Creatine
Sergey Sidoruk 03/05/2019 no comments
2
Why do you take Creatine in bodybuilding?
5 (100%) 1 vote
Creatine is the most popular and frequently used sports supplement that helps many athletes achieve excellent results. There are over a hundred studies confirming the effectiveness of this type of supplement. Most users, including elite athletes and non-trained individuals, use creatine to increase fat-free mass and improve anaerobic and aerobic performance. Speaking about professional sports, in bodybuilding, in rare cases, athletes do without creatine.
What does the supplement do and why do athletes drink it?
The main task of creatine is to provide the body with the necessary energy during intense physical activity. With any strength training, energy is initially consumed from this substance, and then from other nutritional compounds. However, a noticeable effect from the supplement appears gradually, provided that it is taken regularly (the compound must accumulate in muscle fibers and other tissues).
Experienced athletes use creatine not only for additional energy, but also to neutralize acids. Some of them are formed during physical activity and provoke muscle fatigue - this supplement helps reduce their synthesis. There is also a significant increase in muscle volume due to fluid accumulation. The total increase in body weight with regular consumption of nitrogen-containing carboxylic acid can be about 3-5 kg.
Be sure to check out:
Creatine: properties of the supplement and its importance in sports nutrition. Expiration date and storage of creatine. Is it possible to mix BCAA with creatine and what can this lead to? Creatine and protein: rules for taking it together
Biological role of the drug
Creatine molecules help create energy reserves in the body, which allows athletes to lift more weight in strength exercises and increase strength. The muscle enlargement effect is observed due to the additional attraction of nutrients and water to the structural muscle fibers.
Note! Also, taking the supplement can increase the natural level of testosterone in the male body (by about 20-25% within 10 weeks after starting use). This mechanism has a positive effect on strength indicators and the rate of muscle mass gain.
Benefits of creatine
- Increases strength endurance
Muscles can work on creatine phosphate synthesis for 6-15 seconds. By increasing creatine reserves in the muscles, the duration of explosive work increases by 20-30%.
When switching from creatine-phosphate energy supply to glycolysis, acidification begins. But here creatine helps out too - it delays the moment of acidification to 1 - 1.5 minutes.
- Increases muscle mass and strength
The increase in muscle mass and strength occurs indirectly due to an increase in performance. Creatine helps you work out longer, so your muscles grow faster. It is important not to confuse swelling with muscle gain. Creatine retains water and increases cell size. The muscle becomes “inflated”.
Important! The effect of creatine, like any other sports nutrition, corresponds to the load. When working on mass in the gym, it will help you gain mass. Creatine will not make a skier, track and field athlete, cyclist, or swimmer “jump,” but it will speed up recovery and increase muscle power.
- Improves muscle definition
Taking the drug allows you to improve muscle definition. This is due to both increased endurance during training and water retention - the greater the supply of creatine in the muscles, the more water it contains and the larger it looks.
- Serves as a lactic acid buffer
The familiar burning sensation after training serves as a signal that lactic acid has accumulated in the muscles. Creatine can inhibit the release of lactic acid and reduce recovery time after exercise.
- Protects the cardiovascular system
Helps restore the heart muscle after a heart attack, with arrhythmia and ischemia. Promotes vascular restoration. Protects the heart muscle when working in conditions of lack of oxygen.
- Protects the central nervous system
Helps the development of the brain and the entire nervous system. Improves the conduction function of the nervous system and the contractile function of muscles, including the heart.
- Normalizes blood cholesterol levels
We recommend reading: Why do we need bcaa and how to take it?

Functions of this type of sports nutrition
Creatine has a long list of benefits for athletes' performance. Among the most popular are:
- pumping effect on early repetitions;
- significant increase in muscles;
- increasing the efficiency of anabolic processes in the athlete’s body;
- increased overall endurance due to increased oxygen levels in muscle fibers;
- accumulation of glycogen reserves to increase energy potential;
- gradual increase in strength indicators to overcome the “plateau” and build muscle mass;
- beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart and the entire vascular system;
- lowering the level of bad cholesterol in the body.
The listed properties of creatine can only be observed with regular use of the supplement. The substance gradually accumulates in the body, which affects the progress of visible results.
What sport is needed: bodybuilding, swimming, strength sports
Creatine helps the body more easily tolerate short bursts of increased intensity. For this reason, it is necessary for sprinters for races, athletes in team sports with the need for frequent acceleration (football, basketball, hockey, etc.), and short-distance swimmers. In these cases, the supplement allows you to increase overall performance and improve previous performance, and reduce the level of fatigue.
Additional intake of this substance is justified if it is necessary to increase muscle strength and volume. This is why creatine is so in demand in bodybuilding and strength sports.
Note! When used in endurance sports (for example, before the start of long-distance swimming, as part of cycling marathons), creatine is ineffective because it will not increase your overall endurance.
Why do I need it?

