- The essence
- Efficiency
- Contraindications
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Product Lists
- Recommendations
- Options
- Sample menu
There are quite a lot of nutritional systems based on bad and good carbohydrates. As practice shows, a diet based on the glycemic index is especially effective among them, if it is properly organized. At first it seems complicated, because you need to calculate the total GI of foods consumed per day. In fact, everything is quite simple if you learn to use tables, focus on sample menus and prepare recipes that have already been developed in advance for this. But the result can exceed all expectations.
The essence
The hypoglycemic diet is based on the concept of the glycemic index (abbreviated as GI), which is assigned to each carbohydrate-containing product. These numbers are not pulled out of thin air. Ever since Dr. Jenkins introduced this term into medical practice in 1981, studies have been constantly conducted to determine this indicator for different food categories. Therefore, the corresponding tables are regularly updated with new data.
Some foods, once ingested, cause a sharp jump in blood sugar. This leads to increased insulin release. Its excess blocks the lipolysis process, and food is used not for energy production, but for fat storage. These are the so-called “bad” carbohydrates, which are assigned a high GI. They lead to excess weight gain.
Other foods are digested and absorbed slowly, without causing sugar spikes. It rises, but slightly and evenly. Insulin is produced in moderation - so as to spur lipolysis and, instead of storing fats in reserve, direct them in the right direction, for energy production. This is how “good” carbohydrates act, which are characterized by a low GI. They promote weight loss.
Now the principle of the glycemic diet is clear: eat foods predominantly with low GI and lose weight. But you have to avoid bad carbohydrates. Unfortunately, a lot of tasty and sweet things fall into their category. But that’s why they go on hunger strikes, to endure food restrictions.
A low GI is considered to be less than 35. Average is 40-55. High - more than 60. The first group of foods can be eaten as part of a glycemic diet (but within reason). The second is to add it to the diet occasionally (no more than once a day). The third one is to exclude it from the menu completely.
You can learn more about fast and slow carbohydrates from the article: “Carbohydrates for weight loss.”
Efficiency
What a diet with low glycemic index foods can achieve:
- losing 2-3 kg in 1 week - yes, the result is far from stunning, but lasting;
- maintaining energy and performance throughout the day by consuming carbohydrates;
- reducing harmful cholesterol in the blood;
- strengthening the cardiovascular system (provided that there were no problems with it initially);
- improvement in diabetes mellitus.
In addition, on a glycemic diet there are rarely breakdowns, because the feeling of hunger is blocked by the same carbohydrates. And proteins and fats are not prohibited, which is also good news.
Useful video
For information on the glycemic index diet, watch this video:
Similar articles
- Diet according to body type: what is suitable if you are sandy...
A diet according to body type is suitable for everyone, because it takes into account the individual characteristics of the body. How to choose products if you are an hourglass, apple, pear, rectangle, triangle? Our article will help. Read more - Diabetes and diet for weight loss: how you can and cannot lose weight...
If you have diabetes, a weight loss diet will help maintain insulin. It is important to understand how, whether and when not to lose weight with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Read more
- About what the glycemic index is...
Michel Montignac's diet is compiled according to the principle of taking into account the glycemic index. The menu is quite varied, the recipes are suitable even for people with health problems, although there are a few exceptions. Read more
Contraindications

There are no jokes with the glycemic diet, because such nutrition most directly affects the composition of the blood and the condition of the cardiovascular system as a whole. Therefore, not everyone will enjoy its effectiveness. There are a number of contraindications - a list of diseases in which this technique can worsen health. These include:
- ulcers, gastritis and other gastrointestinal problems;
- mental disorders;
- renal failure;
- chronic diseases;
- prolonged depression;
- heart failure;
- varicose veins, thrombosis, hemophilia and other pathologies of the circulatory system.
Special mention should be made about pregnant and breastfeeding women. These provisions in themselves are contraindications for any diet, and glycemic is no exception. Age restrictions are also present here: a lack of insulin is fraught with consequences for children, adolescents and the elderly.
