What is fiber
Natural fiber is a coarse fiber of plant origin.
It is found in many products. The pulp that remains after making juices is fiber. There are two types of fibers: soluble and insoluble. Each food product has an individual ratio of the listed types of fibers. Some contain more insoluble fiber, while others contain more soluble fiber. The role of insoluble cellulose is to systematically cleanse the intestines. Soluble fibers absorb carcinogens, cholesterol, heavy metals and other harmful substances that stimulate the development of cancer cells in the human body . Food that does not contain coarse fiber lingers longer in the body, which can provoke fermentation in the stomach, which in turn creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Foods rich in soluble fiber for weight loss:
- apples;
- cabbage;
- citrus;
- wholemeal flour;
- berries;
- seeds.
Foods rich in insoluble dietary fiber:
- legumes;
- grain crops;
- peel of vegetables and fruits.
Eat whole grain cereals
Whole grain products are minimally processed, so they contain many times more fiber. Grains that have been peeled contain less hull. Such products have a longer shelf life, but lack nutrients and are a source of fast carbohydrates.
Therefore, it is recommended to include whole grain cereals in the diet, including:
- Barley.
- Oatmeal.
- Brown rice.
- Buckwheat.
- Bulgur.
- Millet.
- Wheat grains.
- Freekeh (farik) is a cereal made from young wheat.
Benefits for weight loss
In order to lose excess weight, many people prefer diets based on foods high in fiber. They have a beneficial effect on the entire body as a whole. Benefits of fiber for weight loss:
- Acceleration of metabolic processes and digestion.
- Restoration of intestinal microflora.
- Reduces blood sugar levels, which prevents fat deposition.
- Cleansing from waste, toxins, gastric and intestinal mucus (cellulose is a natural absorbent).
- Reducing the risk of developing colon cancer.
- Restoring proper functioning and activating intestinal motility.
- Ensuring a long-lasting feeling of fullness (when it enters the stomach, fiber swells, which creates a filling effect; foods rich in fiber are a great way to satisfy hunger).
Use fiber supplements
If the body gets fiber from food, this is an ideal option, but it is not always feasible in real life. Therefore, you can increase the amount of plant fiber in your diet with the help of nutritional supplements.
Scientists have found that the most beneficial supplements are:
- Guar fiber. It promotes rapid saturation and allows you to reduce daily caloric intake.
- Psyllium is the main component of Metamucil (fiber used to relieve constipation). Its inclusion in the diet helps suppress the feeling of hunger, which has been confirmed experimentally [2].
- Beta glucans. They are found in barley and oats. Once in the intestines, beta-glucans are fermented, act as a prebiotic and improve intestinal microflora.
- Glucomannan. It is found in some 0% fat dairy products and also acts as a base for shirataki. Its inclusion in the diet can reduce appetite and speed up the onset of a feeling of satiety.
Nutritional supplements should be taken only if the menu is truly deprived of fiber. Otherwise, they will provoke flatulence and intestinal discomfort. To reduce bloating, you need to drink less water.
Fiber can slow down the absorption of some medications, so supplements are taken an hour before or 4 hours after taking medications.
