Review of Asparkam and Furosemide
Asparkam is a medicinal drug that supplies minerals to the body.
Potassium imbalance can disrupt metabolic processes in the body and provoke deviations in vital biochemical processes. Potassium is part of all organs in the human body; without it, the synthesis of proteins, as well as glycogen and acetylcholine molecules, is impossible. Potassium ions accelerate the work of nerve fibers at the intracellular level, which allows for rapid transmission of impulses and accumulation of energy elements in the fibers. Magnesium ions enhance the effects of potassium, so the simultaneous replenishment of both elements has a positive effect on the functioning of the body.
Pharmacological action of Asparkam
Potassium deficiency, as well as magnesium deficiency, provokes the development of such pathologies:
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries;
- cardiac ischemia;
- heart rate disturbance.
Furosemide is a diuretic potassium-sparing medication. Available in the form of a powder for the preparation of a suspension, as well as in the form of a solution for parenteral administration and in tablet form.
The active ingredient in the medicine is furosemide. It is prescribed to relieve severe swelling in many metabolic disorders, and is also a mandatory remedy as part of the complex therapy of diseases of the urinary system, liver pathologies and cardiac disorders.
How to take furosemide and asparkam for high blood pressure - All about hypertension
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day...
Read more "
“Asparkam” is used for high blood pressure for a number of reasons: both the antiarrhythmic effect of taking the drug and its antihypertensive effect play a role here. The good tolerability of the medicine makes it quite popular, but in any case it is advisable to take Asparkam as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision.
Release form and main components
It will be easier to figure out whether Asparkam increases or decreases blood pressure if you analyze the composition of the product and the principle of its action.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use ReCardio to treat hypertension. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
The drug is available in the following dosage forms:
- tablets of 175 mg of active substance - 20 or 50 pieces per package;
- injection solution, 40 mg/ml or 45 mg/ml – ampoules (5, 10 and 20 ml);
- infusion solution 7.9 or 11.5 g/l – bottles (200 or 400 ml).
The main active substances of Asparkam are:
- potassium aspartate;
- magnesium aspartate.
The list of excipients includes:
- starch (potato or corn);
- magnesium stearate;
- talc;
- water, etc.
Pharmacological action of "Asparkam"
To reasonably answer the question whether “Asparkam” reduces blood pressure or not, let’s look at the pharmacological action of its main components:
- the drug acts as a source of potassium and magnesium ions (the maximum concentration of ions is recorded 1–2 hours after administration);
- under the influence of Asparkam, the excitability of the heart muscle decreases (due to a decrease in conductivity), which provides an antiarrhythmic effect;
- taking the drug helps restore electrolytic balance in the body;
- as a result, high blood pressure (BP) decreases, and at the same time blood circulation in the coronary vessels is normalized.
An additional effect of taking Asparkam is to stimulate the synthesis of a number of aminocarboxylic acids in the body.
The drug has high bioavailability and is excreted by the kidneys.
Indications for use
“Asparkam” is prescribed quite often for blood pressure and other pathologies. Main indications for its use:
- heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmia) and associated pathologies;
- deficiency of potassium ions;
- deficiency of magnesium ions;
- elevated blood pressure;
- increased intraocular/intracranial pressure;
- tendency to epileptic seizures;
- pathologies of the inner ear;
- some joint diseases.
Asparkam is used for high blood pressure almost always as part of complex therapy. The dosage and duration of the course in each specific case should be determined by the attending physician.
Analogues of the drug
Asparkam is a fairly old drug that is produced today by many pharmaceutical companies. You can buy it under the following names:
- "Asparkam-UBF";
- "Asparkam-Farmak";
- "Asparkam-L";
- "Asparkam-ROS", etc.
Analogs of Asparkam include:
- "Panangin";
- "Panangin-forte";
- "Propanorm";
- “Meksari et al.
In addition, as an alternative to Asparkam, other magnesium and potassium preparations, antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic drugs can be prescribed.
Dosage and method of administration
“Asparkam” lowers blood pressure and relieves arrhythmia, so its effectiveness is not disputed by experts.
Most often, it is recommended to take the drug according to the following regimen:
- Frequency of administration: 3 times a day, regardless of meals.
- Dosage for relieving symptoms of high blood pressure - 2 tablets per dose (no more than 6 tablets per day), for prevention - 1 tablet.
- The tablets are swallowed whole, without crushing or chewing. To facilitate the absorption of the drug, tablets should be taken with a sufficient amount of water.
