4.8
(8)
The formation of cells of the immune, bone and cardiovascular systems occurs with the participation of vitamin B9. It plays a major role in the functioning of the male reproductive system, supporting spermatogenesis, and in the early stages of gestation in women. In order to increase the intake of the substance from food, you need to know which foods contain folic acid.
Folic acid in foods.
The role of vitamin in the human body
Folic acid (folate, pteroylglutamic acid) is a water-soluble B vitamin that is not produced in human tissues. The main synthesis in the body occurs due to the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, the remaining part of the substance comes from the outside (from food, synthetic forms of the vitamin in preparations).

Functions of folic acid.
Folates perform the following biological functions:
- regulate the production and development of new cells, which is important in early childhood and childhood (due to intensive growth, an increased amount of nutrients is required);
- participate in the synthesis of DNA molecules (disruption of this process threatens the appearance of cancerous tumors);
- support the formation of bone tissue cells, which is why they are prescribed for osteoporosis, restless legs syndrome and other musculoskeletal disorders;
- promote hematopoiesis, influence the synthesis of erythrocyte precursor cells (red blood cells);
- stimulate the immune system, provoking the formation of new cells in it, which increases the body’s resistance and protective functions;
- participate in the production of organic compounds (choline, nucleic acids, purine), individual amino acids (serine, glycine, histidine, methionine);
- improve the activity of the cardiovascular system, reducing the concentration of homocysteine in the body (blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood clotting are stabilized);
- regulate the functions of the central nervous system (reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease, prevent the development of depression and nervous exhaustion);
- have a healing effect on infectious lesions of the oral mucosa;
- stimulate the production of viable sperm.
The effect of vitamin B9 is enhanced in the presence of ascorbic acid, tocopherol, and B vitamins.
For pregnant
When planning or carrying a pregnancy, folic acid is prescribed to prevent the following pathologies :
- early termination of pregnancy;
- intrauterine disorders in fetal development;
- anemia;
- placental insufficiency;
- premature birth.
The positive effect of the substance on the reproductive functions of the female body has been established.
Folic acid for pregnant women.
Planning pregnancy against the background of thrombophilia requires complex treatment with vitamin B9 to correct the level of homocysteine, which increases thrombosis.
Pregnancy in this case is associated with the risk of eclampsia and decreased placental function, and therefore also requires the administration of folic acid.
With the participation of the substance, the risk of pathologies of the fetal neural tube, brain development disorders (anencephaly, microcephaly), and congenital spinal canal bifida is reduced.
Folic acid stimulates the full formation of organs and systems of the unborn child, ensures the replication of cells of the nervous, hematopoietic, skeletal and visual systems.
Eggs
Including eggs in your diet is a great way to increase your intake of some essential nutrients, including folate.
Just one large egg contains 23.5 mcg of folate, or about 6% of the RDI ().
Including even a few servings of eggs each week is an easy way to increase your folate intake and help meet your needs.
Eggs also contain protein, selenium, riboflavin and vitamin B12 ().
They also contain high amounts of lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that may help reduce the risk of vision disorders such as macular degeneration (,).
Summary:
Eggs are a good source of folate, with about 6% of the RDI coming from just one large egg.
Daily requirement
The daily dose of folic acid required for the body , depending on age and hormonal levels:
- from birth to 1 year - 0.05 mg;
- 1-3 years - 0.07 mg;
- 4-6 years - 0.1 mg;
- 6-10 years - 0.15 mg;
- adults and adolescents over 11 years of age - 0.2 mg;
- pregnant women - 0.4 mg;
- during breastfeeding - 0.3 mg.
It is recommended to increase the dosage by 0.05 mg per day if:
- puberty;
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- heavy sports loads and physical work;
- nervous tension or depression.
The synthetic (medicinal) form of folic acid is absorbed better than vitamin B9 obtained from food. The maximum permissible daily intake of the substance is 1 mg.
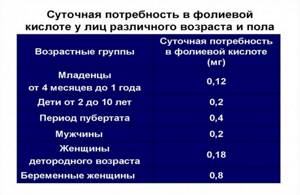
Daily requirement table.
Asparagus
Asparagus contains concentrated amounts of many vitamins and minerals, including folate.
In fact, a 90-gram serving of cooked asparagus contains about 134 mcg of folate, or 34% of the RDI ().
Asparagus is also rich in antioxidants and has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties ().
What's more, it's an excellent source of heart-healthy fiber, providing approximately 7% of the RDA for fiber in just one serving ().
Summary:
Asparagus contains a lot of fiber and a good amount of folate - about 34% of the RDA per 90-gram serving.