Fiber-rich foods
Below is a table that lists fiber foods. It will help you plan your diet to lose or maintain weight. For convenience, products rich in fiber for weight loss are divided into categories, and the table also shows the amount of cellulose in grams in a specific quantity of product:
| The product's name | Amount of fiber, grams | Serving Size |
| Fruits | ||
| Grapefruit | 12,3 | 1 medium |
| Avocado | 11,8 | 1 medium |
| Raspberries | 8,3 | 1 cup |
| Pear | 5,1 | 1 medium |
| Apple with peel | 5,0 | 1 average |
| Blueberry | 4,2 | 1 cup |
| Strawberry | 4,0 | 1 cup |
| Banana | 3,9 | 1 medium |
| Dried date | 3,7 | 2 pieces |
| Orange | 3,4 | 1 medium |
| Dried peach | 3,2 | 3 pieces |
| Dried apricot | 2,9 | 5 items |
| Peach | 2,0 | 1 medium |
| Raisin | 1,6 | 40 grams |
| Plum | 1,0 | 1 medium |
| Apricot | 1,0 | 3 medium |
| Vegetables | ||
| Peas | 8,8 | 1 cup |
| Cabbage | 7,2 | 1 cup |
| Potatoes baked in their jackets | 4,8 | 1 medium |
| Corn | 4,7 | 1 cup |
| Broccoli | 4,5 | 1 cup |
| White cabbage | 4,2 | 1 cup |
| Cauliflower | 3,4 | 1 cup |
| Onion | 2,9 | 1 cup |
| Beet | 2,9 | 1 cup |
| Brussels sprouts | 2,8 | 1 cup |
| Zucchini | 2,6 | 1 cup |
| Bell pepper | 2,6 | 1 cup |
| Pumpkin | 2,5 | 1 cup |
| Carrot | 2,0 | 1 medium |
| Celery | 1,1 | 1 stem |
| Tomato | 1,0 | 1 medium |
| Cereals, pasta | ||
| Bran bread | 20,0 | 1 cup |
| Oats | 12,0 | 1 cup |
| Brown rice | 8,0 | 1 cup |
| Whole grain pasta | 6,4 | 1 cup |
| Whole wheat bread | 2,0 | 1 slice |
| Beans, nuts, seeds | ||
| Lentils | 15,6 | 1 cup |
| Black beans | 14,9 | 1 cup |
| Beans | 13,3 | 1 cup |
| Soybeans | 7,6 | 1 cup |
| Flax seeds | 6,9 | 60 grams |
| Chickpeas | 5,8 | 1 cup |
| Almond | 4,2 | 30 grams |
| Pumpkin seeds | 4,1 | ¼ cup |
| Pistachios | 3,1 | 30 grams |
| Walnut | 3,1 | 30 grams |
| Sunflower seeds | 3,0 | ¼ cup |
| Peanut | 2,3 | 30 grams |
| Cashew | 1,0 | 30 grams |
Considering all the variety of food, it is quite reasonable to ask the question: where is the most cellulose? The following are foods that are high in fiber:
- Whole grains (oatmeal, buckwheat).
- Berries and fruits (apples, blackberries, grapes, raspberries, peaches, pears, watermelon, plums).
- Vegetables rich in fiber (green peas, broccoli, carrots).
- Nuts and dried fruits (almonds, dates).
Fiber and bran: are they the same thing or not?
Those who try to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right know how important dietary fiber is for the body. Their main sources, fiber and bran, are considered by many to be one and the same product.
But this opinion is wrong. Both ingredients are extracted from plants and provide similar benefits to the body, but there are differences between them. Fiber is just one of the components of bran.
What is fiber

Cellulose is a polysaccharide. In its purified form, it is a carbohydrate without any foreign impurities. However, in practice it is not so highly refined, so it contains other compounds (proteins, fatty acids) in small quantities.
The substance is included in the group of dietary fibers, since a significant part of it is not absorbed by the body. Only a small proportion of cellulose derivatives (soluble fiber) is broken down.
The main benefits of dietary fiber:
- activation of intestinal function;
- cleansing the body of waste and toxins;
- reducing the feeling of hunger due to swelling in the stomach.
These substances are found in all plants in varying quantities. Cereals and legumes, vegetables, herbs, fruits are rich in them, and they are also found in nuts.
List of allowed foods during pregnancy
Coarse dietary fiber in the diet of young mothers is a prevention against constipation and obesity . The daily fiber intake for pregnant women should not exceed 30 grams. This amount is quite enough for stable blood sugar levels and regular bowel movements. Follow these tips for consuming cellulose during pregnancy:
- Focus on fresh vegetables and fruits, without removing the skins.
