All human cells are more than half water. It is not surprising that all chemical reactions in the human body function with the help of water. It is quite natural that if there is no required amount of water in the body, it begins to work in saving mode. That is, he first tries to provide fluid to the most important human organs, without which normal functioning is not possible. These are primarily the kidneys, liver, heart, lungs and brain.
In addition, since there is a catastrophic lack of fluid, the body begins to pull it from other organs, such as the skin, intestines and joints, which in turn does not allow them to work as usual. Therefore, the skin deteriorates, arthritis appears and constipation begins to torment. If you constantly feel unwell and always suffer from a lack of energy, this is the first sign that you are becoming dehydrated.
Attention! Since we are constantly losing fluid reserves, it is necessary to constantly replenish these losses, and not just when you are thirsty.
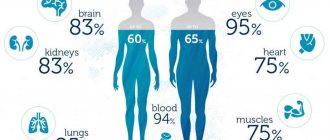
The human body is 2/3 water, namely:
- brain - 73%
- lungs - 83%
- liver - 71%
- bones - 31%
- leather - 64%
- heart - 73%
- kidneys - 79%
- muscles - 79%
- blood - 79%
Why do you need to drink a certain amount of fluid per day?
The human body retains moisture very poorly .
It is lost throughout the day through sweating, urination and breathing. A certain amount drunk during the day allows you to replenish the balance in the body.
Thanks to this, all its systems will be able to work properly. Drinking the right amount allows a person to avoid life-threatening dehydration.
People need enough water throughout the day
- maintaining energy;
- delivery of nutrients to cells;
- removal of toxins;
- improved metabolism and weight regulation;
- normalization of blood pressure.
A certain amount of water per day can help prevent headaches.
What is water for?
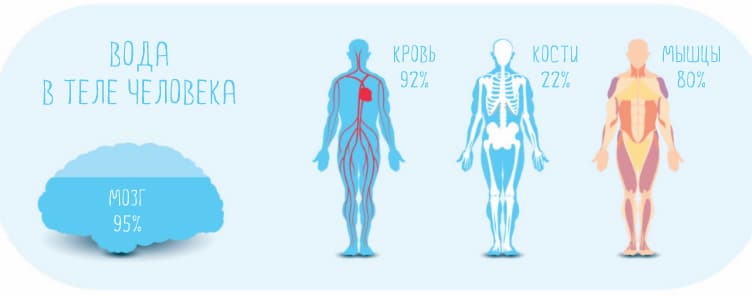
A person can live without food for several weeks, but without water - only a few days. On average, we are 60% water. It is the basis of blood, digestive juices, urine and sweat. Water is found in large quantities in muscles, adipose tissue, and the brain. Even bones are almost a quarter made of water.
We cannot store water and are losing it daily. Thus, up to 200 grams of water leaves the body daily in stool, from 500 to 1500 g in urine, up to 500 ml through the skin, and up to 400 ml through breathing. Water loss and need for it are affected by nutrition, air humidity and temperature, respiratory rate, metabolic rate, and activity level.
Water does many important things in the body:
- transports hormones, nutrients, oxygen to cells;
- acts as a solvent, making substances digestible;
- removes waste metabolic products from cells and from the body;
- an important molecule in most chemical reactions in the body;
- protects joints by acting as a lubricant and protective cushion;
- regulates body temperature through sweating;
- regulates blood pressure;
- Serves as a shock absorber inside the eye and spinal cord.
If the body loses more water than it takes in, varying degrees of dehydration occur. Among the symptoms:
- extreme thirst
- dry skin and mucous membranes (mouth, nose, eyes)
- fatigue and weakness
- decreased concentration
- fast fatiguability
- increase in body temperature
- headache
Consequences of underconsumption
If a person does not drink enough during the day, the main consequence of this can be dehydration. It is also called dehydration. Dehydration is accompanied by extreme thirst, weakness and fatigue.

