In this article we will talk about how to set up your program for training the back muscles, how to focus on lagging muscle groups and develop the overall volume of muscles, strength and symmetry.
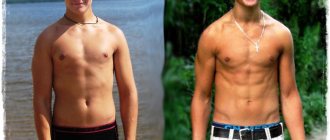
If you want to achieve an ideal physique, increase strength and muscle size, not to mention overall health, your back needs special attention.
A well-developed back will not only give your figure beautiful posture and sexiness, visually narrow your waist, straighten your shoulders, but also provide your body with functional strength in every day to day movement.
There are many muscle groups that make up the back, but we will focus on the main muscles that your training program should target.
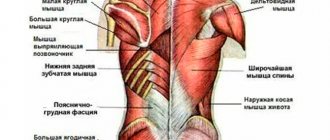
- Latissimus dorsi muscles
- Trapezius muscles of the back
- Erector spinae muscle (the most powerful longus dorsi muscle)
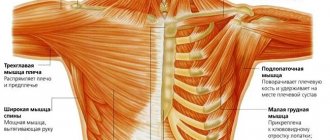
These are the three main muscle groups of the back. Also, in many back exercises, the synergistic muscles are the large (teres major) and small (teres minor) round muscles of the shoulder girdle, which are involved in abduction, supination, rotation and adduction of the shoulder. Few people pay attention to these muscles, but they are just as important as the biceps, triceps, glutes, etc.
The function of the latissimus muscle is to bring the shoulder toward the body and pull the upper limb back toward the midline, rotating it inward—pronation.
If the upper limb is fixed, it brings the torso closer to it (pulls up) and can expand the chest, serving as an auxiliary respiratory muscle.
The erector spinae muscle, when contracted bilaterally, straightens the spinal column and holds the torso in an upright position. With unilateral contraction, the spinal column tilts in the appropriate direction. The upper muscle bundles pull the head in their direction. With part of its bundles it lowers the ribs and thus participates in the breathing process.
The trapezius muscle has many functions, but the main one, of course, is the movement of the scapula, which provides lifting, lowering and rotation of the upper limbs.
There are even smaller muscle groups that make up the overall bulk of the back that provide a beautiful appearance if you get into the competition pose, the "back double biceps"
You can effectively target all of these groups with a well-designed training program that focuses on variety and intensity.
Multi-joint exercises.
Most of the compound (multi-joint) exercises listed below target the latissimus dorsi, trapezius dorsi, extensors, and smaller groups (teres major and minor). Perform 2-3 exercises from this list during each workout.
Pull-ups
- Execution options: with additional weight, with counterweight (gravitron)
- Grip width: wide, neutral, narrow
- Grip type: pronated (straight), supinated (reverse), neutral (hands parallel to each other)
Deadlift
- Execution options: dumbbells, Smith machine, trap bar (trap)
- Grip type: pronated (straight), mixed, neutral
Upper block pull
- Execution options: to the chest, behind the head
- Grip width: wide, normal, narrow
- Grip type: pronated (straight), supinated (reverse), neutral
Bent-over barbell row
- Execution options: lying with a curved bar, Smith machine
- Grip width: wide, normal
- Grip type: pronated (straight), supinated (reverse)
T-bar pull
- Grip type: pronated (straight), supinated (reverse), neutral
Bent-over dumbbell row
- Execution options: one hand, two hands, two hands lying face down on an inclined bench.
- Pull width: along the body, to the sides of the body
- Grip type: neutral, pronated (straight), supinated (reverse)
Horizontal pull of the lower block
- Execution options: at an angle from above, at an angle from below
- Grip width: wide, narrow
- Grip type: pronated (straight), supinated (reverse), neutral
Horizontal row of the lower block with one hand
- Execution options: at an angle from above, at an angle from below

Rules for maintaining posture
To keep your back straight and maintain a healthy spine, in addition to regular exercises for posture, you must follow the following recommendations:
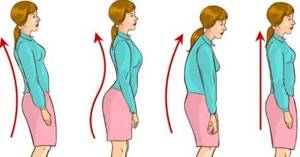
- It is important to regularly monitor the position of your back: while walking, while sitting and standing. Shoulders should be straightened, chest forward, back straight, stomach pulled in. While walking, look forward and not at your feet.