- Give preference to whole grain bread.
- Prepare dishes from peas and lentils.
- Consume rice, rye or wheat bran regularly.
While breastfeeding, carefully monitor your baby's reaction to each product in your diet, as your baby may have an individual intolerance. During this period, you should avoid foods high in fiber:
- beans;
- dill;
- Bell pepper;
- broccoli;
- brown rice;
- corn;
- soy;
- wholemeal flour.
Instead, eat foods from the following list:
- porridge with water;
- plums;
- potato;
- beet;
- prunes;
- pears;
- peeled rice

Include vegetables in your meals
To ensure that the body does not experience a deficiency in plant fibers, the menu should contain a lot of vegetables. Their beneficial properties:
- Reduce blood cholesterol levels.
- Contains few calories.
- They are a source of vitamins and microelements.
It is better to eat vegetables before meals, which has been proven experimentally. A group of women were asked to eat a vegetable salad first, and then other dishes. As a result, they began to eat 23% more vegetables during each meal [1]. At the same time, the total calorie content of foods eaten during the day decreased.
How to use for weight loss
Despite all the benefits of high-fiber foods, over-consuming a fiber-based diet can negatively impact a person's health. The daily norm of cellulose is 30-40 grams. This can be fiber in food or dry fiber, which is sold in pharmacies. If you exceed the norm of dietary fiber, along with harmful substances, beneficial substances will also begin to be removed from the body. Increased gas formation and bloating will be added to this point.
American nutritionist Julia Upton from the Health Association has developed a number of simple rules that will help you navigate your daily fiber intake for weight loss and weight loss:
- 800 g of fresh vegetables and fruits with skin provide up to 20 g of dietary fiber every day.
- An additional 5-7 g will come from porridge made from barley, buckwheat, oatmeal, and brown rice.
- Another 5-6 g contain 100 g of whole grain bread.
- Introduce lentils, peas or beans into your diet twice a week.
- Do not use confectionery sugar, replace store-bought sweets with dried fruits.
- For small snacks, eat nuts and seeds (up to 40 g per day).
- Eat steamed bran (up to 6 tablespoons per day).
For good digestion of food and weight loss, fruits should be eaten in the first half of the day. Nutritionists recommend giving up the habit of drinking water. It is important to remember that a quarter of the daily menu should consist of salads, another quarter - fruits, the same amount - vegetables, fresh or cooked, a tenth - cereals and legumes, the same amount - milk, dairy products, nuts, a twentieth - vegetable fats.

Looking for foods high in fiber
The list of such products is quite long, so do not rush to buy special dietary supplements at the pharmacy. With proper organization of the diet, even dietary food can be varied and tasty; the main thing is to introduce such products in stages, determining the body’s reaction.
The undoubted leader among products in terms of dietary fiber content is bran. There are a lot of them in legumes, mushrooms, cereals, seed products, nuts, fruits, dried fruits, vegetables and berries. Below is a list reflecting the amount of fiber per 100 grams. product.
So, foods rich in fiber - table 1.
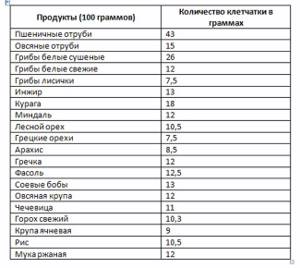
For your convenience, the fiber content in vegetables, fruits and berries is shown in Table 2.
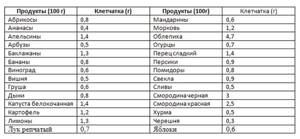
There is practically no dietary fiber in flour products, animal fat, vegetable oil, fruit and vegetable juices, meat and fish. And this is not a reason to completely abandon their use in favor of coarse plant foods, but you can gradually replace wheat bread with whole grains, and instead of sweet juices, make cocktails with the addition of fruits and berries.
What are the dangers of a lack of fiber in foods?
