Diabetes is a serious endocrinological disease that imposes restrictions on many areas of life, including diet. In case of illness, extra pounds are detrimental: excess fat in the body destabilizes blood sugar levels and overloads organs. If the patient feels that he is on the path to obesity, then it is better to take action quickly. One of the adequate and popular methods is diet.
When compiling a diet, the following are taken into account:
- type;
- severity of the disease;
- Lifestyle;
- presence of related problems.
Important! Doctors will help you correctly calculate all meals, taking into account the calorie content and vitamin and mineral composition of foods. A nutritionist and endocrinologist will tell you how to lose weight with type 1 diabetes.
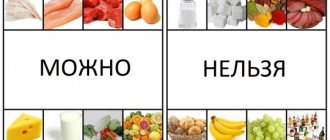
Permitted and prohibited products
Type 1 is not a sentence to starvation. Meals should be regular and balanced, and there is quite a lot of food that can be eaten constantly. Refusal of “harmful foods” will provide stable glucose and help the body lose weight.
Useful products for the gastrointestinal tract
For healthy weight loss, the body’s functioning is adjusted so that it is able to:
- fully absorb nutrients;
- remove breakdown products without accumulating toxins.
Most of these functions fall on the gastrointestinal tract. By including certain ingredients in the daily menu, a person with type 1 can easily improve metabolism and normalize intestinal function:
- Bread made from flour with bran. The fiber in its composition acts as a “brush”, and the glycemic index of the product is low.
- Low-fat soups with 2 broths and vegetables.
- Unsweetened fruits and berries.
- Cereals. Rich in minerals and fiber. Semolina porridge and white rice are not acceptable types.
Authorized Products
Vitamins and fiber are obtained from fruits in season:
- citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits);
- pomegranate;
- berries (cherries, currants, gooseberries, sea buckthorn).
Vegetables and dishes made from them are healthy and low-calorie:
- low-fat soups;
- okroshka.

A salad of fresh vegetables will saturate the body with useful substances. Suitable for diabetes:
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- beet.
Porridge will add strength and help you feel full. Dietary options:
- buckwheat;
- millet;
- oatmeal
Prohibited Products
It is strictly not recommended to allow the following into food:
- sugar and any store-bought sweets with chemical additives;
- jam (homemade, store-bought);
- pickles, marinated dishes;
- everything is fatty and salty;
- alcohol;
- sugar-containing drinks – compotes, fruit drinks, packaged juices;
- baked goods and derivatives made from white flour.
Important! The list of products in each specific case must be clarified with the attending physician. Only a specialist will be able to take into account the characteristics of the patient’s body and select a healthy and safe diet for type 1 diabetes.
Losing weight with type 2 diabetes
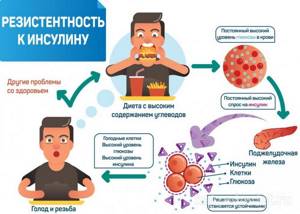
Everyone dreams of losing weight. But for people with type 2 diabetes, weight control is especially important. “Having excess fat in the body increases its resistance to insulin, which destabilizes blood glucose levels,” says Sue McLaughlin. “According to the World Health Organization, 90 percent of people with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese.”
It's no secret that losing weight—and keeping it off—is not easy. But it is possible, and the benefits for people diagnosed with diabetes are great. Experts say a surefire way to lose weight is to incorporate a healthy diet into your overall diabetes management plan. If you are diagnosed with prediabetes or suspected of having type 2 diabetes, then by simply losing about 10% of your total body weight (which for many people is no more than 10-15 pounds, i.e. 4.5-7 kg), you you can radically change the situation. Up to remission of the disease or complete stop of its further development. By losing excess weight, people with type 2 diabetes can improve their glucose tolerance, which allows the body to use insulin more efficiently. If you need more proof that shedding pounds makes sense, let us remind you that maintaining an optimal body weight will prevent you from developing certain complications associated with diabetes. For example, eye diseases (retinopathy), neuropathy (a nerve disorder that particularly affects the lower limbs and can lead to amputation), kidney failure, liver dysfunction, high blood pressure. By the way, the latter, in turn, is fraught with stroke and heart disease.
