrates, meat with flour products and potatoes in one meal.
- A diet for gastritis for weight loss is not designed for a short time, the duration of therapeutic nutrition with weight correction is 5-6 months, during which time it is possible to lose 7-10 kg without harming your health. Rapid weight loss increases the risk of exacerbation of the disease with a complication in the form of erosive gastritis.

- Calculation of caloric intake:
- We determine our normal weight (subtract 100 from the height expressed in cm), subtract its value from the actual weight. The resulting difference is extra pounds that need to be gotten rid of;
- We calculate the calorie content of the diet to maintain the existing weight: 30/32 kcal for each kg of normal weight for women / men + 9 kcal for each excess kg of weight + 500 kcal for hard physical work + 200 kcal for training;
- from the resulting calorie content we subtract 400 kcal - this is the amount of food that you need to give up daily in order to lose weight. The remaining calories are the daily intake, which must be constantly counted at first.
Note. Tested techniques for healthy people who have successfully lost weight (fasting days, mono-diets, abstaining from food after 6 pm) for chronic gastritis are absolutely unacceptable and lead to an exacerbation of the disease.
A gentle diet for intestinal diseases: menu for the week

A gentle diet for gastrointestinal diseases is also indicated for intestinal dysfunction. It is usually prescribed for a long period - from 6 months to 2 years. The menu for a person suffering from intestinal diseases can be quite varied, the choice of allowed dishes is large, it all depends on the preferences of the patient.
A gentle diet for the intestines is based on the principles of proper nutrition:
- In the process of cooking, you need to completely avoid frying dishes; everything is cooked exclusively in a double boiler, slow cooker, oven, or stewed over low heat.
- The consumption of fatty meat, fish, poultry and sausages is prohibited. To prepare dishes during a therapeutic diet for intestinal diseases, you can use lean meat - veal, beef, rabbit, fish.
- Dishes for this dietary table should be prepared without oil and fat.

The range of dishes for intestinal diseases is quite wide; as liquid food you can eat a variety of cereal soups - rice, oatmeal, wheat, semolina. They should have a slimy consistency with well-cooked grains. Using vegetables - carrots, celery, potatoes, pumpkin, zucchini, cauliflower, you can prepare pureed soups of a uniform consistency. For intestinal diseases, nutritionists recommend that their patients consume milk-based cereal soups.
General information
Gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the gastric mucosa.
Over a long period of time, gastritis leads to disruption of various functions of the stomach, mainly by disrupting the production of hydrochloric acid and the associated digestion process. For a long time it was believed that the main cause of gastritis lies in a violation of the diet. However, today a number of authoritative studies have established that a violation of the diet is an insignificant factor in the development of gastritis. There are several real reasons for this pathology:
- The bacterium Helicobacter pylori. According to statistics, up to 90% of all gastritis have a bacterial etiology. In the aggressive environment of the stomach (where there is concentrated hydrochloric acid), the vast majority of bacteria die. However, Helicobacter pylori manages to survive and reproduce in such unfavorable circumstances. During their life, H. pylori bacteria release toxic substances that cause an inflammatory reaction and encourage the stomach lining to secrete more acid. Thus, the walls of the stomach become defenseless and ulcers can form on them.
- Alcohol abuse. Alcohol negatively affects the condition of the epithelial tissues lining the inner wall of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition to direct irritation, alcohol also increases the production of gastric juice, thereby increasing the likelihood of damage to the mucous membranes by hydrochloric acid.
- Reflux. A continuation of the stomach is the duodenum, into which the bile duct opens. If the functioning of the pylorus (the sphincter that separates the stomach from the duodenum) is impaired, reverse reflux of bile is possible. This process is called duodenogastric reflux. Bile and intestinal contents irritate the gastric mucosa, which leads to the development of inflammatory processes. It is noteworthy that attacks of duodenogastric reflux also occur in healthy people. Gastritis develops only after a number of such episodes. Often, the reflux of intestinal contents into the stomach causes chronic gastritis.
- Autoimmune processes. As you know, cells of the immune system fight foreign microorganisms that enter the body from the outside. However, with some disorders, the immune system begins to attack the body's own cells. The cells of the gastric mucosa are no exception, and their immunity can also be attacked. Autoimmune gastritis is a relatively rare phenomenon and accounts for only 5% of cases.
