As you know, proteins (proteins) consist of amino acids. The latter includes the amino group NH2. Thus, proteins, among other things, are nitrogen suppliers for our body.
What does this have to do with the title of this article? The fact is that the daily protein intake covers the amount of nitrogen per day that is necessary to maintain nitrogen balance.
At equilibrium nitrogen balance, the amount of nitrogen entering the body is equal to the amount of nitrogen excreted in urine and feces.
To maintain this balance, we need 19 g of nitrogen per day, which corresponds to 90 g of protein.
It is important to note that when there is a lack of protein, the body begins to consume it from its own tissues, which leads to loss of nitrogen and, as a result, the emergence of a negative nitrogen balance.
The causes of this disorder may be incomplete absorption of proteins, low-protein diets, fasting, and certain diseases (for example, oncology, tuberculosis).
What are the signs of protein deficiency?
- chronic fatigue;
- deterioration in performance;
- decreased concentration;
- loss of muscle mass;
- decreased metabolism - excess weight gain;
- hair falls out, nails peel, wrinkles appear;
- hormonal disbalance;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- swelling;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- decreased immunity;
- decreased vascular strength - risk of developing cardiovascular diseases;
- prolonged wound healing;
- craving for sweets (carbohydrate addiction).
However, an excess of protein, just like a deficiency, has an adverse effect on the condition of the body. First of all, the liver and kidneys are affected.
In addition, a significant amount of nitrogenous waste is formed, the processes of fermentation and decay begin in the intestines with the formation of harmful toxic substances.
Thus, to prevent a deficiency or excess of proteins in the body, it is necessary to know the daily protein requirement.
On average, as noted earlier, it is 90 g. However, this value can vary depending on gender, age, and labor intensity (level of physical activity).

The daily protein requirement can be calculated by knowing your height and Body Mass Index, the so-called Quetelet Index (BMI or BI).
BMI is calculated using the following formula: BMI = Weight (kg) / Height2 (m)
For example, I am a woman and my weight is 48 kg and my height is 1.58 m. BMI = 48 (kg) / 1.582 (m) = 19.2.
Next, look at the table below and find the amount of protein per day that corresponds to these parameters.
How much protein do athletes need per day?
Sports and bodybuilding require an additional source of protein. Therefore, protein is the main compound for athletes. How to calculate the required quantity? For this, the number of training sessions and the athlete’s body weight are also taken into account. So, the calculation is made using the following formulas:
- Exercising 3 times a week - 1.7 grams of protein per 1 kilogram of body weight;
- Exercise up to 5 times a week - 2.1 grams of protein per 1 kilogram of weight.
From time to time, athletes adhere to drying routines. Drying is a little different from the usual process of losing weight. In the first case, a person strictly controls himself. Not only the amount of food, but also water and liquids is carefully calculated. During drying, the body quickly “says goodbye” to fats and excess fluid. The process of losing weight is more gentle and gradual. With a simple diet, the body does not experience much stress, so you will not be able to lose weight so quickly.
Protein food during drying is allowed as a light snack, or as the last meal of the day. But dairy and fermented milk products should be completely abandoned during this period. Therefore, proteins are necessary when losing weight. The daily amount of protein should be no more than 140 grams. But carbohydrates should be excluded.
As for dry protein, you should be careful with such a product. Protein in powder form is not absorbed by the body. The fact is that in order to be broken down and absorbed, the protein molecule must be surrounded by water. Therefore, only cocktails are prepared from protein powder. The benefits of such food in dry form cannot be traced. In addition, you need to consume sports nutrition under medical supervision. A change in amino acid levels in one direction or another can cause complications.
Table 1. Daily protein intake for women depending on height and Body Mass Index (BMI)
| BMI | Height (m) | |||
| 1,47-1,53 | 1,54-1,63 | 1,64-1,73 | 1,74-1,83 | |
| 19 | 54 | 66 | 80 | 93 |
| 20 | 56 | 70 | 82 | 95 |
| 21 | 56 | 72 | 85 | 97 |
| 22 | 59 | 73 | 85 | 100 |
| 23 | 61 | 74 | 88 | 102 |
| 24 | 61 | 76 | 89 | 104 |
| 25 | 62 | 77 | 92 | 106 |
| 26 | 63 | 78 | 94 | 108 |
| 27 | 66 | 81 | 97 | 110 |
| 28 | 66 | 82 | 97 | 113 |
| 29 | 67 | 84 | 98 | 115 |
| 30 | 69 | 84 | 102 | 117 |
| 31 | 71 | 87 | 103 | 119 |
| 32 | 72 | 89 | 105 | 121 |
| 33 | 74 | 91 | 106 | 124 |
| 34 | 74 | 93 | 109 | 126 |
| 35 | 76 | 95 | 110 | 128 |
| 36 | 77 | 96 | 113 | 129 |
| 37 | 80 | 97 | 115 | 131 |
| 38 | 80 | 99 | 117 | 133 |
| 39 | 82 | 102 | 118 | 136 |
| 40 | 83 | 103 | 120 | 138 |
| 41 | 85 | 105 | 122 | 141 |
| 42 | 86 | 106 | 125 | 143 |
| 43 | 86 | 108 | 126 | 146 |
| 44 | 88 | 109 | 128 | 148 |
| 45 | 89 | 111 | 130 | 150 |
Types of proteins that come with food
Proteins are complex biochemical compounds consisting of amino acids; 22 amino acids participate in the formation of protein substances that ensure human life. All types of protein compounds are divided into two categories: some are called complete proteins, others are called incomplete proteins. Complete proteins include animal proteins found in foods such as meat, fish, eggs, poultry, seafood and dairy products. Their use allows you to provide the body with eight amino acids that are classified as essential, i.e. to those that are produced in the body in insufficient quantities and which must be replenished from the outside. Incomplete proteins include proteins of plant origin, found in large quantities in legumes, nuts, seeds and cereals. Incomplete proteins do not contain the entire set of essential amino acids, so they need to be consumed with the addition of a small amount of complete proteins. Nutritionists believe that eating two types of proteins together is more beneficial than eating them separately. This should also be taken into account when determining a daily diet, tailored to a person’s daily protein requirement.