- Love an active lifestyle. Exercise can help you lose weight. “Our research has shown conclusively that people who increase their physical activity while cutting back on their daily calorie intake will lose weight faster than those who diet exclusively,” says McLaughlin, now a board-certified diabetes educator at the Nebraska Clinic. The extensive database for the study included more than 10,000 men and women who not only managed to lose more than 10 kg of weight, but also maintained the results achieved. Only 10 percent of respondents achieved their goal and maintained their new weight without increasing physical activity. Note that the majority of participants in the experiment chose regular walking as their preferred form of exercise.
- Eat breakfast yourself. The most effective diet for type 2 diabetes certainly includes breakfast. Skipping your first meal can lead to overeating later in the day when your hunger pangs begin. This can ruin your weight loss efforts and, more importantly, cause an immediate rise in your blood sugar levels. Research shows that eating a regular breakfast, especially one based on whole grains, is associated with better weight loss. The best choice is those cereals that have a low glycemic index and contain a lot of fiber. Combining them with high-protein foods (such as regular low-fat milk) can help control blood sugar levels. A common feature of the participants in the above study is that most of them ate breakfast.
- Fewer calories. The exact number of calories people on a special type 2 diabetes weight loss diet should eat depends on a number of factors, including age, gender, current weight, activity level and body type. A reasonable goal for people with type 2 diabetes is 1,200 to 1,800 calories per day for women and 1,400 to 2,000 calories per day for men. Your healthcare provider, whom you should always consult with before making any significant changes to your diet, can help you determine the optimal calorie range for weight loss while maintaining blood sugar levels.
- More good and varied fiber. High amounts of fiber help lower blood sugar levels and speed up weight loss. Research shows that if you are accustomed to eating a certain amount of fiber, you are less likely to be overweight. Thus, women between the ages of 31 and 50 should aim to consume at least 25 grams of fiber daily, while men at the same age are recommended to consume about 31 grams. As the human body ages, the need for fiber decreases. Women aged 51 and older need about 22 grams of fiber per day, and men need at least 28 grams of fiber. We, of course, rarely reach this level in everyday life. One trick you can take to help you increase your fiber intake is to spice up your meals with fiber-rich legumes such as chickpeas and black beans. Add them to salads, stews and soups.
- Watch your portion size. For diabetes, a diet that includes three or more small meals a day is better than one that includes only one or two meals. Large meals, and even with long breaks, can cause a sharp jump in blood sugar levels, while eating small meals more often helps reduce glucose levels. And also - you never experience hunger pangs, and therefore, the risk of slipping and eating the “wrong” product is reduced.
- Small but confident steps. “Don’t try to change your habits and your body overnight,” advises McLaughlin. “Ultimately, such haste can lead to failure.” Instead, set small but realistic goals, such as going for a walk around the neighborhood four times a week, only having dessert on the weekends instead of every day, etc. Once these goals become habits, move on to the next, more global problem. You will experience joy and a sense of accomplishment, and you will confidently lose those extra pounds without stress or breakdown.
- Make sure you have proper support. Staying motivated and sticking to your weight loss plan may be more difficult than you think. Especially if you are left alone with the problem. Communication with other people can provide emotional support, which will help you in difficult times and prevent you from giving up halfway through. Group weight loss programs, which are now in great demand, are based precisely on communication on social networks, mutual support and motivation. Keep in mind that support can come in many different forms. “For some people, online social media groups can be just as effective as face-to-face meetings, and a more convenient and cost-effective alternative,” says McLaughlin.
- Deceive yourself without a twinge of conscience. Sometimes clever strategies can help you stop overindulging in foods that are harmful to your body. Try the following:
- Low-calorie foods first. "Start each meal with the foods on your plate that contain fewer calories," suggests McLaughlin. Non-starchy vegetables are an ideal choice to start with. By the time you get to other foods, you won't be as hungry.
- What do you top your diet salad with? Instead of pouring a generous amount of dressing over your salad, lightly dip your fork in the bowl of sauce before spooning into your mouth. You'll be amazed at how much less gas you use and how many calories you save.
- Find a hobby you like. If you have nothing to do, you risk unexpectedly finding yourself in front of the refrigerator. Engage in activities such as walking, knitting, scrapbooking, crossword puzzles, or gardening. Anything to keep thoughts of food from popping into your head every minute!
- Carry a toothbrush and toothpaste with you. Keep them in your purse or briefcase. When the urge to chew something at an inopportune hour reaches its climax, brushing your teeth with mint paste can ease the craving.
