December 5, 2015 Admin Home page » For weight loss
It describes how alcohol affects the process of losing weight, provides scientific facts and experimental evidence, important tips and recommendations.
Alcohol and figure
Everyone knows “Fire Water,” which, when consumed, makes the sea knee-deep and the mountains shoulder-deep. Heroism is overwhelming, but in addition, alcohol suppresses the central nervous system, disrupts liver function and causes addiction.
In addition, for every 1g. An alcoholic drink contains 7 calories, and this cannot please your waistline in any way, in an effort to remove excess calories.
In simple terms, if your goal is to maintain a slim figure without excess fat, for example, drinking beer is not the best solution for getting rid of excess calories.
It is often taken in the evening, before bed, after a hard day of work for relaxation - but few people know that it consists of a large number of carbohydrates with a high glycemic index, which quickly release calories into the body, and since our body is at rest and is preparing for When you sleep, the released calories are consumed in a minimal amount and the remainder goes directly into subcutaneous fat.
The reason why alcoholics are thin
Scientists and doctors have proven that alcohol is a high-calorie product. 1 gram of alcohol can provide 7 kcal. But it is impossible to find people who drink and are fat.
There is an idea that alcoholics are thin because they eat poorly and drink a lot. But if alcohol is a high-calorie product, then the calories received should be enough for them. Boston scientists conducted multi-year studies with 20,000 people. They showed that during the experiment it was those who did not drink alcohol who gained weight. The rest lost weight in different ways.
Alcohol has a low energy return with high calories. In other words, this can be called bioavailability. The body receives empty calories, which do not provide anything positive for the functioning of the body. Therefore, alcoholics are thin because alcohol calories are not available to the body.
ALSO READ: What will happen if you stop drinking alcohol completely, said an expert from the Moscow drug treatment center
Alcohol and fats
It’s not for me to tell you that alcohol is a toxin for the body; imagine that endless processes of metabolism, breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates take place in our body. After drinking a dose of alcohol, our body switches to processing alcohol, while inhibiting natural metabolic processes, including the processing of fats.
According to science, it happens like this - only after drinking alcohol (or ethanol) it is split into 2 substances - nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and acetaldehyde, this all happens with the participation of the enzyme - alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), it is this process that causes excess calories to accumulate and be stored in fat deposits.
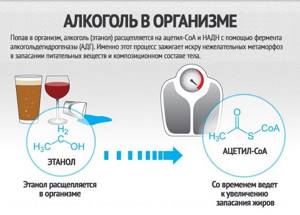
The final component of the breakdown of alcohol is the acetyl-CoA molecule, which is directly involved in the transformation of fatty acids, in simple words it leads to the accumulation of fatty deposits. The more alcohol you consume, especially at night, the more fat accumulates in the body.
Over time, acetyl-Coa causes changes, as a result of which the main task becomes the accumulation of fat, so creating a sculpted figure becomes a problematic task.
Impact on body processes
Every person, be it a man or a woman, needs to know that alcohol is a psychoactive substance through which alcohol addiction occurs. It should be taken into account, because alcoholism appears when drinking alcohol every day. The result of such actions is personality degradation and the development of serious diseases, gradually leading to death. The situation can be improved if you stop drinking and lose weight. The second is a great addition. It is impossible to completely get rid of addiction, but improvement is still evident. However, the condition can worsen at any time.
However, ethyl alcohol affects some processes:
- When drinking alcohol, a person refuses proper rest and sleep. According to numerous studies, it has become known that thanks to alcohol, rapid falling asleep is blocked, during which the alcoholic rests. That is why it is not possible to restore one’s strength after severe intoxication. The solution to this problem is to stop drinking, and at the same time adjust your weight;
- a drinker must take care of his health. After all, it is his fault that irreversible processes begin in the body. The liver and pancreas suffer more damage from ethanol. In the absence of full activity of these organs, it is impossible to produce the required amount of enzymes. A person needs them for proper digestion of food and fat deposits. In addition to them, the stomach and intestines also suffer from alcohol. This leads to the fact that most beneficial substances are not fully absorbed, and sometimes even absent;
- Also, adverse effects from alcohol can be observed on the liver. The fact is that this organ can function normally if there is a minimal amount of alcohol in it. This removes carbon dioxide and water (the final elements of decomposition). But when put in reverse, something different happens - it is not possible to cope with a large load, so acetic acetaldehyde is formed during decomposition.