To maintain health for many years, you need to adjust your diet so that the body receives all the necessary substances, and fiber should be present in food daily.
For many years, the role of coarse dietary fiber was underestimated, and only relatively recently did scientists around the world come to the conclusion that food must contain fiber, otherwise a person cannot avoid serious diseases. Let's look at what diseases are threatened by a lack of fiber.
- Intestinal diseases accompanied by constipation, intestinal atony, spastic colitis, dysbacteriosis, hemorrhoids;
- Atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, threat of heart attack and stroke;
- Formation of gallstones;
- Diabetes;
- Obesity;
- Rectal cancer.
Products containing fiber
Foods rich in fiber are bran, dried fruits, legumes, mushrooms, cereals, wholemeal bread, nuts, vegetables, berries, and fruits. By consuming all these products regularly, you can get the amount of fiber necessary for the body without resorting to special supplements containing it. Now such drugs are very relevant and are sold in pharmacies, but it is still better to give preference to natural products, their health benefits are much greater. But bran deserves to be discussed in more detail.
Bran
Bran is a unique product that prevents and heals many diseases, but for some reason is not popular with most of us. The benefits of bran have been proven, and you can now buy them at any pharmacy or in the health food departments of large stores. Bran can be wheat, rye, rice, oat, corn, barley. All of them have nutritional value, as they contain a large amount of fiber, which cleanses our body.
In addition to the fact that bran has an absorbent effect in the intestines, which in itself has invaluable benefits, bran contains a lot of useful substances, including B vitamins, vitamin E, carotene, and nicotinic acid. Bran contains minerals, such as potassium, magnesium, zinc, chromium, selenium, copper and others.
It is recommended to steam the bran with hot water before use. After cooling, the water should be drained, and the remaining softened bran should be eaten before meals, washed down with water.
You need to introduce bran into your diet gradually, starting with half a teaspoon, so as not to provoke bloating and other unpleasant intestinal dysfunctions. Gradually, over several weeks, you can increase the amount of bran introduced into the diet to a tablespoon three times a day.
Pharmacies sell bran in the form of crispy balls; this is a ready-to-eat product; they do not need to be steamed, but simply eaten according to the attached instructions. Such bran is often enriched with various vegetable additives to increase their value; I have come across bran with carrots, seaweed, Jerusalem artichoke, and blueberries.
Since bran has the ability to cleanse the body of everything foreign, you should not take medications at the same time as bran. There should be at least 6 hours between taking the medication and consuming the bran.
If you want to know more about the benefits of bran, you can read my articles
Wheat bran for health and weight loss Oat bran for our health

Cereals
One of the important suppliers of fiber are cereals, such as buckwheat, brown rice, millet, and oatmeal. It is important to eat whole grains, and the instant foods that are so popular and convenient to eat are processed in such a way that they do not contain coarse dietary fiber, and therefore dishes made from them are not as valuable as those made from whole grains.
Vegetables and fruits
A good supplier of coarse plant fibers are vegetables and fruits, which should be present on our table every day. It is very important to eat vegetables raw, thereby getting the maximum fiber from them. It is clear that this is not always possible, and not all vegetables can be eaten raw, but cabbage, carrots, sweet peppers, celery root, radishes, turnips, rutabaga, daikon, leeks, all leafy vegetables must be added to salads raw form.
There is a lot of fiber in the peel of fruits. As for apples, you need to take into account where these fruits grew, and in the season when local apples appear on sale, they should be eaten without peeling so that the body receives as much pectin as possible. This does not apply to imported apples; the peel must be cut off, since all apples that will undergo long-term transportation and storage are treated with special substances that are not harmless to us.
If you like fruit and berry juices, then try to squeeze them with pulp, which contains a lot of fiber, but it is still healthier to eat whole fruits, receiving much more useful substances for your body. It is right to eat sweet fruits before meals or an hour after meals, so they give maximum of their benefits.
