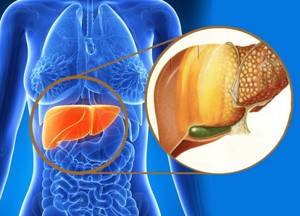
Fatty liver occurs in all age groups – in children and adults. This process can lead to serious complications - cirrhosis and carcinoma (cancer).
Treatment of the disease is carried out comprehensively and is aimed at eliminating the etiological factor and its consequences. There are a number of medications on the pharmaceutical market, the most effective of which are described in this article. In addition, it is necessary to adhere to a special diet aimed at reducing weight and fat deposits in the patient’s body.
What it is?
Fatty liver (fatty hepatosis) is a disease in which the liver tissue degenerates into fatty tissue. Fatty liver disease affects both men and women equally often.
There are many reasons that can lead to this condition, but the most common is the abuse of fatty foods and alcohol. Fatty liver can also develop as a result of metabolic disorders, protein and vitamin starvation, and chronic poisoning with certain toxic compounds. The risk of the disease is increased in people suffering from diabetes and thyrotoxicosis.
Causes of obesity
To find out how to get rid of fatty liver, you need to find out for what reasons adiposis occurs and what treatment methods exist in medicine. The causes of fatty liver are as follows:
- Excessive alcohol consumption. Methanol disrupts metabolism, destroys liver cells, and as a result, the organ begins to accumulate fatty tissue cells, replacing their own.
- Fasting with rapid weight loss or excessive consumption of fatty foods can equally lead to fatty degeneration. The likelihood of developing the disease increases with a sedentary lifestyle.
- Toxins. Pathology can be caused by pesticides, poisonous mushrooms, and some medications whose active ingredients are methotrexate, tetracycline, and estrogen.
- Metabolic disorders in conditions such as diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, Reye's syndrome, Konovalov-Wilson disease, Weber-Christian disease.
Smoking combined with other factors only exacerbates the risks. Rare, but possible cases where hepatosis is endogenous and develops as a result of enteritis and pancreatitis in severe form. Among other things, hepatosis can be triggered by a deficiency of protein and vitamins in the diet, excess iron, chronic intoxication, hypovitaminosis, and general obesity of the human body.
Treatment of fatty liver
It is based on four important principles:
- Elimination or weakening of the influence of factors that negatively affect hepatocytes (liver cells).
- Compliance with dietary nutrition in combination with physical activity.
- Treatment with herbal preparations.
- The use of medications in combination with herbs.
Do not self-medicate, especially with regard to the use of various dietary supplements (uncontrolled, untested pseudo-pills), as well as some unsafe folk methods of “cleansing” the liver.
Symptoms and stages
With fatty liver, symptoms may not appear for a long time. They are often disguised as other pathologies (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes).
Fatty hepatosis is often characterized by the appearance of signs of dyspepsia:
- pain in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- general weakness;
- pressure and heaviness in the abdominal (abdominal) cavity;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach.
Palpation reveals a moderately enlarged liver. Often a person feels pain during palpation.
With the development of liver pathology, symptoms of failure gradually appear:
- At stage 1, drowsiness, nausea, and aversion to food develop. The patient has some loss of coordination of movements and decreased performance. These symptoms worsen after eating or drinking alcohol. There is an unexpressed enlargement of the liver. Sometimes the body temperature rises, a slight yellowness of the eyeballs appears, itching of the skin, spots appear on the skin, which go away on their own without additional treatment.
- At stage 2 of the disease development, jaundice, swelling, diathesis, and severe general weakness appear. In women, signs of fatty liver at this stage of development of the pathology are often disguised as gynecological problems.
- At stage 3, severe metabolic disorders appear. Internal organs undergo dystrophic changes. In severe cases, the functioning of the nervous system is disrupted.
Severe forms of pathology lead to loss of consciousness and the development of a coma. In coma there is a high risk of death.
Symptoms of the disease by degree
Fatty liver disease has three degrees, each of which has different symptoms:
- The first degree is characterized by the presence of initial pathological changes in the organ in the absence of specific symptoms. A feeling of bitterness in the mouth and digestive disorders may occur, but this clinical picture is typical for many gastrointestinal diseases and is rarely recognized specifically as a symptom of liver problems. At this stage, the disease can only be detected using special biochemical blood tests.
- The second stage – symptoms of the disease begin to appear against the background of a general deterioration in the patient’s well-being. These are sensations of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, discomfort in the abdominal area. Enlargement of the organ can be determined by palpation. Ultrasound shows an increase in liver density.
- The third stage is characterized by severe nausea, aching pain under the ribs extending to the stomach, a feeling of fullness, and flatulence. Problems with stool and gastrointestinal disturbances appear. If you look below at the photo of the liver in stage 3 obesity, you can see that it is greatly increased in volume and has cysts and lumps.
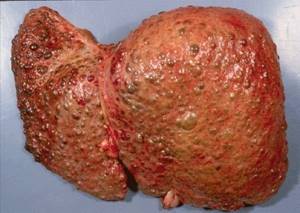
Complications
Without treatment and diet, liver failure, chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis may develop. With alcoholic fatty disease, the risk of complications is higher than with non-alcoholic obesity.
