How does this supplement affect the body? Application in sports. Negative effects and recommendations for use. Finding a truly safe and high-quality supplement that could speed up the process of muscle growth and increase training efficiency is a task for many athletes. At the same time, more and more athletes prefer creatine - one of the most scarce and important elements for our body. It is he who is the source of “explosive” strength and energy. With its help, it is much easier to build muscle, increase endurance and achieve unique sports results.
The effect of taking creatine
Remember the most important thing: creatine monohydrate will not help you gain weight, it will help you increase your strength in exercises, which in turn will lead to muscle growth. Physical activity and intense training increase the consumption of creatine, so its reserve must be constantly replenished from internal synthesis of this substance and supply of building material in the form of proteins with food.
Creatine monohydrate is a natural substance that is converted in the human body into creatine phosphate. Creatine phosphate helps produce the substance adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP supplies the energy needed for muscle contraction.
The human body can produce some creatine itself, and can also obtain creatine from foods (for example, red meat or fatty fish). But the creatine content in foods may decrease during cooking. A creatine monohydrate supplement is a product that contains a very pure form of creatine and is often taken pre/post workout with other supplements like whey protein or on its own.

Creatine monohydrate is the most effective and popular form of creatine used by athletes to increase muscle mass, strength and endurance.
What does creatine do for strength sports?
For strength sports, the use of creatine helps achieve the following results:
- Increased strength . Regular use of this type of sports supplement saturates the muscle tissue with the necessary components and provides additional strength to perform more strength exercises.
- Muscle building . Due to the fact that fluid retention occurs and additional endurance appears, muscle volume increases. This happens due to the accelerated growth of muscle fibers due to frequent training.
Thanks to regular use of the supplement, it is possible to overcome large strength masses and train for a long time.
How does creatine monohydrate work?
To understand how creatine monohydrate works, you first need to know what ATP is and what this substance does. ATP is the immediate source of energy needed for muscle contractions. Muscle fibers contain reserves of ATP sufficient for only a couple of contractions; additional ATP is “drawn” from the body’s reserves. Creatine monohydrate is converted to creatine phosphate in the human body, maintaining ATP reserves in the body. How does this manifest itself in real life? Having greater ATP stores can help you lift heavier weights and do more reps, providing your muscles with the amount of quickly converted energy they need for peak performance. You've heard about this often. This was called "explosive energy, explosive force."
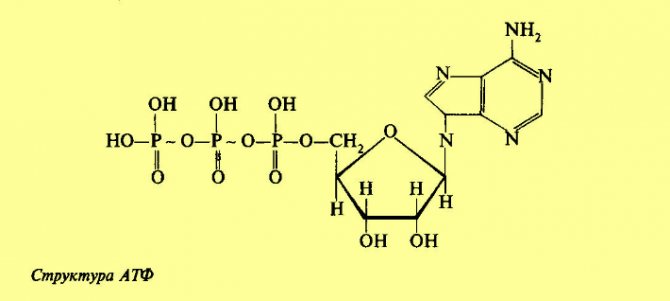
ATP is a source of energy that is necessary for muscle contractions. Muscle fibers contain reserves of ATP sufficient only for a couple of contractions; the rest is drawn from the body's reserves.
How does creatine affect muscles?
Creatine retains water in the muscles, that is, it accumulates it. And since muscles are almost 75% water, with such accumulation they visually increase. Your biceps become voluminous and pumped.
As for protein, thanks to creatine it is synthesized faster and delivered to the muscles. In addition, creatine helps the human body recover better and faster after active training.
Creatine also prevents the process of catabolism - muscle breakdown at night, when the body is resting. Interesting to know! A study was conducted at the University of Saskatchewan (Canada) where one group of people was given creatine and the other a placebo. Then the experiment participants were given the task: to train the muscle group of one arm separately 2 times a week. After 6 weeks, the scientists compared the results, and it turned out that in the group that took creatine, the size of the trained arm increased significantly, but the participants in the second group could boast of a barely noticeable result.
Positive influence
Achieving high results in sports (especially in strength sports) is impossible without an adequate supply of energy to the body obtained from ATP (adenosine triphosphate). All sources of organic fuel are first converted into this compound, which, when broken down, supplies the body with energy. Creatine is a direct participant in the production of ATP. This is why an athlete needs to involve additional creatine monohydrate in energy processes. Regular use of drugs containing creatine by athletes is accompanied by the following effects:
