The concept of refeed in weight loss
Carbohydrate loading is the deliberate consumption of carbohydrates, even if a person is on a diet.
The frequency and duration of the refeed is determined individually. Main functions of the refeed food strategy:
- Psychological - includes high-carbohydrate foods in the diet, eliminates hunger and associated discomfort, and allows you to stick to a diet without unplanned breakdowns.
- Physiological - sets the body up for weight loss, launching the necessary processes; neutralizes side effects that can be caused by fasting.
Conditions for proper loading organization:
- the main diet should be no-carbohydrate or low-carbohydrate;
- regular physical activity.
Effect on the body
Following a low-carb or no-carb diet reduces the intensity of your workouts. A person becomes less resilient, and difficulties arise when performing physical activity.
The refeed system provides the body with the energy it needs, so you can continue to eat right and exercise at your usual pace.
Loading with carbohydrates helps normalize hormonal levels, so weight gradually decreases. The processes of hormone production and metabolism are restored, digestion improves.
Carbohydrate loading on a low-carb diet helps normalize hormonal levels.
Differences from a cheat meal
A cheat meal is a planned diet break that makes it easier to endure psychological discomfort.
A cheat meal involves one additional intake of prohibited food with a set frequency - once every 7 days or once every 14 days. But this technique is not recommended for overweight people.
A refeed is also a planned disruption to your diet, but it lasts longer.
People who are not overweight and want to build muscle tissue resort to this method. Difference between cheat meal and refeed:
| Cheatmeal | Refeed |
| It is allowed to consume prohibited and harmful foods, including snacks and fast food. | Only healthy carbohydrates are allowed: honey, legumes, cereals, dried fruits, potatoes. |
| One meal. | Duration - from 5 hours to 2 days. |
| Caloric intake is not controlled. | Increase in caloric intake within acceptable limits. |
| Does not comply with the principles of proper nutrition (PN). | Based on PP. |
What it is

Supporters of proper nutrition, diets, and exercise in the gym are familiar with the situation when weight stops falling. If previously there was stable weight loss, then over time there is a so-called plateau (metabolism slows down, weight loss stops). At the same time, the person continues to strictly adhere to the diet and regularly visits the gym. In such cases, experts recommend using cheat meals and refeeds.
So what is a refeed? This is a short-term, pre-planned increase in the consumption of healthy carbohydrates. This is where you exceed your calorie target for weight loss. However, this is a great way to break the monotony of your diet and increase motivation. After all, as soon as weight loss stops, a person’s motivation also decreases.
Here it should be understood that the correct approach to the eod nutrition system does not lead to weight gain. Its main goal is to increase the effectiveness of the diet and promote further weight loss.
When choosing a refeed, it is very important to understand what the difference is between a refeed and a cheat meal. Refeed operates within the framework of proper nutrition and does not violate its principles. A cheat meal is enjoying the taste of your favorite dishes, so it’s more like a psychological release.
General benefit
The refeed period not only helps to cope with hunger and replenish the body with necessary carbohydrates. This system has a beneficial effect on the condition of many organs and systems.
Replenishing muscle glycogen stores
Low-carb diets deplete muscle glycogen stores, making it difficult to train at your usual pace. Carbohydrate loading normalizes the concentration of this substance.
Temporarily “turning off” catabolism
In the process of losing weight, the body not only gets rid of fat reserves, muscle tissue also suffers. A protein diet and constant exercise do not always cope with this problem, and refeeding helps block the process of breaking down muscle fibers in the body.