Due to lack of moisture, human urine becomes concentrated. It takes on a rich dark yellow hue.
If you reduce your water intake, severe dehydration can occur.
Against this background, a person’s pulse and blood pressure decrease, the limbs on the arms and legs acquire a bluish tint.
Insufficient water load during the day also provokes:
- confusion;
- circulatory disorders;
- dry mucous membranes;
- deterioration of kidney function (appearance of stones in them);
- development of diseases in the oral cavity;
- deterioration in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (constipation);
- increased viscosity of sputum in the lungs;
- deterioration of the skin condition;
- muscle weakness.
Insufficient drinking regime is fraught for a person with vision problems, the appearance of arthritis and arthrosis.
How dangerous is dehydration?
Prolonged dehydration is dangerous; it affects the brain, immunity, and blood cells.
The condition leads to:
- obesity;
- deterioration of skin condition;
- rapid wear and tear of the heart;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- organ failure;
- coma and death.
To eliminate the possibility of consequences, you should not bring the body to dehydration. It is easy to recognize and take timely action.
Consequences of excess drinking
Due to excessive drinking of water during the day, a person develops poisoning called overhydration.
Water poisoning has the following possible consequences:
- the appearance of swelling in the face and legs;
- abdominal dropsy;
- edema of the lungs and brain;
- severe pain in the head;
- weakness and fatigue;
- muscle spasms;
- frequent urination.
What happens if you drink too much water - is it beneficial or harmful: consequences
Despite all the benefits of clean drinking water, if consumed in large quantities, it can cause harm to the body.
- When drinking a large amount of water at once, vomiting occurs. This property is used when washing the stomach in case of poisoning, but under normal conditions this phenomenon only brings discomfort.
- The risk of edema increases, which can even affect the brain and lungs.
- Together with excess water, salts and minerals are washed out of the body, the water-salt balance is disrupted, which can lead to a decrease in muscle and mental activity and even cramps.
- The body will try to get rid of large amounts of fluid through diarrhea.
“Everything is poison and everything is medicine. And only the dose makes the medicine a poison, and the poison a medicine.” (Paracelsus)
Is drinking too much water bad for your kidneys?
There is an opinion among doctors that the best prevention of kidney disease is their continuous work. In order not to suffer from urolithiasis or inflammation of the urinary tract, you need to drink enough fluid per day (at least 2 liters). This volume must be reduced if there is already kidney disease.
With excessive consumption of water, the kidneys work in an enhanced mode, and it can be assumed that over time such overloads will begin to affect their health and performance. However, to date, no reliable relationship has been established between kidney disease and large amounts of fluid consumed.
Situations in which you need to drink more water
In some cases, the volume of fluid consumed can be increased to 3 liters per day.
- Physical exercise
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Increased urination
- Increased sweating
- Body burns
- Poisoning and intoxication of the body
- ARVI, flu

How to determine how much the body needs?
You can calculate the daily need for water based on a person’s weight and physical activity. The lower the weight, the less quantity a person needs to drink during the day. The greater your weight, the greater your need to drink.
The more active a person leads, the more water load he will need throughout the day.
The daily need of the human body for drinking is 30 ml for every kilogram of its weight. So, a person weighing 70 kg who leads an inactive lifestyle needs to drink 2.1 liters of water in one day.
If he has average physical activity throughout the day, then another 300 ml should be added to his minimum norm. With high physical activity, you need to add another half liter to the minimum norm.
How much fluid do people of different genders and ages need to drink on average?
Different consumption rates are established for men and women. Separate recommendations for water load are provided for pregnant women and nursing mothers. Children of different ages also have their own norm. Separate regulations regarding this are also provided for athletes.
For men

Men have more lean body mass. Because of this, their body loses moisture faster.
The more a man weighs and the more active his lifestyle, the more fluid he needs during the day.
For adult representatives of the stronger sex, an approximate norm of water load has been established. It is equal to 35 ml for every kilogram of weight. On average, it is enough to drink about 2-2.5 liters.
Women
For representatives of the fairer sex, the norm of water load per day is equal to the standard values - 30 ml for every kilogram of weight.
This also takes into account the woman’s weight and her level of activity throughout the day. Representatives of the fairer sex who lead an active lifestyle need intensive drinking. The norm will be 1.5 liters per day.
Pregnant
When carrying a child, a woman's need for water increases. In addition to the need to saturate her body with moisture, the expectant mother has a need to provide water to the fetus. For this reason, pregnant women are recommended to drink about 2-2.5 liters per day.
Whether it is acceptable for pregnant women to drink water with gas can be found out here.
Excessive drinking can cause swelling in a pregnant woman. To avoid their occurrence, it is recommended to reduce the amount of salt consumed.
When breastfeeding