- The duration of treatment is from 3 weeks to a month. Periodic repetition of the course is allowed after 1–3 months.
For persistently high blood pressure, Asparkam is prescribed in the form of injections or droppers. In this case, self-medication is completely excluded: the dosage is determined exclusively by a specialist.
Overdose and side effects
When taking an excessive dose of Asparkam, patients experience an excess of potassium and magnesium ions in the blood.
This may be accompanied by:
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- disruption of the heart muscle;
- disorientation;
- muscle weakness;
- dry mouth (possibly with a metallic taste) and thirst.
In case of severe overdose, you must stop taking the drug and consult a specialist to relieve symptoms.
In general, Asparkam is well tolerated. But in some cases, unpleasant side effects may occur:
- urge to vomit;
- defecation disorders (diarrhea);
- flatulence;
- excessive sweating;
- dry mouth;
- decreased heart rate;
- dizziness;
- allergic reactions.
If these symptoms appear, as well as if the blood pressure decreases too intensely, the drug should be interrupted, as in the case of an overdose. The specialist should prescribe symptomatic treatment and select an alternative drug to control blood pressure and normalize potassium/magnesium levels.
"Asparkam" during pregnancy
The use of the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding is generally permitted. If a number of rules are followed, Asparkam does not have a negative effect on the child’s body.
Wherein:
- “Asparkam” is used only for therapeutic purposes; its use for prophylaxis is highly undesirable;
- exceeding the dosage can upset the potassium/magnesium balance and provoke premature birth;
- in any case, therapy should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician and at the slightest sign of complications, stop taking the drug.
The principle of action of the drugs
Furosemide is a fast-acting diuretic drug that becomes an emergency treatment for severe life-threatening pathologies - cerebral and pulmonary edema. The mechanism of action of this medication is due to blocking the reabsorption of chlorine and sodium in kidney cells.
The diuretic effect occurs quickly after taking the medicine, but lasts a short period. The time of the diuretic effect directly depends on the dosage taken; after a single use, this effect lasts up to 4 hours.

Mechanism of action of furosemide
The mechanism of action of Asparkam is associated with the action of the aspartate component. This component is involved in the transport of potassium and magnesium ions throughout the body to participate in metabolism. Magnesium takes part in more than 300 metabolic processes in the body.
The main purpose of potassium is to influence cardiomyocytes and prevent the development of arrhythmia. Magnesium helps potassium penetrate the cell membrane of cardiomyocytes, which helps restore myocardial functionality.
Furosemide is quickly absorbed in the digestive tract, bioavailability is 50-70%. The maximum concentration in the blood is 1-2 hours. 90% binds to plasma proteins albumin. The drug penetrates the placental barrier and affects the fetus; the drug has also been detected in breast milk. The pharmacokinetics of Asparkam have not been studied in clinical studies.
The problem of benefit and harm
The use of drugs such as diuretics in the treatment of hypotension and hypertension, edema, disorders of urine production and excretion should only be prescribed by the attending physician according to established indications.
These drugs can have not only useful, but also unnecessary effects: they remove useful substances along with urine, for example, trace elements potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, which play a huge role in energy and metabolic processes occurring in the body at the cellular level.
Since components necessary for the normal functioning of organs and systems can be washed out during treatment with diuretics, experts recommend increasing their intake by taking special medications. That is why Furosemide and Asparkam tablets are almost always prescribed for joint use.
Indications and contraindications
Furosemide is used as a diuretic drug in monotherapy or in complex therapy of pathologies that provoke swelling. Main purposes of using the medicine:
- heart failure grades 2 and 3;
- liver cirrhosis in complex treatment with aldosterone hormone antagonists;
- heart asthma;
- swelling due to renal failure;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- eclampsia;
- hypertension – to relieve a hypertensive crisis;
- relieving swelling in a pregnant woman before the birth process;
- pulmonary edema;
- cerebral edema;
- with hyperkalemia and hypermagnesemia.

Eclampsia
Asparkam is used in monotherapy and in complex treatment of the following diseases:
- myocardial pathology;
- post-infarction period;
- heart failure 1, 2, 3 degrees;
- heart rhythm disturbance (ventricular tachyarrhythmia);
- in complex therapy with digitalis-based medications;
- hypomagnesemia and hypokalemia;
- after an overdose of saluretics.