Dry fiber for weight loss. For weight loss

This is the kind of madness people usually reduce their diet to
So, how to take fiber correctly for weight loss. So, let’s debunk the ancient myth; in fact, fiber does not contribute to weight loss.
It is traditionally recommended that those who are obese or overweight increase the amount of fiber in their diet, with the expectation that fiber-rich foods will make you feel fuller and keep you fuller longer.
Let us remember that fiber is not digested by enzymes in the human stomach, but can be broken down under the influence of intestinal microflora in the intestines.
For those who want to lose weight, a whole bunch of “healthy” products enriched with dietary fiber are produced, including various bars that should satisfy hunger quickly and for a long time, but supposedly do not have a very high energy value.
Read about it in detail:.
However, according to a study published online in July 2012 in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, eating these foods does not help you stick to your diet. It is a pity that the study is not large-scale.
To determine how fiber affects the volume and energy value of a person's food intake, scientists asked 22 healthy young women, who had no dietary restrictions at the time of the study, to eat specially made sweet bars every day.
Of the 5 varieties offered, 4 contained various dietary fibers and 1 was a regular candy bar.
Each type of sweet was offered to women after dinner and then after breakfast the next day. After this, the women had lunch in the research laboratory, where they rated their feelings of hunger, fullness, and “full stomach” on a standard scale. In addition, a list of all foods eaten during the day was recorded.
It turned out that both on those days when women ate exclusively “healthy” sweets, and on other days, the volume and energy value of the food they consumed practically did not change. So it doesn’t matter whether you eat chocolate or “healthy” fiber sweets. Horseradish is not sweeter than radish.
In addition, by interviewing study participants, it was found that such bars did not create an additional feeling of fullness in them and did not in any way affect the feeling of hunger. Among the side effects, mild bloating and flatulence were noted, which were complained about mainly after consuming fiber.
Conclusion: Having fiber in your diet alone will not help you lose weight.
And by the way, vegetables themselves don’t really help with weight loss. Many people who are losing weight follow the recommendation to “eat more vegetables” too zealously and begin to look like rabbits. You just need to supplement your diet with vegetables, and not cost it on them!
American scientists undertook to test the effectiveness of the basic recommendation of nutritionists - “to lose weight, eat 1-5 servings of fruits and 2-3 servings of vegetables every day.”
More than a thousand people took part in the study. His results showed that such diets are not as effective as expected. The study compared a “plant-based” diet with a Mediterranean diet based on olive oil, meat and seafood. It turned out that the second one worked better.
Moreover, heart patients who followed the Mediterranean diet were 30% less likely to experience a heart attack. Katherine Kaiser, the head of the research group, argues that simply replacing regular foods with vegetables and fruits that contain high amounts of dietary fiber is not effective.
The conclusion suggests itself: now the main attention is paid to vegetables and fruits, and other equally important elements of the diet are often forgotten. There is no need to give up other foods in favor of vegetables, it won’t do much good, but hunger and stress - 100% yes.
Which is healthier?
It all depends on what goals a person pursues:
- If you need to saturate your body with nutritional components, then it is definitely better to purchase bran. With a stable weight, they can be included in baked goods, added to porridge, and prepared in cocktails. From a nutritional point of view, this product is much healthier.
- If the main goal is cleansing the intestines and losing weight, then you should give preference to fiber. It is lower in calories and needs to be eaten in smaller quantities.
You can first practice a diet using cellulose, and after getting rid of extra pounds, switch to eating crushed shells.
Health Benefits of Dietary Fiber
You may have heard that adding fiber to your diet can improve your gastrointestinal health.
Indeed, dietary fiber has many beneficial effects on your gut, such as increasing stool mass, reducing constipation, and feeding beneficial gut bacteria.
High-fiber foods are also richer in vitamins, minerals and antioxidants than low-fiber foods such as refined grains. Plus, they may even help you lose weight ().