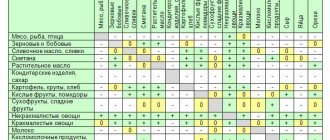
Table of folic acid (vitamin B9) content in foods
Most folic acid is found in fresh vegetables, fruits, and herbs (especially spinach, cilantro, and seaweed). Nuts (hazelnuts, pistachios, almonds, peanuts), cereals and some animal products also contain a lot of this substance.
List of plant foods high in vitamin B9:
| Name | How many micrograms (mg) of substance are in 100 g of product |
| Mango | 43 (0,04) |
| Grapefruit | 38 (0,04) |
| Tangerines | 30 (0,03) |
| Coconut | 26 (0,03) |
| Kiwi | 25 (0,03) |
| Strawberry wild-strawberry | 24 (0,02) |
| Cherry | 25 (0,03) |
| Pomegranate | 16 (0,02) |
| Papaya | 14 (0,01) |
| Raspberries | 8 (0,008) |
| Peach | 7 (0,007) |
| Apple | 6 (0,006) |
| Beet | 110 (0,11) |
| Avocado | 89 (0,09) |
| Cauliflower | 63 (0,06) |
| Broccoli | 57 (0,06) |
| Asparagus | 52 (0,05) |
| Eggplant | 22 (0,02) |
| Bell pepper | 23 (0,02) |
| Potato | 14 (0,01) |
| Green beans | 11 (0,01) |
| Carrot | 8 (0,008) |
| Cilantro | 194 (0,19) |
| Kelp | 180 (0,18) |
| Parsley | 150 (0,15) |
| Dill | 68 (0,07) |
| Lettuce leaves | 46 (0,05) |
| Onion | 30 (0,03) |
| Arugula | 13 (0,01) |
| Almond | 240 (0,24) |
| Sunflower seeds | 228 (0,23) |
| Hazelnut | 50 (0,05) |
| Flax seeds | 10 (0,01) |
| Cashew | 98 (0,1) |
| Pumpkin seeds | 58 (0,06) |
| Peas | 229 (0,23) |
| Oatmeal | 56 (0,06) |
| Chickpeas, corn | 42 (0,04) |
| Millet | 38 (0,04) |
| Buckwheat | 30 (0,03) |
| Pearl barley | 19 (0,02) |
Animal foods rich in folic acid:
| Name | How many micrograms (mg) of substance are in 100 g of product |
| Beef liver | 240 (0,24) |
| Pork liver | 110 (0,11) |
| Mutton | 50 (0,05) |
| Pork bacon | 30 (0,03) |
| Cod liver | 48 (0,05) |
| Salmon | 30 (0,03) |
| Chinook | 35 (0,04) |
| Perch, carp, pike perch | 18 (0,02) |
| Trout | 15 (0,02) |
| Halibut | 14 (0,01) |
| Herring, anchovy | 13 (0,01) |
| Sardine, mullet, catfish | 10 (0,01) |
| Flounder, tilapia, sea bass | 6 (0,006) |
| Pink salmon, chum salmon | 5 (0,005) |
| Tuna, pollock, mackerel | 4 (0,004) |
| Kefir | 16 (0,02) |
| Whole milk | 5 (0,005) |
| Hard cheese | 25-50 (0,03-0,05) |
| Processed cheese | 15 (0,02) |
| Butter, cream, sour cream | 10 (0,01) |
Consumption rate
You already know that folic acid is found in certain foods—in excess. You can get the required amount from your regular diet if you prepare it correctly. In addition, it is much better absorbed this way.
It is definitely worth talking about what the daily requirement of the vitamin is established by experts - you must follow the recommendations and know which foods are rich in folic acid. We selected the most common categories of people based on age and the presence of relevant indications. Let's take a closer look - the data in the table of content in products is presented in mcg per day!
- Up to a year – 25-35;
- From one to seven years – 50-75;
- Up to 14 years – 100-150;
- From fifteen – 200;
- Pregnant women – 400;
- Nursing mothers – 300;
- When planning pregnancy for women - 400;
- Elderly people – 200;
- To eliminate hypovitaminosis – 500;
- When increasing body weight – 600-1000;
- When planning conception for men – 700;
- To increase immunity seasonally – 200;
- For schizophrenia – up to 200;
- For migraines – up to 500;
- For anemia or problems in the gastrointestinal tract - up to 500.
Of course, folic acid is found in some common foods. If you decide to correct the deficiency with special tablets, follow these simple rules:
- Take only during meals with plenty of water;
- Avoid drinking alcohol during the course;
- Do not drink alkaline drinks - mineral water, tea or coffee in large quantities.
They told us what foods contain folic acid and in what quantities it should be taken. Follow the specialist’s recommendations, monitor your health regularly - then you won’t have to think about treatment! This element is necessary for the body, so you should make sure that you consume the appropriate food or special supplement. Don't neglect our advice!