- Eating disorder. Some eating habits can cause inflammatory pathologies of the esophagus and stomach. For example, a passion for eating too rough food, which injures the mucous walls. It was previously believed that spicy foods and coffee contribute to the development of gastritis, but recent research does not confirm this. If a person does not have diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), then spicy food will not harm him. The national cuisines of many southern countries are replete with spicy dishes, but this does not in any way affect the incidence of gastritis and other gastrointestinal pathologies. The opinion regarding long breaks and fasting is also questionable. There is no convincing evidence that short-term fasting (up to 24 hours) contributes to the appearance of gastritis.
- Medications. Some drugs (particularly non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can cause gastritis. If you need to take these medications regularly, be sure to talk to your doctor about side effects.
- Other factors. Gastritis can also occur due to allergic reactions, parasites and radiation exposure.
Gastritis goes through several stages in its development. Initially, when exposed to unfavorable factors, the gastric mucosa turns red and swells. As the disease becomes chronic, the stomach wall thickens. As the disease progresses, the affected areas of the gastric mucosa become thinner and atrophy. At this stage, the epithelial cells of the stomach are replaced by connective tissue cells (scars appear). At the last stage, erosions and ulcers appear.
Important! Since advanced stages of gastritis are fraught with the appearance of erosions and ulcers, it is important to begin treatment measures as early as possible. This will stop the pathological process and avoid complications.
Depending on the nature of the course and etiological factors, different types of gastritis are distinguished.
According to the nature of the flow:
- Acute - develops suddenly, for example, with an allergic reaction, alcohol abuse or poisoning. The acute form of the disease is characterized by severe pain, heartburn and nausea. A characteristic feature of acute gastritis is its transience. With proper treatment and timely elimination of the unfavorable factor (allergen, alcohol, toxins), the disease goes away within a few days.
- Chronic - develops slowly and has mild symptoms. A person may not be aware of chronic gastritis for years, which makes it more dangerous than acute gastritis.
According to the nature of inflammation:
- Erosive - characterized by the appearance of erosions on the gastric mucosa. This is one of the most common types of gastritis. As a rule, it develops in adults and very rarely in children.
- Atrophic is a type of chronic gastritis in which the secretory cells of the stomach atrophy. Thus, the production of gastric juice is reduced, which leads to a number of serious complications, including stomach cancer. Subatrophic gastritis is also distinguished, the clinical picture of which is similar to atrophic gastritis, but less pronounced.
- Catarrhal is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa caused by certain aggressive agents, such as infections, too hot or cold foods, toxins and other damaging factors. Catarrhal gastritis occurs in both acute and chronic forms. The development of a chronic form can be avoided if treatment is started on time.
- Superficial - represents the initial stage of inflammatory damage to the stomach. This is the most favorable stage of gastritis, which is easier to treat than others.
By localization:
- Antral - localized in the pyloric part of the stomach, where the hormone gastrin is secreted, which stimulates the production of gastric juice. With antral gastritis, gastrin synthesis increases, which leads to increased secretion of hydrochloric acid.
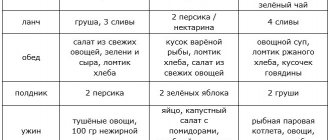
Menu of a gentle diet for acute pancreatitis for 5 days
A gentle diet for pancreatitis is prescribed to reduce or completely eliminate pain and reduce the activity of the pancreas. The duration of the diet is 5–6 days.
A gentle diet menu for acute pancreatitis for 5 days for adults may have the following option:
- 1st breakfast: boiled meat, oatmeal with milk, tea.
- Lunch: steam omelette, rose hip decoction.
- Lunch: soup from chopped vegetables, beef stroganoff from boiled meat, boiled potatoes, compote.
- Afternoon snack: sour cream cottage cheese, tea with milk.
- Dinner: boiled fish, carrot puree, tea with milk.
- At night: kefir.
This gentle diet menu for 5 days for pancreatitis is prescribed after 1–2 fasting days.
Causes of pain
Pain in the stomach is a response of nerve endings to mechanical, inflammatory damage, spasm of the muscles of the organ, and is a signal for help when the stomach is unable to cope with the problem on its own.
Poor nutrition leads to stomach pain:
- eating sandwiches, fast food;
- mono-diets;
- sharp restriction of caloric intake;
- eating hot or cold food;
- lack of diet;
- eating rough food;
- the predominance of animal fats in the daily diet;
- consumption of canned products;
- replacing water and tea with sweet carbonated drinks;
- the predominance of sour and salty foods in the menu.