Please note that a person leading a physically active lifestyle or under the influence of a stressful situation needs more protein; in these cases, the norm can almost double.
Table 2. Daily protein intake for men depending on height and Body Mass Index (BMI)
| BMI | Height (m) | |||
| 1,54-1,63 | 1,64-1,73 | 1,74-1,83 | 1,84-1,93 | |
| 19 | 82 | 97 | 107 | 126 |
| 20 | 84 | 98 | 113 | 130 |
| 21 | 86 | 99 | 115 | 132 |
| 22 | 87 | 102 | 118 | 133 |
| 23 | 89 | 104 | 119 | 137 |
| 24 | 92 | 106 | 122 | 140 |
| 25 | 92 | 107 | 125 | 141 |
| 26 | 93 | 110 | 127 | 143 |
| 27 | 95 | 110 | 129 | 147 |
| 28 | 97 | 114 | 131 | 149 |
| 29 | 98 | 115 | 132 | 151 |
| 30 | 99 | 118 | 135 | 154 |
| 31 | 102 | 119 | 137 | 157 |
| 32 | 104 | 120 | 139 | 159 |
| 33 | 105 | 122 | 141 | 162 |
| 34 | 107 | 125 | 143 | 162 |
| 35 | 109 | 127 | 146 | 165 |
| 36 | 110 | 131 | 148 | 169 |
| 37 | 111 | 131 | 150 | 171 |
| 38 | 114 | 132 | 151 | 173 |
| 39 | 116 | 135 | 153 | 176 |
| 40 | 117 | 136 | 155 | 177 |
| 41 | 119 | 139 | 159 | 180 |
| 42 | 120 | 140 | 161 | 183 |
| 43 | 122 | 141 | 163 | 185 |
| 44 | 125 | 143 | 165 | 187 |
| 45 | 127 | 146 | 168 | 191 |
Thus, my minimum daily protein intake is 66 g per day. However, this figure may vary depending on your age and level of physical activity.
With age, metabolism slows down, and physical activity, on the contrary, increases it. It follows that when playing sports, the need for protein increases.
Below is a table from which you can find out the amount of protein per day, taking into account your gender, age and intensity of work. Let's take a look there...
My age ranges from 18 to 29, in addition, by the nature of my activity, I most of all fit into the category of average physical labor.
So, taking into account these adjustments, I should consume between 66 (minimum) and 81 g (maximum) protein per day. What is your daily protein requirement?

Essential amino acids in protein

So, knowing how much protein you need to consume per day, it would seem that you can start selecting a menu, but here’s the thing - protein is different from protein. It is necessary to consider what amino acids the protein food you eat consists of. All protein products contain amino acids, from which the body creates its own proteins necessary for life. In total, 20 amino acids are involved in the formation of proteins, 12 of which can be produced by humans independently. The rest do not know how to do this, so they must do so with food, otherwise disruptions in the body will begin, in particular, stunting and weight loss. For example, leucine prevents the destruction of muscle tissue during active physical activity and promotes fat burning; together with other amino acids, it participates in muscle recovery and increases the production of growth hormones.
Isoleucine is also essential for physically active people, as it increases endurance and provides the body with energy. There are at least 6 more essential amino acids that a person must obtain from food. Protein products with such essential compounds are considered the most valuable. Nonessential acids are also very important, but with enough essential acids they can be synthesized from them. That is why it is important to consider not only how much protein a person needs per day, but also from which products the nutrient is best obtained.