Improves digestion and intestinal health
Dietary fiber plays many different roles in gut health.
Insoluble fiber helps relieve constipation by adding bulk to stool, while the gel-like consistency of soluble fiber helps move food more easily through the digestive tract ().
One study of more than 62,000 women found that those who ate at least 20 grams of dietary fiber per day were much less likely to experience constipation than those who ate only 7 grams or less per day ().
Another study of 51 people looked at the effects of fiber intake on constipation. Every day for 3 weeks, participants ate 240 grams of bread - rye or white. Rye bread contained 30 grams of fiber, while white bread contained 10 grams.
Compared to the white bread group, the rye bread group experienced 23% faster fecal transit time, 1.4 more bowel movements per week, and softer stools that passed more easily ().
Dietary fiber also acts as a prebiotic, which feeds the beneficial probiotic bacteria in your gut, allowing them to thrive and limit the growth of harmful bacteria.
Prebiotics in dietary fiber may also reduce the risk of colon cancer by promoting healthy intestinal motility and strengthening the layer of tissue lining the intestines ().
Helps control body weight
Consuming dietary fiber can also help you reach your target body weight and maintain a healthy weight.
In one study, 28 adults increased their fiber intake from 16 to 28 grams per day. They followed one of two high-fiber diets daily for four weeks - consuming either 320 grams of beans or a combination of fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
On both high-fiber diets, participants ate about 300 fewer calories per day and lost an average of about 4 pounds. At the same time, they reported higher levels of satiety and lower levels of hunger than before starting the high-fiber diet ().
Eating more fiber may also increase your resting metabolic rate—that is, the number of calories you burn at rest.
A 6-week study of 81 adults found that those who ate a diet that included about 40 grams of fiber per day had a higher metabolic rate and burned 92 more calories per day compared to those who stuck to the diet. meals with only 21 grams of fiber per day ().
In addition, many high-fiber foods, such as whole fruits and vegetables, are low in calories. Try to eat more of these foods to feel full and satisfied. They will help keep your calorie intake low, which can promote weight loss.
May benefit blood sugar control
Eating foods high in fiber helps slow digestion, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream (,).
In fact, some studies have shown that fiber may help regulate blood sugar and insulin levels. Insulin is a hormone that helps transport sugar present in the blood into your cells and tells your body to burn it for energy or store it as fat ().
Maintaining moderate blood sugar levels is very important because spikes in blood sugar levels can damage your body over time and lead to diseases such as diabetes ().
One study of 19 people with type 2 diabetes examined the effects of eating a high-fiber breakfast on blood sugar levels.
Those who ate a high-fiber breakfast, which included 9–10 grams of fiber, had significantly lower post-meal blood sugar levels than those who ate a low-fiber breakfast, which contained only 2–3 grams () .
What's more, a study of 20 overweight adults found that those who ate at least 8 grams of fiber at breakfast had lower postmeal insulin levels ().
Keeping your insulin levels low can also help you lose weight by reducing the number of calories your body stores as fat ().
May lower cholesterol and blood pressure
Dietary fiber may help reduce high cholesterol and blood pressure, which are risk factors for heart disease.
One 28-day study of 80 people with high cholesterol looked at the heart-healthy effects of consuming fiber.
Researchers observed that people who ate 3 grams of soluble fiber from oats daily experienced a 62% reduction in total cholesterol and a 65% reduction in LDL (bad) cholesterol compared to the control group ().
In another 4-week study, 345 people consumed 3-4 grams of beta-glucan, a soluble dietary fiber found in oats, daily. This group experienced a significant reduction in LDL (bad) cholesterol levels compared to the control group ().
Additionally, eating fiber can lower your blood pressure.
A review of 28 studies found that people whose diets included higher levels of beta-glucan—a type of dietary fiber found in oats—had lower blood pressure than people whose diets contained little fiber ().
To date, most research on dietary fiber and blood pressure has focused on the effects of dietary supplements rather than dietary fiber. In this regard, additional research is needed (, ,).