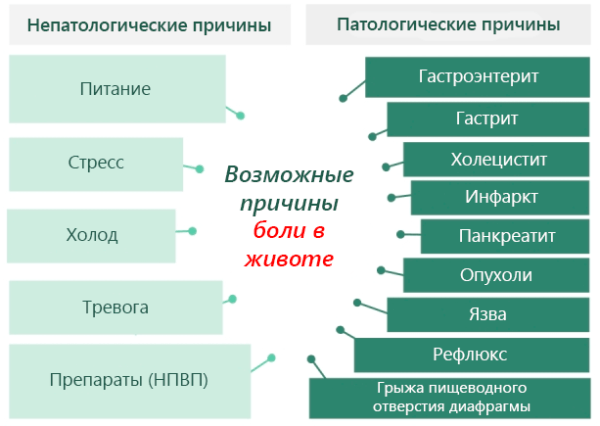
Common causes of stomach pain
The next most common reason is long-term use of certain medications that have an aggressive effect on the gastric mucosa, namely:
- medicines based on acetylsalicylic acid;
- syrups, suspensions Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Nurofen;
- sedative drugs with motherwort.
Heartburn is a feeling of discomfort, burning in the stomach, radiating to the upper parts of the digestive tract. Occurs some time after eating, less often after physical activity.

Causes of heartburn
Could be the result:
- intensive production of gastric juice due to abuse of chewing gum;
- intolerance to certain foods and their components;
- pregnancy, against the background of which a change in hormonal balance occurs, which affects the functioning of the digestive tract; also, during the process of growth and development, the fetus can put pressure on the stomach;
- stressful situations, against the background of which there is a change in the functioning of internal organs and endocrine glands;
- presence of bad habits: consumption of alcohol-containing products, smoking have an irritating effect on the mucous membranes of the digestive tract, which entails disturbances in their functioning.
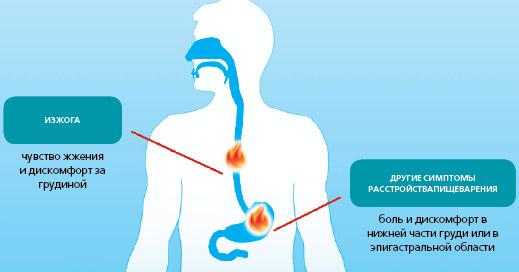
Heartburn symptoms
Weight loss based on gastrointestinal tract conditions
Losing weight with gastritis is possible. Before deciding on a diet, you should know about the diseases that accompany gastritis. The pancreas, intestines and gall bladder are susceptible to pathologies. Based on the painful factors, the menu and duration of the diet are determined. During the acute period, you need to adhere to a strict diet.
Diet
The menu depends on the course of the disease. The acute form limits the consumption of a number of foods. During remission, the diet expands (does not include alcohol, cigarettes, spicy seasonings, fried foods).
Food with low or high (from 57 degrees) temperature irritates the gastrointestinal tract. The optimal food temperature is 37 degrees.
In the acute period, the first 24 hours should pass without eating. You are allowed to drink clean water and warm tea. Porridge and jelly are taken from the second day of illness. The diet is strict, but after the acute phase the diet is allowed to be varied and more foods consumed.
Products aimed at increasing hydrochloric acid should be eaten by people suffering from low acidity. Increased acidity requires food that reduces acid production. The types of nutrition in both cases are discussed below.
Habits to break
We are not talking about bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol, but about food habits - they will be harmful to the general condition of the body, and to the figure, and to gastritis. You will have to give up:
- lack of breakfast - it provides the bulk of the daily calories needed for normal activity;
- a limited lunch and an overly aggressive dinner - there will definitely be no weight loss;
- eating in front of the TV or reading a book/gadget - food should be thoroughly chewed, which will make it easier for the stomach to digest it;
- “weekends” on a diet - gastritis does not forgive indulgences in the form of barbecue (“just one piece”), cake (“once a month is fine”), fried potatoes.
And here is more information about Dr. Myasnikov’s diet.
You can lose weight in any case, despite the presence of stomach diseases. Gastritis is not a reason to ignore too much body weight, but you will need to properly plan your diet and stick to it for a long time.
Foods to avoid after functional gastrointestinal disorder
Insoluble fiber
There are two types of fibers: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber (fiber) absorbs water and becomes slimy or gel-like. Insoluble fiber does not absorb much water, so it does not change the consistency much.