Diabetes mellitus is a controversial contraindication for such a nutritional system. On the one hand, it was originally developed for its treatment. On the other hand, doctors say that there is no officially confirmed scientific data on the benefits of such weight loss for such a diagnosis. Today this is just a theoretical assumption, but diabetologists strongly discourage their patients from going on a glycemic diet.
Advantages and disadvantages
For all its advantages, the glycemic diet remains a fast, and it has disadvantages that you need to know about in advance.
Advantages:
- high efficiency;
- normalization of metabolic processes;
- acquiring healthy eating habits;
- successful fight against addiction to sweets;
- lack of hunger;
- minimal risk of failure;
- strengthening the immune system;
- saturating the body with essential vitamins (there are plenty of fruits and vegetables in the diet);
- no imbalance in the ratio of BZHU;
- control of insulin and cholesterol levels in the blood;
- pressure stabilization;
- improved mood.
Flaws:
- the need for willpower and strength of character, since you will have to give up sweets, pastries, bread and many other “joys of life”;
- the dubiousness of the scientific basis: the effect of GI on weight loss is just a theoretical assumption that has yet to be proven;
- there is a risk of getting hooked on fats, which reduce the effectiveness of the diet;
- decent results can only be achieved with long-term compliance;
- Throughout your weight loss, you will have to keep a table of the glycemic index of foods before your eyes, so as not to accidentally eat something forbidden.
What to cook?
To ensure your meals keep your glucose levels normal while still being comfortable, take the time to prepare delicious meals. Low GI foods you can cook and eat:
- Soups. Vegetarian mushrooms and vegetables with permitted cereals are welcome. But cabbage soup, pickles and borscht cooked in low-fat broth are not prohibited. Just do not overcook the vegetables, but immediately throw them into boiling water.
- Fresh salads with seafood and vegetables. But forget the boiled beets and potatoes.
- Low-fat sour cream as a dressing, cottage cheese, cheese without salt.
- Egg white omelettes.
- Porridge with low-fat milk. Barley and oatmeal, buckwheat and pearl barley are allowed.
- Any meat except pork, goose and beef. Sometimes you can treat yourself to cookies.
- Vegetable side dishes that go well with meat.
- From sweets, everyone can make jelly and fruit pastilles.
- Drinks: herbal teas, vegetable juices, unsweetened compotes.
The food is boiled or a steamer is used. Fried foods should be excluded.
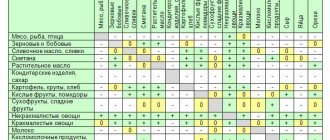
Product Lists

We will not provide complete lists of permitted and prohibited products here, as they are too long. You will find them in special tables. They have three sections:
- Products with a low glycemic index (less than 35), which are allowed as part of such fasting, form the basis of his diet.
- Foods with an average GI (40-55), which can be eaten in small quantities no more than once a day.
- Foods with a high GI (more than 60) that need to be completely excluded from the diet.
Below are approximate lists that, even before working with the table, will orient you on what menu you can create and what kind of sacrifices you will have to make.
Important note. Please note that the list is for raw foods. After heat treatment, their glycemic index changes significantly, most often upward, and in such situations the product moves from permitted to prohibited. Example: GI of raw celery root = 15, and GI of boiled celery = 85.
Allowed:
- fruits, dried fruits, berries: apricot, avocado, quince, orange, green banana, pomegranate, grapefruit, pear, lemon, tangerine, nectarine, peach, plum, apple, dried apricots, figs, goji, strawberries, raspberries, red and black currants, cherries, blueberries;
- all nuts (including coconut) and seeds;
- vegetables, greens: eggplant, broccoli, zucchini, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, carrots, cucumber, peppers, tomatoes, radishes, lettuce, beets, beans, garlic, onions, rhubarb, celery, asparagus, spinach, sorrel;
- peas, chickpeas, lentils;
- cereals: pearl barley, sprouted wheat, egg;
- sweets: creamy ice cream with fructose, dark chocolate;
- dairy products (with a minimum percentage of fat): feta cheese, plain yogurt, kefir, milk, fermented baked milk, cream, most cheeses, cottage cheese;
- eggs;
- lean meat and fish, seafood;
- soy vermicelli, nut and soy flour, Essene bread;
- drinks: alcohol (except beer), coffee, tea, tomato juice.
