press - Bodybuilding with a scientific approach to training the abdominal muscles
06/16/2016 Training
You can't build a strong, muscular body without beautiful, strong abdominal muscles. Learn the anatomy and function of the abdominals to achieve the physique of your dreams.
When people talk about abs, they usually mean abs. In fact, the abdominal muscles, thanks to which the external relief appears, are located deep inside the body. Now we will learn how these muscles work and why they are so important for building a beautiful body.
In this article you will find a lot of information about what the core muscles are and what functions they perform. You will understand how exactly their coordinated work develops strength and endurance in a person, because it is these muscles that give us the opportunity to lift heavy weights. The condition of your abs is of great importance, so you need to plan your workouts wisely, devoting enough time to abdominal exercises. And for this to happen, you need to know the anatomy of the muscles and approach this issue from a scientific point of view.
Abdominal muscle anatomy
Although the abdominal muscles are deep and cannot be seen (unlike abs), let's still go to the mirror and carefully look at our stomach.
Upper muscles
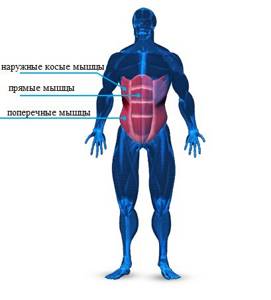
These are the abdominal muscles located in the front of the abdomen. They consist of three layers: a deep layer, an intermediate layer and a superficial layer.
Deep layer
These three muscles always work together. Due to this, the internal relief of the muscles is built. Thanks to the deep muscles, we can do deadlifts, squats and dumbbell presses.
Diaphragm
The diaphragm is not involved when performing strength exercises, but this does not detract from its advantages. It is very important for breathing. The diaphragm begins at the front of the chest, encircles it, and converges at the lower back.
Pelvic floor
The pelvic floor consists of the muscles located below the level of the pelvis. When you take a deep breath, the diaphragm lowers and the pelvic floor holds the breath. The diaphragm and pelvic floor are the main parts of the body that stabilize the spine.
Transverse abdominis muscles
The transverse muscles are located slightly below the oblique muscles. They provide stability to the pelvic floor, keeping it immobile. The transverse muscles are located directly on the linea alba - the connective tissue that runs exactly down the middle of the torso and adjacent to the lower back.
Intermediate layer
The intermediate layer is located between the deep and superficial layers. It is made up of several muscles, but the most important is the internal oblique.
Internal oblique muscles
These muscles originate from the linea alba, a vertical line in the middle of the torso, and attach to the femur. They run perpendicular to the external oblique muscles. The main functions of the internal oblique muscles are to regulate breathing and rotate the torso.
Surface layer
These muscles are familiar to everyone. If you are thin enough, you do not have large reserves of subcutaneous fat - you can even see it. These are the so-called “abs cubes”.
External oblique muscles
The external obliques run from the chest to the hips. Many of us believe that thanks to these muscles we can turn and tilt our body, this is a true statement, but not entirely complete. Also, the external obliques are muscles of stability and balance.
The external oblique muscles help stabilize the pelvis. Some people have a tendency to push their hip bones too far forward, thereby arching their lower back. This is very harmful: it creates strong pressure on the spine. Thanks to the external oblique muscles, the pelvis restores balance by tilting back and returning to a neutral position.
Rectus muscles
The rectus muscles originate from the pubic bone. Further, their locations are the 5th, 6th, 7th vertebrae and the lower part of the chest. These areas are separated vertically by the linea alba and 3-4 layers of connective tissue horizontally. These divisions create 6 or 8 separate abdominal muscles, which we call “abs.”

Posterior muscles
The core muscles are not only the front muscles, but also the back ones. It's important to know what's going on on our backs. We'll focus on three specific muscle groups in this section: multifidus, quadratus lumborum, and erector spinae.
Multifidus muscle
The multifidus muscle is a group of small muscles that span 2-4 parts of the back. You may never see them, but they are important because they provide feedback to your brain about where your body is in space. These muscles also help control the position of the spine.
Quadratus lumborum muscle
This large muscle runs from the upper thigh to the lower back. It is responsible for lateral tilts of the body, as well as for preventing these very tilts. The quadratus muscle is essential for controlling body movements.
Erector spinae muscle
This group of muscles starts from the sacrum and upper thigh and connects to the rib cage, upper neck, and even the base of the skull. Muscles are important for regulating movement during squats and deadlifts.