- To maintain posture, it is important to work on the muscle corset, working out the abdominal and back muscles.
- To prevent spinal curvature, it is recommended to walk at home with a book on your head from time to time. You can only hold it with a straight back.
- Most people (due to work or study) spend a lot of time sitting. It is important to pay attention to proper posture to maintain spinal health.
- During work, you need to do small warm-ups for your back and whole body.
- Everyday shoes should be comfortable; daily wearing of heels provokes a curvature of posture and puts a powerful load on the back.
- When bending over, it is advisable to straighten your back or squat; you should not slouch or round it. A bad habit is to carry a bag or bag of groceries in one hand. The weight should be distributed to both limbs.
- A sedentary lifestyle contributes to numerous health problems, including the spine. You need to move as much as possible, walk and play sports.
- In order to prevent back diseases, it is recommended to sleep on a hard orthopedic mattress.
- Special bandages that improve posture are used only after consultation with a specialist. Otherwise, you can cause even more harm to the health of the spine.
Isolation exercises.
There are also several single-joint movements that target the upper and mid-back muscles.
Upper and middle back
- Straight arm lat pulldown
Lower back
- Hyperextensions - execution options: Roman chair, lying on the floor, in special. exercise machine, fitball, hands on chest, hands behind head
- Straight-legged barbell row - execution options: dumbbells, Smith machine
- Good morning
Set of exercises No. 6
1. I. p.
-
stand against the wall
with correct posture. After taking a step forward, maintain the pose for 2-3 seconds. Return to i. n. Check your posture. 8-10 times.
2. I. p.
-
Same.
Step forward, arms to the sides. Squat down, arms forward. While sitting, move your arms to the sides and lower them down. Return to i. n. Make sure to maintain the correct position of the head, shoulders, abdomen, and pelvis. 8-10 times.
While doing exercises 1 and 2, you can put a book on your head.
3. I. p.
-
sitting on a chair.
Raise your arms to the sides - up, bring your shoulder blades together. In this position, bend your arms, place your palms on your shoulder blades as low as possible. Extend your elbows as much as possible. Return to i. p. 10-12 times.
4. I. p.
-
O.
With. Right hand up, left hand down. Bend your elbows and try to interlock the fingers of both hands behind your back. Return to i. n. Repeat the exercise, changing the position of your hands. 6-8 times from each hand.
5. I. p.
-
O.
With. For each count, push your shoulders forward and back. 10-15 times.
6. I. p.
—
sitting on the edge of a chair.
Rest your hands on the seat, elbows back. Bend strongly in the thoracic part of the spine, head back. Return to i. p. 10 times.
7. I. p.
-
kneeling position
with support on hands, head down. On the count of one, bend over, head up, try to tighten your lower back muscles more strongly. On the count of two, bend your back, head down. 10-15 times.
8. I. p.
-
O.
With. Place a book on your head and walk around the room with various arm movements (sideways, forward, up) with light and deep squats.
Synergetic movements.
In addition to exercises that directly target the back muscles, there are many exercises where the back plays a synergistic role. A synergist is a muscle that works unidirectionally, i.e. assists the primary muscle in lifting weights.
Incorporate these exercises into your chest and shoulder workouts to further stimulate your back muscles. It is in these exercises that the back is a synergist.
Front delts
- Pullover with dumbbells (chest)
- Bent-over dumbbell raises (shoulders)
- Bent-over barbell rows (shoulders)
- Stretching dumbbells, barbells while standing (shoulders)
A well-planned back training program should consist of at least three multi-joint rowing movements that focus on the upper and middle back muscles and 1-2 isolation exercises for the lower back.
The choice and order of exercises in the program should vary from workout to workout or at least every 2-3 weeks to ensure optimal muscle development.
Set of exercises No. 2
Posture is part of your image. Good posture: straight back, straightened shoulders - and those around you look at you with respect. But achieving good posture is not easy in today's lifestyle. We often work in a sitting and bending position. And we stay in this position for a long time. Naturally, our body involuntarily “learns” this position of the back, and we, without noticing it ourselves, not only sit, but also walk hunched over. Slouching has become so common that specialists, to save the situation, have developed and are producing special correctors to correct posture. Now they are on sale in all health stores: back correctors under clothes, and vest-belts.