Prohibited:
- fruits: papaya, melon, watermelon;
- raisin;
- vegetables: rutabaga, corn, pumpkin;
- cereals: white rice, wheat, millet;
- sweets: chocolate bars, glucose, honey, ice cream, sugar, waffles, cookies, jam and jams with sugar;
- dairy products: curd cheese, condensed milk;
- wheat and rice bread, baguette, crackers, dumplings, wheat flour, lasagna, donuts, crackers, croutons, rolls, bagels;
- drinks: beer, soda, protein shakes.
Moderate consumption:
- fruits: pineapple, persimmon, mango, kiwi, grapes, ripe banana;
- dried fruits: prunes, dates;
- berries: cranberries, lingonberries;
- beans;
- cereals: buckwheat, red and wild rice, basmati, oats, semolina;
- sweets: maple syrup, lactose;
- dairy products: yogurt with additives, sour cream, processed cheese, feta;
- sushi;
- buckwheat pancakes, whole grain pasta, whole grain rye bread, al dente spaghetti, ravioli, pizza, buckwheat flour;
- fruit and vegetable juices.
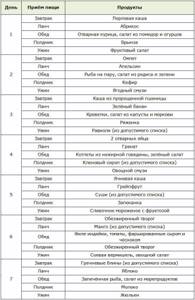
An example of a diet according to the glycemic index for a week (first stage)
Monday
Breakfast: oatmeal with milk. Snack: a handful of nuts and an apple. Lunch: baked chicken fillet and a couple of fresh cucumbers. Afternoon snack: a glass of kefir. Dinner: buckwheat and orange.
Tuesday
Breakfast: a couple of whole grain breads and a glass of milk. Snack: baked apple. Lunch: baked fish fillet and an empty cucumber salad with white cabbage. Afternoon snack: a glass of homemade yogurt without additives or kefir. Dinner: lean beef fillet baked with broccoli.
Wednesday
Breakfast: oatmeal, to which you can add a little milk and a few nuts when boiling. Snack: apple and whole grain bread. Lunch: a portion of boiled rice and a slice of baked fish; fresh cucumber. Afternoon snack: a glass of kefir. Dinner: baked fish fillet and apple.
Thursday
Breakfast: buckwheat with milk and a glass of yogurt. Snack: salad of cucumbers and white cabbage. Lunch: oatmeal and a slice of baked fish; apple. Afternoon snack: a glass of kefir. Dinner: boiled chicken fillet and lettuce leaves.
Recommendations
In addition to the fact that the glycemic diet forces those losing weight to constantly refer to tables, its observance also involves a number of rules. They allow you to increase efficiency and endure all hardships. If you plan to achieve maximum results without harm to your health, listen to the advice of experts.
- Get examined at the hospital and get your doctor's permission.
- The daily calorie intake for weight loss for men should not exceed 1,500 kcal (athletes are allowed 1,800), for women - 1,200.
- The basis of the menu should be foods with a GI of less than 35. They should be eaten daily. Food with a GI from 40 to 55 inclusive is allowed once a day. Everything else is prohibited.
- For fats, give preference to olive oil, but do not fry anything with it. Proteins are low-fat (they make an ideal tandem with carbohydrates).
- Duration: no less than a week and no more than 3 months.
- Daily volume of drinking water: 2 liters.
- Sports activities are required.
- Dinner no later than 4 hours before bedtime.
- Small meals: eat 5-6 times a day.
- If your health worsens, you should stop the diet and check your health.
Options

There are different diets based on the glycemic index of carbohydrate-containing foods.
Option 1. Montignac
The most famous of all glycemic diets. Developed by French nutritionist Michel Montignac. Assumes 2 phases:
- Direct weight loss, which should last 3 months (to lose 5 kg) or more (to lose more than 5 kg).
- Consolidation of results on which you can stay.
It is based on the principle of separate nutrition: during the day, meals are divided into protein-lipid (GI of foods should not exceed 35) and protein-carbohydrate (GI = 40 to 50). Offers three meals a day.