- Increased strength. For bodybuilders and powerlifters, the need for ATP during training increases hundreds of times. Muscle contractions in athletes occur at the peak of possible intensity, so the cells require additional sources of energy, which creatine provides them with.
- Increased muscle mass. Taking creatine monohydrate together with systematic training and special high-calorie sports nutrition can provide athletes with a weight gain of up to 5 kg monthly.
- Relief formation. Creatine monohydrate, stored in muscle tissue, attracts more fluid. Well-hydrated muscle fibers appear more rounded and defined. This effect is especially noticeable in the abdominal muscles. In addition, creatine prevents protein breakdown and promotes its regeneration.
- Increased internal secretion of testosterone and somatotropin - anabolic hormones.
- Partial neutralization of lactic acid, which contributes to the rapid rehabilitation of athletes after intense training and relieves pain in the muscles after strength training.
- Anti-inflammatory effect in arthritis.
- Reduced risk of ischemic diseases due to improved oxygen supply.
Side effects of creatine monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate is a generally safe substance that can cause side effects in only 4% of cases. All adverse reactions of creatine are reversible and are often caused not by the compound itself, but by the components included in creatine preparations.
Another reason for possible side effects may be the use of creatine in excessive amounts above the recommended levels. Side effects of creatine include:
- Swelling due to water retention in the muscles;
- Dehydration associated with partial dehydration (the bulk of the fluid accumulates in the muscles, causing an outflow of water from other parts of the body);
- Indigestion (gastrointestinal distress) - a reaction occurs when the dosage is increased;
- Convulsions (occur very rarely).
Do girls need creatine?
Currently, many girls go in for sports, which allows them not only to lose weight and keep their figure in shape, but also to achieve great results in various sports. Like men? girls supplement their diet with various sports supplements to improve training.
The following important features of using creatine for girls should be highlighted:
- Efficiency of training - with regular use of the supplement, the girl will gain additional endurance, which allows her to train more actively and for a longer time. Also, the female gender has additional strength, which also cannot be ignored.
- Promotes weight loss - the use of a summer substance allows you to exercise much more effectively, which in turn promotes the burning of fat cells and promotes weight loss. In addition, creatine preserves muscles and helps to acquire a beautiful body due to the relief of muscle fibers.
Some benefits of using this substance by women should be highlighted:
- Harmful cholesterol is removed, due to which the body is cleansed and all harmful toxins are eliminated.
- The likelihood of the formation of inflammatory formations of muscle tissue is reduced.
- Improves skin functioning
- There is a reduction in the risk of heart disease
- The metabolic process improves.
- It becomes possible to replace some types of meat products
The disadvantages include:
- Fluid retention in the body, which can negatively affect the overall health.
- Many people may experience individual intolerance to the product, which is manifested by stomach upset and other symptoms of poisoning.
- For many women, the use of this component contributes to an increase in body weight due to muscle tissue.
For the female body there is no need to resort to the use of special supplements. Depending on the required results, the girl can develop special programs for classes that will be aimed at intensive training of muscles of all groups and achieving the desired effect.
In addition to exercise, it is necessary to properly develop a special diet, which will be aimed at enhanced nutrition with fiber and proteins, which reduces the likelihood of fat cell deposition.
Types of Creatine
- Creatine monohydrate is popular among athletes who want to increase their muscle mass.
- Crealkaline - a mixture of pure creatine and alkali, helps neutralize the acidic environment in the stomach.
- Creatine ethyl ester is a combination of creatine and ester (creatine ethyl ester). Easily dissolves in fats thanks to the ester in the composition.
- Creatine anhydrous is simple creatine from which water molecules have been separated.
- Creatine phosphate - this form appeared at the same time as the substance creatine monohydrate. The right combination of creatine and phosphate molecules allows you to neutralize the effect of lactic acid, which is the cause of muscle fatigue.
- Creatine citrate is a form in which citric acid molecules are added to creatine molecules. It perfectly saturates the muscles with energy.
- Creatine tartrate is a form in which the molecules of creatine and tartaric acid interact.