There is, however, an alternative! A simple set of exercises to straighten your back (instead of or in addition to a spinal corrector), as well as to prevent slouching and maintain a straight back. These exercises will be useful not only for those who already slouch, but also for everyone who wants to maintain their impeccable back.
Find a comfortable wall in the office without furniture (just not plastered or freshly painted - otherwise your whole back will be white). For the “spinal complex”, a free wall measuring two meters wide and two meters high is sufficient.
Exercise one
Lean your whole body firmly against the wall, press your back, shoulders, arms, palms, buttocks, and heels against the wall. Stand in this position for a minute and take 7 deep breaths ( in through your nose, out through your mouth)
). Then, without changing the position of your body (fix it - imagine that the wall is stuck to your back and you are taking it with you). With such a straight back-the-wall, walk around the room (take steps in any direction, with any gait, without changing the position of your back) - the longer, the better. I warn you right away: for those who have been hunching for some time, it will hurt a little at first.
Exercise two
Lean against the wall again ( loosely now)
) and, bending your knee, make 7 swings with each leg. This exercise can be easily performed in any shoes, even high heels.
Exercise three
Lean loosely against the wall and, bending your elbow, make 7 swings with each arm. This exercise can be easily performed in any clothes, even tight ones.
Exercise four
Now swing your right arm and left leg at the same time - 7 times. Then, on the contrary, swing your left arm and right leg – also 7 times.
Exercise five
Relaxation: 7 deep inhalations and exhalations with the body tilted forward and the arms “dangling” below.
Wall exercises help maintain good posture and, therefore, youth. So, don’t waste your time and don’t be lazy, your beauty is in your hands.
Sets and reps.
Most people's muscles respond well to performing 10-15 reps of 2-3 working sets of a particular exercise.
Of course, this range will vary depending on your training, current fitness level and goals.
Women focused on maintaining muscle shape can stick to 2-3 sets of 12-15 reps.
If the goal is to gain muscle mass, work in the range of 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions. The strength version is 3-4 sets of 6-10 repetitions.
For variety, you can include one, two, or all three rep ranges in your program. For example, women looking to add muscle size and strength could work between the 8-12 and 6-10 rep ranges alternating between each back workout.

Tips for morning workouts
In order for morning exercises to correct your posture to become a habit and become part of your daily routine, it is important to familiarize yourself with some tips and recommendations. Then it will be performed with pleasure and will not become a duty:
- There is no need to jump up and run to exercise immediately after waking up. This creates additional stress on the heart. First you need to perform hygiene procedures, walk around the house and slowly begin to exercise.
- For sedentary people and pregnant women, there are several exercises that can be done right in bed. They are not suitable for everyone else, since they do not carry physical activity as such.
- Classes are best conducted with musical accompaniment, and the melody should be selected in time with the movements.
- Exercises indicated for back pain should not cause discomfort. It is wrong if as a result a person experiences severe fatigue and unpleasant feelings. It is important to monitor how you feel and reduce the load if necessary.
Muscles trained together with the back.
When you train your back, many exercises also include muscle groups such as the rotator cuff and posterior deltoids.
In addition, you can add exercises to your program that target the teres major, teres minor, and trapezius muscles. You can also link biceps training with back training. These two muscle groups that are involved in pulling movements are often combined together for an effective workout that minimizes training days in the gym.
What are the consequences of poor posture?
First of all, the incorrect position of the back is expressed in appearance: protruding abdomen, sunken chest, shuffling gait. That is why stooping equally affects human health and the aesthetic component.
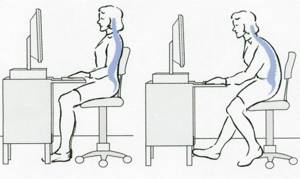
Exercises for posture come to the fore here. Often the curvature causes:
- severe back pain;
- chronic fatigue;
- herniated discs;
- protrusion;
- osteochondrosis;
- deterioration of blood circulation;
- compression of internal organs;
- feeling unwell;
- dizziness.
Frequency, duration and intensity of training.