In most processes important for the life of the body, unfavorable but characteristic changes occur and a person can get better or get sick. This is due to the penetration of ethyl alcohol inside. The end result of these actions may be death.
Attention! The human body contains some amount of alcohol. It is formed through metabolic processes. Thus, ethanol provides the necessary activity inside the body.
Evidence and examples
Scientists conducted experiments published in the Journal of Clinical Research, which describe in detail the effects of alcohol intake on the metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
Scientists assessed the concentration of fat and glucose over a 4-hour period after drinking alcohol. To do this, the subjects were given a drip of insulin and glucose at the same time. Next, blood samples were taken after 30 minutes and every 15 minutes thereafter to see how the energy source was used.
After 2 hours, instead of a glucose dropper, they put in a standard (alcohol) dropper, equivalent to 200 grams of vodka, after which fat oxidation decreased by 87%. In other words, after drinking alcohol, the body began to use alcohol rather than fat as energy . At the same time, the process of fat oxidation remained at a very low level, even after 4 hours when alcohol was last consumed, which is terrible news for those trying to lose weight.
Of course, everyone’s body is individual and the rate at which alcohol is eliminated is different, but the fact that it inhibits the burning of fat deposits is a fact .

The same scientists performed another experiment - at the same time, a standard (alcohol) and glucose were injected into the test subjects’ bodies through a dropper, since many people like to snack on high-calorie foods between drinks, the results exceeded expectations - the combined use of alcohol and glucose reduced the process of fat breakdown down to 0 mg. per minute, that is, fat burning stops and it accumulates at a tremendous speed.
Simply put, it sounds like this - a snack with beer in the form of chips, crackers, snacks, pizza, Bavarian sausages, and so on, will greatly slow down fat burning and then don’t be surprised why you don’t eat anything all day, in the evening you drank beer with a light snack, and your waist increases in size.
Of course, you can compensate for this with intense training in the gym, but it is better to reduce the amount of alcohol consumption during the process of losing weight or preparing for the beach season.
You can find the right nutrition for weight loss here.
Recommendations
Why do alcoholics sometimes lose weight? This is influenced by many factors, the main one being the volume and strength of alcohol. You can get rid of excess weight with the help of special diets. However, if the disease has already developed into a chronic form, then it will be much more difficult to accomplish the plan.
To prevent irreparable harm to health, you should adhere to certain recommendations from specialists:
- In no case is it permissible to drink alcoholic beverages if a person has not yet had breakfast. Eating food is a prerequisite.
- Treatment for severe intoxication or obesity should be done in consultation with an experienced specialist. It is better to give up alcohol than to eat less.
- Any feast is accompanied by drinking. But even in this case, we must not forget about fluid consumption. It is preferable to use non-carbonated drinks, but it is better not to purchase products with gases.
- In order to improve your well-being after intoxication, you need to use medication. An excellent remedy for this is activated carbon. But before using it, you should study the instructions to calculate the dosage.
- The next day after drinking alcohol, it is not recommended to change your eating routine - it should be normal. A fasting day can be arranged after some time, when a person becomes confident that the body has fully recovered.
Each person is individual, and therefore approaches to correcting the figure should be prescribed by a doctor. A scale will help you keep track of your calories. However, ethanol can also affect the final result.