The main contraindications to the use of Furosemide:
- sensitivity to the drug;
- dehydration;
- anuria;
- severe renal failure;
- poisoning with nephrotoxic and hepatotoxic medications;
- severe hypokalemia;
- hyponatremia;
- encephalopathy of the hepatic type, provoking a state of coma.
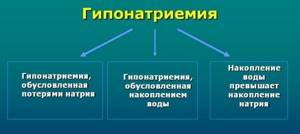
Hyponatremia syndrome
The main contraindications of Asparkam are:
- sensitivity to the drug;
- renal failure;
- hypermagnesemia and hyperkalemia;
- Addison's disease;
- atrioventricular block;
- cardiogenic shock;
- anuria and oliguria.
What works in the anti-edema medicine?
Edema is evidence of serious problems in the body. Not only do they not look aesthetically pleasing enough and interfere with everyday life, they show that a person needs a thorough diagnosis to determine the cause of their appearance.
Drugs such as loop diuretics are used to remove excess water from the body. Furosemide belongs to them. These tablets are named after the active ingredient that works in them. This diuretic is one of the most popular diuretic drugs used in medical practice for decades. Many experts recommend complex therapy with the drugs Asparkam and Furosemide.
Instructions for use
With a long course of medication, you need to constantly monitor the concentration of magnesium and potassium in the blood, as well as the functionality of the heart using an ECG.
Dosage
Intravenous or intramuscular administration of Furosemide is carried out in rare cases in severe pathologies when the patient cannot take the medicine on his own. The dosage of intravenous or intramuscular administration is 40 mg. If there is no therapeutic effect, after 2-3 hours the drug is administered again at a dosage of 20 mg. The maximum amount of medication per day is no more than 6 mg per kilogram of weight.
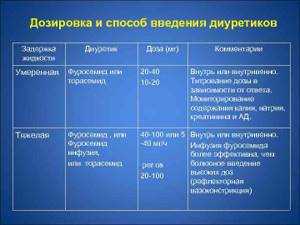
Furosemide dosage regimens
When taken orally in the morning on an empty stomach, you need to take from 20 to 80 mg of the medicine. If no diuretic effect occurs, after 6 hours a dose of 40 to 120 mg should be taken. For the treatment of hypoproteinemia, the daily dosage is 600 mg per kilogram of weight. For hypertension - a dose of 20 to 40 mg. If there is no decrease in pressure, it is necessary to take hypertensive medications.
Asparkam is prescribed 1-2 tablets 3 times a day. It is not recommended to take the product after meals.
How to take Furosemide together with Asparkam? They should be taken in the morning along with a diuretic. The regimen for taking tablets is 2-3 times a day after meals. The tablets should be taken whole and not chewed.
To treat hypokalemia, you need to take 2 tablets three times a day. The therapeutic course of the drug lasts 21-30 days. A course of treatment with Asparkam can be carried out 3-4 times a year.
If you take the pills as a course, then 2 weeks after the start of treatment, you need to donate blood to study the concentration of magnesium and potassium in it.
Use of drugs in pediatrics
Furosemide is actively used in the treatment of premature newborns. The dosage is prescribed depending on the stage of development of the urinary system and kidneys. The metabolism of the drug decreases with glucuronidation. The half-life in newborns is 12 hours.
In children after 2 months of birth, clearance does not differ from that of an adult body. The oral drug is prescribed to children weighing over 10 kg, at the rate of 2 mg per 1 kg of child weight. The maximum dosage should be no more than 40 mg.

Asparkam solution for injection
Asparkam is prescribed to children from the moment of birth for hypokalemia. The drug is rarely administered intravenously, only in resuscitation cases. From the moment of birth and up to 6 years, the drug for treatment should be taken once a day, from 6 to 12 years - twice a day, from 12 to 18 - three times a day.
Medicine dosage for children:
- from 0 to 12 months – a quarter of the tablet;
- from 1 year to 12 years – half a tablet;
- from 12 to 18 years – 1 tablet.
Drug compatibility
It is important to consider the compatibility of the products with other medications:
- It is not recommended to take Furosemide with chloral hydrate.
- Blockers of tubular secretion increase the concentration of diuretic in the blood serum.

When glucocorticosteroids and diuretics are used together, there is a high risk of developing hypokalemia.- Co-administration with Digoxin increases the concentration of cardiac glycosides and develops hypokalemia.
- Concomitant use of diuretics and antihypertensive drugs in treatment increases the risk of developing hypotension.
- Furosemide and Risperidone are used with caution in joint therapy.
- A diuretic in combination with Cyclosporine leads to gout or arthritis.