It is important to know! Fatty hepatosis, which occurs against the background of visceral obesity of the abdominal cavity, increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and arterial hypertension. And the recent conclusion of scientists completely shocked the world community - patients with deposits of internal fat in the abdominal area have a smaller lung volume and are at risk of gradual narrowing of the airways. According to the observations of specialists, they also have a smaller brain volume, while they are more at risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
Therefore, patients suffering from intra-abdominal obesity are recommended not only to undergo regular liver examinations, but also to undergo adequate treatment of the pathology.
Obesity never starts suddenly. It always develops gradually, without causing much concern at first. Many people believe that weight gain is generally characteristic of age and do not see any particular problem in the fact that they have to update their wardrobe every two to three years. Meanwhile, the accumulation of fat in the body is not only an aesthetic problem. A particular danger is that the fatty “layer” appears not only under the skin, but also on many internal organs.
It begins to cover the heart, blood vessels, lungs, liver... In overweight people, fat and carbohydrate metabolism is disrupted, all organs work under overload, as a result - a predisposition to diabetes, hypertension, arthritis and other diseases, including fatty liver.
HOW DOES THIS HAPPEN?
As you know, all the food we eat consists of proteins, carbohydrates and fats. The main task of carbohydrates is to provide the body with energy. Both during heavy physical activity and during life. Carbohydrates have a special ability to quickly release energy when broken down. At the same time, they can accumulate in the body “for a rainy day”, if necessary, easily leaving the storage cells.
Carbohydrates themselves of any origin are considered by our body as a kind of “universal fuel”: when they all enter the small intestine, they form glucose, which then enters the blood and liver. The liver acts as a “depot” where glucose is stored in the form of glycogen and, if necessary, returned to the blood.
The scheme is debugged to the smallest detail. With the exception of one circumstance: like any warehouse, the liver has limitations on storage volume. The average adult liver can store about 90 grams of glycogen. Everything that is formed in excess of this amount (as a rule, people who do not follow a diet and lead an inactive lifestyle have several times more excess) turns into fat. Fat is also sent to reserve - but not to the liver, but to any other suitable places.
Due to excess glucose, the liver ceases to perform its function and becomes a real factory of fat reserves. Instead of simply maintaining a normal level of glucose in the blood, liver cells - hepatocytes - very soon find themselves filled primarily with fat, and the reserves of unclaimed glycogen are reduced to a minimum.
The result is the so-called steatosis, or fatty liver . The most dangerous thing about this disease (besides the general dysfunction of the liver) is that any amount of carbohydrates coming from food causes an increase in blood glucose levels. This happens because there is simply no room for glucose in hepatocytes - all the free space is occupied by fat. And such jumps in glucose levels are nothing more than the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus...
Interestingly, the pancreas in such people works completely normally, and increased blood glucose levels automatically cause increased insulin production. It is obvious that treatment of this condition should primarily be aimed at combating obesity. Liver steatosis is a completely reversible process; it is enough to get rid of excess weight.
But you also need to lose weight with caution. A gradual weight loss of 10 percent or more will correct the level of liver enzymes, help reduce the fat content in the liver tissue and weaken the manifestations of steatosis. While losing weight too quickly (especially through a low-calorie diet or fasting) can become a “trigger” of the inflammatory process.
HOW TO LOSE WEIGHT WITHOUT HARM TO THE LIVER?
Hepatologists unanimously say: rapid weight loss causes much more damage to the liver than gradual weight gain. The fact is that with a sharp weight loss, a process occurs that is the opposite of what we described above, talking about excess glucose. Fat begins to flow from the subcutaneous layer into the blood, and from there to the liver, where it accumulates.
Favorable conditions are created for hepatitis (and subsequent cirrhosis). In the minds of the average person, these diseases are usually associated with infections or alcoholism, but in reality, one of the causes of hepatitis may be losing weight too quickly. There is even a special term - non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. This is a pathology in which changes occur in the liver of even non-drinkers that are characteristic of alcoholics with many years of experience.
Abuse of various dietary supplements, which are supposedly powerful “fat burners,” can have an extremely adverse effect on the condition of the liver. As a rule, all these products consist of dozens of components that can cause a severe blow not so much to fat as to the liver, leading to acute or chronic liver failure.
You should not lose sight of the fact that during the breakdown of fats, a lot of toxins are formed. The more intense and faster the weight loss, the more of these toxins there are. The body does not have time to get rid of them naturally, and they manage to cause damage not only to the liver, but also to many other internal organs.
WHAT TO DO?
Don’t try to lose all those extra pounds at once. The optimal weight loss rate for liver health is 0.5–1 kg per week. Strong and rapid weight loss often causes fatty liver disease (also known as fatty liver). When you suddenly lose weight, the fats and carbohydrates in your body rush straight to the liver, forming excess deposits in it. The resulting fatty liver progresses to hepatitis and cirrhosis.
In addition, if you lose weight too quickly, the body adjusts to storing fat along the way, that is, the predisposition to obesity returns.
BMI AND LIVER
How can you tell if you are overweight or obese? “By eye” is not our method. The World Health Organization (WHO) uses a special indicator - body mass index (BMI) - to determine the degree to which a person's weight corresponds to his height. You can calculate your BMI here. A separate calculator is for athletes.