When used immediately after a workout, creatine allows you to perform exercises that previously stumped you. It serves as a backup generator to increase adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels, your primary source of energy during high-intensity exercise. It also allows you to better resist fatigue and recover faster. A review of 22 studies on creatine found that it can increase strength by 5% and endurance by 14%.
What's more: A recent study out of Louisiana State University suggests that taking creatine may improve glycogen levels during muscle exertion, which may provide benefits during endurance exercise. Finally, it may also improve mental performance - your brain uses creatine phosphate during intense periods of brain activity, so if you do a lot of calculations, for example, then creatine may help you focus.
Pros and cons of the supplement
Creatine in powder or capsules has many benefits. It is easy to take and combine with other supplements; with moderate consumption, it practically does not cause such effects. At the same time, this substance increases strength and performance indicators, helps to pump up muscles faster.
However, consuming nitrogen-containing carboxylic acid also has some disadvantages:
- you need to correctly calculate the daily portion, do not forget about breaks;
- the substance promotes fluid retention in the body, which can cause swelling;
- if an athlete abuses creatine, digestive disorders may occur;
- increase in body weight (this disadvantage is not suitable for athletes who perform in a certain weight group).
If you take the supplement wisely, the benefits to the body will significantly outweigh the negative aspects. When combined with other types of sports nutrition, it is worth taking into account the weight and physical characteristics of the athlete, goals, etc.
Which creatine is best?
Creatine monohydrate powder is more profitable and of higher quality. Creatine powder is almost always cheaper than capsules and tablets. In addition, it is better absorbed. most effective supplement . The most studied form of creatine - all the effects and recommendations are associated with it. The remaining forms of creatine are creatine monohydrate + something else. Many brands are trying to invent their own type of creatine and present it as a scientific breakthrough. This is nothing more than marketing. None of these forms showed better effectiveness compared to the monohydrate.
We prefer well-known and proven brands:
- Optimum Nutrition
- Universal Nutrition
- NOW
- muscletech
- MyProtein
There are other good brands, but these are the ones we trust. By the way, it is at the top of most world sports nutrition ratings.
Hydrochloride or monohydrate: which is better?
In the range of sports nutrition, you can observe competition between two types of creatine: hydrochloride and monohydrate. The following features are in favor of the first:
- it does not provoke typical adverse reactions from the stomach and the entire digestive system (bloating, heaviness, etc.);
- there is no negative effect on the liver, kidneys and other organs of the human excretory system (especially when taken according to the “loading” scheme).
The disadvantage of hydrochloride remains its price. Even when using a reduced dosage, the cost of the supplement is much higher than that of products with a competitive form. Creatine monohydrate remains the most profitable purchase in terms of price/effectiveness ratio.
Monohydrate

ALLMAX Nutrition, Creatine, Pharmaceutical Grade, 3.53 oz (100 g)
Price – ₽631.06
Buy from a partner
Creatine HCl

Kaged Muscle, Proprietary Dietary Supplement, Creatine HCL, Unflavored, 1.98 oz (56.25 g)
Price – RUB 1,578.83
Buy from a partner

Now Foods, Performance Nutrition, Creatine Monohydrate, Pure Powder, 8 oz (227 g)
Price – ₽616.05
Buy from a partner

Kaged Muscle, Patented Creatine Hydrochloride, 75 Vegetable Capsules
Price – RUB 1,578.83
Buy from a partner

Dymatize Nutrition, Micronized Creatine, Unflavored, 10.6 oz (300 g)
Price – ₽631.06
Buy from a partner

Muscletech, Performance Series, CREACTOR, Creatine HCI, Blue Raspberry Blast, 9.31 oz (264 g)
Price – ₽1,525.28
Buy from a partner
Note! If you have chronic diseases of the kidneys, liver and gastrointestinal tract, it is better to stick to the hydrochloride form. In these cases, it will be absorbed faster and will not cause discomfort.
Who should use it?