One of the best training methods is split training, where each part of the body is worked once a week or in pairs with 1-2 other muscle groups. This will allow you to fully fatigue your muscles to stimulate growth.
If your back is a weak part of your body, you can give it priority by training it twice a week. We'll look at priority a little later.
As for the duration of the workout. The results of numerous studies show that the total amount of time spent on physical work matters; for example, 10 hours per month will be almost 2 times more effective than 5.
At the same time, the duration of each workout is not of fundamental importance, but still the average duration of a workout that will give the best results is 1 - 1.5 hours. The training of a professional athlete should take less time, due to his narrow specialization, that is, approximately 40-60 minutes.
Remember that each workout involves approximately 10 minutes of warm-up and 10 minutes of cool-down. Exercising too long causes an increase in the secretion of cortisol, a hormone that breaks down muscles and can also lead to overtraining.
The overall intensity of the workout may vary from week to week to eliminate muscle adaptation to the load and maintain muscle growth. This principle is called periodization.
To obtain optimal results, it is recommended to vary the training intensity each week according to the following scheme: high, medium low.
Set of exercises No. 5
Correct posture is important not only for the health of the spine. People who keep their back straight look slimmer, younger, and feel more confident. Simple exercises that you can do casually on the go will help you maintain good posture. With good posture, all internal organs are positioned correctly - digestion and overall well-being improve. Correct posture improves your mood, and, moreover, people who keep their backs straight look slimmer and younger than those who hunch over. Even their clothes fit better on them. Exercises that strengthen your back and correct your posture are not at all difficult, even fun, and you can do them casually, whenever you remember about it. "The Book on the Head"
Take a large book with a hard, but not glossy cover, place it on your head and try to stand, maintaining your balance so that the book does not fall.
If this is not difficult for you, start walking with a book on your head, you can even try to dance a little. When this exercise becomes too easy for you, pick up some books. Correct posture is important not only for the health of the spine. People who keep their back straight look slimmer, younger, and feel more confident. Simple exercises that you can do casually on the go will help you maintain good posture. “Puppet on strings”
While walking, for example, along the street, imagine that there is a thread tied to the top of your head, by which someone is pulling you straight up, and two more strings to your shoulders, pulling them slightly back.
The chest will straighten, the back will stretch, the neck will look longer, and the gait will become light. Correct posture is important not only for the health of the spine. People who keep their back straight look slimmer, younger, and feel more confident. Simple exercises that you can do casually on the go will help you maintain good posture. “Seagull”
Standing straight, raise your arms to the sides to shoulder level.
At the count of “one-two-three,” move them back as far as possible, and at the count of “four,” return them to their original position. Correct posture is important not only for the health of the spine. People who keep their back straight look slimmer, younger, and feel more confident. Simple exercises that you can do casually on the go will help you maintain good posture. Hanging on a horizontal bar
If you have a children's sports complex at home with a horizontal bar or a crossbar on which you can hang by grabbing it with your hands, “hang” on it periodically for 1-2 minutes.
This relieves tension in the back muscles and helps the spine straighten. It is especially useful to hang like this after a working day spent at the computer, or after a workout. Correct posture is important not only for the health of the spine. People who keep their back straight look slimmer, younger, and feel more confident. Simple exercises that you can do casually on the go will help you maintain good posture. Fidget
This is not a joke.
When sitting down somewhere - on a soft sofa or on a wooden bench, listen carefully to yourself: what sensations does your body experience? Fidget in place, try sitting in different ways, choose a comfortable position. But staying in the same position for too long is also not very useful: you feel that you are getting tired, which means you need to fidget again. Are you not sure whether you need these exercises, because you are convinced that you can keep your back straight without them? Find out how to check if your posture is correct. Correct posture is important not only for the health of the spine. People who keep their back straight look slimmer, younger, and feel more confident. Simple exercises that you can do casually on the go will help you maintain good posture. Why straighten up?
“Bad posture is, first of all, weak muscles, and not only the back muscles, as is commonly believed, but almost all major muscle groups,” says Professor of the Academy of Physical Culture named after A.
P.F. Lesgafta, specialist in the field of prevention and treatment of spinal diseases M.V. Devyatova. This means that posture problems can be solved by trying to move more and doing special exercises that strengthen the back muscles. How to check your posture?