What is the connection between BMI and liver? Yes, the most direct one. The liver is the most important organ of our body responsible for metabolism. It helps process and absorb dietary fat, redistributes lipids in the body, and actively cleanses the blood of toxins and waste. The bulk of our fats are located under the skin, but about 10% accumulates in the muscles and internal organs, in particular in the liver.
Regular overeating leads to the development of negative changes in the liver - it ceases to cope with the load, and excess fat accumulates in it more and more. The organ designed to cleanse the body of toxins and process fats is no longer able to do this. As a result, fatty hepatosis develops, which causes serious problems in the body. For example, resistance to insulin, which is necessary to regulate glucose levels in the body.
Another problem is an increase in the number of particles in the blood that increase triglyceride levels.
Fatty hepatosis is not a very dangerous disease in the early stages, so patients rarely consult a doctor about it. Periodically, patients experience dull pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting, weakness, headache, dizziness, and fatigue during physical activity. Upon examination, an enlarged, slightly painful liver is revealed. The course of the disease is usually not severe, but it can develop into more severe forms - for example, hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver.
According to various sources, 80% of people with a BMI above 30 have fatty hepatosis. The only thing that should reassure people with excess weight problems is the reversibility of the fatty liver process. If you lose even a little body weight, the fat content in your liver will immediately decrease. Just a few days of low-calorie eating can improve insulin sensitivity.
HOW CAN I FIND MY BMI?
You can calculate your body mass index (BMI) using our special calculator.
BMI less than 18.5
You are slim and graceful. Maybe even too much.
If you have always been thin but wiry, ate regularly and well, but did not gain weight, easily tolerated all illnesses and the consequences of surgical interventions, then your thinness is healthy, and, most likely, you are a man. This type of thinness is rarely seen in adult women. Healthy thinness does not have a negative effect on health, in particular on the condition of the liver.
Even if you don't really like your figure, be glad that you are a candidate for longevity. 12% of people with this type of thinness live to an old age.
If you have weakness and poor appetite, you cannot stand cold and heat, then such thinness is unhealthy. It is probably associated with metabolic disorders, improper functioning of the digestive organs, thyroid gland or liver.
If, along with the above symptoms, you feel nausea, have abdominal pain, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, dark urine, then this may indicate possible liver damage. Be sure to consult a doctor!
BMI from 18.5 to 25
What can we say? Keep it up! Your liver, like your other organs, will thank you. They will ensure the fight against diseases, the proper breakdown of fats and other nutrients, strength and beauty, and even forgive small weaknesses - for example, a New Year's feast.
The main thing is - at any time of the year, do not forget about sports and continue to eat right.
BMI from 25 to 30
This is a serious call. Maybe you still think that you are pleasant in all respects - chubby cheeks, a small tummy. But do not forget that fats are deposited not only on the stomach and sides. Fat also accumulates in the liver, which is very sensitive to various dietary deviations. By continuing to eat a lot and move little, you risk ruining not only your appearance, but also the functioning of your digestive tract. Following the fullness comes the inability of the liver to withstand the functional load.
At this stage, everything can still be corrected, but only through targeted efforts. If you let everything take its course, at one “wonderful” moment you will lose control of the situation and fall into the category of people with a body mass index above 30. This will mean obesity, which will lead to serious diseases of the internal organs and fatty hepatosis.
BMI above 30
Sadly, obesity has greatly ruined not only your appearance, but also the functioning of many internal organs. It is no longer possible to restore the full functioning of some of them, but this does not apply to the liver.
For the treatment of fatty hepatosis, drugs are prescribed that improve fat metabolism - B vitamins, folic and lipoic acids, choline chloride, progepar, ripazone, sirepar. Vitamin E also has a good effect on the liver with this diagnosis. But the most important thing is that you need to reduce your fat intake, try to eat healthy foods and move more. It is also necessary to limit other risk factors for the liver, such as alcohol and, if possible, medications.
If you do not change your lifestyle, then the diagnosis of fatty liver disease may be followed by hepatitis or even cirrhosis of the liver.
HEALTHY EATING ON A MODEST BUDGET
How to eat healthy on a modest budget? Very simple! The main thing in this matter is the plan. Follow it and everything will work out.
- Buy in bulk
Buy large packages, portion them and freeze them. This is especially useful for meat products and poultry.
Shop at discount stores. Prices for whole grain cereals, pasta, meat, fruits and vegetables are noticeably lower there.
Many food supermarkets have departments where rice, beans, and other cereals and products can be bought in bulk - they are cheaper than those packaged in bags.
If possible, purchase fruit by the box rather than by the kilogram.
Avoid pre-packaged snacks like 100-calorie packets. Buy the necessary products and divide them into portions.
- Cook for several times
On the weekend, prepare meals that you will eat all week, place the food in containers and freeze. A large pot of bean soup or chili can serve as both lunch and dinner for a day or two. This will stop you from buying expensive frozen entrees, fast food takeout, or going out to eat.
- Freezing meat products
Buy lean meats, poultry and fish on sale and then freeze.
Sometimes replace meat with other sources of protein. Beans, bean curd and eggs are an excellent and inexpensive alternative.
- Eat seasonal foods
Seasonal vegetables and fruits taste better and are much cheaper than imported out-of-season ones.
Visit local farmers or farmers' markets.