A protein diet may not always help block the breakdown of muscle fibers.
Improving hormonal levels and increasing testosterone levels
The refeed period restores the balance of hormones that help the body cope with hunger.
Dietary intake in men decreases the level of the hormone testosterone. By arranging a planned diet break, you can increase its concentration, maintain men's health and libido normal.
Maintaining women's health
Calorie deficiency in women can cause fertility problems and menstrual irregularities. If this problem is not eliminated in time, the entire body will suffer. For this reason, frequent refeeds are recommended for women following low-carb diets.
Improved immunity
A lack of calories negatively affects the functions of the immune system. With the help of refeed days, you can support a weakened body and improve its protective functions.
The difference between refeeds and cheat meals
Although the effects are similar, here are the main differences:
Cheat meals are planned deviations from the diet . They are scheduled in advance for certain dates or days of the week. In a sense, this is a reward for strictly following the diet, and for most people it is a refreshing change for the psyche and a break from boring dishes (if the diet is made up of the same foods). Please note that “cheat” meals cannot be every day, then this is a regular diet. (Call it “cheatlife” then – Zozhnik’s note).
Refeeds are added into the diet as needed when required for a specific appearance, training performance, and athletic record (or lack thereof). Refeeds are not planned in advance; they are used according to your well-being/condition.
Usually, a refeed is resorted to when an athlete has been on a diet with a calorie deficit (usually carbohydrates) for quite a long time, and his glycogen reserves have depleted. Refeeds are used even in pre-competition preparation, in the last weeks before a performance. It all depends on individual characteristics: how a person digests carbohydrates, at what speed they are processed into glucose.
In the case of bodybuilding (and other body assessment competitions), refeeds are needed when the muscles begin to “deflate” and need to be “filled up” again. Refeeding also helps maintain muscle mass, because when glycogen reserves are depleted, the body triggers gluconeogenesis (the process of converting non-carbohydrate compounds, such as amino acids, into glucose. Even muscles can be used if you are in a calorie deficit). And usually a refeed is much “cleaner” than an “unbridled” cheat meal.
Of course, a cheat meal gives similar effects: it replenishes glycogen stores and increases the level of leptin (the hormone that controls appetite), and most importantly, it brings psychological relief if you have been dieting too strictly and have been in a calorie deficit for a long time.
A cheat meal is a planned reward after a certain period of dieting, and a refeed is required when glycogen is used up and leptin is reduced . But neither one nor the other is at all necessary as long as there are no physiological obstacles to losing weight in the body. And while you still have a lot of excess fat.
Nutritional Features
Refeed days should not be seen as a way to eat a lot of prohibited foods in a short period of time.
An increase in the amount of carbohydrates is allowed, provided the correct proportions of fat and protein are observed. Among unhealthy foods, you should choose those that contain little fat and a lot of carbohydrates. Too sweet and fatty foods are not suitable.
Required Products
The diet may consist of:
- soy products;
- fruits, nuts, berries, herbs;
- legumes;
- dried fruits;
- whole grain cereals (rice, oats);
- durum wheat pasta;
- unsweetened pastries and rye bread.
You can eat sherbet, dark chocolate, marmalade, honey, halva, marshmallows, and jam. Sugar is limited to a minimum.

Fruits, nuts, and berries can be included in your diet on refeed days.
Prohibited:
- milk chocolate, sweets;
- sweet pastries;
- alcohol, carbonated drinks, energy drinks;
- cakes, cookies, pies, puddings;
- meat by-products (sausage, frankfurters);
- ice cream.
It is recommended to boil, stew or bake products. Fried foods should be avoided.
Sample menu
For a refeed day, you can use the following diet option:
| Meals | Menu |
| First breakfast | Oatmeal with nuts and fruits, cooked in milk; hard-boiled egg, sweet coffee, whole grain bread |
| Lunch | Nuts (handful) |
| Dinner | Pasta soup made with chicken broth; Vegetable Salad; baked chicken; a piece of rye bread; green tea; permitted sweetness |
| Afternoon snack | Milkshake with honey; dried fruits |
| Dinner | Pasta with seafood; Vegetable Salad; bread made from rye flour; Herb tea; jam |
| Late dinner | Kefir or unsweetened yogurt |
When actively involved in sports, it is allowed to consume dried fruits and nuts between meals.