- Asparkam is prescribed with caution with ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, potassium-sparing diuretics and cyclosporine.
Using medications for weight loss
Furosemide is a diuretic that patients often use to lose weight. This medication does not burn excess fat in the subcutaneous tissue, and also does not reduce appetite, but simply removes fluid from the body. A person taking a diuretic experiences dehydration of the body, which is fraught with health problems, because all the beneficial elements potassium and calcium, as well as magnesium, sodium and chlorine, leave the body with the fluid.
After such a weight loss procedure, the patient feels a rapid heartbeat and cardiac arrhythmia, blood pressure drops sharply, and muscle cramps appear in the limbs.
To reduce excess weight, doctors do not prescribe Furosemide without Asparkam. Taking diet pills while self-medicating is prohibited. These medications can be used in addition to therapeutic treatment and under the supervision of a physician.
Asparkam for weight loss is taken in combination with dietary nutrition and increased physical activity. The drug restores metabolism and replenishes magnesium and potassium deficiency, and also helps eliminate toxins from the body. The use of the medication accelerates the burning of fat from subcutaneous tissue. You need to take 1 tablet three times a day for a month.
How to take furosemide and asparkam for high blood pressure: treatment, consequences, recipes, list
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day...
Read more "
According to WHO estimates, more than a billion people in the world suffer from hypertension. This anomaly requires a systematic and comprehensive approach to its treatment.
However, even experienced patients who scrupulously follow the doctor’s recommendations are susceptible to exacerbations and complications of this disease. Unexpected stress, which can be caused by various factors, does not give the body the opportunity to rebuild itself in the shortest possible time.
In such cases, there is a high probability that a hypertensive crisis may develop, which never warns in advance of its appearance.
Causes
A hypertensive crisis, in which the pressure increases significantly, can be provoked by shocks of various types - an emotional outburst, physical activity, a sharp change in climatic conditions, exacerbation of concomitant diseases, and a violation of the diet.
Doctors include factors that significantly increase the risk of a crisis:
- regular psychological stress;
- predisposition transmitted from parents;
- disorders in the endocrine system;
- nervous system failures – various neuroses;
- overstrain of the organs of vision and hearing;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- magnetic storms and sudden changes in weather conditions;
- abnormal kidney function;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- menopause;
- stopping taking medications prescribed to lower blood pressure;
- accumulation of excess fluid and salts in the body due to violation of the diet recommended for hypertensive patients.
Patients suffering from arterial hypertension should be wary of the overlap of several provoking factors, as this increases the risk of worsening the condition and can lead to very serious consequences, including death.
Medicine distinguishes two types of hypertensive crisis:
- hyperkinetic, also called systolic or cardiac;
- hypokinetic, the second name is edematous.
The symptoms of the disease are somewhat different. The first type most often affects men, the second is characteristic of women with excess weight gained during menopause.
A systolic crisis develops incredibly quickly and can strike a hypertensive patient at any time and anywhere. It is characterized by the following manifestations:
- there is a sharp rise in pressure;
- there is redness of the face;
- the headache is throbbing in nature;
- there is pain in the heart;
- the patient sweats profusely;
- the mouth feels dry;
- tachycardia appears against the background of general overexcitation;
- tremor of the limbs is common.
If the blood pressure during a hypertensive crisis is not brought back to normal in a timely manner, then, developing according to the hyperkinetic type, it can lead to a sharp deterioration and bring the following consequences:
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- heart attack;
- visual impairment;
- cerebral edema;
- kidney failure.
The edema crisis progresses much more slowly. Its symptoms are also different:
- skin is dry and pale;
- the headache is “bursting” in nature;
- there is general weakness, often accompanied by dizziness;
- nausea is common;
- darkening of the eyes, general decrease in vision function;
- general state of sleepiness, decreased performance;
- the patient urinates significantly less.
In this case, urgent medical intervention is also necessary, since the consequences of prolonged exposure to high blood pressure on the body are, unfortunately, predictable.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use ReCardio to treat hypertension. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Consequences of the attack
If for some reason measures are not taken to immediately stop the crisis, then there is a high probability of serious complications, such as:
- stroke;
- swelling of the lungs or brain;
- impaired kidney function up to complete failure;
- loss of vision.
Abnormalities in the blood flow of the brain, which are especially dangerous for this disease, lead to the fact that half of the patients who received this pathology as a result of a pressure surge die within three years after the problem occurs.