Detailed description.
Option 2. Sports
There is a sports diet for men based on the glycemic index. The first option is for those who are working to build muscle mass. They are asked to eat proteins and foods with a GI of up to 80 for a month.
The second option is for those who are focused on losing weight and cutting. They should exclude from their diet all foods with a GI of more than 60 for a month.
Option 3. Carbohydrate
It is based on consuming only good carbohydrates, i.e. low GI foods. Some versions of this diet allow you to eat food with an average glycemic index (then the weight loss process slows down and stretches out to 1-2 months), and some, more stringent ones, prohibit it (their duration does not exceed 3-4 weeks).
Detailed description.
Option 4. South Beach
Developed by English scientists: cardiologist A. Agatston and nutritionist M. Almon. It was prescribed for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, but at the same time it led to persistent weight loss. Based on two principles:
- Good carbs (low GI) vs bad carbs (high GI).
- Good fats vs bad fats.
Preference is, of course, given to good (healthy) carbohydrates and fats. Moreover, the diet was an unprecedented success among men, as it allows beer in moderate quantities.
Option 5. Bread
This diet can only conditionally be called glycemic, since it is based on a different quantitative characteristic of carbohydrates to separate them into bad and good, but this does not change the essence. To calculate the GI of each product, pure glucose was taken as the initial unit, whose index = 100. Other researchers took a different route and took white bread as the starting point.
Detailed description.
Option 6. Slow Carb (slow carbohydrates)
Developed by American writer and healthy lifestyle promoter Timothy Ferris. He suggests eating as many low-GI foods as possible and avoiding those whose GI is off the charts. True, the first list is also very limiting. Basic principles:
- “No” to fast carbohydrates, alcohol and fruits.
- “Yes” to separate meals and permissiveness on a cheat day (this is the name for 1 day a week when you can eat anything and in any quantity).
This technique is subject to frequent and justified criticism.
These are all just options for glycemic diets. In its classical form, it does not involve such extremes as giving up alcohol, fruits, and adhering to the principles of separate nutrition. Here everything is much simpler: we looked at the GI table and determined the range of consumed and excluded products.
What food is prohibited?
The following foods are contraindicated in case of hypoglycemia:
- Buns, muffins and other bakery products made from premium flour;
- Cream, salty cheeses, glazed sweet curd cheeses;
- Fatty and milky soups seasoned with noodles;
- Fatty meat, sausages, smoked meats;
- Fish: fatty, salted and smoked;
- Cooking fat and vegetable oil;
- Fried eggs;
- Semolina and white rice;
- Pickled vegetables;
- Dried fruits;
- Sweets;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Factory-made sauces: mayonnaise, ketchup.
It can rightfully be called a list of harmful products, can’t it?
Sample menu
To make sure that the glycemic diet can really be followed, just look at the sample menu for the week, which you can use as a basis to create your diet. It is varied, balanced and very satisfying.
Menu note on serving sizes:
- breakfast - 200 g;
- lunch - 1 fruit;
- lunch - 350 g;
- afternoon snack - 150 g;
- dinner - 200 g.
During breaks you can drink permitted drinks.
Now you know what the glycemic diet is in its classical sense, as well as its different variations. What to choose is up to you. But in any case, do not forget that weight loss can only be achieved in a comprehensive manner: while absorbing calories, they must be spent.
Why did my sugar drop?
A decrease in blood glucose leads to starvation of all living tissues, including the brain. Hypoglycemia usually occurs in the following cases:
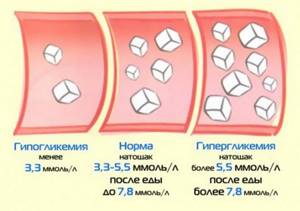
In case of insulin overdose, which most often occurs in chronic diabetics;- Excessive production of insulin by the body due to the appearance and growth of tumors and severe infections;
- After a stressful situation;
- As a response to excessive mental and physical stress;
- During a low-calorie diet and with alcohol abuse.
But sometimes, with an innate fast metabolism, such indicators are considered the norm. Changes are easily detected by regular blood tests. If they threaten human health, a special diet is followed.