Pasta soup made with chicken broth can be eaten for lunch on fast days.
Correct structure
The correct ratio of BJU and calories:
- Minimum fat.
- Consistent protein levels.
- The main source of calories is carbohydrates.
- The daily caloric intake of a refeed day can be increased by 35-40% in comparison with a diet.
When preparing a salad, you should not use vegetable oil, and you should also choose only low-fat dairy products.
If a refeed is accompanied by dizziness, increased blood sugar levels, or hunger that is difficult to tolerate, then the nutritional structure is adjusted. Healthy fats are added to it: fish, nuts, olive oil, and the amount of grains and vegetables is increased.
Duration and frequency
Regular refeed days are recommended for diets and active training according to the planned scheme:
| Duration | Carbohydrates |
| 5 hours | from 3 to 6 g per kilogram of dry weight* |
| Day | from 8 to 12 g per kilogram of dry weight* |
| 2 days | from 4 to 6 g per kilogram of dry weight* |
*Lean mass is determined by subtracting fat weight from total body weight.
You can find out your fat percentage using a scale with an analyzer. The frequency of carbohydrate nutrition is influenced by:
- calorie content of the diet (the lower the calorie content, the more often it is necessary to use refeed);
- percentage of fat in total body weight;
- intensity of physical activity.
Five hours
The duration of the carbohydrate load is 5 hours, and it must be completed during dinner. The next morning they return to diet.
Day
The daily refeed starts in the morning with breakfast and ends in the evening. The last meal should be organized an hour before going to bed. You should eat in equal portions of 150-200 g.
Two days
The amount of carbohydrates that the body needs is distributed over 2 days and consumed from breakfast to dinner. This way, the optimal level of glucose in the blood is achieved, and there is no feeling of acute hunger.

The frequency of refeed days depends on the caloric content of the diet and the intensity of physical activity.
Types of carbohydrates for refeed
The optimal products are bread, low-fat pastries, pasta, buckwheat and rice groats, potatoes and carrots (primarily baked), grapes, bananas and any foods that a low-carbohydrate diet does not allow. A small amount of sweets is allowed, but excess sucrose and fructose carry the risk of regaining lost body weight.
The fructose content in fruits is low, so there is no reason to worry. However, corn syrup, which is characterized by an increased amount of fructose and is now added almost everywhere, is a problem.
Some people feel worse during a refeed. First of all, these are people who adhere to low-carbohydrate diets or have poor insulin sensitivity. In such people, the level of glucose in the blood sometimes changes sharply, resulting in a decrease in the amount of energy and a feeling of hunger. Possible solutions to the problem:
- Consumption of proteins, fiber and fats with carbohydrates,
- Selection of whole grain products,
- Absolute refusal of refined products.

Diet categories
To determine your dietary category, you will need a scale that measures your body fat content.
Distribution table:
| Diet categories | Fat percentage | |
| women | men | |
| 1 | Up to 24% | Up to 15% |
| 2 | From 25 to 34% | From 16 to 25% |
| 3 | From 35% | From 26% |
First
This category includes people who meet the following conditions:
- intense training;
- drying the body;
- strict protein or keto diet.
These conditions eventually lead to hormonal imbalances (decreased libido in men, disruption of the menstrual cycle in women) and a slowdown in metabolic processes. To eliminate these phenomena, regular and long-term carbohydrate loading is needed.
Second
This category includes former athletes and those who periodically visit the gym or run in the morning. Such exercises, combined with a low-carb diet, help get rid of fat deposits and control weight. But losing weight can be accompanied by a plateau effect - the weight stops. You can avoid this by using infrequent refeeds lasting 5 hours.

People who go to the gym can use refeeds infrequently and lasting 5 hours.
Third
This group consists of overweight and obese people who often overeat and do not exercise. For category 3, refeeds are dangerous because they can disrupt the weight loss process. To begin with, nutritionists recommend sticking to a strict diet for a month and exercising regularly, after which you can try this nutritional strategy.
How often should I refeed?
This depends on several points, including:
- The strictness of the diet - the greater the calorie deficit, the more often you refeed.
- The percentage of body fat - the lower, the more often the refeed.
- Activity level - the more active your lifestyle and the harder your workouts, the more frequent and longer your refeeds should be.
Average recommendations are in the table:
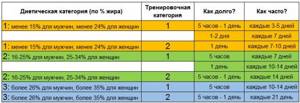
What is a training category?
Category 1 - Anyone who trains intensely 2-3 times a week (strength training or very intense cardio) for at least an hour.
Category 2 - everyone else: those who do not exercise at all; those who only do low-intensity cardio; those who do strength training, but not very heavy.
What is a dietary category?
It may seem counterintuitive: the slimmer a person becomes, the more and more often they need to do carbohydrate loading (as can be seen from the table). The fact is that the lower the percentage of fat, the more noticeable the slowdown in metabolism on a diet. A diet and a low percentage of fat are perceived by the body as starvation, and carbohydrate loading is just a way to control this.
Category 1