Stand in front of the mirror, strip down to your underwear, and take the position in which you usually stand. Look how symmetrically your shoulders and hips are. With correct posture there should be no distortions. Then go to the wall and lean your back against it. Try to feel (or better yet, ask someone to help you and see) which points of your body you touch the vertical surface. With correct posture, the back of the head, the middle thoracic spine (located between the shoulder blades), buttocks and heels should touch the wall. This is important: when checking, do not try to reach up or straighten your shoulders, stand in the position to which you are accustomed. This will help you determine if you have back problems.
Gaining muscle mass.
Whether you're a competitive athlete or building a body just for the love of it, a wide, thick back is the number one sign that you're not training for nothing.
Core exercises such as deadlift variations are best for adding size and thickness to your back muscles.
Add to this a variety of rowing movements performed with heavy weights and you are sure to have a beautiful, athletic back in no time! The traditional deadlift is the core exercise of a good back program. During this exercise, the erector spinae muscle, lats, buttocks, quadriceps, hamstrings, trapezius, deltoids, and biceps are involved.
To perform deadlifts safely and correctly, do the first two to three sets with an empty bar. Make sure your movement technique is perfect before slowly adding weight.
Performance. Stand facing the bar, place your feet shoulder-width apart, squat down, leaning slightly forward, arch your back and grab the bar with a mixed grip, slightly wider than your shoulders.
Inhale and begin to lift your whole body, keeping your back straight. First, raise the barbell to knee level while starting to stand up, then gradually straighten up until you are upright and your legs are fully extended.
Smoothly, as you exhale, return to the starting position and repeat the movement the required number of times.
Remember that the deadlift can be a dangerous exercise if not performed properly. It's important to properly warm up your entire body with moderate cardio and warm-up sets before performing heavy work sets.
It would also be a good idea to use equipment - gloves or wrist straps so that the bar does not slip out of your hands and wear a weightlifting belt, especially on the last 2-3 heaviest approaches, to prevent injury to the lower back.
Other great ways to focus on gaining mass is to train at high intensity. Also make sure you lift the weight as hard as you can, doing the last 2-3 reps at maximum effort - this means you can't do another rep of the exercise without breaking your form.
Perform four working sets in the 6-10 rep range to focus your training on bulking and strength.

Set of exercises No. 1
Without correct posture, you can’t even dream of a beautiful figure.
To check if your posture is correct, do the following. Stand with your back to the wall so that the walls touch the back of your head, shoulder blades, buttocks, and heels. Now take a step forward, trying to maintain this posture. Count to 10, take a step back and check whether the back of your head, shoulder blades, buttocks, and heels are pressed against the wall. But every now and then standing against the wall, pressing the necessary parts of the body against it, is quite boring. For those who prefer variety, we present a set of exercises specifically designed to develop correct posture.
Exercises for neck muscles
1. Sit on the floor
, bending your knees and hugging your knees with your arms. Straighten your back, bringing your shoulder blades closer together. As you inhale, tilt your head back, trying to stretch your neck as much as possible (Fig. 1). Repeat 10 times.
2. Sit cross-legged
, clasping your shins or socks with your hands; the back is straight. On the count of 1, turn your head to the left, on the count of 2-3 - even further to the left, jerkily, on the count of 4, smoothly return to the IP (Fig. 2). Repeat 4-6 times in each direction.
3. Get on your knees
and lean on straight arms placed shoulder-width apart. Both arms and hips are at right angles to the floor, the weight of the body is evenly distributed. Perform circular movements with your head: down, left, back, right, then in the other direction (Fig. 3). Repeat 3-6 times in each direction.
4. Lie on your stomach
clasping your hands at the back of your head and moving your elbows so that your shoulder blades are close together; rest your forehead on the floor. As you inhale, raise your head, simultaneously preventing this movement with your hands, and return to the PI (Fig. 4). Repeat 8-10 times.
ATTENTION!
The last two exercises cannot be done with severe osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Back straightening exercises
1. Lie on your stomach
bending your elbows and placing your forehead on your closed hands. Toes extended, heels together. While inhaling, raise your upper body and at the same time spread your arms to the sides; There is no need to throw your head back. Return to IP (Fig. 5). Repeat 6-10 times.