There are various types of creatine on the modern market: creatine monohydrate, crealkaline, creatine ethyl ester, creatine anhydrous, creatine phosphate, creatine citrate, creatine tartrate.
Not all types of creatine are listed here, but only the most popular ones. It is also worth noting that athletes most often use creatine monohydrate, as it is most effective in increasing endurance and increasing muscle mass.
Interesting to know! The sports nutrition market today offers about two dozen types of creatine, but monohydrate is the most optimal type among the rest. It is not destroyed in water or in the stomach, is well absorbed and settles directly in the muscles.
Creatinine and creatine: what is the difference
Creatine is involved in the processes of energy metabolism and protein synthesis, but is not part of its structural composition. Creatinine is the end product of the creatine phosphate chemical reaction, which provides the body with natural energy.
It is formed as a result of the breakdown of creatine in the body. The concentration of creatinine in the blood depends on the rate of its formation (the state of muscle mass) and the characteristics of excretion by the kidneys. Also, creatinine levels can be affected by gender, weight, dietary habits, and the presence of inflammatory processes in the athlete’s body.
Elevated creatinine levels may be a marker that indicates kidney failure.
Application
Let's figure out how to take creatine monohydrate. Creatine can be taken on an ongoing basis, but it is more advisable to use it in the form of a course lasting 2 months and a recovery period lasting a month. On training days, it is recommended to take 5-10 g of creatine daily, before and after training, together with a protein shake or amino acids (in an amount of at least 5 g). On days without exercise, it is recommended to take the drug in the morning at the same dosage.
- We take a jar of creatine, no matter what brand (you will find the rating below)
- Pour plain water into a glass. Better, of course, not tap water, but something from a bottle.
Also, instead of water, you can take any drink with a high sugar content (Pepsi or Coca-Cola): sugar speeds up the absorption of creatine
- Take 5-10 grams of creatine powder and pour into water
- Mix thoroughly, very thoroughly.
- And we drink. We do all this 15-20 minutes before training and immediately after

