Is counting calories really that important?
Even if you meticulously count the calories in your daily menu, no one can vouch for the accuracy of the count. When calculating the calorie content of a dish based on the indicators stated on food packaging, it is impossible to predict how the food will behave during heat treatment. However, here the error may be insignificant. A serious error in the numbers may arise based on the individual characteristics of each specific organism. Did you know that the caloric content of food is not commensurate with the amount of energy that our body absorbs? Nutritionists have only recently begun to take these discrepancies into account.
Regina Todorenko was pleased with her son’s refusal to sleep with his parents. What do psychologists think?
Scientists have discovered how people with “dark” personality traits survive the pandemic
I spotted a blogger’s recipe for celery tea for weight loss. I was pleased with the result
How many calories can the body extract from the food it eats?
For example, sometimes the human body is able to extract much less energy than was stated on the label of the product eaten. There is good news for nut lovers. Studies have shown that almonds or walnuts are digested 21% less than the stated calorie content. Therefore, if you are overweight, you can safely include nuts in your diet as a snack. This significant difference is due to the structure of the product, which consists of vegetable protein and fats. Nuts, enriched with fiber and proteins of plant origin, take a long time to digest. In addition, these solid foods are not easy to chew thoroughly. As a result, some elements remain closed to the body, which means they are not converted into energy.

Time for complete digestion of food in the human stomach by product category

Anyone who is familiar with the rules of separate nutrition knows that products are conventionally divided into the following categories.
- Carbohydrates. This includes vegetables, various juices, cereals, honey, potatoes, fruits, berries. They are quickly absorbed and do not stay in the stomach for more than 1 hour. The stomach will need more time to digest complex carbohydrates – up to 3 hours. For more information about foods that are complex carbohydrates and their benefits, read the article: Complex carbohydrates.
- Protein. These are dairy products, lean meats of various types, fish, eggs, legumes. To process them, the gastrointestinal tract will have to spend 2-4 hours.
- Fatty (high in fat). They are divided into two subgroups: - vegetable: nuts, avocados, vegetable oil; - animals: fatty fish and meat, lard, butter. It takes the stomach up to 6–8 hours to digest fats.
- Partially digestible or completely indigestible. They go in “transit” through the gastrointestinal tract.
What is better: raw food diet or cooking?
Have you ever wondered why people eat so often and become hungry so often? Consider the daily menu of our “brothers” chimpanzees. For the whole day, monkeys can only eat raw fruits, seeds, leaves, and feast on ants. So why can animals follow the principle of a raw food diet, but we prefer to steam, fry and boil our food? This is the main problem of human nutrition.

Jesus Christ was not white: many cultures portray him as dark-skinned
Avoiding Travel: The Benefits of the Pandemic for Mental Health and Peace of Mind
1 apple, 3 eggs, flour, sugar, milk and cornstarch: “magic” cake
Harvard University employee and author of books on nutrition, Richard Wrangham, says the following: “We are used to eating thermally processed food, but this circumstance causes our intestines to work not at full capacity. Cooked food forms microscopic structures. The energy contained in the products is bound, and this, in turn, reduces the load on the digestive organs. As a result, very little time passes, and the person is hungry again.”