Abdominal trainers: expander and roller
One of the most effective and affordable exercise equipment for training the abdomen and abs at home is an expander and a roller.
Exercises for a flat stomach
An expander is a device based on a special tight tourniquet covered with rubber. The action is based on stretching the expander using special handles. This simulator allows you to pump up many muscle groups, including the abdominal area.
To train the abdominal muscles, you need to take a lying position with your knees bent, fix one handle of the expander horizontally between your legs, take the second with your hands and pump up your abs by squeezing and unclenching the exercise machine.
The roller is a simulator for the abdomen and press in the form of a wheel with a central axial rod. The edges of the rod are held with hands on both sides. There are lightweight models for training with two rubberized wheels, which are more suitable for independent training at home.
Important! Classes with a roller require more effort and are suitable for creating relief during more in-depth training. They are aimed at maintaining balance and stretching the body along the floor while rolling the roller.
Skeletal structure in the abdominal area
Often we don't even think about the importance of bones in our body, focusing all our attention on the muscles. But bones and cartilaginous joints are of great importance for the development of muscle tissue.
Pelvis
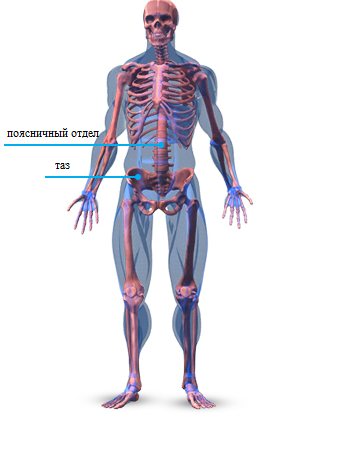
The pelvis has two main movements: a forward tilt, in which the hips move back, and a posterior tilt.
Lumbar
The lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae located between the rib cage and pelvis. It affects the lumbar curve (movement forward, backward, lateral bending, rotation of the torso).
You can feel how important all these movements are during training: the resistance force holds the spine in place and prevents the vertebrae from bending. The lumbar region is not particularly flexible except for forward and backward bending, so the more you can control or resist the movement, the healthier and stronger your back will be. And this is the first and, perhaps, main condition for strength exercises.
About professional and home exercise machines for the abdomen and abs
Exercise machines allow you to thoroughly work out your abdominal and abdominal muscles. Professional equipment is used in gyms and health centers under the supervision of experienced trainers and requires adherence to a clear individual training program. It has high strength and is designed for heavy loads, has a long service life, but is very expensive and has quite large dimensions.

Abdominal trainers
For home use, small but no less effective devices are used, which are suitable even for inexperienced people without sports training; they allow you to independently tighten your abdominal muscles according to an individual training program. Such devices can be purchased at a sports store or made with your own hands at home from available materials.
Advantages of home abdominal exercise machines compared to professional ones:
- minimal expenditure of money and time on visiting the gym;
- the ability to independently choose the regularity and complexity of the loads;
- absence of unauthorized persons during training;
- convenience of individual use of a clean device.
Among the wide range of modern abdominal exercise equipment used at home, the most popular are: expander, parallel bars, abdominal bench, roller, as well as electrical stimulators for the abdomen and abdominal muscles, and other exercise equipment.
Functions of the abdominal muscles
Below are the functions performed by the core muscles. Some of them are probably already familiar to you: squats, body bends. It turns out that the task of muscles is not only to flex and extend parts of the body. Here are the main five functions of the abdominal muscles:
Intrathoracic pressure
Take a deep breath and hold your breath. In this case, the diaphragm begins to put pressure on the pelvic floor and the transverse abdominal muscles. It is this process that is so important for maintaining the strength of the spine, and also allows us to perform exercises such as squats, deadlifts and various presses.
Anti-extension
Most people, especially those who have just begun their acquaintance with fitness, believe that the abdominal muscles, like the spine and back, are given to us only for bending the torso. Now try leaning back? Does not work? This is because our spine is securely secured by the rectus abdominis and oblique (external and internal) muscles to prevent sagging and curvature.

Lateral flexion and anti-lateral flexion
The internal and external oblique muscles help us bend in different directions. This is lateral bending. In addition, it is the oblique muscles, as well as the quadratus lumborum muscle, that perform the function of anti-lateral flexion. This is necessary to maintain the spine in a neutral position and maintain balance. Imagine you are carrying a heavy bag. One side of the body takes on the entire load and makes further movement possible, while the other has to maintain balance so that you do not fall on your side.
Anti-rotate
The rectus abdominis, transverse and oblique (external and internal) muscles are responsible for turning the body to the sides. They not only help rotate the body, but also prevent uncontrolled movements and keep the torso in a straight position. This muscle function is very important, especially when lifting weights with one arm.