Broccoli
A well-known vegetable for its many health benefits. Including broccoli in your diet can provide your body with a range of essential vitamins and minerals.
When it comes to folate, a 90-gram serving of raw broccoli contains about 57 mcg of folate, or about 14% of the RDI ().
Cooked broccoli contains even more folate—each 80-gram serving provides 84 mcg, or 21% of the RDI ().
Broccoli also contains a lot of manganese and vitamins C, K and A.
It also contains a wide range of beneficial plant compounds, including sulforaphane, which has been extensively studied for its powerful anti-cancer properties ().
Summary:
Broccoli, especially when cooked, is rich in folate. 90 grams of raw broccoli provides 14% of the RDI, while 80 grams of cooked broccoli can provide 21% of your daily needs.
Brussels sprouts
This nutrient-rich vegetable is a member of the cruciferous vegetable family and is closely related to other types of vegetables such as cabbage, broccoli, kale and kohlrabi.
Brussels sprouts contain high amounts of many vitamins and minerals, and are especially rich in folate.
An 80-gram serving of cooked Brussels sprouts can provide 47 mcg of folate, or 12% of the RDI ().
It is also an excellent source of kaempferol, an antioxidant associated with numerous health benefits.
Animal studies suggest that kaempferol may reduce inflammation and prevent oxidative damage to cells (, ).
Summary:
Brussels sprouts contain a large amount of antioxidants and microelements. 80 grams of cooked Brussels sprouts contains approximately 12% of the RDA for folate.
Bananas
Bananas are rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals and are a good source of nutrients.
They are especially rich in folate and can easily help you meet your daily needs when combined with several other folate-rich foods.
An average banana can supply 23.6 mcg of folate, which is equal to 6% of the RDI ().
Bananas are also rich in other nutrients, including potassium, vitamin B6 and manganese ().
Summary:
Bananas contain high amounts of folate. One medium banana contains about 6% of the RDI.
Beef liver
Beef liver is one of the most concentrated sources of folate.
An 85-gram serving of cooked beef liver contains 212 mcg of folate, or about 54% of the RDI ().
In addition to folate, one serving of beef liver can meet and exceed your daily requirements for vitamin A, vitamin B12 and copper ().
It also contains protein, providing a whopping 24 grams per 85 gram serving.
Protein is essential for tissue repair and the production of important enzymes and hormones.
Summary:
Beef liver is rich in protein and folate—containing about 54% of the RDA for folate in one 85-gram serving.
Features of assimilation
Folacin is better absorbed by the body with the simultaneous presence of other vitamins in food: E, B12 and B6. In this sense, nuts are an ideal balanced option, especially since they can be eaten raw.
At the same time, salads made from green vegetables should be seasoned with corn or sunflower oil; they contain a lot of tocopherols. It is beneficial to add cottage cheese and hard cheese to these dishes. These dairy products are a source of three B vitamins at once.
What you cannot combine beneficial compounds with is alcohol and nicotine . Also, do not consume foods or medications containing folate and zinc at the same time. These substances interfere with the absorption of each other.
If there are problems with the intestines, then folacin will not be formed in the body, and if it comes with food, it will be poorly absorbed. Therefore, it is necessary to regulate the microflora of this organ by regularly consuming fermented milk drinks, fiber, fruits and vegetables.
Anti-seizure medications, hormones and contraceptives significantly affect the intestines, so taking them makes folate less absorbed. Stress and chronic diseases also interfere with their absorption.
Papaya
Papaya is a nutrient-rich tropical fruit native to southern Mexico and Central America.
Besides tasting delicious, papaya is also rich in folate.
140 grams of raw papaya contains 53 mcg of folate, which corresponds to approximately 13% of the RDI ().
In addition, papaya is rich in vitamin C, potassium and antioxidants such as carotenoids ().
Summary:
Papaya is rich in antioxidants and folate. One serving (140 grams) of raw papaya provides approximately 13% of the RDA for folate.
Beet
In addition to adding color to main dishes and desserts, beets are rich in many important nutrients.
It contains plenty of manganese, potassium and vitamin C, which you need throughout the day.
They are also an excellent source of folate, as one 130-gram serving of raw beets contains 148 mcg of folate, or about 37% of the RDI ().
In addition to the micronutrients they contain, beets are rich in nitrates, a type of plant compound that is associated with many health benefits.
One small study found that drinking beet juice temporarily reduced systolic blood pressure by 4 to 5 mmHg. Art. in healthy adults ().
Summary:
Beets contain a lot of nitrates and folate. 130 grams of raw beets contains 37% of the RDA for folate.