24% fat or less - for women. These are fitness people who, in principle, are not overweight, but want to become even leaner. They are usually also included in training category 1 - intense training.
If these people are not gifted by genetics and/or do not use steroids, then it is they who are especially noticeable with all hormonal problems and the associated slowdown in metabolism. Therefore, they need to do longer and more frequent refeeds. Typically, people in this category already have good eating behavior, can control the amount of food and do not break down after loading, violating the diet.
There are also psychological benefits to more frequent refeeds: cutting is not the most fun thing to do, and refeeds make life on a strict diet a little easier.
Training category 2 needs to start at the lower limit of carbohydrates en refeed. They do not exercise or exercise sluggishly, do not use up much glycogen and do not require more carbohydrates to replenish it.
Category 2

16-25% body fat is for men. 25-34% fat - for women.
These are fitness people who, for some reason, have lost their shape, or those who simply want to get rid of excess fat. Physically, it is somewhere between categories 1 and 3 - in terms of metabolic rate, insulin sensitivity, control of eating behavior, etc. In this category, it is always worth starting from the lower limit both in terms of the duration of the refeed and the amount of carbohydrates. You need to evaluate the body’s reaction and only then increase both.
Category 3
26% fat or more - for men.
35% fat or more - for women. Whether refeeds are necessary for people in this dietary category (obesity) is a controversial issue. Most of them have problems with eating control, and carbohydrate loading can bring back old eating habits. It is believed that it takes about 6 weeks to get used to a new eating style and new habits to consolidate them.
In addition, there is always poor sensitivity of the body to insulin, so a large amount of carbohydrates can cause problems: the body is not able to use all the glucose it receives, and the excess can be stored as fat.
So the smart option is to avoid refeeds for the first two months. For psychological relief, you can arrange cheat meals. After you get used to the new diet and establish new eating habits (and perhaps move into dietary category 2), you can start refeeds.
Algorithm for calculating refeed duration
To determine the duration of the carbohydrate diet, you must:
- Find out your fat percentage and calculate your lean body mass.
- Determine dietary category.
- Determine training category.
- Find out the refeed schedule from the table below.
| Categories | Refeed | ||
| dietary | training | duration | periodicity |
| 1 | 1 | 5 hours/day | In 3-5 days |
| 1-2 days | In 7 days | ||
| 2 | day | In 7-10 days | |
| 2 | 1 | 5 hours | A week later |
| day | In 10-14 days | ||
| 2 | 5 hours/day | In 2 weeks | |
| 3 | 1 | 5 hours | In 10-14 days |
| 2 | 5 hours/day | In 3 weeks | |
Power plans[edit | edit code]
Now let's move on to the numbers. Adjustments are made depending on the purpose. Three of the most useful schemes are described.
What might an EOD nutrition week look like?[edit | edit code]
A typical EOD nutrition week looks like this:
- Monday: workout + refeed (lots of calories and carbs)
- Tuesday: low carb, low calorie diet
- Wednesday: training + refeed
- Thursday: low carb, low calorie diet
- Friday: training + refeed
- Saturday: low carb, low calorie diet
- Sunday: training + refeed.
A different order of training days is allowed.
Regardless of whether it is a training day or not, protein intake should be ~2 g/kg body weight. The amount of calories, carbohydrates and fat varies depending on the goal.
Nutrition for weight loss[edit | edit code]
On training days you get a normal or slightly increased amount of calories (+ 200 – 300 kcal). Most food is consumed immediately after exercise. Carbohydrates are 2–5 g per kg of body weight, fats are less than 50 g.
On non-training days, it is necessary to ensure an energy deficit of 1000 - 1500 kcal. Carbohydrate intake is limited to <1 g per kg body weight. Calorie intake is regulated by fat intake. The first meal is the largest.
Nutrition to burn fat and build muscle at the same time[edit | edit code]
The EOD system is excellent for body recomposition. It allows even trained athletes to gain muscle and burn fat at the same time! It should be noted that for beginners there is a simpler technique called “Body Recomposition”.
First, you consume plus 500 kcal on a training day and minus 500 kcal on a non-training day. The values are adjusted depending on the priority task (building muscle or burning fat).
For example, when focusing on burning fat, consume plus 300 kcal on a training day and minus 800 kcal on a non-training day.
- Training day: 2-7 g carbohydrates per kg body weight, fat < 50 g.
- Non-training day: <1 g carbohydrates. There is as much fat as needed to provide the required number of calories.
Nutrition for building lean muscle mass[edit | edit code]
- The EOD system allows even highly trained athletes to gain muscle while keeping their fat levels virtually unchanged. This is suitable for those who have difficulty with classic muscle building and fat burning cycles, or those who need to stay in good shape throughout the year.
Building muscle mass requires a surplus of calories in your weekly energy intake. The diagram might look like this:
- Training day: plus 600 kcal, and on a non-training day minus 300 kcal.
- Training day: 2-7 g carbohydrates per kg body weight, fat < 50 g.
- Non-training day: <1 g carbohydrates. There is as much fat as necessary to provide the required number of calories.
Features of the keto diet
Carbohydrate loading is effective in combination with keto diets, which involve eliminating carbohydrates from the diet.
Schemes:
- Keto diet “Standard” (a small amount of carbohydrates in the menu) without refeed periods.
- Targeted keto diet with refeeds 60 minutes before and 60 minutes after exercise. Limiting carbohydrate foods in the diet.
- Cyclic option with periodic carbohydrate loadings, which can be determined from the table above.