That is why pressure reduction during a hypertensive crisis must be carried out immediately. Experienced patients always prefer to have the necessary set of medications with them to quickly combat the disease.
How to resist
Often, the life and health of a person who has been attacked by an insidious enemy depends on his personal readiness to give immediate resistance and on the quick and correct actions of those around him. If the patient has signs of crisis, it is necessary to act according to the following algorithm.
- Call an ambulance immediately.
- Place the patient in a reclining position.
- Untie the tie, unbutton the collar, and allow the victim to breathe freely.
- Provide fresh air flow, open windows if necessary.
- Give the drug that the patient usually takes. The dose of medication to lower blood pressure should be the usual one. Increasing the dose can sharply reduce blood pressure, leading to collapse.
- If possible, try to warm your feet - apply a heating pad or a bottle of hot water to them.
- Give twenty drops of Corvalol as a sedative.
- Place a captopril tablet under the tongue - the patient must dissolve it.
- For a bursting headache, use furosemide.
- Give the patient one ball of nitroglycerin under the tongue.
Further procedures can be carried out by an emergency medical team. Timely and competent actions during a hypertensive crisis are a fundamental factor that gives the patient a chance to live. According to WHO, patients who do not receive adequate care during a crisis die in 79% of cases within the next year.
Fight back at home
Sometimes it is not possible to call an ambulance or wait a long time for its arrival (especially in remote rural areas). In such cases, it is necessary to keep on hand injections for urgent relief of the crisis and a set of disposable syringes. It is better when one of the household or neighbors has the skills to administer such drugs.
Required set of medications:
- magnesia sulfate;
- dibazole;
- furosemide;
- no-shpa;
- vitamin B6.
Intravenous administration of magnesium gives excellent results, but not everyone can do such an injection on their own.
It is better not to use Dibazole for very high blood pressure, since it has the property of first slightly raising blood pressure readings, after which it gradually lowers them.
Furosemide requires simultaneous use of panangin, as it removes potassium and calcium from the body. During a hypertensive crisis, blood pressure cannot be reduced by more than 25%, so do not overdo it with doses.
The doctor has arrived
Upon arrival of the ambulance team, the doctor on duty is obliged to perform the following actions:
- conduct an initial examination and confirm the diagnosis;
- assess the patient’s response to the use of first aid measures;
- if necessary, use medications prescribed by WHO and Ministry of Health protocols;
- decide on the need for hospitalization.
In the arsenal of an emergency doctor to combat a crisis, the following means are provided:
- magnesia;
- clonidine;
- lasix;
- dibazole;
- benzohexonium.
Doctors decide which of these injections to use based on the severity of the patient, the dynamics of the crisis and the pre-medical care used.
Patients with symptoms of complications are subject to unconditional immediate hospitalization, namely:
- stroke;
- cerebral edema;
- coronary insufficiency;
- formation of acute left ventricular failure.
Also, a decision on hospitalization can be made if, for some reason, doctors are unable to quickly stop the crisis.
Camping first aid kit
An insidious enemy can lie in wait for a hypertensive patient anywhere, therefore, experienced patients prefer not to leave home without a set of necessary medications.
The problem is that at the time of crisis, the patient is often not able to independently figure out which drug and in what order to take for emergency help.
Nowadays, there are traveling first aid kits, similar to those used in the army. These are hermetically sealed compact boxes that are not afraid of water.
Inside there are only two drugs dosed for one-time use:
The first aid kit is equipped with a simple and accessible algorithm for their use. With such a “body armor” in his pocket, a patient prone to crises can feel protected from an unexpected attack.
Restoring strength
If the hypertensive crisis passed without complications, then you can be congratulated - the battle with the enemy was won with almost no losses. However, even if normal blood pressure is quickly restored, it will take at least another seven days to deal with the consequences.
During this period, you should follow a few simple rules:
- eliminate physical or emotional stress;
- lead a measured lifestyle - go to bed and get up strictly at a certain time, eat food according to your daily routine;
- exclude salty and spicy foods from your diet, follow the diet recommended by your doctor;
- reduce the amount of fluid consumed;
- strictly adhere to the medications prescribed by your doctor;
- remember that overeating, alcohol and smoking are allies of your enemy;
- avoid conflict situations - your weakened body does not need stress;
- Try to use the services of a sanatorium in your region these days - climate change will not be beneficial.
The most important advice is don’t be nervous and don’t overexert yourself.
How to avoid being attacked again
Arterial hypertension is classified as an incurable disease that can lead to death. Simply monitoring your blood pressure will not give effective results.