2. Lie on your back
bending your knees so that your feet are as close to your hips as possible. Extend your arms to the sides, palms up. Leaning on your hands and head, arch your chest. The lower part of the body fits tightly to the floor (Fig. 6). Repeat 5-8 times.
3. Get on your knees
resting your hands on the floor, arms and hips shoulder-width apart, at right angles to the floor. Extend your right arm forward and up (toward the ceiling), while simultaneously moving your left straight leg back and up. Return to IP and repeat the same with your left arm and right leg (Fig. 7). Repeat 6 - 8 times.
4. "Japanese bow"
. Get on your knees, legs together, arms straight up, palms forward, back straight. Without changing the position of your head and arms and keeping your back straight, very slowly lean forward while sitting on your heels. Touching your chest to your knees, relax your shoulder muscles and lower your head freely. Leaning your palms on the floor and straining your back muscles, return to the IP position and lower your arms (Fig. 8). When bending, exhale; when straightening, inhale. Repeat 4-8 times.
Symmetry.
To balance the symmetrical development of your back, you need to know which area (upper, middle, lower) needs to be “tightened.” Once you know this, you can tailor your workouts to prioritize the muscle group that is lagging behind.
If your upper back lags behind, perform wide-grip pull-ups and wide-grip lat pull-downs.
To prioritize your mid-back, perform exercises that target this area—dumbbell rows, barbell rows, lat rows.
Focus on the lower back - hyperextensions, good mornings, seated body extensions.
Why do you need morning exercises?
Some people argue that this process can easily be moved to another time of the day. They prefer to sleep an extra 15-20 minutes, missing out on the undeniable benefits of morning exercises for posture:
- A fifteen-minute workout in the morning can be equated to a half-hour workout in the afternoon.
- Simple exercises make it easy to wake up and start the day invigorated, rather than half-asleep. This is due to the fact that physical activity in the morning activates the work of the brain and the whole body.
- Exercise has healing powers because it improves blood circulation in the body's systems.
- A person, especially in childhood, becomes collected and disciplined.
- Doing exercises while listening to rhythmic music lifts your mood.
Priority.
If your back is a weak part of your body and you want to prioritize it, there is a solution - train with heavy weights and do strength exercises.
Women by nature have a hard time gaining muscle mass, so “hardcore” workouts will provide a huge advantage for muscle growth.
But at the same time, it takes 7 to 14 days to recover and recover from such hard work, which is why alternating light and hard training every week is necessary.
It is also necessary to work in different repetition ranges, work the back with different intensities and different exercises.
Additionally, you can add a few rowing movements to your shoulder training day to get even more work done throughout your training week.
The program will focus on adding width, thickness and overall development to your back muscles.
The first week is a hard workout, focused on the most difficult exercise - the classic deadlift.
The second week will complement the first, where you will pump your back muscles with maximum intensity.
Workout No. 1 (Week - 1)
Warm up: 5-10 minutes of moderate cardio and full body dynamic stretching.
1. Deadlift
- Set #1: 20 reps.
- Set #2: 15 reps.
- Set #3: 10 reps*.
- Set #4: 8 reps*.
- Set #5: 6 reps**.
- Set #6: 4 reps**.
2. Close-grip horizontal row while seated
- Set #1: 12 reps.
- Set #2: 10 reps*.
- Set #3: 8 reps**.
3. Wide grip lat pulldown to chest
- Set #1: 12 reps.
- Set #2: 10 reps*.
- Set #3: 8 reps**.
*In this approach, the last 2-3 repetitions should be performed as hard as possible.
**In this set, the last rep is a failure (you are not able to do any more reps)
Rest between sets 2-3 minutes
Workout No. 2 (Week - 2)
Warm up: 5-10 minutes of moderate cardio and full body dynamic stretching.
1. Bent-over dumbbell row
- Set #1: 15 reps.
- Set #2: 12 reps.
- Set #3: 10 reps*.
- Set #4: 8 reps**.
- Set #5: 6 reps**.
2. Pull-ups
- Set #1: 12 reps.
- Set #2: 10 reps*.