Taking creatine is quite simple; you just need to dilute the powder in water or a sweet drink and drink it.
Creatine dosage and administration methods
Method No. 1. With loading
In this method, creatine is taken in courses that consist of two periods/stages. Loading period: Keratin in the first week is taken 5 grams in between meals (four times a day). On training days, one of the servings must be taken immediately after training (read below for the reasons for this). Maintenance period: The rest of the time, creatine is taken 5 g per day. On training days – at the end of training. And on rest days - in the morning. An individual approach is also possible. If for some reason standard doses are not suitable for you, you can use the formula for calculating the dosage of creatine, which is as follows:
- 300 mg/kg body weight during loading period
- 30mg/kg body weight during maintenance period
Method No. 2. Without loading
In this technique, the emphasis is on a uniform, stable intake of creatine. Creatine is taken once a day, 5-6 grams. As in the first method, on rest days it is recommended to take it in the morning, on an empty stomach, and on training days, immediately after training. If you take creatine, then (when using any of the methods) it is recommended to dilute it with sweet juice, add creatine to your portion of a gainer, or other sports supplement that you take. This will help improve the absorption of creatine by your muscle tissue and enhance its effect. If you prefer the capsule form, simply take creatine capsules in the dosage appropriate to the method, washing it down the same way as powdered form - with juice, or take the capsules directly after taking your sports supplements.
Do you need creatine during a steroid cycle?
Yes, and you need to take creatine during a course of anabolic steroids according to the instructions, i.e., taking into account the age category:
| Age | Quantity |
| Athletes under 22 years of age | No more than 3-4 grams |
| Athletes under 27 years old | Up to 8 g |
| For older athletes with extensive training experience | From 12 to 15 g |
The drug is drunk once or twice a day for 2-4 weeks. The daily norm is divided into equal volumes. After each course there is a mandatory break of 21 to 28 days.
When is the best time to take creatine?
The timing of taking any medicine or dietary supplement is, in most cases, a very important nuance that has a significant impact on the effectiveness of the drug taken. Creatine is no exception.
When is the best time to take creatine, according to experts?
Training Days Although commonly recommended, taking creatine immediately before training is far from optimal. This is due to the fact that:
- the body before training is much less “predisposed” to transport creatine into muscle fibers, since the energy balance in them is already normal.
- Creatine, due to the peculiarities of its principle of action, causes dehydration, that is, the removal of certain volumes of fluid from the body, which in no way contributes to high-quality training and harms, to a large extent, the cardiovascular system.
The same arguments make it inadvisable to take creatine during training. The optimal solution, according to all studies and personal observations of athletes, is to take it immediately after training. At this time, the state of skeletal muscles contributes to the most complete absorption of the supplement. Rest days On rest days, taking creatine is not limited in time, but experts still recommend taking it in the first part of the day, and preferably in the morning.
Duration of the course
The course of taking the drug can last up to one and a half to two months, after which it is advisable to take a break. This need is due to the fact that, despite the absence of any harmful effects, taking creatine on a regular basis does not bring benefits, and with long-term use of creatine without breaks, the body may become immune to the drug. Relationship Between Creatine and Food Although creatine generally does not have any dietary antagonists, it is still worth taking between meals. This is due to the fact that creatine is usually taken in combination with the so-called “transport systems” (these include various types of sports nutrition, carbohydrate-containing drinks, etc.)
Side effects
Along with the positive effects of the supplement, there are also a number of negative aspects. Of course, taking creatine rarely causes side effects. If they do occur, they pass as soon as possible. Numerous studies have shown that this supplement is natural and safe for the body. Moreover, in some experiments creatine was used in large dosages and for a long time. But even in this case, there was no danger to health.
However, it is still necessary to be aware of possible negative effects:
- Firstly, taking the supplement is very dangerous from the point of view of water balance. Studies have shown that creatine retains water in the body. This phenomenon is observed in almost all people who take the supplement for a long period of time. This phenomenon can be noticed only by external signs - the appearance of edema on the face, its swelling, and so on. To avoid problems from taking creatine, you need to drink enough fluid and never take diuretics (as some “experts” advise). In this case, even more harm can be done. As a rule, if creatine retains water, it is in small quantities;
- secondly, the process of dehydration occurs when part of the fluid remaining in the body passes to the muscle fibers. As a result, slight dehydration of the body is possible. To avoid this effect, it is important to provide the body with a normal volume of fluid (up to 2.5-3 liters per day). Many athletes who take creatine for cutting often ignore these recommendations. As a result, serious health problems arise;
- thirdly, digestive processes may be disrupted - diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, and so on. As a rule, an overdose of the drug can lead to this.

When and why should you not take creatine?
Creatine is considered one of the most harmless sports nutritional supplements on the market. But in rare cases, its use can cause discomfort such as dizziness, diarrhea and nausea. The restrictions on the audience for taking this drug are very minor:
- Creatine, like most types of sports nutrition, is not recommended for children and pregnant women.
- Also not recommended for allergy sufferers.
- According to some reports, it can cause exacerbation of asthmatic syndrome, so it is not recommended for use by people with this disease.

Creatine is contraindicated for use by children, as well as women during pregnancy and lactation.
If you are absolutely healthy and are in the audience for taking creatine, but are experiencing any side effects, try experimenting with the dosage and release form, as well as varieties. For any serious side effects, be sure to consult a physician.
What is creatine: chemistry, steroids or not