People doing intense exercise in the gym, as it generally has no effect on long, slow aerobic exercise. It will also likely be healthier for vegetarians or people who don't eat a lot of red meat. If your diet is very high in creatine products, then you may not receive any additional benefits from this supplement.
Contraindications
Creatine has a number of contraindications that should be considered before taking it. In the following situations, you should limit or avoid taking the supplement:
- If there are problems with water-salt metabolism. The substance requires large amounts of water and can cause dehydration more quickly than in healthy people.
- For chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver, eating disorders. The substance provokes an increased load on these organs and can cause exacerbation of existing diseases.
- For diagnosed kidney diseases. Since the substance circulates in the blood and passes through the liver, it creates an increased load on it. Products with a high protein content have a similar effect.
You should not take creatine in high dosages. Most side effects occur when there is a multiple excess of the substance in the body and disappear when the daily portion is reduced.
Why should creatine be taken separately?
What is the average daily dose of creatine needed by an ordinary person? Depending on the build, this is 6-8 grams. But for athletes, the need for this element increases to approximately 30 grams of amino acid per day. It is unrealistic to obtain such an amount of substance from meat and fish: to do this you will have to eat kilograms of them, which, of course, is possible, but has an extremely negative effect on the state of the gastrointestinal tract. But creatine in the form of a separate supplement has virtually no effect on the digestive system, being quickly absorbed by the body and distributed in the muscles. So you still need to take it separately if you are involved in professional or serious amateur sports.
Can I take steroids during a cycle or not?
Consumption of creatine allows you to reduce the total number of necessary injections during a course of steroid hormones. The daily norm of carboxylic nitrogen-containing acid depends on the duration of strength training and the age group of the athlete. There are also other small factors that affect portion size. The amount of the substance should be selected by a professional with a medical education and take into account the individual characteristics of the athlete (for beginners it does not exceed 15 grams per day).
When combined with steroids, the creatine dosage regimen should not differ from standard recommendations. The product should be drunk approximately 2-3 times a day, dividing the portion in multiple ways. After each course of the substance, a break of at least 4 weeks is required to restore the natural capabilities of the muscles.
Note! It is important to combine a creatine course with increased water consumption, regardless of the use of steroids. Without a sufficient amount of moisture in the body, rapid dehydration will occur, which will negatively affect metabolic processes.
How to use
Options for taking creatine do not depend on the form chosen (tablets, powder or capsules). The main point is to take into account the dosage of the active substance. There are 2 basic methods of administration:
- "Loading". For the first 3-7 days you need to take approximately 20-25 grams of the supplement per day. Then the portion is reduced to a minimum for 20 days: 2-5 grams per day.
- Classic way. To do this, you need to consume 3-7 grams of creatine daily throughout the course. In this case, it is best to divide the daily dose into several doses for quick absorption.
The second method is more preferable for beginners, as it is characterized by a low risk of side effects. It promotes the gradual accumulation of the substance in the body without overloading the internal organs.
Discovery of Creatine
Creatine was first isolated in the first half of the 19th century, and at the beginning of the next century, scientific experiments were conducted proving that regular use of the substance increases muscle strength. At the same time, “phosphocreatine” was discovered - combined molecules of creatine and phosphate, which, when accumulated in the body, improve metabolism. The most effective form of creatine was recognized as its monohydrate - paired molecules of creatine and water.
The victorious march of creatine in sports began in 1992 after the publication of a study by Swedish doctor Eric Haltman. He has proven that taking 20 grams of creatine monohydrate daily increases muscle creatine content by 20%. A year later, an authoritative publication on sports medicine published an article about the effective use of creatine by Swedish athletes. Later studies showed that for results you do not need to take 20 grams of creatine, but 5-7 grams per day is enough. But the effectiveness of creatine has always been confirmed.
Since that time, creatine monohydrate has become a popular dietary supplement among athletes around the world. Creatine is not included in the list of prohibited doping substances, which means it can be used in any competition.
We recommend reading: What is protein and what is it for?
It is important to remember that creatine is not an essential supplement - it is produced in the body from amino acids (glycine, methionine, arginine), so there is no need to necessarily get your creatine intake from dietary supplements. In sports nutrition, creatine is obtained chemically in laboratories, but there is nothing wrong with that. The process that occurs in the body is reproduced in the laboratory and the same creatine is obtained, no less natural.
How long does it take for it to start working?
In the first week of taking the supplement, you should not expect pronounced changes - creatine only accumulates in the body. From about the second or third week you can notice an increase in performance under standard loads.
After 3 weeks of use, athletes note better load tolerance and a gradual increase in strength indicators, progress in working weight in basic exercises.
Results: before and after photos
The results of proper creatine intake can be easily seen in practice:
- the maximum and working weight in familiar exercises increases;
- performance increases in sets with maximum effort;
- results in one-shot sprints improve noticeably.