Digestion time table for carbohydrate foods
| Vegetables | Time (hour) | Fruits | Time (hour) | Berries | Time (hour) |
| Radish | 0,4 | Persimmon | 1 | Sea buckthorn | 0,4 |
| Puree | 2 | Orange | 0,5 | Cherry | 0,4 |
| Fried potatoes | 2,5 | Grape | 1 | Strawberry | 0,3 |
| Fresh carrots | 1 | Peach | 0,4 | Currant | 0,4 |
| Eggplant | 3,5 | Apricots | 0,4 | Gooseberry | 0,5 |
| Fresh cabbage | 0,4 | Pear | 0,5 | Raspberries | 0,4 |
| Sauerkraut | 3 | Apple | 0,5 | Cherries | 0,4 |
| Cooked beets | 1 | Kiwi | 0,3 | Watermelon | 0,3 |
| Tomatoes | 0,3 | Banana | 1 | Greenery | |
| cucumbers | 0,3 | A pineapple | 1 | Lettuce leaves | 0,3 |
| Pepper | 0,4 | Mango | 2 | Onion, dill | 0,3 |
| Boiled corn | 1 | Prunes | 3 | Parsley | 0,4 |
| Melons | 0,5 | Dates | 2 | Spinach | 0,3 |
Heavy foods include mushrooms (digested in 5-6 hours) and melons (digested in up to 8 hours).
Are all calories equal?
Let us turn our attention to an illustrative experiment conducted on mice. One group of rodents was given raw peanuts and the other a calorie-equivalent amount of roasted peanut butter. The mice that ate the raw nuts ended up losing significantly more weight than their opponents. The same effect will persist in the case of meat.

If you choose between hamburgers or rare steak with the same calorie content, a person will lose more energy from meat cooked in the second case. It turns out that there is a big difference in the way food is prepared. Therefore, when losing weight, give up well-done meat - this way you will save several hundred calories.
Volkswagen's charging robot can refuel its car independently
Winning in quests: what else game theory can teach
The secret to perfect juicy and tender meat in pineapples: I put the fruit into pieces
Here's another interesting example. To digest rice, the body will spend twice as much energy if the dish is prepared correctly. To do this, when cooking rice, you need to add coconut oil and then cool the dish.