Below is a table describing all the essential amino acids and the main protein foods in which they are found.
| Leucine | Chicken, pork, rabbit, goose, squid, mussels, pink salmon, carp, cheese, cottage cheese, eggs, legumes, millet |
| Lysine | Milk, cottage cheese, hard cheese, feta cheese, yogurt, red meat, chicken, turkey, cod, sardine, eggs, soybeans, beans, peas |
| Tryptophan | soy, cheese, milk, yogurt, cottage cheese, oatmeal, peanuts, sesame seeds, walnuts, meat, fish |
| Phenylalanine | soy, cheese, seeds, nuts, beef, poultry, pork |
| Valin | caviar, cheese, soy, lentils |
| Isoleucine | nuts (almonds, cashews), chicken, eggs, sea fish, pork, beef, rye, milk, hard cheese, buckwheat |
| Threonine | beef, lamb, eggs, chicken, turkey, hard cheese, feta cheese, fatty sea fish, barley, rye, buckwheat |
| Methionine | eggs, pork, beef, chicken, sea fish, milk, beans, sesame, soybeans, lentils, walnuts, peanuts, almonds, corn |
Table 3. Daily protein intake depending on gender, age and nature of work
| Type of labor | Age | Men (daily protein value (g)) | Women (daily protein value (g)) | ||
| Total | Including animal proteins | Total | Including animal proteins | ||
| Brainwork | 18-29 | 91 | 50 | 78 | 43 |
| 30-39 | 88 | 48 | 75 | 41 | |
| 40-59 | 83 | 46 | 72 | 40 | |
| Light physical labor | 18-29 | 90 | 49 | 77 | 42 |
| 30-39 | 87 | 48 | 74 | 41 | |
| 40-59 | 82 | 45 | 70 | 39 | |
| Average physical labor | 18-29 | 96 | 53 | 81 | 45 |
| 30-39 | 93 | 51 | 78 | 43 | |
| 40-59 | 88 | 48 | 75 | 41 | |
| Hard physical labor | 18-29 | 102 | 56 | 87 | 48 |
| 30-39 | 99 | 54 | 84 | 46 | |
| 40-59 | 95 | 52 | 80 | 44 | |
| Particularly heavy physical labor | 18-29 | 118 | 65 | — | — |
| 30-39 | 113 | 62 | — | — | |
| 40-59 | 107 | 59 | — | — | |
- Mental work - teachers, managers, accountants, writers, journalists, students;
- Light physical labor - nurses, veterinarians, turners, agronomists, physical education trainers;
- Medium physical labor - surgeons, drivers, food industry workers, water transport workers;
- Heavy physical labor - builders, loaders, miners, lumberjacks, athletes;
- Particularly hard physical labor - masons, concrete workers, miners.
It is worth noting that the protein requirement in pregnant women is on average 100 g per day (5 – 9 months). Of these, animal protein should account for 60 g.
Women during breastfeeding need 112 g of protein per day, with 67 g of animal protein.
Is the protein animal, plant or from a jar?
Normally, the body should receive both animal and vegetable protein. The optimal ratio is from 1:3 to 1:1. That is, one-third to one-half of all protein should come from animal sources, the rest from plant foods.
It is in this proportion that we can extract the maximum benefit from protein foods.
Protein foods should be present in our diet every day - this is necessary for the normal supply of amino acids.
The fact is that plant and animal proteins are of different quality - they have different amino acid composition. Amino acids are the structural units of protein. Proteins are assembled from amino acids, like words from letters.
In this table you will see a list of the most important products - sources of protein (vertical) and the name of amino acids (horizontal). Translation from google [source].
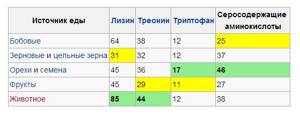
Products marked in green are the best sources of a particular amino acid. Yellow is the minimum sources, and gray is everything between the minimum and maximum.
Despite the fact that plant foods (if there is soy and a high variety of other plant sources of protein in the diet) can completely cover our protein needs, we cannot limit ourselves to them exclusively.
Vegetarianism has the right to exist, but it is mandatory to take vitamin B12.
Nursing vegetarian mothers who do not consume fish, eggs or dairy products are required to take B12 themselves and give it to their baby(!). Talk to your doctor about what dose you both need.
You should have a blood test twice a year:
- general expanded
- on the concentration of vitamin B12
- homocysteine
This is necessary to prevent irreversible changes in the functioning of the body.
Sports nutrition should be added as a last resort. Typically, pure protein or amino acids are prescribed for medicinal or narrow sports purposes. For example, if a person is weak and unable to eat and digest his normal food intake. Or a marathon runner - he only needs liquid food in the form of a sports drink.
Literally 2 words about sports nutrition.
Dry protein is not absorbed by our body. The protein molecule must have a certain spatial structure (unfold from a dried dense package) and be surrounded by water molecules. This is why sports drink is used in cocktails. The digestibility of protein powder from dry food is highly questionable.
Regular consumption of amino acids or whey protein requires medical supervision. Possible side effects:
- low blood sugar
- low pressure
Long-term, regular use of such supplements can lead to kidney problems and bone loss [source].