- Be late for your health. Arrive at the buffet later than others - you eat less, the dependence is simple and obvious.
It is important to adhere to the rules of a healthy diet and monitor regular exercise even when the goal has been achieved and your weight has returned to normal. The kilograms go away, but healthy habits remain with us forever.
Diet menu taking into account XE

When compiling a diet, the number of bread units is taken into account.
1 XE = 12 g carbohydrates = 1 slice of bread = 1 small orange
For type 1 diabetes, following instructions are indicated:
- In each meal, the number of XE should not exceed 8, which is actually equal to 90 g of carbohydrates. The doctor will tell you the daily dosage.
- Before eating, be sure to calculate the exact amount of XE and the dosage of the insulin injection.
- Sweet drinks are prohibited (tea or juices).
Foods that improve digestion
It’s worth taking a closer look at the list of foods that improve digestion. Their consumption also has a positive effect on metabolism. Losing weight with diabetes can often be difficult, especially if the patient is obese.
So, foods that are beneficial for digestion include:
- wholemeal bread with bran;
- soups or broths with low fat content, such as mushroom, fish or meat (as a rule, a second meat broth is used), and vegetables are added as filling;
- low-fat meat: rabbit, beef, pork, poultry (excluding geese, ducks and other high-fat meat);
- ham, boiled sausages or sausage;
- baked or boiled lean fish;
- chicken eggs (no more than 2 pieces per day);
- dairy products with low salt and fat content;
- cereals, with the exception of rice and semolina;
- butter or vegetable oil;
- fresh vegetables and herbs;
- fruits, berries (low sugar);
- any sweet drinks.
Pay attention to foods that lower blood sugar levels, these include eggs, seafood, fish, meat (including poultry), mushrooms, green vegetables, butter and cheese.
General diet rules
In type 1, the reasons for gaining excess weight are the following factors:
- physical inactivity;
- improper diet;
- taking certain medications.
To lose weight, you should never stop treatment or insulin administration. Nutritionists advise:
- adjust eating habits, do not overeat, choose healthy ingredients for dishes;
- establish regular, but not exhausting workouts.
The result is usually directly dependent on willpower and personal responsibility.
If a person suffers from type 1 diabetes, then he must:
- keep a constant count of carbohydrates;
- Accurately calculate your insulin dose for each meal and before bed.
The amount of hormone depends on the severity and frequency of exercise.
Fractional meals in small portions are recommended.
Excess weight is associated with increased levels of bad cholesterol. Its main source is animal products: butter, eggs, fatty meats. When losing weight, it is better to completely abandon such foods.
Important! Diet and exercise are different for type 2 and type 1 diabetes.
Method three - giving up bad habits
Bad habits contribute to a person gaining weight. This happens especially quickly with diabetes of any type.
This is why it is vital to give them up. It is recommended to do this gradually so as not to cause even more significant harm to the body.
Endocrinologists point out that when a diabetic stops smoking or drinking alcohol, his weight approaches normal 50% faster.
It should be noted that even if blood glucose levels and other physiological criteria return to normal, the regimen must be strictly followed. This will truly preserve your health, and not aggravate its condition.
Additional measures that help to lose weight and bring glucose back to normal include fortifying the body and using certain folk remedies: ginger, certain types of greens.
All of them will help cope with the accumulated fat, as well as reduce the one that is already present on the body. This measure is more of a preventative measure, but this should not make it less effective.
In combination with diet and exercise, the results will be simply amazing.
Losing weight with diabetes is not beneficial for everyone, but those who need it simply must follow certain rules. We are talking about introducing a diet, starting exercise and eliminating the effects of bad habits. In this case, the body will be 100% prepared for weight loss and will not “suffer” because of it.
Physical training

Physical activity burns fat, promoting weight loss. The calorie content of the diet is increased by correlating it with the amount of exercise.
Note! The permissible volume is determined by the doctor; independent exercise without consultation will harm the patient.
The main thing is to remember: it is better to increase the intensity gradually. If the patient led a sedentary lifestyle before the illness, then in the first stages it is preferable:
- charger;
- bike;
- walking in the fresh air.
If the body is accustomed to sports, then, observing the boundaries agreed with the doctor, it is permissible to engage in aerobics, combining it with adequate strength elements, but limiting the time and under constant medical supervision.