- Avoid name brand products
Products produced under the brand of a store or little-known manufacturers can be just as tasty, but will cost much less.
- Groceries and canned goods
If food spoils quickly, try buying it frozen. As for canned food, it is better to purchase it in its own juice and without the use of salt or sugar.
Buy cheaper foods such as brown rice, barley, beans or whole wheat pasta. They last a long time, and the dishes are very inexpensive. Try adding brown rice to a canned vegetarian soup or making ground lean beef with a side of canned beans or noodles.
- Plan your menu and don't go to the store on an empty stomach
Then the food will spoil less, and you will have to throw it away less often.
Research shows that people who go shopping without a list buy a lot of unnecessary things. And if you go grocery shopping hungry, the amount of the check will be many times larger.
- Avoid junk food
Ice cream, chips, muffins, and frozen ready meals are not healthy and may be the most expensive items in your diet. Spend the money you save on fresh vegetables and fruits - these are the vitamins and minerals that the body needs so much.
Follow these tips and you will not only stay within your budget, but also save on medications and stay healthy.
10 HEALTHIEST PRODUCTS
So that you understand which products should definitely be present on your table, we will tell you about the ten most useful ones. Take it with a pencil.
- Avocado
Benefits: Many people don't eat avocados due to their high fat content. But oddly enough, this particular fruit helps lower blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of developing cancer and diabetes.
Nutrients: Vitamins E, C and B6, potassium, fiber, vitamin K and folic acid salts.
Recipe: spread on bread, melt a piece of low-fat cheese on top and put a slice of tomato.
- Apples
Benefits: contain many antioxidants, as well as vitamin C, which protects blood vessels and improves iron absorption. All this reduces the risk of developing cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Especially if there are apples with peel.
Nutrients: fiber and vitamin C.
Recipe: Cut the apple into small slices and mix with green salad leaves.
- Berries
Benefits: All berries are very nutritious and are an excellent preventive measure against many diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, diabetes and coronary heart disease. Regular consumption of blueberries improves memory and slows down the aging process. In addition, research shows that blueberries are better than other berries for preventing cancer.
Nutrients: fiber, vitamins C and K, manganese.
Recipe: Mix blueberries with yogurt or homemade cottage cheese. You can add some crushed nuts.
- Broccoli
Benefits: Broccoli is in the same family as spinach, cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, kale and kale. Broccoli is highly nutritious and helps prevent diabetes, heart disease and some types of cancer.
Useful substances: calcium, potassium, folic acid salts, fiber, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, manganese, vitamins B, C and K.
Recipe: Lightly fry in a little olive oil, adding garlic and chicken broth.
- Salmon
Benefit: Try to eat fish at least twice a week. Salmon, herring and sardines are especially healthy. They contain heart-healthy omega-3 fats. Eating fish reduces the risk of cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, diabetes, arthritis and depression.
Nutrients: B vitamins, phosphorus, protein, selenium and omega-3 fats.
Recipe: River salmon is healthier than salmon raised in special reservoirs, as it is less likely to contain chemicals such as mercury. Pour freshly squeezed orange or lemon juice over the piece of salmon, add salt and pepper and bake until done.
- Legumes (beans, split peas, lentils)
Benefit: Legumes provide the body with energy for a long time. They are high in fiber, which reduces the risk of heart disease and normalizes blood sugar levels. All legumes, especially soybeans, are rich in protein and therefore are an integral part of a vegetarian diet.
Nutrients: fiber, proteins, vitamin B6, folic acid salts, manganese, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, thiamine, calcium and zinc.
Recipe: Rinse canned beans and add them to your favorite salad.
- Mushrooms
Benefit: Mushrooms stimulate the immune system. They help prevent and treat cancer, viral diseases, normalize blood cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
Nutrients: Fiber, proteins, B vitamins, vitamins C, D, folic acid salts, iron, zinc, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, copper and selenium.
Recipe: Fry finely chopped mushrooms, onions and zucchini in a little olive oil. Adding tomato sauce makes a healthy addition to pasta dishes.
- Walnuts and almonds
Benefits: contain a lot of useful substances and have a beneficial effect on the heart. Monounsaturated fats present in almonds reduce blood cholesterol levels. Walnuts contain small amounts of omega-3 fats. Although in general nuts are a fairly fatty and high-calorie food, they can help you lose weight, since the proteins, fiber and healthy fats they contain create a feeling of fullness and help you avoid overeating.
Nutrients: magnesium, vitamin E, fiber, riboflavin, magnesium, iron, calcium.
Recipe: Grill a piece of whole grain bread, spread with cream cheese and top with crushed walnuts or flaked almonds.
- Flax-seed
Benefits: Flaxseed contains omega-3 fats, which reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Nutrients: magnesium, phosphorus, copper, fiber, thiamine, manganese, potassium and zinc.
Recipe: Sprinkle flax seeds on porridge, yogurt or homemade cheese. You can also add them to dairy desserts.
- Grenades
Benefit: This product is the stuff of legends. Pomegranates have three times more antioxidants than wine or green tea. Pomegranate juice helps prevent heart disease and stroke. Drinking pomegranate juice over a long period of time slows down the aging process and prevents some forms of cancer.
Nutrients: Vitamin C and potassium.