Distribution of carbohydrate intake
Michael McCormick IM No. 7, 2000
Strategy for achieving mass and relief
They taste good, help achieve phenomenal muscle pumps, and are widely believed to be the healthiest of all nutrients. What are the disadvantages of carbohydrates? The other side of the coin here is the accumulation of fat. A consistent carbohydrate-dominated diet stimulates the release of insulin, which in turn causes body fat levels to rise. Of course, as a bodybuilder you need to consume a large amount of carbohydrates. But the art is to find the right relationship between the type and timing of intake, since not all carbohydrates are created equal. Consuming large amounts of the “wrong” carbohydrates at the “wrong” time of day can turn even a genetically gifted bodybuilder into a kind of fat-filled endomorph. Let's try to offer an effective method of consuming carbohydrates that easily fits into your daily routine. As mentioned, it is consuming a specific type of carbohydrate at a specific time. This strategy will allow you to achieve maximum lean muscle mass with a minimum amount of fat. In general terms, the method is to reduce the amount of carbohydrates as the day progresses. In the morning, the percentage of calories obtained from them should be maximum, and the glycemic index of foods should be average. About six hours after waking up, it is time to reduce this percentage and switch to foods with a low glycemic index. The glycemic index (GI) divides all foods into groups depending on their effect on blood sugar levels when measured 3-4 hours after consumption. The goal is to optimize the ratio of carbohydrates, fats and proteins at each meal, thereby establishing a balance between the release of insulin and its antagonist, glucagon. It's all about the anabolic effect of insulin on fat cells - too many carbohydrates at the wrong time and you will cause them to increase in size. Insulin is a hormone released by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas in response to increased blood glucose levels. It regulates glucose metabolism and processes necessary for the normal metabolism of fats, carbohydrates and proteins. Insulin lowers glucose levels and ensures its transport and penetration into muscle and other fibers. Eating carbohydrates increases insulin levels and decreases glucagon, a hormone produced by the alpha cells of the same islets of Langerhans that stimulates the conversion of glycogen into glucose in the liver. Its release is caused by hypoglycemia and growth hormone. Protein and fat increase glucagon levels, suppressing insulin.
Glycemic index of foods
| Low glycemic index foods Peanuts 21 Soybeans 25 Rice bran 27 Red beans 27 Cherries 32 Fructose 32 Dry peas 32 Brown beans 34 Barley 36 Grapefruit 36 Red lentils 36 Whole milk 39 Dried beans 40 Sausages 40 Lentils 41 Beans 42 Green lentils 42 Black beans 43 Apricots 44 Split peas yellow, boiled 45 Skim milk 46 Low-fat fruit yoghurt 47 Rye 48 Vermicelli 50 Medium Glycemic Index Foods Unflavored yogurt 51 Spaghetti, boiled 5 minutes 52 Fresh pears 53 Wholemeal spaghetti 53 Apples 54 Brown beans 54 Fish fingers 54 Barley bread 55 Plums 55 | Ravioli with meat 56 Apple juice 58 Canned peas with meat 58 White spaghetti 59 Fresh peaches 60 Canned peas 60 Oranges 63 Canned pears 63 Thin noodles 65 Instant rice, boiled for 1 minute 65 Grapes 66 Pineapple juice 66 Canned peaches 67 Instant vermicelli 67 Peas green 68 Grapefruit juice 69 Chocolate 70 Low-fat ice cream 71 Barley flakes 72 Sweet potatoes 73 Orange juice 74 Canned beans 74 Canned green lentils 74 Instant wheat 77 Bananas 77 Sweet potatoes 77 Oat bran 78 Buckwheat 78 Sweet corn 78 Rice brown 79 Oatmeal cookies 79 Fruit cocktail 79 Popcorn 79 Mango 80 Boiled potatoes 80 Pita bread 82 Honey 83 Rice vermicelli 83 | Pizza and cheese 86 Pea soup 86 Hamburger 87 Oatmeal 87 Ice cream 87 Rolls 88 Raisins 91 Beetroot 91 Rye bread 92 Macaroni and cheese 92 Black bean soup 92 Sucrose 92 Steamed potatoes 93 Pineapples 94 Semolina 94 Pies 95 Bagels 96 Corn tortillas 98 Wheat bread 99 Mashed potatoes 100 High glycemic index foods Carrots 101 White wheat bread 103 White flour bagels 103 Watermelons 103 Wheat cereal 105 Corn chips 105 French fries 107 Donuts 108 Waffles 109 Wheat bread 112 Breakfast rice 117 Instant potatoes 118 Corn flakes 119 Baked potato 1 21 Instant rice, boiled 6 minutes 128 Glucose 137 Maltodextrin 137 Maltose 150 |
| *Carbohydrates can affect blood sugar levels in different ways. * A rise in sugar levels causes a rise in insulin levels. *Increased insulin levels are associated with increased body fat. * The glycemic index is a measure of the effect of food on blood sugar levels. * Early morning is the best time to replenish glycogen stores. * Medium GI carbohydrates should dominate your morning menu. * Reduce your carbohydrate intake for six hours after waking up, and then switch to low-GI foods. * Eat high glycemic index foods and protein within two hours of your workout. |
Glycemic index