Adjustment of insulin therapy
When adding sports activity to your usual lifestyle for weight loss, the insulin dosage is adjusted. This is done by a specialist. Usually the following recommendations are followed:
- If a person is planning an active day with high energy consumption, then in the morning they inject 2-4 units of insulin less, and it is useful to have sweet tea and a snack for 7-6 bread units.
- If some medications reduce sugar, then the amount of insulin does not change.
- Before training, you need to eat, and after 2 hours have a snack for 2 or 3 XE.
Important information! Physical activity can trigger the development of hypoglycemia. Therefore, it is always good to have something sweet with you.
Special preparations
In an effort to find a way to lose weight with diabetes, some look towards various drugs that supposedly allow you to get rid of excess weight. They are often positioned as fast-acting remedies that do not require increased stress.
Some of them really allow you to achieve what you want, but what matters is at what cost. Quite often, diet pills contain substances that, when ingested, cause severe harm to the body.
Of course, against the background of this, a person loses kilograms sharply and quickly. But this is unhealthy weight loss. It is caused by intoxication of the body, which spends all its energy and strength fighting harmful components.
Also among the drugs there are those that may contain parasites. Once in the stomach, the parasite begins to feed on its contents, which is why a person is constantly hungry, can eat incredible portions and at the same time lose weight.
Both of these options are harmful for a healthy person, and even dangerous for a diabetic. At best, taking the drug will simply be ineffective and will only slightly affect the body’s hormonal levels.
Finding a truly effective and safe weight loss drug is now quite difficult, since there are countless options. It is also worth considering that why a friend, neighbor, etc. lost weight is not a fact that it will help your own body.
Taking any drug should be discussed with your doctor. However, many competent experts advise to completely throw this option out of your head and put your body in order using natural and healthy methods.
Other methods

In addition to diet and active sports, there are a number of activities that help reduce body weight. When choosing such “helpers”, you should focus on contraindications and safety precautions.
Hydromassage
Passive way to burn fat. It can be quite painful. Type 1 diabetes is not an obstacle to its use. Its effectiveness is similar to gymnastics.
Bath
Significant temperature changes and hot air overload the organ systems of the human body, so diabetics must consult their doctor before visiting the sauna. People suffering from problems with the cardiovascular system are advised to refrain from visiting the baths.
By sweating, the patient also loses some hormones, including insulin. This may negatively affect the stability of your glucose levels.
To make going to the bathhouse a pleasure, you need to follow a number of rules:
- Visiting the steam room is only possible in company. If a diabetic becomes ill, there should be someone who will take them out of the high-risk area and call a doctor.
- If there are signs of discomfort, stop the procedure immediately.
- Diving into the snow or taking a sharp contrast shower is prohibited!
- Self-control is required.
- There should be something on hand to bring glycemia back to normal.
You cannot visit the bathhouse if you are decompensated, if there is acetone or any deviations from normal blood sugar!
If you adhere to the described rules and follow medical instructions, then from visiting baths and saunas you can achieve a decrease in sugar, the effect of which will last up to 6 hours. The procedure can be repeated no more than 3 times every 30 days.
Visiting public places is a cause of fungal infections. Examination of the feet and disinfectant measures that are approved for use in diabetes will prevent skin infections.
Herbal teas will strengthen the body, rejuvenate the skin and improve blood circulation.
The onset of hypoglycemia often goes unnoticed by a diabetic, so it is worth asking others to keep an eye on you. First aid for the mild option is sweet tea or juice. In more severe cases, glucose is injected or specialized medications are used. Before this, be sure to measure the sugar level so as not to harm the victim, since its different levels in the blood require different methods of influence.
If you have type 1 diabetes
I'm not going to call for an immediate and decisive war on carbohydrates, or remind you that olive oil and maple syrup are full of calories that people often forget to count. No, experience shows that a balanced but nutritious diet with a low glycemic index, combined with physical activity, is the best way to lose weight if you have type 1 diabetes. It also helps you live and think at the proper level throughout the day, keeping you alert. If you are reading this article, you have probably already thought about the problem and decided for yourself why it is important for you to lose weight. But I argue that the main thing is quality of life!
By quality of life I mean a longer and healthier life.