Recipe: Sprinkle pomegranate seeds on vegetable and fruit salads. Add them to yoghurts and oatmeal.
Diagnostics
Signs of fatty liver may not appear for a long time. Often the disease is detected accidentally as a result of a general medical examination. To determine an accurate diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- Biopsy. A small amount of liver cells are collected from an adult. After studying them, it is possible to accurately determine the condition of the organ. The selection of material is carried out by laparoscopy or puncture using a special needle.
- Ultrasound diagnostics. During the examination, it is possible to assess the size and condition of the liver.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This technique is considered completely safe. It allows you to study the structure of the liver in detail and identify all pathologies. Using specialized equipment, it is possible to obtain images in all projections. Such examination is not used in all cases due to its high cost.
- Laboratory blood test. Helps determine cholesterol levels, as well as ESR, which may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process.
The choice of technique will be determined by the clinical picture of the disease and the characteristics of the human body. In addition, the doctor must analyze all existing symptoms, the patient’s medical history and his living conditions. Only after this is a conclusion made about the presence of the disease and its severity.
How to treat fatty liver?
Fatty liver disease requires an integrated approach to therapy. You will have to completely reconsider your lifestyle and give up bad habits. It is possible to develop the right strategy to combat the disease only after a medical examination. There are the following main methods for treating fatty liver:
- Lifestyle adjustments.
- Drug therapy.
- Dietary diet with the obligatory inclusion of a large number of fortified foods.
- Application of traditional methods.
It is more likely to be possible to get rid of the disease by using all therapeutic methods simultaneously. The patient must constantly monitor his well-being. Even with the slightest deterioration, you should immediately consult a doctor and review the treatment program.
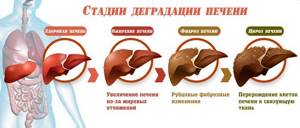
What are the risks of organ obesity?
When a diagnosis is made, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment for fatty hepatosis and adhere to the above rules. If you do not treat the disease, abuse bad habits, do not lead a healthy lifestyle and overeat, then the pathology will transform into fibrosis, and then into cirrhosis. Hardening of the liver with scarring of normal cells, the formation of liver failure, and oncology can occur. The consequences in 30% of obese patients are the formation of hepatitis. Liver disease leads to decreased immunity, hormonal imbalance, and poisoning of the body.
If a specialist has diagnosed fatty hepatosis, everything possible must be done to eliminate it. Take a comprehensive approach to treatment, use prescribed medications, follow a diet, and exercise. To fully restore the liver, several months of intensive therapy will be required.
Do something useful, it won't take much time
source
Drug treatment
There is no specific therapy for hepatic steatosis. The regimen is selected to eliminate factors contributing to gland dystrophy, correct metabolic processes, and improve the restoration and detoxification of hepatocytes.
The doctor prescribes medications with antioxidant and membrane-stabilizing properties. Among them is a group of sulfoamino acids and phospholipids designed to protect the liver:
- Phosphogliv.
- Essliver forte.
- Essentiale.
- Dibikor.
- Heptral.
An effective cure for fatty liver is the drug Hofitol based on artichoke leaf extract. Has choleretic properties. Vitamins from its composition normalize metabolism. Taurine also deserves attention, providing stabilization of plasma membranes and dissolution of fatty acids, increasing blood flow in the liver. It also has antioxidant, antisclerotic and hypotensive effects.
Vitamins help detoxify the gland:
- A nicotinic acid.
- Riboflavin.
- Betaine.
The drug Holosas reduces the density of bile, improves its outflow, and relieves heaviness in the right side.
Medicinal plants and medications
One of the main criteria according to which the choice of medicine for hepatosis is made is their hepatoprotective and antioxidant properties.
- Hepatoprotective effect of the drug
- its ability to increase the resistance of hepatocytes to the influence of pathological factors and enhance the neutralizing function of the organ. This effect is realized due to the integration of hepatoprotectors into the membrane of liver cells and stabilization of its structure, activation of the synthesis of phospholipids, functional and structural protein components of the membrane of damaged liver cells. They inhibit the growth of connective tissue structures in it, accelerate cellular regenerative processes, reduce the content of bile acids, and stimulate the secretion of bile. Drugs with hepatoprotective effects are effective in the prevention and complex treatment of fatty liver hepatosis.
- Antioxidant property
- the ability of the drug to slow down biochemical oxidation reactions, which involve highly active elements such as free radicals. When the systems regulating these reactions fail, free radicals damage cell membranes. Antioxidants enter into biochemical reactions with combined radicals and neutralize them, thus inhibiting oxidative processes and preventing cell damage. In addition, they reduce inflammatory reactions by blocking the synthesis of leukotrienes and prostaglandins.
Diet and nutrition rules
Usually, in case of fatty liver, a fairly strict diet is prescribed, since it is poor nutrition that most often becomes the cause of the disease. Therefore, when confirming the diagnosis, the first thing the doctor does is describe in detail what you can eat and what foods you need to exclude in order to stop the growth of adipose tissue.
| What can you eat? | What is better to exclude from the diet? |
|
|
Sample menu for a week of dietary table No. 5:
Additional recommendations:
- The diet should consist of alternating protein and cereal dishes.
- The approximate menu for the week of dietary table No. 5 can be modified according to your preferences, but without going beyond the permitted products.