Taking creatine helps increase lean muscle mass and improve athletic performance. The effect of use occurs gradually and depends on the accumulation of the substance in the body.
Reviews from professionals
Brad Scheinfeld
If I had to recommend only one supplement for rapid muscle growth and strength gains, it would be creatine. I am impressed by the fairly high level of knowledge of the product and its natural composition. Based on practical experiments, it has been proven that the use of creatine predictably increases its concentration in muscles and leads to an increase in the anabolic potential of muscles. With this supplement, the effectiveness of training increases noticeably, and these changes motivate the athlete to new sports goals. With creatine, the aesthetic component also improves, muscles increase in volume and become more pronounced. On average, I see a 1-2 kilogram gain after starting creatine in beginners.
B. Scheunfeld, experienced sports physiologist, PhD in “Mechanics of Muscle Growth”
Chrissie Kendal
Thanks to misinformation in the media and some myths in the sports community, women consider creatine an exclusively male supplement, doubt its safety and are wary of taking it. The situation is aggravated by the fact that manufacturers regularly remove such a product from the recommended list of “female” supplements.
In practice, creatine is one of the most researched and versatile supplements. In addition to increasing strength indicators, it can give female athletes greater productivity during training and facilitate the process of losing weight.
K. Kendal, sports nutrition expert, PhD and lecturer at the Western Australia School of Health
Maxim Glotov
I advise my clients to practice a “loading” course with creatine for one month, and then take a break for 30 days. This combination is completely safe for the body and does not allow the muscles to forget about the need to produce their own creatine from incoming amino acids. For standard use, be sure to take the capsules or powder with plenty of water - at least 1 glass.
Regarding the time of admission: there are some nuances, depending on the specific purpose. Take the supplement before active training if you need to provide the body with the necessary amount of energy to carry out the exercises. If you take it afterwards, the substance will be more active in restoring (due to nitrogen compounds) and increasing the volume of muscle tissue.
I would like to draw the attention of older athletes - this supplement may increase blood pressure. This effect is extremely undesirable in case of hypertension: well-being and tolerance to the strength complex loads worsen.
M. Glotov, master of sports in powerlifting, sports nutrition consultant
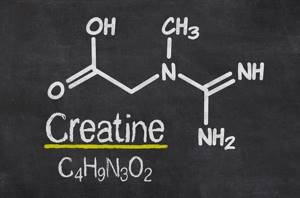
Chemical structure
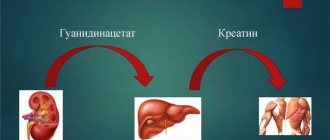
Creatine is a non-essential amino acid. If necessary, the body is able to independently synthesize creatine phosphate and transport it to muscle tissue, containing:
- arginine
- glycine.
- methionine
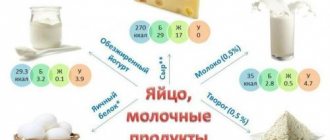
Creatine phosphates are found in small quantities in meat foods.
Interesting fact: the amount of creatine in the muscles of poultry and wild birds differs by more than 20%. The same applies to aquarium fish, which contain 40% less creatine than those caught in ocean waters. The answer to this question lies in the training of organisms. As you know, if a calf/chicken or other domestic animal moves a lot, its muscles become stiffer, which is why sedentary animals are specially raised on farms for meat lovers. Mobility stimulates anabolism in any animal - as a result, more creatine is found in trained muscles
Why has creatine become a revolution in the world of sports nutrition? It's simple. The body can synthesize very small amounts of the substance (maximum 1 g), while at the same time its concentration is negligible compared to other amino acids in meat. During heat treatment, it breaks down into arginine, glycine and methionine, which deprives the value of fried and heavily cooked foods.
© Zerbor — stock.adobe.com