“Normal blood pressure” is a rather arbitrary concept and depends on the constitution, height, weight, and individual characteristics of the patient.
What pressure to consider critical during a hypertensive crisis and what not is determined only by the patient’s well-being.
To avoid a second attack by a deadly enemy, there is only one way - you need to make adjustments to your lifestyle:
- regularly take medications prescribed by your doctor to normalize your blood pressure;
- work activity should be without physical and emotional overload, rest should be complete;
- reconsider your diet - in addition to eliminating salt from the diet as much as possible, you should adhere to the established meal schedule and not overeat;
- forget about bad habits such as drinking alcohol and smoking;
- regularly take courses in massage and physical therapy, paying special attention to the collar area;
- treat salt deposits in the cervical spine;
- try not to drink strong tea and coffee;
- Plan a resort vacation only in sanatoriums of your climate zone;
- Take sedatives regularly - stress is not for you.
Experienced patients know that they cannot escape this disease. With experience comes the understanding that no medications will give a 100% guarantee that you will no longer see pressure numbers on the tonometer during a hypertensive crisis.
No doctor will help you avoid relapses if your attitude towards the disease does not change. The first crisis is just a test of the strength of an insidious disease.
If you do not take serious care of the condition of your blood vessels, then a recurrence, fraught with deadly complications, is inevitable.
Originally posted 2017-09-18 11:48:07.
Source: https://bol.lechenie-gipertoniya.ru/gipertoniya/kak-prinimat-furosemid-i-asparkam-pri-vysokom-davlenii/
Main differences, effectiveness and safety
The main difference between both drugs is the different pharmacological group. Furosemide is a loop diuretic, and Asparkam is a source of potassium and magnesium. The mechanism of action of both medications is completely different, as is the composition.
Both medications effectively complement each other when used together. Furosemide removes potassium from the body, and Asparkam restores its concentration.
Since both drugs under consideration are not in the same pharmacological group and have completely different purposes, it would be incorrect to compare them in effectiveness. Furosemide in its group is one of the fastest-acting diuretics, which allows it to be used in resuscitation of cerebral and pulmonary edema. Asparkam is a drug that is the most effective and popular in its medicinal group.
If the correct dosage and dosage regimen are followed, drugs rarely cause negative effects. Side effects often occur during self-medication. Possible negative reactions of the body are presented in the table.
| Organs | Negative effects | |
| blood flow system and myocardium | Furosemide | Asparkam |
|
| |
| CNS |
|
|
| Digestive tract |
|
|
| Metabolism |
|
|
| Allergy |
|
|
Reviews
Reviews about the combined use of Furosemide and Asparkam are mostly positive. The drugs effectively lower intracranial pressure in both newborns and adult patients. The use of medications in combination allows you to fight neurological and cardiac pathologies:
Reviews from patients who took weight loss medications on their own are not always positive:
Furosemide together with Asparkam should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Taking it as self-medication will not only not bring a therapeutic effect, but can also aggravate cardiac pathologies.
Furosemide and Asparkam are two drugs that are recommended for simultaneous use for existing indications. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to study the effect of these drugs, as well as become familiar with possible side effects.
Analogs
Analogues of these medications are medications that are similar in their composition or therapeutic effects. Analogues of Furosemide can be considered:
- Torsemide is a modern diuretic that is more effective than the original and is used to treat heart failure, as well as pathologies associated with renal failure and disorders of the urinary system.
- Diuver is an effective medication that reduces swelling in heart pathologies. Not prescribed for swelling in the peritoneum due to cirrhosis of the liver.
Analogues of Asparkam:
- Panangin is a drug prescribed for heart pathologies, as well as during the period of taking cardiac glycosides. Effectively replenishes potassium deficiency during hypokalemia.
- Rhythmocor - a drug prescribed for cardiac ischemia, cardiopathy, impaired rhythm and conductivity of the myocardium, and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Release forms and price
Furosemide
Can be found by price:
- 40 mg tablets:
- 20 pcs. – 20 – 30 rub;
- 50 pcs. – 20 – 35 rub;
- Solution for injection 1%, 2 ml, 10 ampoules – 20 – 50 rub.
- Pills:
Asparkam
Prices vary depending on the manufacturer:
- 10 pieces. – 10 rubles;
- 20 pcs. – 40 – 50 rub;
- 56 pcs. – 80 – 85 rub;
- 60 pcs. – 40 – 50 rub;