Creatine is a nitrogen-containing carboxylic acid that is present in the body of all vertebrates. Such a compound can be synthesized by internal organs from amino acids (arginine, glycine, methionine). However, the body receives the overwhelming dose of the substance from food. This type of food includes red meat; you cannot get creatine from plants.
An athlete weighing 80 kg needs approximately 2 grams of creatine per day. To obtain such a portion of the beneficial substance, you will need to eat at least 900 grams of beef or veal daily.
Interesting! Creatine was discovered back in 1832 by French researchers. But it wasn't until 1926 that the scientific community was able to prove the substance's important role in muscle building. Now this additive is approved for use by the Olympic Committee.
Creatine is one of the most studied and safest supplements. This is a natural substance that is produced daily in the body and consumed with food. This compound does not belong to chemical stimulants and steroid hormones.
Be sure to check out:
Shelf life and storage of creatine Is it possible to mix BCAA with creatine and what can this lead to? Creatine and protein: rules for taking it together How to take creatine and gainer together
Release forms and types of creatine
Creatine is available in two forms on the market: powder form and capsules. Capsules are more expensive due to the extremely complex production technology, but they are also more convenient for taking outside the home. Powder, on the contrary, is cheaper, but, as you understand, it must be dissolved before use, which is not always convenient (especially if you are away from home). However, this is where the differences end. The principle of action for both forms is similar.
Varieties
Today there are approximately 20 varieties of creatine. Despite this enormous abundance, the most popular forms of creatine are creatine monohydrate and creatine hydrochloride. The leader in popularity on the market is creatine monohydrate. Its effectiveness and efficiency have long been proven and have many confirmations in the form of scientific research.
Creatine hydrochloride, in turn, is one of the newest developments that claims to be of higher quality and effectiveness. However, these data have not yet been confirmed by official studies.
In general, as with any sports supplement, you need to choose what best suits your body.
How to take creatine monohydrate?
How to take creatine powder correctly? Creatine monohydrate in powder form should be taken by diluting it in liquids. Below is a sequential instruction:
- Measure out the required dose of creatine using the included measuring container, or using a regular teaspoon (a heaped teaspoon holds approximately 5 grams of creatine powder, which is equal to a standard single dose)
- Dilute a measured dose of keratin in one liter of liquid
- Stir the liquid thoroughly until the creatine monohydrate crystals are completely dissolved. If the container allows, you can stir the liquid with repeated shaking.
- Drink the resulting solution.

It’s easy to prepare the solution, but you shouldn’t stock it up, because... it is not characterized by long-term storage, it loses its properties.
A few additional tips:
- Do not leave creatine in a diluted state for a long time - creatine begins to decompose already at the time of preparing the solution, so it is important to prepare it immediately before taking it.
- As a liquid for dissolving creatine monohydrate powder, you can use water, juice or an energy drink with dissolved electrolytes. You can also add creatine to multi-ingredient sports shakes.
- Drink plenty of fluids after taking creatine. The effect of creatine is also associated with the absorption of liquids, so it is important to drink a large amount of liquid after taking the main solution.
- You can, without any worries, eat your usual foods, since creatine, as proven by many studies, has no dietary antagonists.
- To avoid unwanted effects, you should not drink strong coffee or alcohol after taking creatine.
How to take creatine capsules?
The principle of administration of creatine capsules is similar to creatine powder. The main difference is that it is significantly more convenient for reception outside the home. For example, taking a package of your favorite juice to the gym, you can drink a certain number of capsules (according to the dosage you choose) and immediately wash them down with the juice. Or take the capsules while taking your protein shake or gainer solution.
Instead of an afterword
Sports nutrition allows people of all age groups to stay in shape with a minimum of effort, but it is worth remembering that any medications, nutritional supplements and other substances coming from outside can harm our body.
You should always choose creatine responsibly. This is especially true for people who have any diseases and need constant medical support. If you belong to this category of people, be sure to consult your doctor. This is necessary to determine the feasibility and safety of taking creatine in your particular case. And about the compatibility of this supplement with your medications. Your doctor will also help you determine the required dosage and regimen for taking creatine. We should not forget about strict adherence to dosages, since any drug or dietary supplement in large doses ceases to be beneficial, and in most cases, even the opposite: it begins to cause harm to the body.

Creatine in capsules is just a convenient form of administration; you can always take it with you, but the main thing is to take it with enough water.
How much does creatine cost for muscle growth?
Creatine comes to the market in different forms: powder and special capsules. Powder versions are more popular due to their favorable price; capsules are on average 15-20% more expensive. The only drawback of the powder is the need to dissolve it before taking it, which is not always convenient.
Powder:

Muscletech, Essential Series, Platinum 100%, Creatine, Unflavored, 14.11 oz (400 g)
Price – RUB 1,299.09
Buy from a partner
Capsules:

Optimum Nutrition, Micronized Creatine Capsules, 2.5 g, 200 Capsules
Price – ₽2,240.52
Buy from a partner