Restoration of the body

The process of weight loss depends on the characteristics of the human body, some people immediately lose a lot of kilograms and boast: without alcohol they have lost 5 kilos or more, while others need a couple of months to regain their normal shape. In any case, by limiting your drinking, you can lose a sufficient number of kilograms, and here’s why:
- Refusal of high-calorie products (alcohol);
- The snack turns into a regular meal, and the distended stomach returns to normal and the amount of food consumed decreases;
- Physical activity increases - this happens by itself: I quit drinking and there is a desire to go for a walk, play sports - this is what all patients who give up drinking say;
And one more positive argument: more money appears. This is also true: the financial costs of beer with chips, shrimp or vodka with caviar are high, and if this part of the costs goes away, there is money left for something else. It would be a good idea to have a separate wallet and put there the amount that would be spent on drinking. There will be a very pleasant surprise at the end of the month.
Is it possible to lose weight if you don’t drink? The answer to the question already exists, but this does not mean that you should completely give up alcohol. Doctors themselves say that a glass of wine once every two weeks will not harm at all, and may even benefit the body. The main thing is not to overdo it in your desire to lose weight and understand that it is much easier for men to lose weight - for a woman, if she drank for a long time, then it will take much longer to recover. This is due to the peculiarities of physiology and hormonal levels: the female hormone itself “stores” a certain amount of fat. So, take action today if you want to fit into your favorite jeans or dress.
What alcohol leads to obesity?
The table shows the calorie content of alcohol, as well as carbohydrates per 100 grams.
| Beverage (% ethanol) | Calories per 100 g | Carbohydrates per 100 g |
| Beer (4-5%) | 45 | 3,8 |
| Low alcohol beer (2%) | 29 | 4,3 |
| Champagne (12%) | 88 | 5 |
| White wine (12.5%) | 78 | 4 |
| Red wine (12.5%) | 76 | 2,3 |
| Gin (40%) | 220 | 0 |
| Rum (40%) | 220 | 0 |
| Vodka (40%) | 235 | <0.1/td> |
| Vermouth (13%) | 158 | 15,9 |
| Whiskey (40%) | 220 | 0 |
| Schnapps (40%) | 200 | 4 |
| Absinthe (60%) | 83,1 | 8,8 |
| Sambuca (40%) | 240 | 40 |
| Cognac (40%) | 240 | 1,5 |
Considering that the indicated data is calculated for 100 g of drink, and no one is usually limited to such a dosage, then during a feast the amount of calories received at least doubles.
Alcoholic cocktails are considered the most high-calorie, since various types of alcohol and other additives are used in their preparation. For example, one serving of Long Island contains 270 kcal, and 100 ml of Cosmopolitan contains 181 kcal.
Beer and weight loss. Beer diet for weight loss: pros and cons
- Why beer? Everything is very simple. Beer has a huge amount of vitamins and microelements that the female body needs. The drink is rich in vitamin B, the so-called beauty vitamin, which is responsible for skin elasticity, hair thickness and nail strength. Losing weight on a beer diet does not increase the risk of decreased skin tone; on the contrary, due to the high content of vitamin B, the skin tightens and becomes smoother. In addition, beer contains calcium, potassium, magnesium, copper, zinc, selenium and other beneficial substances that improve immunity and have a beneficial effect on health.
- Our body often confuses the signals sent by the brain, replacing thirst with the desire to chew solid food. Beer is a liquid that not only perfectly copes with the feeling of hunger and dulls appetite, but also activates diuretic processes. Thus, by drinking a small amount of beer, you disperse bile, thanks to bitter intoxicating additives, and speed up the process of removing stagnant fluid from the body.
- A liter of beer contains approximately 440 kcal, and this figure is less than the same amount of cow's milk. The myth of the “beer belly” is just that, a myth. It is formed not due to the consumption of the drink itself, but due to an incorrect and excessive choice of snacks. Salty snacks: nuts, fish or squid, crackers and other beer delicacies retain moisture in the body, negatively affect metabolic processes, which leads to the formation of edema and excess weight.
- The disadvantage of the beer diet can be safely called ethanol: a liter of beer contains 30-50 grams of alcohol, so in case of individual intolerance to the drink, you can choose non-alcoholic beer.