Here are some things to keep in mind when fighting excess weight with type 1 diabetes:
- Basal and bolus insulin - dose and time calculation
- Insulin levels in the body
- Getting the right amount of nutrients (planning appropriate menus)
- Total daily fat and calorie intake
- General activity level
- Sleep quality and duration
- Amount of sugar in food
- Alcohol consumption
- Stress level
Why High Carbohydrate Diets Are Not for Us
Let's start our discussion with insulin, the key player in this game. Insulin is a hormone in the human body that facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells for energy metabolism and blood sugar balance. (For those with type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin, so levels must be raised artificially, through injections or an insulin pump.) Having higher doses of insulin in your body, whether you have type 1 diabetes or not, will help you build muscle or fat tissue.
If you are a type 1 diabetic, this may seem obvious to you: increasing the amount of carbohydrates in your diet will also lead to unfavorable fluctuations in your blood sugar levels. Eating 55% of your daily calories from carbohydrates dramatically increases your insulin requirement. Increasing the daily dose of glucose and keeping insulin active in the body can, in turn, lead to a situation where insulin causes the body to “store” fat and “burn” glucose or glycogen from the muscles (absorbing sugar from the blood).
Whether you are a type 1 diabetic or a completely healthy athlete, this way of eating will not be beneficial. So how much carbohydrates do we need? The human body works on the same principle as your car, and carbohydrates are the gas tank. Your car can hold, say, 60.5 liters of gasoline, but trying to put 64 liters of fuel into the same gas tank will not lead to anything good. The trick is to learn how to achieve the right balance when refueling your body. For type 1 diabetics who must constantly monitor their blood sugar levels, this gas tank analogy is equivalent to their total daily insulin dose. This means that your average total daily intake (assuming relatively stable blood sugar levels and no weight gain) is the baseline for knowing whether your gas tank is full or half empty. For those of us who don't have diabetes, we can simply track our total carbohydrate intake using an app or other convenient tracking method. But the bottom line is the same.
Note: for those who lead a very active lifestyle (more than 8 hours of training per week), carbohydrates should be cut down even more, and when compiling a diet, focus on lean proteins (20-30% of daily calorie needs) and moderate amounts of healthy fats (15-25% of daily calorie needs).

Why high-fat diets aren't good either
A high-fat, high-carbohydrate diet has its pros and cons, but as a primary source of nutrients, it doesn't hold water. Here are two serious professional voices in favor of this strategy:
- Lower insulin levels are generally great for balancing your blood sugar levels and keeping your energy levels up. When you eat primarily fat, it digests VERY slowly and it can take up to 8 hours for a high-fat meal to be completely digested. Fats during this period of time can slow down any breakdown of carbohydrates and create a slow but steady flow of energy, and the need for insulin is relatively lower.
- Fat burning metabolism accelerates due to low levels of total daily insulin. With less insulin circulating in the body, fat is burned faster. Think about it, the lower the amount of insulin in your system, the higher the rate of fat burning.
So why not go all in and make this approach the basis of your diet? But then here are two serious disadvantages of a system based on a large amount of daily fat consumption:
- Compared to carbohydrates and protein, fat provides as many as nine calories per gram. If the goal is to lose weight and get a more toned body, it is imperative to consider the total number of calories you consume. And fat gives us more than twice as much. In addition to double the amount of calories, we end up with a situation where they are also absorbed slowly and require maintaining a constant level of insulin in the body for many hours. And add here carbohydrates and proteins, which are burned faster and also require certain body resources. No one will benefit from diets with excess fats and carbohydrates - neither a healthy person, nor, especially, a type 1 diabetic!
- High fat diets cut off energy levels. That is, when you eat healthy fats that break down slowly, it will take many hours before the energy your body needs finally starts flowing. This will result in increased fatigue, irritability, yawning and a feeling of general apathy, to the point that you will no longer be active at all. Using the previous analogy with a car, we conclude that in this situation our car receives only a small portion of gasoline at a time and is forced to stop every now and then.
In addition, fat can satisfy and mask hunger for a long time, which is very healthy. However, at some point the body will still need a certain amount of calories, and often we compensate for the shortfall in the form of sources of quick energy. And this is where sweets and unhealthy snacks come into the picture. The lack of timely energy that we get from carbohydrates prevents us from being active enough to lose weight, burning calories, and only delays us from achieving our goal.

Why is a balanced, nutritious, low-glycemic diet coupled with physical activity the best choice?