MusclePharm, Assault Energy & Strength, Strawberry Ice 12.17 oz (0.76 lbs) (345 g)
Price – ₽2,044.33
Buy from a partner

EFX Sports, Kre-Alkalyn EFX, 240 Capsules
Price – ₽2,051.12
Buy from a partner

Optimum Nutrition, Creatine Fine, Unflavored Powder, 5,000 mg, 10.5 oz (300 g)
Price – ₽1,133.28
Buy from a partner

Now Foods, Sports, Creatine Monohydrate, 750 mg, 120 Vegetarian Capsules
Price – ₽662.13
Buy from a partner
Prices for creatine on average start from 1,000-1,500 rubles, depending on the packaging, the specific company and other factors. When purchasing, you should focus solely on your own budget and personal preferences, since different forms of the supplement are equally effective.
Cheapest on iHerb:

ALLMAX Nutrition, Creatine, Pharmaceutical Grade, 3.53 oz (100 g)
Price – ₽630.57
Buy from a partner
The most expensive:

Muscletech, Performance Series, CELL-TECH, The Most Powerful Creatine Formula, Grape, 6.04 lbs (2.74 kg) (Discontinued Item)
Price –
Buy from a partner

Now Foods, Performance Nutrition, Creatine Monohydrate, Pure Powder, 8 oz (227 g)
Price – ₽615.57
Buy from a partner

Kaged Muscle, Creaclear, Unflavored, 2.2 lbs. (1000 g) (Discontinued Item)
Price –
Buy from a partner
RSP Nutrition, Creatine Monohydrate Powder, 5 g, 10.6 oz (300 g)
Price – ₽631.36
Buy from a partner

ALLMAX Nutrition, CVOL, Post, Raspberry Kiwi Flavor, 13.2 oz (375 g)
Price – ₽2,271.62
Buy from a partner
Note! The most popular option is creatine monohydrate. It is inexpensive to produce and contains a high percentage of the active ingredient in one serving. This product can easily be purchased at your local sports supply store.
When choosing a suitable additive, it is worth considering not only the shape, but also the particle size. The smaller the grind, the faster the product will be absorbed. Some manufacturers add an additional portion of glucose to the powder for better absorption and ease of preparation.
At what age can you take creatine?
It is worth noting that scientists have not conducted research on the effects of creatine on children’s and adolescents’ bodies, and every trainer should remember this. But in theory, creatine is a natural protein substance, so people can consume it at any age. Even under the Soviet Union, children were given creatine from the age of 9, but young athletes 9-12 years old only need to take half the adult dose. The introduction of creatine into a child's diet should be done with caution, since neither the bones nor the internal organs of children are yet fully formed. Athletes taking creatine receive an extra dose of energy to improve their performance. Older people who lead an active lifestyle, thanks to creatine, forget their biological age, as they feel younger.
Can diabetics, pregnant women and allergy sufferers take creatine?
As mentioned above, creatine is a dietary protein supplement that can be consumed by almost everyone, without age restrictions. Should people with diabetes worry? According to doctors, nutritionists and athletes themselves, creatine is completely harmless for diabetics, provided that it is consumed without glucose. Not long ago, scientists conducted research and proved that creatine stimulates the production of insulin, and therefore can help patients with diabetes. You just need to regularly monitor your blood glucose levels, as it may happen that you have to reduce your insulin dose. But doctors do not recommend that pregnant women take creatine. Although studies in this regard have not been conducted, experts argue their refusal by the fact that the kidneys of pregnant women are already subject to increased stress. Moreover, the expectant mother is prohibited from heavy physical activity, which means the need for creatine is reduced to zero. Allergy sufferers are allowed to take creatine. There is only a small percentage of people who are allergic to creatine. As usual, people with allergies should avoid taking the supplement.
Which creatine is best to buy?
According to authoritative publications and websites dedicated to bodybuilding and sports, the top 10 best keratin preparations are as follows:
- SuperPump (manufactured by Gaspari Nutrition);
- naNo Vapor (manufactured by MuscleTech);
- NO-XPLODE Creatine (BSN);
- CM2 Alpha (from SAN manufacturer);
- Xpand (from Dymatize);
- Lava (from Universal Nutrition);
- Hardcore Musclebuilding Stack (manufactured by MuscleTech);
- GlycerGrow (manufactured by Controlled Labs);
- Storm (manufactured by Universal Nutrition);
- JetFUSE NOX (from German American Technologies).
The choice of a particular drug, the method of its use and dosage depend on the individual qualities of the athlete, his sports tasks and goals. Before using any drugs, it would be a good idea to consult with a trainer and a medical specialist. FAQ
What is Creapure® Creatine Monohydrate?
Creapure® is recognized as the “gold standard” among creatine monohydrate manufacturers. Creapure® is a branded creatine monohydrate manufactured in Germany and can be found in hundreds of creatine products sold worldwide. Finding out if your powder or capsules contain Creapure® Creatine Monohydrate is easy - just search for “Creapure®” in the product description.