Anti-bending
Abdominal exercises are a prime example of flexion. We can all bend forward – it’s natural. But if you're doing barbell squats or deadlifts, it can be difficult to keep your balance without falling on your face. Thanks to the abdominal muscles, our torso is able to maintain position without loading the spine.
Features of training
The abdominal muscles are one of those muscle groups that are difficult to work on, and it is in this area of the body that fat deposits accumulate. A thick layer of subcutaneous fat hides muscle relief, and even in trained people, six-pack abdominal muscles are visible only when the amount of subcutaneous fat does not exceed 10–12% .
- Perform 2-3 exercises twice a week, each in 3-4 sets, with a maximum of 10-20 repetitions. The principle “the more often the better” is not suitable for the stomach! Due to excessive load, the abdominal muscle wall thickens and its relief becomes blurred, but the abs do not become stronger.
- Learn the correct technique from photos and videos, perform the exercises consciously, feeling how the muscles stretch and contract, and you will get more benefit from the exercises.
- For 30–60 seconds, fix the position of the body at the point of highest tension. Return to the starting position slowly, without jerking. When you feel that you no longer have the strength to continue, repeat the exercise through force (“to failure”), and then several times partially, at half the amplitude.
- Make a chart of your workouts and record how many reps and sets of different exercises you do. It will help you evaluate your successes and see your shortcomings.
Monotonous abdominal exercises can be done between sets of other exercises. If you are a beginner athlete, don't get carried away with dumbbells and hold off on block exercise machines. To gain abs of steel, it is enough to exercise with your body weight, but at the same time there is less chance of getting injured.
Basic abdominal exercises
Now that we have studied the structure of the skeletal skeleton and muscles, and also understood the biomechanical processes of the core muscles, it’s time to apply all this knowledge experimentally. Here are a few basic exercises that require no special training and will allow you to get the most out of it.
Exercise #1 – TRX loops
The TRX is a very effective machine that can give you rock-hard 6-pack abs and improve your balance. Many people have completely untrained lower backs, as this is a rather difficult place to work the muscles. Therefore, they need additional measures to compensate for the tension and create the best balance of the anterior and posterior muscle groups.

Starting position – stand up straight, fasten the loops on your hands. Exhale, tense your body muscles.
Then bring your arms together vigorously in front of you. Watch your back - it must be straight!
This exercise works the rectus abdominis, internal and external abdominal muscles. The spine, neck and upper back are actively trained. You can control the strength and intensity of the movements yourself, which is very convenient.
Exercise No. 2 – dead beetle
The exercise perfectly works the abdominal muscles without putting unnecessary stress on the lower back.

Lie on your back, raise your arms up. Then lift your leg at a 90-degree angle and, at the same time, lift your opposite arm. Hold the top position for a bit and return to the starting position. Please note: your back should be pressed tightly to the floor, no need to rise. Try to touch your heel, stretch the muscles.
Exercise No. 3 – Pallof press
This is a great exercise to strengthen your oblique abdominal muscles. Allows you to control the rotation of the body to the sides.

To perform this you will need an expander with a handle for your hands. The challenge is to do a forward press with a pulley at your side. Take the handle in your hands and begin to pull forcefully towards yourself. This is not easy, the force of resistance will actively hinder you. The quadratus lumborum muscle, transverse, internal and external oblique abdominal muscles are well worked out. Hold the handle against your chest for 20-30 seconds, then return to the starting position.
Exercise #4 – One Arm Deadlift
The one-arm deadlift is a very useful exercise for improving balance. Take one dumbbell and stand straight. Bend forward, holding a dumbbell in one hand and squeezing your abs. Then return to the starting position. Gradually make the exercise more difficult by bending down as low as possible.

Since the weight is on one side, you will have to make every effort to maintain balance. This exercise is also great for increasing your strength and developing endurance. The oblique muscles and quadratus lumborum muscles are involved.
How much time should you devote to the press?
Abdominal training does not take much time. It is enough to do only 2 exercises. By doing 4 sets (20-50 crunches), you will provide the rectus muscle with a good load. The interval between approaches should be no more than 1 minute. Daily exercises allow you to achieve amazing results. The abs are being restored right before our eyes! To increase the load, you need to speed up the pace. The faster the speed of twisting, the greater the load the muscle experiences.
There are other exercise options for the rectus abdominis muscle. Some experts advise doing the “bicycle” exercise. But in order to get sculpted abs, it is enough to perform basic crunches.
Tips for doing exercises
- Focus solely on the exercises, do not be distracted by thoughts (especially any negative ones).
- Perform the exercise “without departing from the instructions.”
- Don’t be lazy to do the exercises well : you do them for yourself, and not to report to laziness.
- There is no need to be lazy: learn and get used to performing absolutely all exercises (of any difficulty level) exactly “on schedule”.
- Do not be distracted by cell phone calls or conversations : a break between classes is highly undesirable.
- Drink plenty of fluids (not including carbonated drinks). You can have coffee, tea, water, mineral water, juices, fruit drinks, cocoa, compotes.
- Do not open the window or window during class.
- Remember: the main thing is not how much exercise you do, the main thing is how you do it. (it’s better to do three high-quality exercises than thirty-five low-quality ones).
Abdominal exercise video
How to pump up your abs correctly
Crunches with legs raised

This exercise works the rectus abdominis, external oblique, quadriceps, and tensor fasciae lata (thigh muscles). This exercise is more aimed at burning fat, rather than working out the relief.
Performance. Lie on the floor, raise your knees bent (the angle should be 90 degrees), stretch your arms in front of you. Raise your upper body towards your knees, reaching forward with your arms. Exhale while going up, and inhale when going down. Try not to lift your lower back off the floor or lower your legs. Make sure that your chin is not pressed against your neck.