Yes, we recognize that there are positive aspects to both high-carb and high-fat diets, but finding a healthy balance and timing your physical activity will result in an optimal diet. The key is to take into account the regulation of insulin, which coincides with the regulation of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Insulin is produced differently at different times of the day and especially during periods of high activity. Let's look at an example:
In the morning you plan to exercise, be it walking, jogging or cycling. What will be the serving size? What's the best thing to eat for breakfast? For any activity up to 60 minutes, it is completely appropriate to not eat anything, because your body has a reserve of stored glucose (glycogen) that it can access for just about an hour. This means you don't need to immediately consume carbohydrates to maintain your health during activity, and you won't need insulin before or during exercise. It also means you can burn more fat. (Insulin signals the body to store fat and burn its own supply of carbohydrates, which, as you already know, is stored in muscles.)
If you're still hungry and just need to eat before your workout, you should opt for small amounts of healthy fats (e.g., eat almonds or a few avocado slices). This is enough to satisfy your hunger and survive until you have a full breakfast. Lean proteins will also work in your favor, but for type 1 diabetics this may require some insulin, which in turn may make fat burning less successful.
The key is to plan to perform your workouts on an empty stomach or with a minimal amount of pre-eaten food, just enough to keep you full and sustain you during the activity. For type 1 diabetics, the most important factors to consider before exercising are the amount of insulin in the body, basal rate, and boluses. If the body's insulin is at the proper level, it is necessary to add some glucose to prevent low blood sugar. Because synthetic insulin has a duration of action of 3.5 to 4.5 hours, you will need to plan both your meals and periods of physical activity accordingly.
After your workout, you can eat carbohydrates and proteins. Carbohydrates are to replenish lost muscle glycogen, and protein is to maintain blood sugar levels, repair and develop muscle tissue. After exercise, you may experience increased sensitivity to insulin and the effect of “washing out” glucose from your body’s own tissues. The amount of insulin your body needs to metabolize glucose before exercise can be up to 50% more than it needs after exercise (up to 70% less). Also during this period, it makes sense to give up fats in favor of proteins and carbohydrates due to the speed of action of insulin. Outside of the recovery period, you can replenish your macronutrient balance, including healthy fats.
If the physical activity is not too intense (determined on an effort scale of 1-10, with the maximum type of effort being 10, and 3 being very light), there is no need for a large amount of carbohydrates. However, a large portion of protein and some healthy fats with a small amount of slow carbohydrates after such a workout will only be beneficial.
For a high or moderate level of activity, a balanced diet should include macronutrients (protein, fat and carbohydrates) in the following ratio:
Inactive people - % of average daily calorie needs (on average 30 minutes to 2 hours per week of activity)
- carbohydrates 30-40%
- proteins 15-30%
- fats 25-40%
Basal: 45-50% Bolus: 45-50%
Highly active people - % of average daily calorie needs (8 or more hours of activity per week)
- carbohydrates 50-60%
- proteins 20-30%
- fats 15-30%
Basal: 40-45% Bolus: 55-60%
It's not easy to maintain balance, but who promised it would be easy?! There is so much going on, it’s difficult to find time for insulin injections and proper nutrition. Only practice, trial and error and advance planning will be the key to success. Ultimately, choosing a balanced diet based on foods with a low glycemic index and optimal nutrition will lead to long-term weight loss and stabilization of blood sugar levels.
Diet (non-insulin diabetes)
For many patients, the question arises of how to lose weight with type 1 diabetes with the least harm to the body. There are such types of diet as 9A and 9B. The first is used when the patient is in the initial stage of the disease and insulin has not yet been administered or is used in small doses. This diet has more stringent restrictions.
To achieve the maximum effect, careful attention to foods is very important, so the amount of calories throughout the day should be evenly distributed across meals. Below is a list of products recommended for inclusion in the diet:
- mandatory vegetable variety, including any varieties of cabbage, tomatoes and cucumbers;
- the presence of all main types of greenery;
- inclusion of root vegetables: radishes, turnips, carrots and radishes;
- mushrooms;
- green beans;
- zucchini;
- eggplant;
- cream and mayonnaise.
It is not recommended to include sweets in your diet, including drinks containing sugar; you should not consume jam and honey, as well as baked goods, cookies, and candies. Cheeses containing more than 30 percent fat and alcoholic beverages are prohibited. It is also not recommended to eat pates and nuts.