Causes of the problem
Alcohol and obesity may be more related than we realize: both conditions are caused by periods of loss of control, whether that loss of control results from a moment of personal weakness, genetics, or the environment. People with these conditions spend a lot of time preoccupied with managing their addiction, manifested by struggling to maintain control, feeling guilty, or planning how and when they will next be able to access alcohol or food. Both conditions can progressively worsen and, when taken to extremes, can be fatal.
Part of what makes alcoholism and obesity similar is how the disease's tools—ethanol and food—affect the brain. Ethanol stimulates the "reward centers" in the brain in the same way as sugar, salt and fat. Because of this, people with a predisposition to binge drinking may also have a tendency to overeat.
Alcohol is an important source of energy and, despite having an energy content of 7.1 g/kcal, it remains controversial whether moderate amounts are a risk factor for weight gain and obesity. Epidemiological data show radically opposite research results:
- positive
- negative
- no relationship between alcohol consumption and body weight.
Although it is difficult to estimate alcohol consumption and control for the various factors that influence the energy balance equation, conflicting epidemiological data are understandable. Each component of the energy balance equation is influenced by alcohol consumption, whose moderate amount improves energy intake through its caloric content as well as its appetite-enhancing effect.
Alcohol-induced thermogenesis is approximately 20% in healthy non-alcoholic subjects, i.e. moderate drinkers, which is higher than for other energy substrates but significantly lower than for hard drink consumers.
Experimental data from several metabolic studies have shown a suppression of lipid oxidation by alcohol and thus an improvement in positive fat balance. Unoxidized fat is predominantly deposited in the abdominal area. Experimental metabolic evidence suggests that moderate alcohol consumption should be factored into the energy balance equation and may represent a risk factor for the development of positive energy balance and therefore weight gain.
How is alcohol processed?
To understand why ethanol affects the body in the form of a set of extra pounds, you need to understand how it is processed.
When drinking alcohol, ¼ of what you drink enters the blood through the stomach, the remaining ethanol passes through the small intestine.
Alcohol absorption occurs quickly, but this process can be accelerated by certain factors:
- If before the start of the feast a person has eaten heavily, then the alcohol will be absorbed more slowly.
- The process also depends on the type of drink you drink; if it is carbonated (champagne), absorption will occur faster.
- The strength of the alcohol also plays a role; if the percentage of alcohol in the drink is high, then absorption will occur at an accelerated rate.
On average, the removal of ethyl alcohol from the body is approximately 10 hours, but this figure varies depending on the amount drunk.
The product is processed mainly in the liver, and this process is divided into 2 types:
- Cleavage due to alcohol dehydrogenesis. It converts alcohol into acetaldehyde, and then, reacting with other enzymes, breaks down into acetate. At the final stage, ethanol is excreted from the body in the form of carbon dioxide and water.
- Ethyl alcohol passes through the microsomal ethanol-oxidizing system.
The effect of high-calorie alcohol
Professor Charles Lieber conducted an experiment in which 12 people agreed to participate. The essence of it was to gradually replace part of the food with alcoholic drinks and see how much the weight of the participants would increase.
For three weeks, participants received regular food, which is provided in the hospital. But in the first week she was without alcohol, and from the seventh day they began to add a little alcoholic drinks. At the same time, a certain amount of food was reduced, although its total calorie content remained at the same level. Until the end of the experiment, the menu was such that the body had to provide calories from food and alcohol in equal portions.
By drinking high-calorie alcohol, the participants were not supposed to lose weight, but it turned out to be the opposite. The more food was replaced with alcoholic drinks, the more kilograms they lost. As a result, by the end of the experiment, the participants lost almost 1.5% of their total weight. This is not such a small figure, if you remember that the experiment lasted only 3 weeks.
ALSO READ: Category of people who are contraindicated to drink alcoholic beverages