Creapure® is the gold standard among creatine monohydrate manufacturers.
What is Micronized Creatine Monohydrate?
As the name suggests, micronized creatine monohydrate is just regular creatine monohydrate, but micronized. Micronization is the process of grinding powder particles to ultra-fine sizes, such particles are usually 20 times smaller than ordinary powder particles. This means that creatine will dissolve in liquids faster and, in theory, be easier for the body to absorb. If you've ever tried non-micronized creatine, you know that there is quite a bit of "grit" left at the bottom of the glass or shaker. This is not dissolved creatine. The creatine that the body needs, that should have ended up in the body, not at the bottom of the cup. Nowadays, most creatine monohydrate produced is available in micronized form. It is recommended to use a micronized product for best results.
Which is better?
Today on the sports nutrition market you can find many options for a nutritional supplement that is widely known and revered among sports fans, like creatine. With its pros and cons, it can rightfully be considered one of the most effective and actually working supplements. Having a number of advantages, it is simply indispensable for fans of bodybuilding, powerlifting and other strength sports. In fact, it is a natural energy drink. It increases strength characteristics and promotes faster recovery. And at the same time it has no pronounced disadvantages. But which creatine capsules are best? How to choose from the many proposals the option that will be most effective?
Today on the sports nutrition market you can find many options for this sports supplement. In turn, this confuses athletes. After all, they are forced to study this entire range, compare and spend a lot of time finding the optimal solution for themselves. In fact, everything is not that difficult. Today, the best and most effective is monohydrate. Its effectiveness has been tested by time and the experience of many athletes.

Creatine monohydrate can be found in several versions. These are tablets, capsules and powder. Which one do you prefer? Each of these options has its own advantages. Capsules and tablets are more convenient to take. No need to think about what to dissolve them in. This is especially true if you take the drug with you to the gym for training. As for creatine powder, the dosage is important. If it is already dosed in tablets or capsules, then in the case of powder it must first be measured. So sports nutrition with creatine in tablets and capsules is more practical.
But it is worth noting that in powder form, sports nutrition is absorbed faster. After all, the body receives a ready-made product. And in the case of capsules, it takes time to break it down. Creatine tablets are also not absorbed as quickly as powdered ones. After all, tablets contain binders (due to which the tablet retains its shape). They slow down the absorption time of the substance. The main thing is that the risk of side effects from creatine after use is quite low.
It is also worth noting that the price for the drug in capsules and tablets is higher than for the powder version. So if you only take creatine at home and don't take it with you to the gym, then the powder form is the best option. And remember, the best absorption of creatine occurs in the presence of insulin. Therefore, it is better to drink it with sweet juice.
Does caffeine affect creatine?
According to Creapure, one of the most respected manufacturers of creatine monohydrate in Germany, large doses of caffeine can impair the results that could be achieved by consuming creatine. But small doses of caffeine, such as those found in coffee and many pre-workout blends, are fine. Here's a quote from their website: “Consumption of large doses of caffeine (5 mg per kilogram of body weight per day) negates the performance-enhancing effects of creatine supplementation. Small doses of caffeine (contained in 1-2 cups of coffee) have no visible effect on the effect of creatine."

Consuming large amounts of caffeine may impair the functionality of the supplement and reduce the expected results.