Water does not greatly affect the amount of breast milk produced. But it can slightly reduce its fat content.
Due to this, it can be better absorbed by the newborn’s body.
Drinking water helps stimulate breast milk production. In this regard, a woman is recommended to drink more while breastfeeding.
You can drink up to 3 liters. A significant part of it will be used to produce breast milk. For nursing mothers, a daily drinking regimen that includes 2.5 liters of drinking water is considered normal. This amount will prevent dehydration of the female body and make breast milk more liquid.
For children
The drinking rate in children differs depending on their age:
- Children under 3 months. They don't particularly need drinking water. Newborns receive a sufficient amount of it from mother's milk. You can give a few tablespoons of water to your child when he is hot, has diarrhea, vomiting or has a high fever.
- Children from 3 months to one year. Those who are fed breast milk can be given about 100-150 ml. Those who are fed artificial formula should be given up to 200 ml during the day.
- Children aged 1-3 years . They can drink up to 500 ml during the day. The basis is the calculation of 50 ml per 1 kg of weight.
- Children aged 3-7 years. Their drinking regime is gradually increased. At first, the child needs to drink about 1.2 liters. By the age of 7, a child can already consume up to 1.7 liters per day per day.
On average, a child from 7 to 13 years old is recommended to drink about 1.5-1.8 liters of water per day.
Read more here.
For teenagers
From the age of 13, it is recommended that a child start drinking the same amount of water daily as an adult. A teenager can consume about 2-2.2 liters per day.
If a child is intensely involved in sports, and his lifestyle is particularly active, then he is recommended to drink 2.5 liters per day.
For athletes

If he weighs around 70 kg, then during the day he is recommended to drink an average of 2-2.3 liters of clean water.
Athletes weighing 80 kg should drink even more. They are recommended to consume at least 2.5 liters daily.
If the weight of a person involved in sports is about 90 kg, then the daily water load increases to 3 liters. Athletes weighing 100 kg or more can drink over 3 liters per day. If their activities are intense, then they should consume about 3.5 liters.
Read this article about whether you can drink water during training.
An athlete is recommended to drink 1-1.5 liters per workout. This applies when his training is particularly intense. You need to consume 200 ml every 20 minutes of exercise.
For athletes when drying the body
When drying, a person’s body requires even more moisture than during normal training . The water load at this stage should be increased by 2-3 times.
In this case, water should be consumed according to a special scheme. A person needs to drink about 300 ml an hour before class. During training you need to consume at least 1.5 liters.
Of these, 100 ml after warm-up, then 100 ml after each 15-minute training interval. After all the exercises you should also drink another 250 ml. In this case, the main water load for an athlete who is drying his body should occur during exercise.
A person's weight plays a role. When drying, a person weighing 80-90 kg should consume 2.5-3 liters of water. An athlete weighing more than 100 kg needs to drink 3-4 liters when cutting.
It is not recommended to reduce the specified rate and it is prohibited to increase it. In both cases, the person may experience serious health problems.
How long after eating can you drink water and why not during meals?
The tradition of drinking food during meals makes digestion difficult , since the incoming water dilutes the gastric juice and carries the necessary enzymes outside the stomach. For the same reasons, you should not drink water immediately after eating.
It would be correct to drink a glass of clean water half an hour before a meal and 0.5 - 4 hours after a meal.
- 30 minutes after eating fruit
- 1 hour after vegetables
- 2 hours after a carbohydrate meal
- 4 hours after meat products.
How long after training can you drink water and why can’t you drink during training?
It is worth refraining from drinking water during training, so as not to create a feeling of fullness in the stomach and to avoid discomfort during active exercise. In addition, an athlete who uncontrollably drinks water during exercise to quench increased thirst is at risk of water poisoning.
- You can drink water after physical activity, 150-200 ml every 15 minutes. The total volume of liquid drunk should not exceed 1 liter.
- Drink 1-2 glasses of pure water half an hour before exercise to replenish your body's fluid reserves and avoid feeling thirsty during exercise.
Why can’t you drink water quickly, but rather in small sips?
Drinking water in one gulp puts a sharp strain on the kidneys and digestive tract. Without having time to be absorbed, it is largely excreted from the body without being absorbed.
On the contrary, water, drunk in sips, is completely absorbed and perfectly quenches thirst.
Hold drinking water in your mouth before swallowing. This will moisturize the oral mucosa and “deceive” the receptors that signal thirst, creating the effect of drinking a large amount of liquid.
Why can’t you drink water after melon or corn?
To avoid unpleasant effects on the gastrointestinal tract, do not drink melon and corn with water. This will lead to increased flatulence, colic and even diarrhea. For the same reasons, it is not recommended to eat them on an empty stomach.
Maximum allowed quantity per day

Each organism has its own maximum water load that it can tolerate without serious consequences.
The maximum allowable amount for a person is 7 liters of water in one day.
Already at this amount, the human body develops water poisoning.
A figure of 7 liters per day is officially registered as a case of drinking water that led to the death of a person.
The higher your weight, the higher the maximum threshold for a life-threatening amount of water consumed per day. Water poisoning can occur after 10 liters. It is recommended to consume a maximum of no more than 3.5-4 liters in one day.