- Set #3: 8 reps**.
- Set #4: 6 reps**.
3. T-bar pull
- Set #1: 10 reps.
- Set #2: 8 reps*.
- Set #3: 6 reps**.
- Set #4: 6 reps**.
4. Hyperextension
- Set #1: 12 reps.
- Set #2: 10 reps*.
- Set #3: 8 reps**.
*In this approach, the last 2-3 repetitions should be performed as hard as possible.
**In this set, the last rep is a failure (you are not able to do any more reps)
Rest between hikes – 1-1.5 minutes.
LEGS|BACK|CHEST|SHOULDERS|ARMS|ABS, SHINS|
Exercise technique
Before you begin complex exercises, you need to familiarize yourself with the general rules for performing exercises for posture:
- each exercise is performed slowly, without sudden movements;
- An important part of any workout is the warm-up, and after its completion it is important to relax the muscles with a cool-down (stretching);
- It is forbidden to do exercises while overcoming pain; if there is the slightest discomfort, it is better to skip the exercise;
- The basic principles of back exercises are consistency and step-by-step implementation.
How to train a girl's back muscles
All training should be divided into two areas:
- To strengthen a girl’s back at home.
- Strength training with weights in the gym.
- The first option is more about prevention and maintaining muscle tone. In this case, you don’t even have to think about serious hypertrophy or changes in body proportions.
- But the second option is something that will allow you to change the aesthetics of your figure, improving the relief and volume of muscles.
The alternation of high-repetition and strength styles has proven to be maximally effective. You can alternate back exercises in the gym for girls by weeks (strength week and high-repetition week), or in cycles of 1.5-2 months. Training mode:
- Multi-repetition – 4 sets per exercise for 12-15 times.
- Strength – 4-5 sets of 6-8 reps.
- Rest in a multi-repetition format for no more than 1 minute (2-3 minutes between exercises).
- In strength mode, it is optimal to wait 1-2 minutes between sets, as well as 3 to 4 minutes between exercises.
How to pump up a girl’s back muscles: The most effective exercises
Before starting any exercise, always do a 15-minute warm-up to prepare your body for the load.
What are the benefits of back exercises?
• Get rid of most back diseases;
• Create a confident gait;
• They will develop correct posture, which will give you confidence!

Incline with dumbbells. We take dumbbells in both hands, start in a standing position, make a smooth bend with a completely straight back. We lower ourselves to an angle of about 90 degrees, take a short pause and slowly straighten up. We do 3 sets of 8-15 repetitions.

Upper back row. The exercise is performed with a straight back, inhale while exerting effort, and release the exhale. Concentrate on your back muscles. We do 3 sets of 8-15 times, the weight is selected individually.

Pull-ups. A great exercise that works most muscles, including your back. Remember, the wider the grip, the wider the back, so for girls it is better to use a standard grip. Don’t forget that when pulling up, we concentrate on the back muscles, and in no case do we pull our shoulders towards our ears. Exhale at the top, inhale as we lower. We do 3 sets of 5-10 repetitions.
A strong, straight back is the key to health! Develop your back muscles and you yourself will feel positive changes in your life.
Eastern medicine considers the spine not only a support for the body, but also a guarantee of health and longevity of the entire organism. This means that by taking care of your back, a person improves the quality of his life. Today, a sporty, toned silhouette is in fashion, which is simply impossible to achieve if you do not work the back muscles. It is useful for everyone who cares about their health and beauty to know how to pump up their back at home. Knowing the technique of performing exercises, it is possible to achieve excellent results without visiting the gym and personal (not cheap) classes with a fitness trainer.
What is posture
The term “posture” is usually understood as the habitual posture of a person standing at ease with his heels closed and the toes of his feet apart at an angle of 45–50°. Features of posture are determined by measurements and descriptions of the human body as a whole - from head to toe: this is the position of the head and the waist of the upper extremities, the curves of the spine (in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions), the shape of the chest and abdomen, the tilt of the pelvis, the position of the lower extremities, muscle tone, shape of legs and feet.