Soluble fiber can help relieve diarrhea and constipation. When drinking large amounts of water, it promotes the formation of soft stools. People who suffer from constipation may benefit from adding some insoluble fiber to their diet. However, adding insoluble fiber may make diarrhea worse because it speeds up the movement of food through the intestines. This may increase symptoms in people with chronic digestive problems.
Food sources of soluble fiber:
- oat bran
- barley
- nuts
- seeds
- beans
- lentils
- peas
Some food sources of insoluble fiber:
- wheat bran
- whole grain
- vegetables
Recommendations for creating a menu, how to properly create a dietary menu
The principle of creating a menu is quite simple: products allowed for consumption are combined in different options, while undesirable products are excluded from it. In the menu for the week you need to approximately calculate the sufficient amount of calories. This is important because some nuances cannot be ignored. For example, a diet for gastritis, in the case of low acidity of gastric juice, should be focused on stimulating the production of enzymes and accelerating the movement of food into the small intestine. Due to a lack of hydrochloric acid, food is not fully digested, as a result of which the body receives insufficient nutrients and vitamins, and a calorie deficit negatively affects overall well-being. One-day menu for example:
1 For breakfast: boiled (baked) potatoes with cucumber, green tea.
2 For lunch: cereal or vegetable soup, croutons, veal meatballs, compote.
3 As an afternoon snack: a piece of cottage cheese casserole.
4 For dinner: boiled thin vermicelli with steam omelette, herbal tea.
Using your imagination, deciding on a weekly menu will not be difficult. By replacing potatoes with porridge made from buckwheat, semolina or rice, and veal meatballs with poultry or fish cutlets, you can diversify your diet with soft-boiled eggs and biscuits. Different cooking options also help avoid monotony in food. You can make mashed potatoes, boil or bake fish, and make a tender soufflé from chopped lean meat.
A diet with a review of your gastronomic habits, especially during periods of deterioration in health, can be beneficial. For people who are overweight, it will be considered as a diet for losing weight for a sick stomach.
Diet
The menu for a person suffering from gastritis is based on the following points:
- fractional consumption of food;
- food temperature - 37 degrees;
- the period between doses does not exceed 4 hours;
- the amount of food consumed at one time should fit into one glass;
- preference is given to steamed and boiled dishes․
Weekly menu
- milk, kefir;
- semolina, steamed meatballs, omelette;
- fish, pasta, tea;
- buckwheat with milk, cottage cheese.
- steamed meatballs;
- carrot and potato puree;
- oat flakes;
- meat soup with rice;
- fruit jelly;
- dumplings and milk.
- scrambled eggs;
- pasta with a little butter;
- steamed meatballs;
- carrot soup with potatoes;
- buckwheat;
- drinks: milk, unsweetened tea, kefir, decoction of non-acidic berries.
- rice;
- oatmeal soup;
- lean meat;
- vermicelli with meat puree;
- a small amount of low-fat cream;
- drinks: raspberry decoction, jelly, cocoa.
- carrot and potato puree;
- pea soup;
- lean fish;
- buckwheat, curd products;
- drinks: milk and berry infusions.
- buckwheat/semolina;
- carrot soup;
- lean fish;
- steam cutlets;
- drinks: milk, raspberry decoction, tea.
- semolina;
- squash puree soup;
- rice;
- steamed or boiled meat dish with potato and carrot puree;
- drinks: milk, tea with milk;
- baked apple.
Recommendations of the treatment table No. 2
The duration of the diet, based on the recommendations of treatment table No. 2, is set by the doctor in accordance with the characteristics of the course of the disease and the general condition of the patient. Indicated for chronic gastritis, colitis, during recovery after infectious and inflammatory pathologies and surgical intervention on the gastrointestinal tract.
In accordance with the recommendations of dietary table No. 2, all fatty, fried, smoked, pickled, salted, spicy foods, including fatty meats and fish, are prohibited. You should not eat mushrooms, nuts, dried fruits, chocolate, halva, ice cream, which are difficult for a sick stomach to process. For patients with diseases of the digestive tract, coffee, alcohol, strong tea, and carbonated drinks are strictly contraindicated.

Nutrition for colitis
You can replace excluded dishes with the following products:
- porridges cooked with milk;
- vegetable broths and soups;
- boiled and pureed vegetables;
- fruit puree;
- low fat cottage cheese;
- weak tea, adding milk is allowed;
- dairy products;
- cereals and mucous soups based on them;
- honey, marshmallows;
- non-sour jam;
- natural juices;
- compote.

Sample menu for 1 day with meal plan table No. 2