- Daily calorie intake is 1,200 kcal for women and 1,500 kcal for men.
- Fried foods are excluded from the diet.
- It is better to replace sugar with xylitol.
Without following this diet and recommendations, it is impossible to get rid of fatty liver, even if you take the most expensive and effective drugs.
Fatty liver, even in thin people, will soon lead to weight gain. This is due to the fact that the organ, due to illness, loses communication with the brain through hormones, and the body can no longer control the feeling of hunger. And the liver can no longer produce bile in the same volume, which is involved in the breakdown of fats. As a result, they begin to accumulate in different parts of the body.
What medications do not treat fatty hepatosis?
Hepatoprotectors
“Hepatoprotector” translated from Latin means “liver protector.” People call hepatoprotectors such drugs, when taken, theoretically, there should be an improvement in the condition of patients whose liver suffers. Both doctors and patients had high hopes for these drugs:
- Essentiale Forte, Essliver Forte and other products containing essential phospholipids. The walls of liver cells are built from phospholipids: without these molecules, the cells will simply fall apart. However, the term “essential phospholipids” does not exist in medicine: it was invented by manufacturers of hepatoprotectors to make the name of their product sound more impressive. Is it true that if you swallow phospholipids in tablet form, they will be successfully absorbed through the stomach and used to build liver cells? Research has not confirmed this.
- Sirepar, hepadif and other products of animal origin. People hoped that a medicine made from animal livers would be beneficial to the human liver. But experiments showed no benefit. Moreover: it is unknown how well the liver of animals is disinfected from infections; it is better not to take risks and not take such drugs.
- Liv-52 is a herbal preparation that was previously used as a hepatoprotector. But after studies showed its ineffectiveness in this regard, it is considered simply a choleretic agent. But also as a choleretic agent, Liv-52 requires further research. Because it contains many plants with diverse effects. And plants can cause allergic reactions and other side effects. Doctors still consider Liv-52 a controversial drug.
- Gepabene, sibektan, karsil, silymar and other products based on milk thistle. Milk thistle contains the substance silymarin, which in laboratory conditions has shown itself to be a strong antioxidant (that is, a fighter against cell destruction due to oxidation). Unfortunately, this only happens in a test tube, and in the human body the effect of silymarin is much less impressive. Milk thistle preparations, unlike other hepatoprotectors, are sometimes still used as a medicine for fatty hepatosis: both here and abroad. But they have too little effect and too many potential side effects.
Unfortunately, the hopes of scientists were not justified: the research results did not show the benefits of hepatoprotectors. If a person seriously began to lead a healthy lifestyle, monitored his weight, and did not drink alcohol, then the liver returned to normal over time. And this happened at the same rate in people who took the experimental pills and in those who did not. The pills had no effect on anything.
Therefore, if a doctor has prescribed hepatoprotectors for you, this is a reason to think about changing your doctor. Not all of them “keep their finger on the pulse” and follow news in the field of medicine. Some people prescribe these remedies “the old fashioned way,” just in case: maybe they will help. But this treatment can take a long time and is pointless, moreover, there is a risk of completely triggering the disease, because while you are taking the “dummy”, the disease continues to progress.
An expert on the website Pokhmelye.rf, gastroenterologist Daniela Purgina, dispels a popular myth.
The biggest misconception is that phospholipids will protect the liver. These are quite expensive and completely useless drugs. Phospholipids are characterized by low bioavailability. Let me explain: you ate a capsule, it went into the intestines, from there into the bloodstream or lymphatic system, and then... Do you think the phospholipid is so smart - and rushes straight to the liver to patch up leaky cells? No matter how it is! With the blood or lymph flow, phospholipids are distributed throughout the body, not reaching the liver or reaching it in very small quantities. And if a gap has already formed in the cell wall, then the cell dies; it does not wait for the phospholipid to appear and patch up the hole in it.
The only group of drugs that can be conditionally classified as hepatoprotectors and which have shown some positive results in the treatment of fatty hepatosis are ursodeoxycholic acid drugs (Ursosan, Urdox, Livodex, etc.), we have already talked about them above. But they still require further study.
dietary supplements
Dietary supplements are not drugs:
- they are not registered as medicinal products,
- do not undergo the necessary studies,
- do not have strict quality control,
- do not have scientific evidence that they are really as useful as their manufacturers claim,
- advertising of dietary supplements can outright lie - for example, hiding the risk of dangerous side effects.
When buying dietary supplements, you get a pig in a poke. Even under the same name, drugs with different compositions can be sold.
Dietary supplements are herbal remedies. But a plant does not mean healthy and safe. Most of the poisons known to modern science are of plant origin: for the sake of curiosity, find a list of poisonous plants on the Internet, it is very long.
Each plant contains several chemicals. And each dietary supplement contains several different plants. So imagine the complexity of their interaction. Different people with different diseases may be affected differently by this complex mixture. Therefore, not a single competent doctor can vouch for the unequivocal benefits of any dietary supplement.
Quite a few people ended up in a hospital bed because they took dietary supplements and were not even aware of the possible risk. Take dietary supplements only on the recommendation of a doctor!
Teas for weight loss
Of course, it’s impossible to drink tea while lying on the sofa with a cake and lose weight. This is just a publicity stunt.