Posture depends on many reasons. It is connected, firstly, with the state of the muscular system, that is, with the degree of development of the muscles of the neck, back, chest, abdomen and lower extremities, as well as with the functional capabilities of the muscles, its ability to long-term static tension. Posture is influenced by the elastic properties of the intervertebral discs, cartilaginous and connective tissue formations of the joints of the spine (this, in turn, is associated with the mobility of the spine), as well as the pelvis and lower extremities. The shape of the foot and leg as a whole plays an important role.
Good posture usually indicates good health; poor posture usually indicates poor health. Poor posture contributes to a feeling of discomfort, pain in the body, causes skeletal deformities (especially the spine, chest, shoulder girdle, pelvis), and leads to damage to internal organs. The sedentary lifestyle of modern life, unnatural shoes and clothing contribute to poor posture, “stiffness” and muscle atrophy.
Test for correct posture
The simplest way to assess your posture is as follows. Stand with your back close to a cabinet or wall. Close your feet, look straight ahead (your head should touch the cabinet). Hands down. If your palm does not pass between the lower back and the wall, then your posture is good; otherwise, the abdominal muscles are weak and the stomach pulls the spine forward (lordosis).
With correct posture, the head and torso are located on the same vertical, the shoulders are turned, slightly lowered and are at the same level, the relief of the neck (from the tragus of the ear to the edge of the shoulders) on both sides is symmetrical, the shoulder blades do not protrude, the physiological curvature of the spine is normally expressed, the chest is raised ( slightly protruded), the stomach is retracted, the legs are straightened at the knee and hip joints, the foot is without deformities with a clearly visible notch on the side of the inner arch.
When assessing posture, the following points are recorded.
Head position
Is it on the same vertical line with the body, or leaned forward, or tilted to the side (to the right or left).
Shoulder girdle condition
• neck relief – the line from the tragus of the ear to the edge of the shoulder is equally curved on both sides or one side is longer than the other; • shoulders – at the same level or one shoulder is raised and the other is lowered; the shoulders are spread out or leaned forward, and if they are leaned forward, then equally or one more than the other (such asymmetry often occurs in athletes - throwers, fencers, boxers, etc.; we also note that sharply leaned shoulders occur in people with developed muscles, this creates the impression of a false stoop, while true stoop is associated with curvature of the spine); • shoulder blades – at the same level or one higher; whether they perform, and if they perform, then equally or one more.
Spine
Does it have normal physiological curves or are there cervical and lumbar lordosis (convexity forward), thoracic and sacrococcygeal kyphosis (convexity backward). The natural curves of the spine perform a spring function - they reduce body shaking when walking, running and jumping. Normally, the line of the back is wavy, but the depth of the bends should not exceed 3–4 cm. The main feature of correct posture is the symmetrical arrangement of body parts relative to the spine. The chest in front and behind has no recesses or protrusions and is symmetrical with respect to the midline; the stomach is symmetrical, and the navel is located in its center; nipples - on the same line; the shoulder blades are at the same level in relation to the spine, and their angles are located on the same horizontal line; the level of the shoulder girdle and iliac crests on the same horizontal line; The waist lines are the same on both sides.
Spinal mobility
Assessed in a standing position. When bending forward, measure the distance from the end of the middle finger to the floor. If the subject cannot reach the floor with his fingertips, write down: minus so many centimeters; if he can place his palm on the floor, he writes down: plus so many centimeters. When assessing the lateral mobility of the spine, the distance from the ends of the middle fingers to the floor is measured in the position of maximum tilt of the body to the right and left (arms are straightened and extended along the body). Finally, the mobility of the spine in backward bending is measured by the distance from the seventh cervical vertebra to the beginning of the intergluteal fold at maximum backward bending of the torso. Strength endurance of the back extensor muscles is assessed by the time it takes to hold the upper half of the body and head in the “swallow” position. The approximate normal time for holding the torso for children 7-11 years old is 1.5-2 minutes, for teenagers - 2-2.5 minutes, for adults - 3 minutes. Strength endurance of the abdominal muscles is assessed by the number of transitions from the “lying on your back” to the “sitting” position. The movements are performed at a pace of 15–16 times per minute. With normal abdominal development, children 7-11 years old can perform this exercise 15-20 times, and at the age of 12-16 years - 25-30 times, while adults perform this exercise 30-50 times.