Conclusion:
Dietary fiber has many beneficial properties. Eating them helps improve digestion and promotes intestinal health. They may also reduce certain risk factors for heart disease and help you control your weight and blood sugar levels.
Vegetable fiber reviews and comments
Lyudmila
02.10.2014
Fiber contains substances such as cellulose (the fiber itself) and hemicellulose (hexosans and pentosans) along with encrusting substances (cutin, lignin and suberin). The calorie content of fiber is approximately 202 kcal. The listed carbohydrates are not digested by human enzymes and, therefore, are not absorbed by the body. Where does 202 kcal come from?
INOCENTY
24.07.2018
There is a gap between energy value and nutritional (digestible) value. For example, wood sawdust has the same energy value as sugar... but the food value is ZERO. Simply for measurement they use the so-called “calorimetric bomb” - a device that allows you to calculate how many calories of heat are released when 100 grams of a given substance (product) is burned in oxygen..... in oil or anthracite in general, the energy value is the wildest... but what’s the point?
Coarse fiber - where to look?
The majority is usually from the insoluble group. These plant components do not immediately disintegrate in the gastrointestinal tract, but absorb many harmful substances: radionuclides, toxins, viruses and various microorganisms.
The silicon included in the composition helps with this. And also products with coarse fiber normalize intestinal function and remove excess cholesterol. You need to wash down such food with plenty of water to prevent clogging.

Here is a list of the most popular products:
- wheat bran, which can be taken with cereals. For 100 grams of bran there are 11 grams. coarse fibers;
- any bread containing whole grains. One slice of such bread contains 1.2 - 1.5 grams of fiber;
- some vegetables: beets, broccoli, boiled asparagus, corn, fresh bell peppers, carrots, tomatoes, sweet potatoes;
- legumes, especially beans (6 grams of fiber per 100 grams of product), as well as lentils, sweet beans;
- fruits: figs, raspberries, strawberries, pears, apples. But the rough elements are mainly found in the peel.

I give preference, of course, to the last 3 points, because they are gluten-free.
Psyllium seed husks are also a very wonderful cleanser for the intestines. It swells and fills all hidden places and gently removes impurities and toxins. You can drink 1-2 teaspoons of psyllium husk per day immediately with 1-2 glasses of water. You need to drink it quickly because the husk immediately begins to swell.
You can experiment and make salads with fruits, and add nuts, raisins, and prunes to them. An excellent dressing is yogurt. A wonderful summer breakfast, isn't it? Not only healthy, tasty, but also a beautiful, toned figure is guaranteed.
Dry fiber for weight loss, how to take it correctly. How to take fiber for weight loss?
The greatest effect will come from consuming fiber in powder form, since dietary fiber in capsules or tablets takes longer to be absorbed in the body and must be washed down with plenty of water.
So, you have chosen the type of fiber that is most suitable for you in terms of its beneficial properties. But how to drink fiber for weight loss so that its intake is beneficial and not harmful to the body?
- It must be remembered that the largest portion of fiber that can be consumed per day is no more than 50 grams. Exceeding the recommended norm can have a bad effect on the condition of the digestive system, esophagus and stomach, and can lead to gastritis or even peptic ulcers.
- You should start taking dietary fiber with a small portion of approximately 7-10 grams. After three to five days, slightly increase the daily intake, gradually bringing it to the recommended maximum.
- For good absorption of dietary fiber, you need to drink clean, still water at least two liters per day.
- You can consume fiber either in dry form or by making various cocktails based on it, for example, adding it to juice or kefir.
- While adhering to a diet high in fiber, diversify your diet with protein foods; you can also take vitamin and mineral complexes, since fiber, while cleansing the body, can also remove useful substances necessary for health along with toxins.
- Don't forget about physical activity, this will help your excess weight melt off much faster.