Typically, so-called “slimming teas” have a diuretic and laxative effect. They can relieve swelling (remove excess fluid from the body), and also provoke diarrhea - and due to this, you will temporarily weigh a little less. But you are unlikely to become happier.
Liver cleansing products
The liver is not dirty; it does not need to be cleaned. On the contrary, it is like a filter that cleanses your body of toxins. Doctors have never seen any waste in the liver: neither on ultrasound, nor on MRI, nor during other studies.
There are many things in the liver: cysts, tumors, parasites. A diseased liver must be treated. And recipes for “cleansing” the liver (for example, taking vegetable oil or mineral water, enemas, applying a heating pad to the stomach) will not help in this matter, but rather can do a lot of harm.
Supporters of “cleansing” the liver like to call applying a heating pad the word “tubage.” However, tubage is a medical procedure that has long been shown to be ineffective and is no longer used in the treatment of liver diseases.
Fatty liver hepatosis: how to cure it with folk remedies
Folk remedies mean a wide range of remedies that help in the treatment of a particular disease. These products may be plant-based (tinctures) or made from material obtained from animals (for example, badger fat, honey).
The use of folk remedies is usually included in the treatment arsenal of so-called alternative medicine, that is, traditionally not recognized by official medicine. Modern official medicine is based on evidence of the benefits and harms of a particular treatment. Scientists and doctors receive this information after conducting studies that include many people. In contrast, the benefits and harms of many folk remedies are based on the fact that it helped the grandmother on the bench or the cousin of the neighbor upstairs.
These are the recipes for folk remedies for the treatment of fatty hepatosis, which can be found on the Internet. They include, among others, infusions and tinctures from plants. Meanwhile, alcohol itself is toxic to the liver, not to mention plants: for example, celandine can have a seriously damaging effect and cause stagnation of bile in the liver. You can read more about herbs potentially dangerous to the liver on our website.
If a person suddenly decides to use a recipe for a folk remedy to treat fatty hepatosis, he must understand that the one who wrote this recipe may be wrong and will not be held responsible for his mistakes. The entire burden of the mistake in the form of side effects will fall on the shoulders of the one who decided to try such a remedy. At best, there will be no benefit or harm to health. At worst, there is a whole range of side effects.
Proponents of treatment with folk remedies often argue their position by saying that plants as medicines are not studied by scientists and are not taken into account by pharmacological manufacturers. However, it is not. There is a lot of information regarding the benefits and harms of each potentially medicinal plant. The database of studies involving plant components is updated every year. Most of them do not go beyond the first stage: research on cell culture and animals - because they are useless or toxic.
It should also be noted that some folk remedies include components that worsen the condition of the liver. For example, honey, proposed on one of the sites as a cure for fatty liver disease, contains fructose. It is known that fructose serves as a kind of “poison” for the liver, causing the disease to progress. This information is known to doctors and scientists, but is probably not taken into account by anonymous "alternative healers" from the Internet, who are unclear from where they get their prescriptions.
With regard to fatty hepatosis, there is so far no convincing evidence that this or that folk remedy helps relieve inflammation in the liver and normalize its structure. Hepatoprotectors based on plants are not included in the recommendations of leading and respected medical associations around the world because there is insufficient or questionable data on their benefits.
In view of this, modern medicine does not recommend treating fatty hepatosis with folk remedies.
You can contact the hepatologist in the comments. Don't hesitate to ask!
Article published: 2019-08-03
This article was last updated: 08/03/2019
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Try using search
doctor or administrator.
Read the dictionary of terms.
Expert author: Gastroenterologist-hepatologist Ekaterina Kashukh, gastroenterologist Daniela Purgina
Folk remedies you can try at home
Treatment with folk remedies should be carried out in combination with drug therapy. They are as effective as medications and have virtually no side effects.
Useful decoctions and infusions:
- Rosehip infusion. To prepare it, take 50 g of fruit and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. It is best to insist in a thermos for 10 hours. Drink a glass 3-4 times a day for 3 months.
- An infusion of pine needles enriches the body with vitamins. To prepare, you need to pour 1 kg of pine needles into 2 liters of cold water, add 1 kg of sugar to them. Place the container in a cool place for 5 days, strain the mixture and drink 0.5 cups before each meal for 2 months.
- 1 tbsp. l. pour 1 cup of boiling water over a mixture of plantain leaves, eleutherococcus, immortelle, chamomile, and dried herbs and leave for half an hour. Take 25 ml 3 times a day before meals. Duration of therapy is a month.
- Boil 1 tbsp. sorrel root in 1.5 glasses of water over low heat for 10 minutes, leave for 4 hours. Take 15 ml of infusion 3 times a day before meals.
- Grind 3 lemons along with the peel, pour in 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 8 hours. Take this infusion 50 ml 4 times a day between meals. After 3 days of use, take a break of 4 days, after which the course of treatment must be repeated.
- Take milk thistle once a day for six months (1 teaspoon of chopped herb, pour 0.5 cups of water, mix and drink).
It is useful to take cinnamon and apricot kernels with food. They help restore damaged liver cells.
Diet for obesity
After fatty hepatosis has been established, the main thing in treatment remains proper nutrition. Diet No. 5 is recommended.