Keto diet products.
Tips and tricks
It is recommended to organize a refeed before strength training or on the day of it according to the following scheme:
- 1st meal - 60 minutes before training;
- 2nd - within an hour after training;
- 3rd - in 2 hours.
You should not purchase prohibited foods for future use, so as not to provoke a diet failure ahead of time.
The optimal time for a refeed is weekends.
The duration of the first refeed should be minimal, and the condition of the body must be monitored. If the return to the diet goes without problems, the weight increases slightly, which is maintained for several days, the muscles become dense, then you can increase the duration of the load.
If swelling, drowsiness, or decreased endurance occur, you should avoid refeeding. Instead, you can use a cheat meal or take a week-long break from your diet every 3 months.
When are cheat meals and refeeds necessary?
When you restrict calories, your body produces less leptin and your metabolism slows down. This is why most people who go on a strict diet for a long time stop losing weight. The body makes certain changes in metabolism and retains fat to prevent you from dying too quickly - this is a defense mechanism.
How the body resists weight loss or about adaptive thermogenesis
Our body only thinks about survival and reproduction, it doesn't care about the terrain for the beach or the catwalk. If it were possible to somehow explain to the body that relief increases the chances of reproduction, then the reaction to hard training and dietary restrictions would be different.
Also, a lack of calories over a long period is stressful for the body, in response to which cortisol levels increase (which makes it more difficult to lose weight). The psychological benefits of a cheat meal also help reduce cortisol.
Thus, a cheat meal or refeed allows the body to take a little break from dietary stress and continue to burn fat effectively. The body understands that hunger has not yet set in, it can increase leptin production and increase metabolic efficiency.
Mistakes in carbohydrate loading
The main mistake is overeating.
You should not indulge in fast food, pizza and other high-calorie, high-fat foods. If you ignore this rule, the carbohydrate regime will lead to a gain of extra calories and weight. But you can’t limit yourself too much, for fear of gaining extra grams. The main thing is to consume permitted foods in moderation.
Do not confuse a refeed with a festive feast and alcohol on weekends.
Failure to adhere to the download schedule and mode is also a common mistake. It is important to maintain regularity.