Some foods have a high glycemic index, others are digested more slowly, releasing glucose into the blood gradually, and are rated as carbohydrate-containing foods with a low glycemic index. Thus, GI shows how quickly a given nutrient is converted into glucose and ends up in the bloodstream. Simple sugars do not raise glucose levels any faster than some complex carbohydrates. The glycemic index of some foods may be a revelation to you. For example, the GI of baked potatoes is significantly higher than table sugar. The lower the GI, the slower the absorption. Some carbohydrates are digested very quickly and can raise your glucose levels to significant levels almost instantly. These are the foods with the highest glycemic index. And, accordingly, foods with low GI “work” much more slowly. Bodybuilders are able to build lean muscle mass when their diet is planned to minimize blood sugar spikes. In general, foods high in fat and protein have a lower GI than foods high in carbohydrates. But in practice, the concept of the glycemic index does not apply to them.
How to burn fat: 10 best tips 1) Gradually reduce your daily calorie intake (by 50-100 kcal every week).  9) Don't eat after 19.00. Taking growth hormone stimulants before bed can also help burn fat. 10) Use fat burning supplements containing norephedrine, caffeine and yohimbine. And also, increase the activity of the thyroid gland by consuming gagsterones and phosphates. These two supplements, taken in combination, will speed up your metabolism and activate fat cell receptors. Steve Holman |
Power structure
As the glycemic index shows, foods have very different effects on blood sugar levels. Even different types of vermicelli have different GI, for example, some are 95, while others are 45-50. So, if you create a diet taking into account the GI of carbohydrates, then various variations are possible, which will help avoid monotony. There will come a time—pretty soon—when increased muscle mass will push your appetite to new levels. No type of healthy food should be neglected. Here is how the GI value is divided: low - 21-50; average - 51-100; high - 101-150. Most people experience their lowest blood sugar levels in the early morning. After all, a person “survived” seven to nine hours of abstinence from food during sleep. Research has shown that a healthy adult stores the most carbohydrates as muscle glycogen when they consume them within 4-6 hours of waking up. As the day progresses, the body's ability to store carbohydrates in the form of glycogen decreases, and the tendency to convert them into fat and store them in this form increases. Therefore, the correct tactic would be to gradually reduce the carbohydrate content of food throughout the day while simultaneously increasing the amount of protein in it. Most bodybuilders achieve success by distributing their intake of various nutrients as follows: First 6 hours after waking up: 30% protein, 30% fat, 40% carbohydrates with an average GI; From 6 to 12 hours after waking up: 40% proteins, 30% fats, 30% low GI carbohydrates; From 12 to 17 hours after waking up: 50% protein, 30% fat, 20% low GI carbohydrates. In simple terms, this means that you should eat the bulk of your carbohydrates in the first half of the day. For more stable blood sugar levels, choose foods with lower GI. The exception is that short period (2-3 hours) when you have just finished training. Now is the time to pump high-glycemic carbohydrates and proteins into your muscles. The post-workout window allows you to take full advantage of your muscles' increased ability to absorb high-glycemic carbohydrates. Here are some rules to remember when creating a carbohydrate intake plan: We cannot give any guarantees that you will achieve progress using this nutrition strategy, since success depends on many factors. Even the best workout program or miracle diet, if not followed carefully enough, will produce less results than taking a serious approach to a not-so-good workout program or diet. A diet with decreasing levels of carbohydrates throughout the day, in addition to good, sculpted muscles, also brings health benefits that are associated with insulin levels. This reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases, improves oxygen supply to tissues due to better microcirculation, and a constant level of mental energy throughout the day. A low-carbohydrate diet will give you a lean physique and good health.
Tags:
HOW TO EAT
To lose weight
Depending on the physical characteristics of the body
There are no two absolutely identical people on Earth. We all differ in height, degree of completeness, size of internal organs (in particular the liver). We all have different levels of the stress hormone cortisol, and even our gut microbes can also affect the energy we need to maintain basic body functions. If you take people of the same weight, gender and age, the daily calorie expenditure between them can differ by 600 points. And this is almost a third of the daily energy of a moderately active woman.

Digestion of food in the human stomach: how and where are proteins, fats and carbohydrates absorbed?
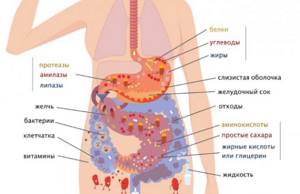
Hydrochloric acid breaks down fruits, berries, and vegetables into carbohydrates. The acidity in the stomach is increased, and the breakdown of carbohydrates requires an alkaline pH. The main process of conversion into fructose, glucose, galactose is observed in the duodenum.
The absorption of proteins is influenced by their origin: animal or plant. Pepsin, present in hydrochloric acid, dilutes proteins as much as possible for their further transformation in the small intestine.
The stomach cannot deal with fatty foods due to the lack of special enzymes. Acid only destroys the structure of fats, turning the pieces into mush, which, if possible, breaks down into components along the way to the large intestine.