Table with unacceptable and recommended products:
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
| Lean meats and fish | Full fat milk, cheese, cream |
| Fermented milk products | Mayonnaise, marinades, seasonings |
| Seafood | Bread, baked goods |
| Vegetables: pumpkin, carrots, zucchini | Alcohol |
| Fruits: apples, peaches, oranges | Sweets, soda |
| Fruit drinks | Sausages, smoked meats |
| Porridge: oatmeal, buckwheat, corn | Coffee, strong tea |
Heat treatment is important; it is advisable to eat baked, boiled, stewed dishes. Throughout the day, do not forget about the drinking regime; you need to drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day. Do not eat spicy, fried, fatty foods.

Prevention
Prevention of fatty hepatosis involves eliminating factors that increase the risk of developing the disease. It is based on a healthy lifestyle that excludes smoking and drinking alcohol. Regular exercise, morning exercises, and walks in the fresh air should become a habit for every person. People suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems and other related diseases need to regularly monitor and, if necessary, adjust their blood glucose and cholesterol levels. Briefly, these methods can be summarized as follows:
- healthy balanced diet;
- reducing alcohol consumption or completely abstaining from it;
- regular exercise;
- control of blood cholesterol levels for people over 45 years of age.
If there is a need to diagnose or treat fatty liver, you should visit doctors such as a gastroenterologist and hepatologist. And in parallel, you may need consultations with a nutritionist, a cardiologist who can prescribe a drug to stabilize lipid metabolism in the body, and an endocrinologist. In some cases, a visit to the surgeon is also possible.
Fatty liver hepatosis: symptoms and treatment Hepatomegaly Hepatitis C: first signs and treatment regimen Cirrhosis of the liver Polycystic ovaries Hemangioma of the liver - what is it? Treatment and symptoms
Methods and methods of treatment
The primary goal of therapy is to normalize the glandular tissue of the liver and biliary tract. Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor, no amateur activities!
Drug therapy
As a rule, a specialist prescribes hepatoprotectors. For hepatosis, the duration of their use is at least 2 months. It is also recommended to take these drugs throughout life as a preventive measure for liver disease.
The most effective drugs:
| Phosphogliv | Essential phospholipid. Available in capsules. Has side effects and contraindications. Before use, be sure to read the instructions. |
| Methionine | Sulfoamino acids. Film-coated tablets. Side effects include allergies and vomiting. Contraindications: children under 6 years of age, renal failure, viral hepatitis. |
| Karsil | It has practically no contraindications, except for individual intolerance to the components. Side effect: rarely laxative effect. |
| Liv-52 | Herbal medicine. Contraindications: intolerance to components, pregnancy, lactation. Side effects include: allergies, digestive disorders. |
| Berlition | Contraindications: individual intolerance, age under 18 years, pregnancy and lactation. There are side effects. |
To prevent destruction of organ tissue, the doctor prescribes Hofitol. To stabilize lipid metabolism, procholesterol drugs are prescribed: Atoris, Vasilip, Crestor. To reduce the specific gravity of bile, Holosas is used. Betaine is required to increase the concentration of adenosyl-methionine in the blood.
It is impossible to overestimate the role of vitamins in the treatment of hepatosis (folic, ascorbic acid, vitamin E, Riboflavin are very important). They help normalize metabolism and remove toxins.
Surgical intervention
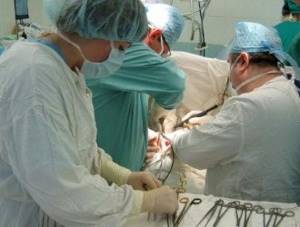
This is an extreme measure, and they resort to it in the most severe cases, when drug treatment is no longer useful. This method means transplanting a new organ.
ethnoscience
Sometimes homemade recipes save you from the most serious diseases. And in this case, you shouldn’t write them off. But before use, you need to consult a doctor.
- Milk thistle infusion. Pour 1 tablespoon of milk thistle seeds into a glass of hot boiled water, cover with a lid, and let steep for 20 minutes. Take before meals. If you add mint leaves and lemon balm, the liver will be cleansed of toxins.
- Pumpkin porridge. Before each meal, you need to eat a few tablespoons of chopped pumpkin pulp.
- Pour dry nettle with a liter of water and boil. Leave the broth overnight, let it brew. Over the next day, drink the entire broth in small portions. Drink the drink every day for a month.
Watch the video for more recipes for hepatosis:
Find out from the video which drinks will help with hepatosis:
Diet
Proper nutrition plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of hepatosis. Depending on the main factors and causes of the disease, it is selected individually.
If the disease develops due to excess weight, then the diet should include a high content of dietary fiber (vegetables, fruits) and foods with a low glycemic index.
With normal weight, the menu composition is aimed at reducing the inflammatory process. Fatty foods, alcohol, preservatives, fried foods, raw vegetables, unripe berries and fruits are prohibited. You should limit your intake of foods that contain cholesterol.
The diet should include:
- dried bread;
- vegetable broths;
- dietary meat;
- lean fish;
- porridge, pasta;
- vegetables;
- fermented milk products with low fat content;
- non-acidic berries and fruits;
- marshmallows, marmalade, marshmallows, and jam can be consumed in limited quantities;
- vegetable oil;
- water up to 2 liters per day. You can have herbal teas, still mineral water.